Leucocyanidin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
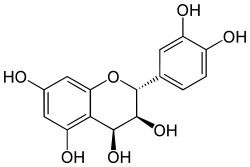
| IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4S)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,4,5,7-tetrol | |
| Other names
Leucocianidol Leucocianidolum Leucocyanidol Leukocyanidine Procyanidol Resivit Leucoanthocyanidol Vitamin P faktor 3,4-Cyanidiol (2R,3S,4S)-3,4,5,7,4-pentahydroxyflavan | |
| Identifiers | |
| 69256-15-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:11412 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL124022 |
| ChemSpider | 389677 |
| PubChem | 440833 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O7 | |
| Molar mass | 306.26 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Leucocyanidin is a colorless chemical compound related to leucoanthocyanidins. Leucoyanidin can be found in Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse chestnut), Anacardium occidentale (Cashew, acajou), Arachis hypogaea (Earth Nut), Areca catechu (Areca nut), Asimina triloba (American custardapple), Cerasus vulgaris (Cherry), Cinnamomum camphora (Camphor), Erythroxylon coca (coca), Gleditsia triacanthos (Honey locust), Hamamelis virginiana (American Witch Hazel), Hippophae rhamnoides (Hippophae berry Sanddorn), Hordeum vulgare (Barley), Humulus lupulus (bine), Hypericum perforatum (perikon Amber), Laurus nobilis, Magnolia denudata (Hsin-I Yulan-Magnolie), Malva silvestris (Blue mallow), Musa acuminata × balbisiana (Banana), Nelumbo nucifera (Baladi bean), Pinus strobus (Eastern white pine), Prunus serotina ssp. serotina (black cherry), Psidium guajava (Common guava), Quercus alba (White oak), Quercus robur (Common oak), Rumex hymenosepalus (Arizona dock), Schinus terebinthifolius (Brazilian pepper tree), Terminalia arjuna (arjun), Terminalia catappa (Indian almond), Theobroma cacao (Cacao), Drimia maritima (Sea Squill), Vicia faba (bell-bean), Vitis vinifera (Common Grape Vine), Zea Mays (Corn, mais), Ziziphus jujuba (jujube, Chinese date).[1]
Chemistry
(+)Leucocyanidin can be synthesized from (+)dihydroquercetin by sodium borohydride reduction.[2]
Molar equivalents of synthetic (2R,3S,4R or S)-leucocyanidin and (+)-catechin condense with exceptional rapidity at pH 5 under ambient conditions to give the all-trans-[4,8]- and [4,6]-bi-[(+)-catechins] (procyanidins B3, B6) the all-trans-[4,8:4,8]- and [4,8:4,6]-tri-[(+)-catechins] (procyanidin C2 and isomer).[3]
Metabolism
Leucocyanidin oxygenase uses leucocyanidin, 2-oxoglutarate, and O2 to produce cis-dihydroquercetin, trans-dihydroquercetin (taxifolin), succinate, CO2, and H2O.
Leucoanthocyanidin reductase (LAR or leucocyanidin reductase LCR) uses (2R,3S)-catechin, NADP+, and H2O to produce 2,3-trans-3,4-cis-leucocyanidin, NADPH, and H+. Its gene expression has been studied in developing grape berries and grapevine leaves.[4] Its activity has also been measured in leaves, flowers, and seeds of the legumes Medicago sativa, Lotus japonicus, Lotus uliginosus, Hedysarum sulfurescens, and Robinia pseudoacacia.[5]
The C-4 stereochemistry of leucocyanidin substrates affects anthocyanidin synthase (ANS) products. This enzyme is an iron(II) and 2-oxoglutarate (20G) dependent oxygenase.[6]
References
- ↑ Leucocyanidin on liberherbarum.com
- ↑ Leucoanthocyanidins as intermediates in anthocyanidin biosynthesis in flowers of Matthiola incana R. Br. Werner Heller, Lothar Britsch, Gert Forkmann and Hans Grisebach, 1984
- ↑ Synthesis of condensed tannins. Part 9. The condensation sequence of leucocyanidin with (+)-catechin and with the resultant procyanidins. Jan. A. Delcour, Daneel Ferreira and David G. Roux, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1983, pages 1711-1717, doi:10.1039/P19830001711
- ↑ Proanthocyanidin Synthesis and Expression of Genes Encoding Leucoanthocyanidin Reductase and Anthocyanidin Reductase in Developing Grape Berries and Grapevine Leaves, Jochen Bogs, Mark O. Downey, John S. Harvey, Anthony R. Ashton, Gregory J. Tanner and Simon P. Robinson, 2005
- ↑ Leucocyanidin reductase activity and accumulation of proanthocyanidins in developing legume tissues, B Skadhauge, MY Gruber, KK Thomsen and DV Wettstein
- ↑ The C-4 stereochemistry of leucocyanidin substrates for anthocyanidin synthase affects product selectivity TURNBULL Jonathan J.; NAGLE Michael J.; SEIBEL Jürgen F.; WELFORD Richard W. D.; GRANT Guy H.; SCHOFIELD Christopher J. 2003