List of web browsers
The following is a list of web browsers that are notable.
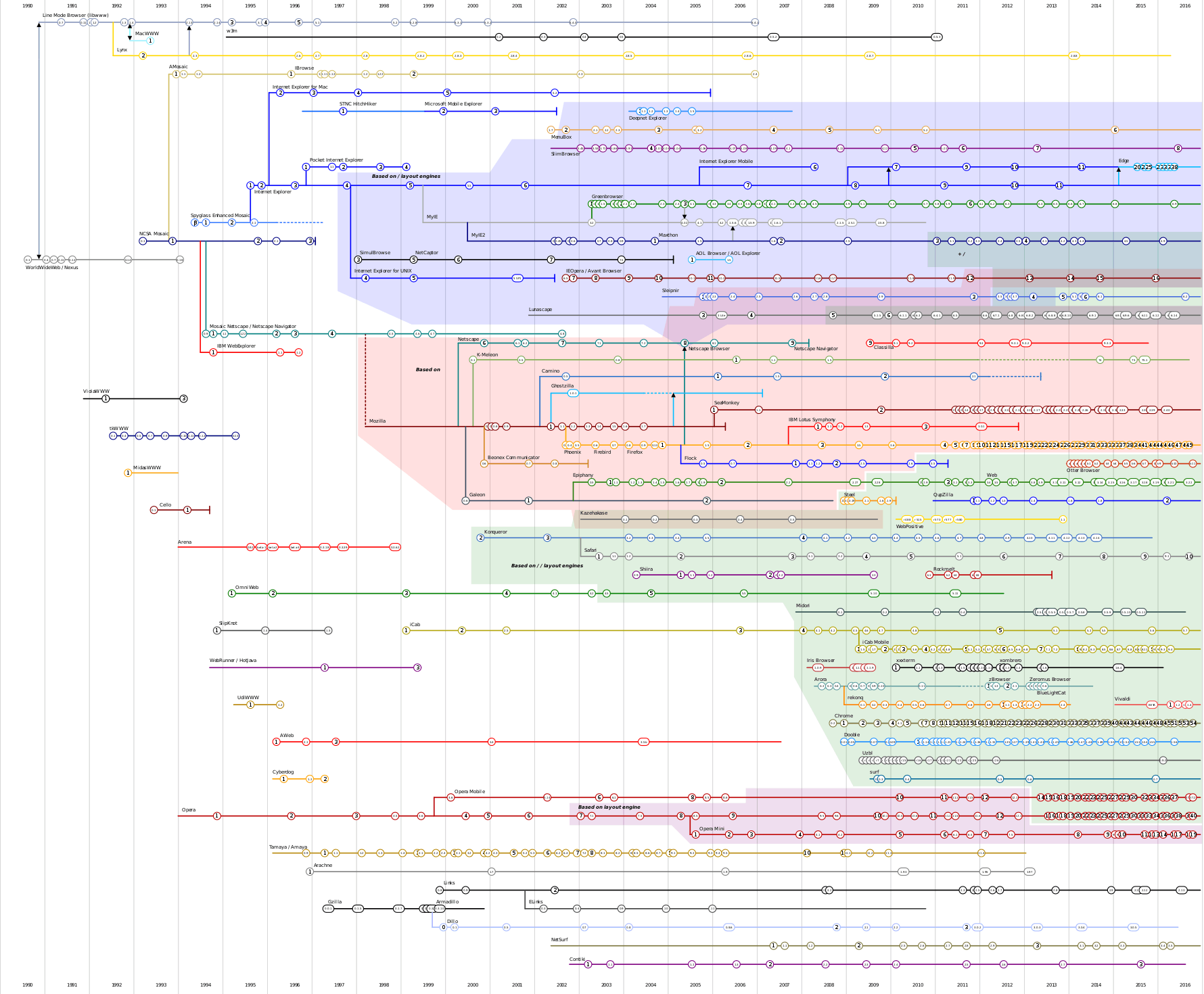
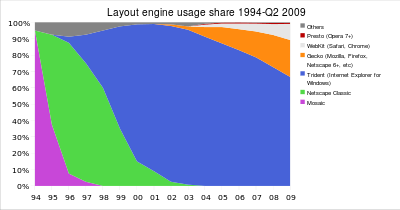
Historical
This is a table of personal computer web browsers by year of release of major version, in chronological order, with the approximate number of worldwide Internet users in millions. Note that Internet user data is related to the entire market, not the versions released in that year. The increased growth of the Internet in the 1990s and 2000s means that current browsers with small market shares have more total users than the entire market early on. For example, 90% market share in 1997 would be roughly 60 million users, but by the start of 2007 9% market share would equate to over 90 million users.[1]
| Year | Web browsers | Internet users (in millions)[1][2][3][4] |
|---|---|---|
| 1991 | WorldWideWeb (Nexus) | 4 |
| 1992 | ViolaWWW, Erwise, MidasWWW, MacWWW (Samba) | 7 |
| 1993 | Mosaic, Cello,[5] Lynx 2.0, Arena, AMosaic 1.0 | 10–14 |
| 1994 | IBM WebExplorer, Netscape Navigator, SlipKnot 1.0, MacWeb, IBrowse, Agora (Argo), Minuet | 20–25 |
| 1995 | Internet Explorer 1, Netscape Navigator 2.0, OmniWeb, UdiWWW,[6] Internet Explorer 2, Grail | 16–44 |
| 1996 | Arachne 1.0, Internet Explorer 3.0, Netscape Navigator 3.0, Opera 2.0, PowerBrowser 1.5,[7] Cyberdog, Amaya 0.9,[8] AWeb, Voyager |
36–77 |
| 1997 | Internet Explorer 4.0, Netscape Navigator 4.0, Netscape Communicator 4.0, Opera 3.0,[9] Amaya 1.0[8] | 70–120 |
| 1998 | iCab, Mozilla | 147–188 |
| 1999 | Amaya 2.0,[8] Mozilla M3, Internet Explorer 5.0 | 248–280 |
| 2000 | Konqueror, Netscape 6, Opera 4,[10] Opera 5,[11] K-Meleon 0.2, Amaya 3.0,[8] Amaya 4.0[8] | 361–413 |
| 2001 | Internet Explorer 6, Galeon 1.0, Opera 6,[12] Amaya 5.0[8] | 499–513 |
| 2002 | Netscape 7, Mozilla 1.0, Phoenix 0.1, Links 2.0, Amaya 6.0,[8] Amaya 7.0[8] | 587–662 |
