Megakaryocyte
| Megakaryocyte | |
|---|---|
 Two megakaryocytes in bone marrow, marked with arrows. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | megakaryocytus |
| Code | TH H2.00.04.3.05003 |
A megakaryocyte (mega- + karyo- + -cyte, "large-nucleus cell") is a large bone marrow cell with a lobulated nucleus responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. Megakaryocytes normally account for 1 out of 10,000 bone marrow cells but can increase in number nearly 10-fold during the course of certain diseases.[1] Owing to variations in combining forms and spelling, synonyms include megalokaryocyte and megacaryocyte.
Structure
In general, megakaryocytes are 10 to 15 times larger than a typical red blood cell, averaging 50-100 μm in diameter. During its maturation, the megakaryocyte grows in size and replicates its DNA without cytokinesis in a process called endomitosis. As a result, the nucleus of the megakaryocyte can become very large and lobulated, which, under a light microscope, can give the false impression that there are several nuclei. In some cases, the nucleus may contain up to 64N DNA, or 32 copies of the normal complement of DNA in a human cell.
The cytoplasm, just as the platelets that bud off from it, contains α-granula and Dense bodies.
Megakaryocyte development
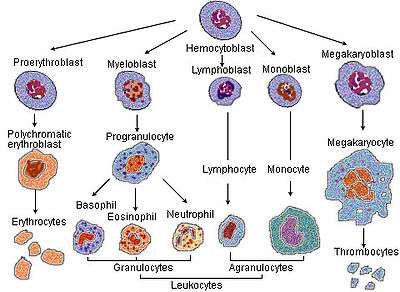
Megakaryocytes are derived from hematopoietic stem cell precursor cells in the bone marrow. They are produced primarily by the liver, kidney, spleen, and bone marrow. These multipotent stem cells live in the marrow sinusoids and are capable of producing all types of blood cells depending on the signals they receive. The primary signal for megakaryocyte production is thrombopoietin or TPO. TPO is sufficient but not absolutely necessary[2] for inducing differentiation of progenitor cells in the bone marrow towards a final megakaryocyte phenotype. Other molecular signals for megakaryocyte differentiation include GM-CSF, IL-3, IL-6, IL-11, chemokines (SDF-1, FGF-4).[3] and erythropoietin.[4] The megakaryocyte develops through the following lineage:
CFU-Me (pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell or hemocytoblast) -> megakaryoblast -> promegakaryocyte -> megakaryocyte.
The cell eventually reaches megakaryocyte stage and loses its ability to divide. However, it is still able to replicate its DNA and continue development, becoming polyploid.[4] The cytoplasm continues to expand and the DNA complement can increase up to 64N in human and 256N in mouse. Many of the morphological features of megakaryocyte differentiation can be recapitulated in non-hematopoietic cells by the expression of Class VI β-tubulin (β6) and they provide a mechanistic basis for understanding these changes.[5]
Platelet release
Once the cell has completed differentiation and become a mature megakaryocyte, it begins the process of producing platelets. The maturation process occurs via endomitotic synchronous replication whereby the cytoplasmic volume enlarges as the number of chromosomes multiplies without cellular division. The cell ceases its growth at 4N, 8N or 16N, becomes granular, and begins to produce platelets.[6] Thrombopoietin plays a role in inducing the megakaryocyte to form small proto-platelet processes. Platelets are held within these internal membranes within the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes. There are two proposed mechanisms for platelet release. In one scenario, these proto-platelet processes break up explosively to become platelets.[7] Alternatively, the cell may form platelet ribbons into blood vessels. The ribbons are formed via pseudopodia and they are able to continuously emit platelets into circulation. In either scenario, each of these proto-platelet processes can give rise to 2000-5000 new platelets upon breakup. Overall, 2/3 of these newly produced platelets will remain in circulation while 1/3 will be sequestered by the spleen.
