Lasers and aviation safety
Under certain conditions, laser light or other bright lights (spotlights, searchlights) directed at aircraft can be a hazard. The most likely scenario is when a bright visible laser light causes distraction or temporary flash blindness to a pilot, during a critical phase of flight such as landing or takeoff. It is far less likely, though still possible, that a visible or invisible beam could cause permanent harm to a pilot's eyes. Although laser weapons are under development by the military, these are so specialized, expensive and controlled that it is improbable for non-military lasers to cause structural damage to an aircraft.
Aviation hazards from bright light can be minimized or eliminated in two primary ways. First, users on the ground can exercise caution, to prevent or minimize any laser or other bright light being directed in airspace and especially towards aircraft. Second, pilots should have awareness of laser/aviation hazards and knowledge of basic recovery procedures in case of laser or bright light exposure.
Pointing a laser at an aircraft can be hazardous to pilots[1] and has resulted in arrests, trials and jail sentences. It also results in calls to license or ban laser pointers. Some jurisdictions such as New South Wales have restricted laser pointers as a result of multiple incidents.
Lasers and bright lights
In addition to lasers, other bright directional lights such as searchlights and spotlights can have the same dazzling, distracting, and flashblinding effects. Searchlight and spotlight operators should take the same basic precautions as laser users. Similarly, pilots and safety officials should keep in mind that a reported "laser" incident may be caused by a non-laser bright light.
Lasers in airspace
There are many valid reasons that lasers are aimed into airspace. Lasers are used in industry and research, such as in atmospheric remote sensing, and as "guide stars" in adaptive optics astronomy. Lasers and searchlights are used in entertainment; for example, in outdoor shows such as the nightly IllumiNations show at Walt Disney World's Epcot. Laser pointers are used by the general public; sometimes they will be accidentally or deliberately aimed at or near aircraft. (Of course, no unauthorized person should deliberately aim any type of laser at or near an aircraft.)
Lasers are even used, or proposed for use, with aircraft. Pilots straying into unauthorized airspace over Washington, D.C. can be warned to turn back by shining eye-safe low-power red and green lasers at them.[2] At least one system has been tested that would use lasers on final approach to help line up the pilot on the proper glideslope. NASA has tested a Helicopter Airborne Laser Positioning System.[3] The FAA has tested laser-projected lines on airport runways, to increase visibility of "hold short" markings.[4]
Because of these varied uses, it is not practical to ban lasers from airspace. This would unduly restrict legitimate uses, it would not prevent accidental illumination incidents, and it would not stop someone who deliberately, out of malice or ignorance, targeted aircraft. For this reason, practical laser/aviation safety is based on informed users and informed pilots.
Primary hazards of lasers and bright lights



(Note: The photos at right flash because most incidents are of flashes and not of steady illumination. In accidental illuminations there may be just one or a few flashes. Even in deliberate illuminations, it is hard to hand-hold a laser on a moving target, so there will be a series of longer flashes. With helicopters at close range, it is possible to have a more or less continuous light. The flashes shown greatly exaggerate the duration of a laser flash and use green rather than less visible red light. With a plane traveling hundreds of miles/hour and a laser beam size of only a meter or so, flash durations would be measured in thousandths of a second.)
There are some subjects which laser/aviation safety experts agree pose no real hazard. These include passenger exposure to laser light, pilot distraction during cruising or other non-critical phases of flight, and laser damage to the aircraft.
The main concerns of safety experts are almost exclusively focused on laser and bright light effects on pilots, especially when they are in a critical phase of flight: takeoff, approach, landing, and emergency maneuvers.[5]
There are four primary areas of concern. The first three are "visual effects" that temporarily distract or block pilots' vision. These effects are only of concern when the laser emits visible light.
- Distraction and startle. An unexpected laser or bright light could distract the pilot during a nighttime landing or takeoff. A pilot might not know what was happening at first. They may be worried that a brighter light or other threat would be coming. It is important that pilots be trained to understand the relatively minor impact of laser flashes caused by laser pointers and not to over react.
