Little Colorado River
| Little Colorado River | |
| Tółchíʼíkooh (Navajo) Colorado Chiquito (Spanish) | |
 The Little Colorado River carves a deep canyon just above its confluence with the Colorado | |
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| States | Arizona, New Mexico |
| Region | Apache County |
| Part of | Colorado River |
| Tributaries | |
| - left | Silver Creek |
| - right | Zuni River, Puerco River |
| Primary source | West Fork Little Colorado River |
| - location | Mount Baldy, White Mountains |
| - elevation | 10,000 ft (3,048 m) |
| Secondary source | East Fork Little Colorado River |
| Source confluence | |
| - location | Greer |
| - elevation | 8,359 ft (2,548 m) |
| - coordinates | 34°00′15″N 109°27′24″W / 34.00417°N 109.45667°W |
| Mouth | Colorado River |
| - location | Grand Canyon, Coconino County |
| - elevation | 2,700 ft (823 m) |
| - coordinates | 36°11′28″N 111°48′14″W / 36.19111°N 111.80389°WCoordinates: 36°11′28″N 111°48′14″W / 36.19111°N 111.80389°W |
| Length | 338 mi (544 km) [1] |
| Basin | 26,500 sq mi (68,635 km2) |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 405 cu ft/s (11 m3/s) |
| - max | 120,000 cu ft/s (3,398 m3/s) |
| - min | 150 cu ft/s (4 m3/s) |
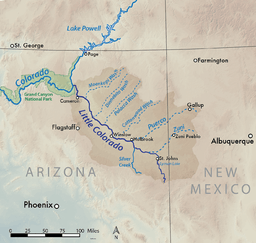 Map showing the Little Colorado River basin. The Little Colorado River flows northwest through eastern Arizona to join the Colorado north of Flagstaff. | |
The Little Colorado River is a tributary of the Colorado River in the U.S. state of Arizona,[2] providing the principal drainage from the Painted Desert region. Together with its major tributary, the Puerco River, it drains an area of about 26,500 square miles (69,000 km2) in eastern Arizona and western New Mexico. Although it stretches almost 340 miles (550 km),[1] only the headwaters and the lowermost reaches flow year-round. Between St. Johns and Cameron, most of the river is a wide, braided wash, only containing water after heavy snowmelt or flash flooding.
The lower 40 miles (64 km) of the Little Colorado forms one of the largest arms of the Grand Canyon, at over 3,000 feet (910 m) deep where it joins the Colorado near Desert View in Grand Canyon National Park.
Course
The river rises as two forks in the White Mountains of mid-eastern Arizona, in Apache County. The West Fork starts in a valley on the north flank of Mount Baldy at an elevation of nearly 10,000 feet (3,000 m), while the East Fork starts nearby. The forks meet in a canyon near the town of Greer, forming the main Little Colorado River. It flows into River Reservoir, then leaves the canyon near Eagar. The river then turns north, meandering through Richville Valley, before emptying into Lyman Lake, impounded by an irrigation dam built in 1912.[3] From there the river continues north, past the town of St. Johns. Shortly afterwards, the river transforms from a perennial stream to an ephemeral wash as it travels northwestwards through Hunt Valley, where it receives the Zuni River, then receiving Silver Creek and the Puerco River—its main tributaries—near the town of Holbrook as it flows into the Painted Desert.[4]


The Little Colorado passes Joseph City and crosses the Southern Transcon route of the BNSF Railway (originally the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad), now winding north into Coconino County. The river enters the Navajo Indian Reservation, and drops over the 185-foot (56 m) Grand Falls of the Little Colorado shortly after. Below Grand Falls, the river flows through a short but rugged canyon for about 15 miles (24 km). Emerging into the desert again, the Little Colorado skirts the eastern edge of Wupakti National Monument and passes the town of Cameron, where it is bridged by U.S. Highway 89.
From Cameron, the Little Colorado River carves an extremely steep and narrow gorge into the Colorado Plateau, eventually achieving a maximum depth of about 3,200 feet (980 m). The depth of the canyon is such that groundwater is forced to the surface, forming numerous springs that restore a perennial river flow. It joins Colorado deep inside the Grand Canyon, miles from any major settlement.[4] The confluence marks the end of the Marble Canyon segment of the Grand Canyon and the beginning of Upper Granite Gorge.[5]
Discharge
The Little Colorado River is one of the two major tributaries of the Colorado River in Arizona.[6] Runoff typically peaks twice a year, first in the early spring (February–April) from snow melt and highland rain; and in the summer (July–September) from monsoon storms. The annual runoff is extremely variable with the possibility of no flow occurring due to a weak snow pack or lack of summer rain. Conversely, years such as 1949, 1973, 1979, 1983 and 1993 have seen massive volumes of spring snowmelt while large monsoon runoff has occurred in 1955, 1964, 1984 and 2006. Monthly average flows in the springtime average several hundred cfs and can reach 2,000 to 3,000 cubic feet per second (57 to 85 m3/s). Only the upper reaches of the river above St. Johns, and the lowermost stretch below Cameron, flow year round; the middle section is basically a huge arroyo that carries water only during the wet seasons.