After budding off platelets, what remains is mainly the cell nucleus. This crosses the bone marrow barrier to the blood and is consumed in the lung by alveolar macrophages.
Effects of cytokines
Cytokines are signals used in the immune system for intercellular communication. There are many cytokines that affect megakaryocytes. Certain cytokines such as IL-3, IL-6, IL-11, LIF, erythropoietin, and thrombopoietin all stimulate the maturation of megakaryocytic progenitor cells.[8] Other signals such as PF4, CXCL5, CXCL7, and CCL5 inhibit platelet formation.[9]
Thrombopoietin
Thrombopoietin (TPO) is a 353-amino acid protein encoded on chromosome 3p27. TPO is primarily synthesized in the liver[10] but can be made by kidneys, testes, brain, and even bone marrow stromal cells. It has high homology with erythropoietin. It is essential for the formation of an adequate quantity of platelets. Mice lacking TPO or the TPO receptor (Mpl) have a 90% reduction in circulating platelet number, although the platelets are normal in morphology and function.[11]
Disorders involving megakaryocytes
Megakaryocytes are directly responsible for producing platelets, which are needed for the formation of a thrombus, or blood clot. There are several diseases that are directly attributable to abnormal megakaryocyte function or abnormal platelet function.[12]
Essential Thrombocythemia
Essential thrombocytosis (ET-Also known as Essential thrombocythemia) is a disorder characterized by extremely high numbers of circulating platelets. The disease occurs in 1-2 per 100,000 people. The current WHO requirements for diagnosis include > 600,000 platelets/μL of blood (normal 150,000-400,000) and a bone marrow biopsy. Some of the consequences of having such high numbers of platelets include thrombosis or clots throughout the body. Thrombi form more frequently in arteries than veins. It seems ironic that having platelet counts above 1,000,000 platelets/μL can lead to hemorrhagic events.[13] Recent evidence suggests that the majority of ET cases are due to a mutation in the JAK2 protein, a member of the JAK-STAT pathway.[14] Evidence suggests that this mutation renders the megakaryocyte hypersensitive to thrombopoietin and causes clonal proliferation of megakaryocytes. There is a significant risk of transformation to leukemia with this disorder. The primary treatment consists of anagrelide or hydroxyurea to lower platelet levels.
Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (CAMT)
Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (CAMT) is a rare inherited disorder. The primary manifestations are thrombocytopenia and megakaryocytopenia, i.e. low numbers of platelets and megakaryocytes. There is an absence of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow with no associated physical abnormalities.[15] The cause for this disorder appears to be a mutation in the gene for the TPO receptor, c-mpl, despite high levels of serum TPO.[16][17] In addition, there may be abnormalities with the central nervous system including the cerebrum and cerebellum that could cause symptoms.[16] The primary treatment for CAMT is bone marrow transplantation.
Bone marrow/stem cell transplant is the only remedy for this genetic disease. Frequent platelet transfusions are required to keep the patient from bleeding to death until transplant has been completed, although this is not always the case.
There appears to be no generic resource for CAMT patients on the web and this is potentially due to the rarity of the disease.
External links
- Megakaryocytes: Mature Many microscopic images of mature megakaryocytes including in disease settings.
- Megakaryocytes
- Cell size comparison
- CAMT Specific Infant Bone Marrow Transplant Journal
References
- ↑ Branehog I, Ridell B, Swolin B, Weinfeld A (1975). "Megakaryocyte quantifications in relation to thrombokinetics in primary thrombocythaemia and allied diseases". Scand. J. Haematol. 15 (5): 321–332. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0609.1975.tb01087.x. PMID 1060175.
- ↑ Bunting S, Widmer R, Lipari T, Rangell L, Steinmetz H, Carver-Moore K, Moore MW, Keller GA, de Sauvage FJ (November 1997). "Normal platelets and megakaryocytes are produced in vivo in the absence of thrombopoietin". Blood. 90 (9): 3423–3429. PMID 9345025.