| 2003 | Opera 7,[13] Safari 1.0, Epiphany 1.0, Amaya 8.0[8] | 719–778 |
| 2004 | Firefox 1.0, Netscape Browser, OmniWeb 5.0 | 817–910 |
| 2005 | Safari 2.0, Netscape Browser 8.0, Opera 8,[14] Epiphany 1.8, Amaya 9.0,[8] AOL Explorer 1.0, Maxthon 1.0, Shiira 1.0 | 1018–1029 |
| 2006 | SeaMonkey 1.0, K-Meleon 1.0, Galeon 2.0, Camino 1.0, Firefox 2.0, Avant 11, iCab 3, Opera 9,[15] Internet Explorer 7 | 1093–1157 |
| 2007 | Maxthon 2.0, Netscape Navigator 9, NetSurf 1.0, Flock 1.0, Safari 3.0, Conkeror | 1319–1373 |
| 2008 | Konqueror 4, Safari 3.1, Opera 9.5,[16] Firefox 3, Amaya 10.0,[8] Flock 2, Chrome 1, Amaya 11.0[8] | 1562–1574 |
| 2009 | Internet Explorer 8, Chrome 2–3, Safari 4, Opera 10,[17] SeaMonkey 2, Camino 2, Firefox 3.5, surf | 1743–1802 |
| 2010 | K-Meleon 1.5.4, Firefox 3.6, Chrome 4–8, Opera 10.50,[18] Safari 5, xxxterm, Opera 11 | 1971–2034 |
| 2011 | Chrome 9–16, Firefox 4-9, Internet Explorer 9, Maxthon 3.0, SeaMonkey 2.1–2.6, Opera 11.50, Safari 5.1 | 2264–2272 |
| 2012 | Chrome 17–23, Firefox 10–17, Internet Explorer 10, Maxthon 4.0, SeaMonkey 2.7-2.14, Opera 12, Safari 6 | 2497–2511 |
| 2013 | Chrome 24–31, Firefox 18–26, Internet Explorer 11, SeaMonkey 2.15-2.23, Opera 15–18, Safari 7 | 2712 |
| 2014 | Chrome 32–39, Firefox 27–34, SeaMonkey 2.24-2.30, Opera 19–26, Safari 8 | 3079 |
| 2015 | Microsoft Edge, Vivaldi |
Notable releases
In order of release:
- WorldWideWeb, February 25, 1990
- Mosaic, April 22, 1993
- Netscape Navigator and Netscape Communicator, October 13, 1994
- Internet Explorer, August 16, 1995
- Opera, 1996, see History of the Opera web browser
- Mozilla Navigator, June 5, 2002[19]
- Safari, January 7, 2003
- Mozilla Firefox, November 9, 2004
- Google Chrome, September 2, 2008
- Microsoft Edge, July 9, 2015
Layout engines
- Gecko is developed by the Mozilla Foundation.
