Manner of articulation
| Manners of articulation |
| Airstreams |
|---|
| Related |
.ogv.jpg)
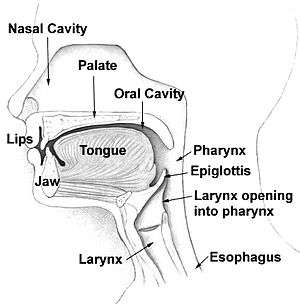
In articulatory phonetics, the manner of articulation is the configuration and interaction of the articulators (speech organs such as the tongue, lips, and palate) when making a speech sound. One parameter of manner is stricture, that is, how closely the speech organs approach one another. Others include those involved in the r-like sounds (taps and trills), and the sibilancy of fricatives.
The concept of manner is mainly used in the discussion of consonants, although the movement of the articulators will also greatly alter the resonant properties of the vocal tract, thereby changing the formant structure of speech sounds that is crucial for the identification of vowels. For consonants, the place of articulation and the degree of phonation of voicing are considered separately from manner, as being independent parameters. Homorganic consonants, which have the same place of articulation, may have different manners of articulation. Often nasality and laterality are included in manner, but some phoneticians, such as Peter Ladefoged, consider them to be independent.
closure(stricture)
From greatest to least stricture, speech sounds may be classified along a cline as stop consonants (with occlusion, or blocked airflow), fricative consonants (with partially blocked and therefore strongly turbulent airflow), approximants (with only slight turbulence), and vowels (with full unimpeded airflow). Affricates often behave as if they were intermediate between stops and fricatives, but phonetically they are sequences of a stop and fricative.
Over time, sounds in a language may move along this cline toward less stricture in a process called lenition, or towards more stricture in a process called fortition.
Other parameters
Sibilants are distinguished from other fricatives by the shape of the tongue and how the airflow is directed over the teeth. Fricatives at coronal places of articulation may be sibilant or non-sibilant, sibilants being the more common.
Taps and flaps are similar to very brief stops. However, their articulation and behavior are distinct enough to be considered a separate manner, rather than just length.
Trills involve the vibration of one of the speech organs. Since trilling is a separate parameter from stricture, the two may be combined. Increasing the stricture of a typical trill results in a trilled fricative. Trilled affricates are also known.
Nasal airflow may be added as an independent parameter to any speech sound. It is most commonly found in nasal occlusives and nasal vowels, but nasalized fricatives, taps, and approximants are also found. When a sound is not nasal, it is called oral.
Laterality is the release of airflow at the side of the tongue. This can be combined with other manners, resulting in lateral approximants (the most common), lateral flaps, and lateral fricatives and affricates.
Individual manners
- Stop, an oral occlusive, where there is occlusion (blocking) of the oral vocal tract, and no nasal air flow, so the air flow stops completely. Examples include English /p t k/ (voiceless) and /b d ɡ/ (voiced). If the consonant is voiced, the voicing is the only sound made during occlusion; if it is voiceless, a stop is completely silent. What we hear as a /p/ or /k/ is the effect that the onset of the occlusion has on the preceding vowel, as well as the release burst and its effect on the following vowel. The shape and position of the tongue (the place of articulation) determine the resonant cavity that gives different stops their characteristic sounds. All languages have stops.
- Nasal, a nasal occlusive, where there is occlusion of the oral tract, but air passes through the nose. The shape and position of the tongue determine the resonant cavity that gives different nasals their characteristic sounds. Examples include English /m, n/. Nearly all languages have nasals, the only exceptions being in the area of Puget Sound and a single language on Bougainville Island.
- Fricative, sometimes called spirant, where there is continuous frication (turbulent and noisy airflow) at the place of articulation. Examples include English /f, s/ (voiceless), /v, z/ (voiced), etc. Most languages have fricatives, though many have only an /s/. However, the Indigenous Australian languages are almost completely devoid of fricatives of any kind.
- Sibilants are a type of fricative where the airflow is guided by a groove in the tongue toward the teeth, creating a high-pitched and very distinctive sound. These are by far the most common fricatives. Fricatives at coronal (front of tongue) places of articulation are usually, though not always, sibilants. English sibilants include /s/ and /z/.
- Affricate, which begins like a stop, but this releases into a fricative rather than having a separate release of its own. The English letters "ch" [tʃ] and "j" [dʒ] represent affricates. Affricates are quite common around the world, though less common than fricatives.