- Glare and disruption. As the light brightness increases, it starts to interfere with vision. Veiling glare would make it difficult to see out the windscreen. Night vision starts to deteriorate. Laser light is highly directional so that pilots may act to exclude the source from their direct field of vision if properly trained. Pointer lasers have an illuminance of about 1 lumen/m2 whereas during the day the pilots have to deal with sunlight which is one hundred thousand times stronger.
- Temporary flash blindness. This works exactly like a bright camera flash: there is no injury, but night vision is temporarily knocked out. There may be afterimages—again, exactly like a bright camera flash leaving temporary spots.
The three visual effects above are the primary concern for aviation experts. This is because they could happen with lower-powered lasers that are commonly available. The fourth concern, eye damage, is much less likely. It would take specialized equipment not readily available to the general public.
- Eye damage. Though it is unlikely, high power visible or invisible (infrared, ultraviolet) laser light could cause permanent eye injury. The injury could be relatively minor, such as spots only detectable by medical exam or on the periphery of vision. At higher power levels, the spots may be in the central vision, in the same area where the original light was viewed. Most unlikely of all is injury causing a complete and permanent loss of vision. To do this requires very specialized equipment and a desire to deliberately target aircraft.
It is extremely unlikely that any of the four elements above would cause loss of the aircraft, especially if the pilots react properly and work as a team.
Analyzing the hazard
The exact hazard in a specific situation depends on a number of factors.
Laser/bright light factors
- The power of the laser or bright light. The more light emitted, the brighter and more hazardous it will be.
- The beam divergence. A low-divergence "tight" beam will be a hazard at greater distances than one which spreads out rapidly.
- Visibility (wavelength) of the beam. An infrared or ultraviolet laser beam does not present any visual effect risk to pilots, as they cannot see it. However, at high powers it can present an eye damage risk. In some cases, this hazard may be greater since a pilot would not know they were being illuminated.
- Color of the beam (for visible wavelengths). In general, the eyes of pilots in an illuminated nighttime cockpit are most sensitive to greenish-yellow light (of wavelength around 500–600 nanometers, peaking at 555 nm). A blue or red laser will appear much dimmer—and thus less distracting—than a green or yellow laser of equal power (wattage).[6][7] To give a specific example, a 10-watt continuous-wave YAG laser at 532 nanometers (green) can appear brighter to the eye than an 18-watt continuous-wave argon-ion laser that outputs 10 watts of 514 nm (green-blue) light plus 8 watts of 488 nm (blue) light.[8]
- Pulsed/continuous nature of the beam. Some laser beams emit their energy in pulses. A pulsed laser presents a greater eye damage risk than a continuous laser of equal (average) power. This is because the power is packed into shorter but more intense pulses.
Operational factors
- Beam movement. If the beam is moving around such as in a laser show, it covers a greater area of the sky and thus has a greater chance to illuminate an aircraft. However, if it did scan across a cockpit, in general the exposure duration would be shorter. (A more precise analysis would look at the relative motion of the beam and aircraft.)
- Location of the beam relative to airports. The beam must avoid airspace around airports and busy air routes. The FAA has established safety zones around airports, which are described in the "Regulation" section below. It is possible to use beams within the zones, if the beam power is below the FAA limit for the zone.
- Projector and laser stability. To avoid accidents, the laser projector must be secured with relation to termination points and beam blocks. If a projector slips, or safety software fails, the beam could enter unsafe areas of airspace.
Situational factors
- Day vs. night. Almost all concern is over nighttime illumination. The three visual effects listed above (distraction, glare and flash blindness) are minimized during the day since the eye is not dark adapted, and since visible lasers are not often used outdoors in daytime.
- Motion and speed of the aircraft. A slow aircraft is at greater risk than a fast one (relative to travel across the viewer's line of sight). Helicopters are at greatest risk because they can hover, presenting a relatively stationary target.