- Goanna is a fork of Gecko developed by Moonchild Productions.
- KHTML is developed by the KDE project.
- Presto is developed by Opera Software for use in Opera. Development stopped as Opera transitioned to Blink.
- Tasman was developed by Microsoft for use in Internet Explorer 5 for Macintosh.
- Trident is developed by Microsoft for use in the Windows versions of Internet Explorer 4 to Internet Explorer 11.
- WebKit is a fork of KHTML by Apple Inc. used in Apple Safari, Chromium and Google Chrome.
- Blink is a 2013 fork of WebKit's WebCore component by Google used in Chromium, Google Chrome and Opera.[20]
- Servo is an experimental web browser layout engine being developed cooperatively by Mozilla and Samsung.
- EdgeHTML is the engine developed by Microsoft for Edge. It is a largely rewritten fork of Trident with all legacy code removed.
Graphical
Current/maintained projects are in boldface.
Trident shells
Other software publishers have built browsers and other products around Microsoft's Trident engine. The following browsers are all based on that rendering engine:
- 360 Secure Browser
- AOL Explorer (discontinued)
- Bento Browser (built into Winamp)
- Deepnet Explorer (discontinued)
- GreenBrowser
- Internet Explorer
- MediaBrowser (discontinued)
- MenuBox
- MSN Explorer (discontinued)
- NeoPlanet (discontinued)
- NetCaptor (discontinued)
- RealPlayer
- SlimBrowser
- Tencent Traveler
- TomeRaider (discontinued)
- UltraBrowser (discontinued)
- WebbIE
Gecko-based
- Camino for Mac OS X (formerly Chimera)[21] (discontinued)
- Conkeror, keyboard-driven browser
- Galeon, GNOME's old default browser (discontinued)
- K-Meleon for Windows
- K-MeleonCCF ME for Windows (based on K-Meleon core, mostly written in Lua)
- K-Ninja for Windows (discontinued; based on K-Meleon)
- MicroB (for Maemo)
- Minimo (for mobile, discontinued)
- Mozilla Firefox (formerly Firebird and Phoenix)
- AT&T Pogo (discontinued; based on Firefox)
- CometBird an optimized fork of Firefox (discontinued)
- Comodo IceDragon (Firefox-based web browser for Windows)
- Flock (discontinued; was based on Firefox until version 2.6.1, and based on Chromium thereafter)
- Iceweasel, Debian's Firefox rebrand
- GNU IceCat, GNU's fork of Firefox
- Netscape Browser 8 to Netscape Navigator 9 (discontinued)
- Timberwolf, AmigaOS' Firefox rebrand
- Tor Browser, patched Firefox ESR for browsing in Tor anonymity network
- Swiftfox (discontinued; processor-optimised builds based on Firefox)
- Swiftweasel (discontinued; processor-optimised builds based on Iceweasel)
- Waterfox (Windows 64-bit-only browser based on Firefox)
- xB Browser (discontinued; formerly XeroBank Browser and Torpark), portable browser for anonymous browsing, originally based on Firefox
- Firefox for mobile (codenamed Fennec)
- Mozilla Application Suite (discontinued)
- Skyfire (for mobile) (discontinued)
- Yahoo! Browser (or partnership browsers e.g. "AT&T Yahoo! Browser"; "Verizon Yahoo! Browser"; "BT Yahoo! Browser" etc.)