According to a streamflow gauge near Cameron, before the river enters the Grand Canyon, the river's average annual flow was 367.2 cubic feet per second (10.40 m3/s) from 1948 to present. The highest annual average was 1,127 cubic feet per second (31.9 m3/s) in 1973, and the lowest was 14.1 cubic feet per second (0.40 m3/s) in 2000.[7] The river's peak flows can be far higher than its average flow, because of quick desert runoff from cloudbursts. At the same gauge, peak flows were recorded from 1923 to 2008, with spotty data from 1924 to 1947. The highest recorded peak was 120,000 cubic feet per second (3,400 m3/s) on September 20, 1923, while the lowest was 1,590 cubic feet per second (45 m3/s) in 1974.[8]
History
Human activity in the Little Colorado River watershed dates back to the early Holocene epoch, in the last glacial period. Nomadic hunter-gatherers inhabited the relatively water-rich and diverse upper basin of the Little Colorado for almost 8,000 years before the Navajo, Apache and Hopi tribes populated the area. Many of these people practiced small-scale irrigation in riverside villages, located in sheltered canyons and cliffs that provided defense.[9]
Early Spanish explorers exploring the Grand Canyon area were most likely the first Europeans to see the Little Colorado River. They called it Colorado Chiquito, the Little Colorado.[10] Other than fur trappers and mountain men, one of the first organized expeditions into the area of the Little Colorado River was led by Amiel Weeks Whipple in 1853–54[11] during one of the expeditions to map out a route for a transcontinental railroad. Called The Great Railroad Expeditions, or Pacific Railroad Surveys, Whipple's expedition consisted of several teams going roughly along the 35th parallel from Albuquerque to the Pacific, following the Santa Fe Trail route.

The Little Colorado River, also known as the Flax River, and the first Rio Chiquito, is depicted and labelled as such on a map compiled by Lt. Joseph C. Ives and published in the official volumes of those expeditions. Ives would again return to the area in 1858 after navigating a steamboat named the Explorer up the Colorado from south of Yuma northwards to Black Canyon, at which point his party went ashore and attempted to go up into the Grand Canyon until the sheer cliffs prevented them from doing so. Leaving the canyon they proceeded overland and someplace in the vicinity of the Grand Falls (also known as the Chocolate Falls) on the Little Colorado, picked up the Whipple trail from four years prior.[12]
The Powell Geographic Expedition, on August 10, 1869, was one of the first American parties to sight the Little Colorado River.[13] Powell and some of his crew explored a segment of the Little Colorado River canyon, although they mainly found it impassable. In diary entries, they recorded its name as "Flax River", for the flax that makes up much of the river's riparian zone[14]—and "Colorado Chiquito"—so, presumably they already knew about the river before they had come on the expedition.[15]
| “ | It is a lo[a]thesome little stream, so filthy and muddy that it fairly stinks. It is only 30 to 50 [yards] wide now and in many places a man can cross it on the rocks without going on to his knees ... [The Little Colorado was] as disgusting a stream as there is on the continent ... half of its volume and 2/3 of its weight is mud and silt. [It was little but] slime and salt ... a miserably lonely place indeed, with no signs of life but lizards, bats and scorpions. It seemed like the first gates of hell. One almost expected to see Cerberus poke his ugly head out of some dismal hole and growl his disapproval of all who had not Charon's pass.[13] —George Bradley and Jack Sumner, August 1869 |
” |
This was in fact an inaccurate depiction of the Little Colorado, as the muddy flow they observed was the result of a rare flash flood. The river is normally a bright blue color caused by dissolved travertine and limestone in the water, similar to Havasu Creek, another major tributary of the Colorado within the Grand Canyon.[13]
In the 1870s, Mormon colonists migrated southwards from Salt Lake City and settled in the lower part of the Little Colorado River valley.[16] Expeditions had been sent into the basin about five years before to determine the qualities of the area. The Mormons founded Joseph City near the confluence with the Puerco River, and four others nearby, although Joseph City is the only one that still exists. Settlers continued traveling into the area through 1876, although many of them had great difficulty in crossing the Little Colorado. Although shallow and slow-flowing, the river flows through soft sand and in some places, even quicksand, creating non-ideal conditions for their wagons.[17]
There were two primary crossings of the Little Colorado—one at the Grand Falls, and one at Black Falls, a smaller waterfall some 10 miles (16 km) downstream. It was easier to ford the river at the two waterfalls because at that point, it flows over hard bedrock, making the crossing much easier. The Mormons also made many attempts to construct dams on the river to provide irrigation water—as far upstream as the confluence of the river's forks and as far downstream as below Grand Falls—but most of them failed because of the Little Colorado's fickle variations in discharge.[18] Finally, they managed to construct one at Joseph City that lasted for 29 years. Despite the continued hardships, the Mormons persisted, successfully established their colonies, and survived in the region for many decades.[18][19] Later, Hispanics began to move into the Little Colorado River watershed from the Rio Grande area, establishing St. Johns and Concho. American ranchers from New Mexico also began to colonize the region, creating Eagar and Springerville.[20] For many years, Mormons were the primary group living in the watershed until the 1960s, when their independent towns and farms were absorbed into the growing Arizonan economy.[9]
River modifications
Because of its isolation, most of the Little Colorado has remained free of human development. However, near its headwaters, the river is dammed twice, first in River Reservoir, then in Lyman Lake, where its water is stored for irrigation. Another reservoir downstream of Springerville, where Mormon colonists dammed the river in 1905 to form Zion Reservoir, is now completely silted in. Many other earthen and masonry dams originally built along the river by the Mormons no longer exist. At very few points is the river confined by levees, with the exception of a 2,300-foot (700 m) floodwall near Holbrook. There are also few bridges for a river of its length.