- ↑ Avecilla ST, Hattori K, Heissig B, Tejada R, Liao F, Shido K, Jin DK, Dias S, Zhang F, Hartman TE, Hackett NR, Crystal RG, Witte L, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P, Eaton D, Lyden D, de Sauvage F, Rafii S (January 2004). "Chemokine-mediated interaction of hematopoietic progenitors with the bone marrow vascular niche is required for thrombopoiesis". Nat Med. 10 (1): 64–71. doi:10.1038/nm973. PMID 14702636.
- 1 2 Deutsch VR, Torner A (September 2006). "Megakaryocyte development and platelet production". Brit. J. Haem. 134 (5): 453–466. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06215.x. PMID 16856888.
- ↑ Yang, H; Ganguly, A; Cabral, F (2012). "Megakaryocyte Lineage Specific Class VI β-Tubulin Suppresses Microtubule Dynamics, Fragments Microtubules, and Blocks Cell Division.". Cytoskeleton. 68 (3): 175–187. doi:10.1002/cm.20503. PMID 21309084.
- ↑ January 2013 "Megakaryocyte and Platelet Production" Check
|url=value (help). - ↑ Choi ES, Nichol JL, Hokom MM, et al. (1995). "Platelets generated in vitro from proplatelet-displaying human megakaryocytes are functional". Blood. 85 (2): 402–13. PMID 7529062.
- ↑ Gordon MS, Hoffman R (1992). "Growth factors affecting human thrombocytopoiesis: potential agents for the treatment of thrombocytopenia". Blood. 80 (2): 302–307. PMID 1627792.
- ↑ Pang L, Weiss MJ, Poncz M (2005). "Megakaryocyte biology and related disorders". J. Clin. Invest. 115 (12): 3332–3338. doi:10.1172/JCI26720. PMC 1297258
 . PMID 16322777.
. PMID 16322777. - ↑ Jelkmann W (2001). "The role of the liver in the production of thrombopoietin compared with erythropoietin". Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 13 (7): 791–801. doi:10.1097/00042737-200107000-00006. PMID 11474308.
- ↑ Murone M, Carpenter DA, de Sauvage FJ (1998). "Hematopoietic deficiencies in c-mpl and TPO knockout mice". Stem Cells. 16 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1002/stem.160001. PMID 9474742.
- ↑ Nurden AT (2005). "Qualitative disorders of platelets and megakaryocytes". J. Thromb. And Haem. 3 (8): 1773–1782. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01428.x. PMID 16102044.
- ↑ Michiels JJ, Berneman ZN, Schroyens W, Van Vliet HH (2004). "Pathophysiology and treatment of platelet-mediated microvascular disturbances, major thrombosis and bleeding complications in essential thrombocythaemia and polycythaemia vera". Platelets. 15 (2): 67–84. doi:10.1080/09537100310001646969. PMID 15154599.
- ↑ Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, et al. (2005-04-28). "A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders". N Engl J Med. 352 (17): 1779–90. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa051113. PMID 15858187.
- ↑ Freedman MH, Estrov Z (1990). "Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia: an intrinsic hematopoietic stem cell defect". Am. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 12 (2): 225–230. doi:10.1097/00043426-199022000-00020. PMID 2378417.
- 1 2 Ihara K, Ishii E, Eguchi M, Takada H, Suminoe A, Good RA, Hara T (1999). "Identification of mutations in the c-mpl gene in congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96 (6): 3133–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.3132. PMC 15907
 . PMID 10077649.
. PMID 10077649. - ↑ Ballmaier M, Germeshausen M, Schulze H, Cherkaoui K, Lang S, Gaudig A, Krukemeier S, Eilers M, Strauss G, Welte K (2001). "C-mpl mutations are the cause of congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia". Blood. 97 (1): 139–46. doi:10.1182/blood.V97.1.139. PMID 11133753.