Goanna-based
- Pale Moon (a fork of Firefox for Windows and Linux that maintains the traditional UI)
Gecko- and Trident-based
Browsers that use both Trident and Gecko include:
- K-Meleon with the IE Tab extension
- Mozilla Firefox with the IE Tab extension
- Netscape Browser 8 (discontinued)
Webkit- and Trident-based
Gecko-, Trident- and WebKit-based
Browsers that can use Trident, Gecko and WebKit include:
KHTML-based
Presto-based
- Internet Channel (for Wii console, Opera-based)
- Nintendo DS Browser (Opera-based)
- Opera (for releases up until 12.17[24])
WebKit-based
- Amazon Kindle (experimental)
- Arora (discontinued)
- BOLT browser (discontinued)
- Chromium
- Comodo Dragon
- Eco Browser
- Epic
- RockMelt (discontinued)
- SRWare Iron
- Torch
- Yandex Browser
- Cốc Cốc
- Dolphin Browser (Android and Bada)
- Dooble
- Firefox for iOS
- Flock (discontinued) (version 3.0 and above)
- iCab (version 4 uses WebKit; earlier versions used its own rendering engine)
- Iris Browser (discontinued)
- Konqueror (version 4 can use WebKit as an alternative to its native KHTML[25])
- Maxthon (version 3.0 and above)
- Midori
- Nintendo 3DS NetFront Browser NX
- OmniWeb
- Otter Browser (aims to recreate the features of old Opera)
- OWB
- QtWeb (discontinued)
- QupZilla
- Roccat Browser
- Rekonq
- Safari
- PhantomJS (a headless browser)
- Shiira (discontinued)
- SlimBoat[26]
- Steel for Android
- Steam ingame browser
- surf
- Uzbl
- Web (previously known as Epiphany)
- Web Browser for S60, used in all Nokia Symbian smartphones.
- webOS, used in the Palm Pre, Palm Pixi, Pre 2, HP Veer, Pre 3 and TouchPad mobile devices
- WebPositive, browser in Haiku
- xombrero
Blink-based
EdgeHTML-based
For Java platform
- ThunderHawk
- BOLT Browser
- HotJava
- Opera Mini
- Teashark (discontinued)
Specialty browsers
Browsers created for enhancements of specific browsing activities.
Current
- Gollum browser (Created specially for browsing Wikipedia)
- Kirix Strata (Designed for data analytics)
- Miro (A media browser that integrates BitTorrent add-on)
- Nightingale (open source audio player and web browser based on the Songbird (see below) media player source code)
- SpaceTime (Search the web in 3D)
- Wyzo (A media browser that integrates BitTorrent-like add-on)
- Zac Browser (For children with autism, and autism spectrum disorders such as Asperger syndrome, pervasive developmental disorders (PDD), and PDD-NOS)
Discontinued
- Ghostzilla (Blends into the GUI to hide activity)
- Prodigy Classic (Executable only within the application)
- Flock (To enhance social networking, blogging, photo-sharing, and RSS news-reading)
- RockMelt (Designed to combine web browsing, and social activities such as Facebook and Twitter into a unified one window experience)
- Songbird (browser with advanced audio streaming features and built in media player with library.)
Mosaic-based
Mosaic was the first widely used web browser. The National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) licensed the technology and many companies built their own web browser on Mosaic. The best known are the first versions of Internet Explorer and Netscape.