- Distance to the aircraft. A low-flying aircraft is at greater risk. Again, helicopters are vulnerable due to their close ground proximity.
- Direction relative to the aircraft and cockpit. A beam aimed directly at an incoming aircraft gives the greatest risk to pilots. One aimed across the aircraft's travel gives less risk, partially because the light enters through the side windows, and partially because it is harder to keep the beam aimed exactly at the cockpit area. A beam aimed straight up gives the least risk, although it is still possible for the beam to illuminate the cockpit during a banking turn.
Pilot/aircrew factors
- Flight phase. The risk is greatest when the exposure comes during a time of high workload: takeoffs, critical or emergency maneuvers, and landings.
- Pilot awareness and response. Ideally, pilots will be aware of laser and bright light hazards, and will know how to recover in case of an incident. Conversely, a pilot can make the situation worse if he or she overreacts, stares at the light to try to locate its source, or takes immediate unnecessary evasive maneuvers.
The U.S. FAA has studied some of these factors.[9] They conducted research using pilots in flight simulators to determine the effects of laser exposure on pilot performance; results were released in August 2003[10] and June 2004.[5]
Accidental vs. deliberate exposure
Laser users must take appropriate precautions to avoid accidents. (Some steps are outlined below in the section "Reducing the hazard".) In most cases, an accidental exposure is likely to be one or a few brief flashes, as the aircraft moves through a stationary beam, or as a hand-held beam sweeps over the cockpit.
There have been cases of deliberate intent, where someone through ignorance or malice deliberately aimed a laser at an aircraft. Note that no one should ever deliberately aim a laser at an aircraft. It can result in pilot distraction, and may well result in searches by authorities to find the source. There have been a number of cases reported where laser pointer users were arrested and tried; a few have even gone to jail. Such incidents also can lead to calls to license or ban laser pointers.
Whether an accidental or deliberate exposure, any pilot seeing a flash should avoid looking in the direction of the light, since it may be quickly followed by additional flashes.
Example laser safety calculations
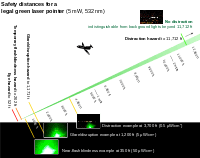
The graphic (right) shows many important laser/aviation safety concepts.[11] For example, it shows that the areas of most concern—eye damage, flash blindness and glare—occur relatively close to the aircraft. The distraction risk covers the longest hazard distance, but fortunately also presents the least concern. The photos in the graphic also give an idea of what the visual effect looks like to the pilot, at various distances.
Note that while the distances given are exact ("52 feet", "262 feet"), the laser's brightness is in fact falling off slowly. It is not as if at 51 feet the laser is an eye hazard and at 53 feet it is eye safe. Effects diminish continuously with increasing distance.
Also, the weaker effects are part of any stronger effect. Even if a laser does not cause eye damage at 25 feet, it can still cause flash blindness, glare and a distraction.
For any given laser, the relative distances shown here may change. For example, an invisible (infrared) laser can be an eye hazard for hundreds of feet, but presents no flash blindness, glare or distraction hazard. Because of this, each laser must be analyzed individually.
To give another example, here are calculations of a more powerful laser—the type that might be used in an outdoor laser show. A 6-watt green (532 nm) laser with a 1.1 milliradian beam divergence is an eye hazard to about 1,600 feet (490 meters), can cause flash blindness to about 8,200 feet (1.5 mi/2.5 km), causes veiling glare to about 36,800 feet (7 mi; 11 km), and is a distraction to about 368,000 feet (70 mi; 110 km).[12]
Reducing the hazard
There are a number of ways that laser users, regulators and pilots reduce the potential hazard from outdoor laser use. These measures include:
Police enforcement
Police have begun using helicopters to patrol and seek out people using lasers to disrupt aviation.[13]
User hazard reduction measures
- Using the lowest power necessary for the task.
- Increasing the beam divergence. The beam spreads out faster, so at any given distance, the amount of light entering the eye or a cockpit windscreen will be less (e.g., lower irradiance).