In one of the worst radioactive spills in the U.S. history, on July 16, 1979, 100 million US gallons (380,000,000 l; 83,000,000 imp gal) of radioactive water containing uranium tailings breached into the North Fork of the Puerco River from a tailing pond of a uranium mine owned by Kerr-McGee Company and United Nuclear Corporation. Approximately 1,100 tons of uranium mine waste contaminated 250 acres (1.0 km2) of land and up to 50 miles (80 km) of the Puerco River, traveling into the Little Colorado River as far as the Navajo Indian Reservation. Traces of the spill can still be found today.[21][22]

See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Little Colorado River. |
References
- 1 2 "USGS National Atlas Streamer". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2015-01-10.
- ↑ "Little Colorado River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. 1980-02-08. Retrieved 2010-01-17.
- ↑ "Lyman Lake State Park". Arizona State Parks. Retrieved 2010-01-17.
- 1 2 USGS Topo Maps for United States (Map). Cartography by United States Geological Survey. ACME Mapper. Retrieved 2010-01-17.
- ↑ "Grand Canyon of the Colorado" (PDF). Fire.biol.wwu.edu. Retrieved 2016-07-16.
- ↑ See File:Coloradorivermap.jpg; the other is the Gila River.
- ↑ "USGS Gage #09402000 on the Little Colorado River near Cameron (Average Annual Streamflow)" (1947–present). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved 2010-01-17.
- ↑ "USGS Gage #09402000 on the Little Colorado River near Cameron (Peak Streamflow)" (1923–present). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved 2010-01-17.
- 1 2 "The Little Colorado River Basin in Arizona". Land Use History of the Colorado Plateau. Land Use History of North America. Retrieved 2010-10-17.
- ↑ "Rivers of Arizona: Size, Extent, Etc.". Books of the Southwest. University of Arizona Library. p. 39. Retrieved 2010-01-17.
- ↑ Worster, Donald. A River Running West: The Life of John Wesley Powell.
- ↑ also see Goetzmann, William H. "Army Exploration in the American West, 1803-1863," 1959.
- 1 2 3 Dolnick, Edward (2002). Down the Great Unknown: John Wesley Powell's 1869 Journey of Discovery and Tragedy Through the Grand Canyon. HarperCollins. p. 234. ISBN 0-06-095586-4.
- ↑ Euler, Robert C. (2009-01-13). "The Archaeology of the Canyon Country". Geological Survey Professional Paper 670: John Wesley Powell and the Anthropology of the Canyon Country. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved 2010-01-17.
- ↑ Powell, John Wesley (2004). Cooley, John, ed. Exploring the Colorado River: Firsthand Accounts by Powell and His Crew. Courier Dover Publications. pp. 148–150. ISBN 0-486-43525-3.
- ↑ Abruzzi, William S. (1993). Dam that river! Ecology and Mormon settlement in the Little Colorado River Basin. University Press of America. ISBN 0-8191-9126-4.
- ↑ Dam that river! Ecology and Mormon settlement in the Little Colorado River Basin, p. 20
- 1 2 Abruzzi, William S. "Ecology and Mormon Colonization in the Little Colorado River Basin, Arizona". Land Use History of the Colorado Plateau. Land Use History of North America. Retrieved 2010-10-17.
- ↑ Abruzzi, William S. "The social and ecological consequences of early cattle ranching in the Little Colorado River Basin". Land Use History of the Colorado Plateau. Land Use History of North America. Retrieved 2010-10-17.
- ↑ Dam that river! Ecology and Mormon settlement in the Little Colorado River Basin, p. 21
- ↑ Brendan Giusti, Radiation Spill in Church Rock Still Haunts 30 Years Later, The Daily Times (Farmington, New Mexico), July 16, 2009, Section: Local
- ↑ Carl Jensen, Project Censored (U.S.) 20 Years of Censored News Seven Stories Press, July 1, 2003, p. 84, ISBN 1-888363-52-5


