Lot's Wife (crag)
| Native name: <span class="nickname" ">Sōfu Iwa | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Izu Islands |
| Coordinates | 29°47′39″N 140°20′31″E / 29.79417°N 140.34194°E |
| Archipelago | Izu Islands |
| Area | 0.0037 km2 (0.0014 sq mi) |
| Length | 84 m (276 ft) |
| Width | 56 m (184 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 99 m (325 ft) |
| Administration | |
|
Japan | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 0 |
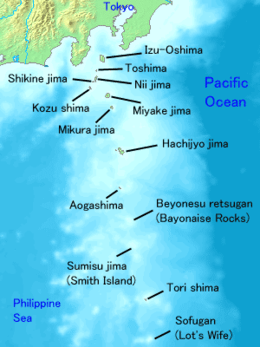
Lot's Wife (孀婦岩 Sōfu Iwa or Sōfu Gan, "Widow's Crag") is a volcanic, deserted island located in the Philippine Sea approximately 650 kilometres (400 mi) south off the coast of Tokyo, in the southernmost tip of the Izu archipelago, Japan. Though only 0.01 km2 in area, it reaches almost 100 m high.
Geography
The island is a basalt pillar with sheer sides, the only visible portion of a submarine volcanic caldera extending 2.6 kilometres (1.6 mi) south-east at an average depth of 240 metres (790 ft). The above sea-level portion measures approximately 84 meters east-west and 56 meters north-south, with a summit height of 99 metres (325 ft). The sides of the island features several geological joints facing the water's surface.
The island lies approximately 650 kilometres (400 mi) south off the coast of Tokyo and 76 kilometres (47 mi) from nearby Torishima. Due to its shape and heavy seas it is almost impossible to disembark on the island, although attempts have been made by rock climbers successfully in 1972 and 2003 (though several accidents have been registered). The site is also known for the transparency of its surrounding waters and abundance of fish, which makes it a popular scuba diving spot.
The only vegetation on the island is a few clumps of Poaceae, and the island attracts a small number of seabirds for nesting.
History
On April 9, 1788, British merchant sailor John Meares sighted what he came to describe as “the most marvellous thing” he had ever set his eyes on, a small island he and the ship’s crew decided to baptize as Lot's Wife, referring to the Book of Genesis 19:26. The Japanese name Sōfu Iwa (“The Widow Crag”) is rather freely translated from English.[1]
During the Pacific War, Sofu Gan was used by US Navy submariners as a reference marker for calibration of instruments as they entered Japanese waters.[2] The uninhabited/uninhabitable island was the southernmost Japanese island not occupied by the United States after the 1952 San Francisco Treaty. It is currently administratively part of Tokyo Metropolis.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sofuiwa. |
References
- ↑ 孀婦岩 (Sōfu Iwa). Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia (Japanese ed.)ja:孀婦岩 browsed 2008-02-23.
- ↑ O'Kane, Richard H. Clear the Bridge! The War Patrols of the USS Tang London Macdonald & Jane's 1978 p.210 ISBN 0354011855
External links
- Sofugan: Japan Coast Guard submarine volcano database (Japanese)
- "Sofugan: National catalogue of the active volcanoes in Japan" (PDF). - Japan Meteorological Agency