- Keeping beams away from areas with many aircraft, such as airports and flight paths.
- Terminating beams on buildings, dense trees, etc. to prevent laser light from entering protected airspace. This is a common protection measure for outdoor laser shows, if there are structures available for termination.
- Using spotters to watch for aircraft. This is commonly done for laser shows which tend to be short-duration (around an hour) and infrequent (nightly shows are rare).
- Using automated detection systems such as radar or sky cameras. These are used for long-duration (all night) and frequent (nightly) applications, such as laser guide stars used at astronomical observatories.
- Developing and following policies for outdoor laser operations, such as the ANSI standard "Safe Use of Lasers Outdoors" [14] or NASA's "Use Policy for Outdoor Lasers".[15]
Regulatory hazard reduction measures
- Restricting the sale or use of laser devices. This is done in some jurisdictions. For example, in April 2008 New South Wales, Australia banned laser pointer possession, except by special permit, in an effort to reduce the number of laser illuminations of aircraft.[16] In October 1997 in the United Kingdom, administrative steps were taken to restrict the sale of laser pointers > 1 milliwatt output, for similar reasons (although the purchase, importation and use of such pointers in the UK remains lawful).[17] In the U.S., the Congressional Research Service notes that a ban could "pose significant challenges because these devices are widely available at low cost and are used in a variety of applications such as laser pointers, laser levels and laser gun sights."[18]
- Requiring review or approval of outdoor laser uses. This is discussed in the Regulation and control section below.
- Amending existing laws, or enacting new ones, to try to discourage irresponsible laser use. One U.S. federal effort in this direction is the "Securing Airplane Cockpits Against Lasers Act of 2005", discussed in the History section below.
- Following a series of accidents caused by lasers, Arizona state passed Bill 2164 (2014) that making it a Class One misdemeanor to point a laser at an aircraft.[19]
Pilot/aircrew hazard reduction measures
- Fixed laser installations (e.g. laser guide stars from observatories) may be marked on aeronautical charts so pilots are aware of potential beams along their flight path. Temporary uses (laser shows) may be described in pre-flight information. For example, in the U.S., laser uses submitted to the FAA are often listed in NOTAMs for pilots.[20]
- Education and training. The SAE G-10T Laser Hazards Subcommittee is working on Aerospace Recommended Practice document 5598, "Laser Visual Interference - Pilot Operational Procedures."[21] This will provide information for pilots on recognizing and recovering from a laser or bright light incident. Articles in aviation publications also have provided helpful information, such as "Laser Illuminations: The Last Line of Defense - The Pilot!".[22]
Active hazard reduction (proposed measures)
Some measures have been proposed to protect aircrews including goggles and windscreen filters.[23] These may work in theory (especially against known wavelengths) and may be useful in some situations such as military operations.[24] However, these measures may not be suitable, practical or recommended for widespread civil air operations.
- Laser safety goggles. Laboratory-type laser safety goggles are not well suited for pilot operation. "The 20% transmission ratio of laboratory laser eyewear would probably have disastrous effects on a cockpit crew who must read instruments while flying at night.... The optical quality of such systems also becomes a factor because slight amounts of distortion or haze which may be of no concern in the laboratory may be a major concern to pilots flying at low altitudes and high speed."[25] Also, there may be a variety of laser wavelengths/colors that may need to be defended against. If all wavelengths are protected, the goggles essentially are opaque. There are also issues with the discomfort of wearing goggles routinely, given that laser incidents are relatively rare.
- Active "smart" goggles which can detect laser light and then activate a blocking/dimming process based on the power and wavelength.[26] It is not known if these are in production or use; if so, it is likely that these are used only in military applications.
- Glare shields that can be pulled down over a windscreen to reduce all incoming light.[27]
- Laser event detectors/recorders[28] that can sense a laser illumination and record information about the wavelength and power. This does not provide protection but does give information about an illumination which may be useful for later analysis or legal action.