- Flap, often called a tap, is a momentary closure of the oral cavity. The "tt" of "utter" and the "dd" of "udder" are pronounced as a flap [ɾ] in North American and Australian English. Many linguists distinguish taps from flaps, but there is no consensus on what the difference might be. No language relies on such a difference. There are also lateral flaps.
- Trill, in which the articulator (usually the tip of the tongue) is held in place, and the airstream causes it to vibrate. The double "r" of Spanish "perro" is a trill. Trills and flaps, where there are one or more brief occlusions, constitute a class of consonant called rhotics.
- Approximant, where there is very little obstruction. Examples include English /w/ and /r/. In some languages, such as Spanish, there are sounds that seem to fall between fricative and approximant.
- One use of the word semivowel, sometimes called a glide, is a type of approximant, pronounced like a vowel but with the tongue closer to the roof of the mouth, so that there is slight turbulence. In English, /w/ is the semivowel equivalent of the vowel /u/, and /j/ (spelled "y") is the semivowel equivalent of the vowel /i/ in this usage. Other descriptions use semivowel for vowel-like sounds that are not syllabic, but do not have the increased stricture of approximants. These are found as elements in diphthongs. The word may also be used to cover both concepts. The term glide is newer than semivowel, being used to indicate an essential quality of sounds such as /w/ and /j/, which is the movement (or glide) from their initial position (/u/ and /i/, respectively) to a following vowel.
Broader classifications
Manners of articulation with substantial obstruction of the airflow (stops, fricatives, affricates) are called obstruents. These are prototypically voiceless, but voiced obstruents are extremely common as well. Manners without such obstruction (nasals, liquids, approximants, and also vowels) are called sonorants because they are nearly always voiced. Voiceless sonorants are uncommon, but are found in Welsh and Classical Greek (the spelling "rh"), in Standard Tibetan (the "lh" of Lhasa), and the "wh" in those dialects of English that distinguish "which" from "witch".
Sonorants may also be called resonants, and some linguists prefer that term, restricting the word 'sonorant' to non-vocoid resonants (that is, nasals and liquids, but not vowels or semi-vowels). Another common distinction is between occlusives (stops and nasals) and continuants (all else); affricates are considered to be both, because they are sequences of stop plus fricative.
Other airstream initiations
All of these manners of articulation are pronounced with an airstream mechanism called pulmonic egressive, meaning that the air flows outward, and is powered by the lungs (actually the ribs and diaphragm). Other airstream mechanisms are possible. Sounds that rely on some of these include:
- Ejectives, which are glottalic egressive. That is, the airstream is powered by an upward movement of the glottis rather than by the lungs or diaphragm. Stops, affricates, and occasionally fricatives may occur as ejectives. All ejectives are voiceless, or at least transition from voiced to voiceless.
- Implosives, which are glottalic ingressive. Here the glottis moves downward, but the lungs may be used simultaneously (to provide voicing), and in some languages no air may actually flow into the mouth. Implosive stops are not uncommon, but implosive affricates and fricatives are rare. Voiceless implosives are also rare.
- Clicks, which are lingual ingressive. Here the back of the tongue is used to create a vacuum in the mouth, causing air to rush in when the forward occlusion (tongue or lips) is released. Clicks may be oral or nasal, stop or affricate, central or lateral, voiced or voiceless. They are extremely rare in normal words outside Southern Africa. However, English has a click in its "tsk tsk" (or "tut tut") sound, and another is often used to say "giddy up" to a horse.
- Combinations of these, in some analyses, in a single consonsant: linguo-pulmonic and linguo-glottalic (ejective) consonants, which are clicks released into either a pulmonic or ejective stop/fricative.
See also
- Index of phonetics articles
- Articulatory phonetics
- Place of articulation
- Basis of articulation
- Diction
- Phonation
- Airstream mechanism
- Relative articulation
- Nonexplosive stop
- Vocal tract
- Human voice
- Source-filter model of speech production
Bibliography
- Ladefoged, Peter; Maddieson, Ian (1996). The Sounds of the World's Languages. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-19814-8.
External links
- Movie clip showing the human articulators in action
- Interactive place and manner of articulation
- Interactive Flash website for American English, Spanish and German sounds