- AMosaic
- IBM WebExplorer
- Internet Explorer
- Internet in a Box
- Mosaic-CK
- Netscape
- Spyglass Mosaic
- VMS Mosaic
Others
- Abaco (for Plan 9 from Bell Labs)
- Amaya
- Arachne (for DOS)
- Arena
- Ariadna (AMSD Ariadna) (first Russian web browser, discontinued)
- AWeb (AmigaOS)
- Baidu Mobile Browser
- Charon (for Inferno)
- Dillo (Small, fast, free, minimalistic, and multi-platform)
- DR-WebSpyder (for DOS, discontinued)
- Embrowser (for DOS, discontinued)
- Gazelle (from Microsoft Research, OS-like)
- IBrowse (for AmigaOS)
- Mothra (for Plan 9 from Bell Labs)
- NetPositive (for BeOS)
- NetSurf (An open source web browser for RISC OS and GTK+ written in C)
- Planetweb browser (discontinued for Dreamcast)
- Qihoo 360 mobile browsers
- Phoenix, a browser based on tkWWW
- tkWWW, based on Tcl
- Voyager (for AmigaOS)
Mobile browsers
The most popular mobile browsers as of June 2014 are:[29]
Text-based
See also
- Browser timeline
- Comparison of web browsers
- List of layout engines
- List of search engines
- List of web browsers for Unix and Unix-like operating systems
- Usage share of web browsers
References
- 1 2 "History and Growth of the Internet". Internet World Stats. June 21, 2011. Retrieved July 23, 2011.
- ↑ "Internet users". The World Bank Group. 15 December 2010. Retrieved 2011-04-13.
- ↑ "Internet user stats by areppim". areppim AG. Archived from the original on 14 September 2013. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ↑ http://www.internetlivestats.com/internet-users/
- ↑ Brennan, Elaine (13 Jun 1993). "World Wibe Web Browser: Ms-Windows (Beta) (1/149)". Humanist Archives Vol. 7. Retrieved 27 March 2010.
- ↑ Großmann, Prof. Dr. Hans Peter. "Department of Information Resource Management". University of Ulm. Retrieved 22 March 2010.
- ↑ "Oracle Introduces PowerBrowser". Oracle Corporation. 18 June 1996. Retrieved 2007-10-31.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Release history". W3C. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ↑ "Opera Software Releases 3.60" (Press release). Opera Software. 1998-05-12. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
- ↑ "Opera 4.0 for Windows Released" (Press release). Opera Software. 2000-06-27. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
- ↑ "The Browser War Lights Up in Europe" (Press release). Opera Software. 2000-12-06. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
- ↑ "Opera 6.0 for Windows launched after record-breaking beta" (Press release). Opera Software. 2001-11-29. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
- ↑ "Opera 7 Ready to Rock the Web" (Press release). Opera Software. 2003-01-28. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
- ↑ "Speed, Security and Simplicity: Opera 8 Web Browser Released Today" (Press release). Opera Software. 2005-04-19. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
- ↑ "Your Web, Your Choice: Opera 9 Gives You the Control" (Press release). Opera Software. 2006-06-20. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
- ↑ "Opera redefines Web browsing yet again" (Press release). Opera Software. 2008-06-12. Retrieved 2008-06-12.
- ↑ "Turbocharge your Web experience with Opera 10" (Press release). Opera Software. 2009-09-01. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- ↑ "The world's fastest browser for Windows" (Press release). Oslo, Norway: Opera Software. 2010-03-02. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ↑ "Mozilla 1.0". mozilla.org. 2002. Retrieved 2008-09-07.
- ↑ "Google going its own way, forking WebKit rendering engine". Ars Technica. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ↑ http://caminobrowser.org Camino reaches its end
- ↑ "Try Avant Browser 2012 for a Choice of Rendering Engines". PC World. 2012-01-03. Retrieved 2012-01-03.
- ↑ "Have it all: Lunascape, the browser with three engines". CNET News. 2008-11-24. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- ↑ "300 million users and move to WebKit". Opera Developer News.
- ↑ "Projects/WebKit/Part — KDE TechBase". KDE TechBase. Retrieved 2010-03-30.
- ↑ "Slimboat". slimboat.com. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ↑ "A first peek at Opera 15 for Computers". Opera. Retrieved 2013-06-24.
- ↑ "Slimboat". slimjet.com. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ↑ NetApplications Summary of Mobile Browsers. Retrieved 2 July 2014
External links
- Adrian Roselli, evolt.org Browser Archive (2004). List and archive of many current and obsolete web browsers.
- Daniel R. Tobias, Brand-X Browsers (2002).
- Michael Bernadi, DOS Applications for Internet Use (2006).