Macintosh 512Ke
 | |
| Also known as | M0001E |
|---|---|
| Release date | April 14, 1986 |
| Introductory price | US$2,000 (equivalent to $4,325 in 2015) |
| Discontinued | September 1, 1987 |
| Operating system | 1.0, 1.1, 2.0, 2.1, 3.0, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 4.0, 4.1,[1] 4.2, 4.3, 6.0-6.0.8 |
| CPU | Motorola 68000 @ 8 MHz |
| Memory | 512 KB RAM (built-in) |
| Predecessor | Macintosh 512K |
| Successor |
Macintosh SE Macintosh Plus |
The Macintosh 512K enhanced (512Ke) was introduced in April 1986 as a cheaper alternative to the top-of-the-line Macintosh Plus, which had debuted three months previously.[2] It's the same as the Macintosh 512K but with the 800K disk drive and 128K of ROM used in the Macintosh Plus. Like its predecessors, there was little room for expansion. Some companies did create memory upgrades that would bring the machine up to 2 MB or more. It is the earliest Macintosh model able to run System 6 OS. It is also the earliest Macintosh model that can be used as an AppleShare server, and with a bridge Mac, communicate with modern devices.[3]
Model differences
Originally, the case was identical to its predecessor, except for the model number listed on the rear bucket's agency approval label. It used the same beige-like color as well. But like the Macintosh Plus, at some point in 1987 the 512Ke adopted the standard Apple "Platinum" color, as well as exactly the same case-front design as the Plus (without the name), though keeping its original rear bucket. Later in its lifespan, the 512Ke was discounted and offered to the educational market, badged as the Macintosh ED (M0001D & later M0001ED).
The 512Ke shipped with the original short Macintosh Keyboard, but the extended Macintosh Plus Keyboard with built-in numeric keypad could be purchased optionally.[4] A version of the 512Ke sold outside of North America only included the full keyboard and was marketed as the Macintosh 512K/800.[5] Later, the larger keyboard would be included standard in North America as well.
Although the 512Ke included the same 128K ROMs and 800K disk drive as the Mac Plus, the 512Ke retained the same port connectors as the original Mac. For this reason, 512Ke users' only hard disk option was the slower, floppy-port-based Hard Disk 20, or similar products for the serial port, even though the 512Ke ROMs contained the "SCSI Manager" software that enabled the use of faster SCSI hard disks (because the ROMs are the same as the ones used in the Mac Plus which does have a SCSI port). Apple did point users to certain third-party products which could be added to the 512Ke to provide a SCSI port.[6]
Official upgrades
A Macintosh 512K could be upgraded to a 512Ke by purchasing and installing Apple's $299 Macintosh Plus Disk Drive Kit. This included the following:
- 800 KB double-sided floppy disk drive to replace the original 400 kB single-sided drive
- 128 KB ROM chips to replace original 64 KB ROM
- Macintosh Plus System Tools disk with updated system software
- Installation guide
One further upgrade made by Apple replaced the logic board and the rear case (to accommodate the different port configuration) with that of the Macintosh Plus which essentially added built-in SCSI functionality and up to 4MB RAM. As Apple's official upgrades tended to command a premium, many third party manufactures offered add-on SCSI cards as well as RAM upgrades to achieve the same functionality. The new ROM allowed the computer to run much newer system and application software and though it loaded more data into RAM it only slightly decreased the amount of available memory by 1.5K, leaving well over 370K available for applications.[7][8]
System software
After June 1986, the 512Ke shipped with System 3.2. After it was discontinued, Apple changed the recommended OS for the 512Ke to System 4.1. System 6.0.8 is the maximum OS for the 512Ke.[9]
Timeline of compact Macintosh models
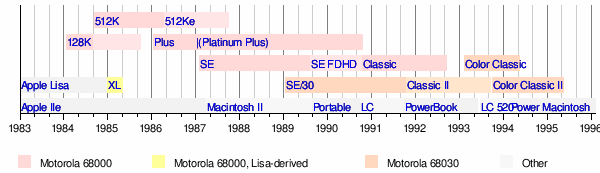
See also
References
- ↑ System Software: Configs for Mac 128K, XL, 512, & 512KE (7/94)
- ↑ Macintosh 512Ke: Specifications (Discontinued) (8/94)
- ↑ Macs and FTP
- ↑ Macintosh Plus Upgrade Kits
- ↑ The Computer Museum
- ↑ Macintosh 512K: Adding a SCSI Port
- ↑ Macintosh 512K ROM Upgrade: Memory Available
- ↑ Macintosh Plus: Description (Discontinued) The Macintosh Plus Logic Board Kit
- ↑ Macintosh 512Ke: Technical Specifications
External links
- Macintosh 512Ke technical specifications at apple.com]