Regulation and control


In the United States, laser airspace guidelines can be found in Federal Aviation Administration Order JO 7400.2 (Revision "G" as of April 2008), Procedures for Handling Airspace Matters, Part 6, Chapter 29, "Outdoor Laser Operations".[29] Bright light airspace guidelines are in Chapter 30, "High Intensity Light Operations".[30]
In the United Kingdom, CAP 736 is the "Guide for the Operation of Lasers, Searchlights and Fireworks in United Kingdom Airspace." [31]
For all laser users, the ANSI Z136.6 document gives guidance for the safe use of outdoor lasers.[14] While this document is copyrighted by ANSI and is relatively costly, a flavor of its recommendations can be seen in NASA's Use Policy for Outdoor Lasers.[15]
Airspace zones
The U.S. FAA has established airspace zones. These protect the area around airports and other sensitive airspace from the hazards of safe-but-too-bright visible laser light exposure:
- The Laser Free Zone extends immediately around and above runways, as depicted at right. Light irradiance within the zone must be less than 50 nanowatts per square centimeter (0.05 microwatts per square centimeter). This was set at "a level that would not cause any visual disruption."[18]
- The Critical Flight Zone covers 10 nautical miles (NM) around the airport; the light limit is 5 microwatts per square centimeter (μW/cm²). This "was determined to be the level at which significant glare problems can occur."[22]
- The optional Sensitive Flight Zone is designated by the FAA, military or other aviation authorities where light intensity must be less than 100 μW/cm². This might be done for example around a busy flight path or where military operations are taking place. This "was identified as the level of exposure at which significant flash blindness and afterimages could interfere with a pilot's visual performance."[22]
- The Normal Flight Zone covers all other airspace. The light intensity must be less than 2.5 milliwatts per square centimeter (2500 μW/cm²). This is about half of the Class 3R power level, and is not considered hazardous for a brief exposure.
For non-visible lasers (infrared and ultraviolet), the irradiance at the aircraft must be eye-safe—below the Maximum Permissible Exposure level for that wavelength. For pulsed visible lasers, the irradiance at the aircraft must be both eye-safe and must be at or below any applicable FAA laser zone.
In the UK, restrictions are in place in a zone that includes a circle 3 nmi (5.6 km) in radius around an aerodrome (airport) plus extensions off each end of each runway. The runway zones are rectangles 20 nmi (37 km) in total length and 1,000 meters (3,300 feet) wide, centered about each runway.
Reporting
In the U.S., those persons operating outdoor lasers are requested to file reports with the FAA at least 30 days in advance, detailing their laser power(s). They must reference their operation location with respect to local airports and describe the laser power emitted within the Sensitive, Critical and Laser Free zones. Note that it is possible to use lasers whose output exceeds the limits of these zones, if other control measures are in place. For example, spotters could be used to watch for aircraft, and turn off the laser if a potential conflict is sighted. (This raises separate issues about the number, training and effectiveness of the spotters; the FAA must be satisfied that these issues are answered for the particular operation.)
FAA Advisory Circular 70-1[32] "Outdoor Laser Operations" contains two forms plus instructions. One form is a "Notice of Proposed Laser Operations", the other is a "Laser Configuration Worksheet" which is filled out for each laser or each different laser configuration. The FAA will review the report, and will either send a letter of objection or will send a letter of non-objection. The language is important; the FAA does not "approve" or "disapprove" as this implies a higher level of regulatory authority which the FAA does not have.
If the laser use is for a show or display in the U.S., there is a more stringent regulatory process. In the U.S., any use of lasers in a show or display requires pre-approval from the FDA Center for Devices and Radiological Health. This is required both for the laser equipment, and separately for the show itself (site, audience configuration, beam effects, etc.). As part of the CDRH's show approval ("variance") process, the CDRH will require a letter of non-objection from the FAA. Without this, the laser show cannot legally proceed.
In the U.S., laser activity in a given area is communicated to pilots before their flight via a NOTAM.[20] Pilots exposed to a laser or bright light during flight should follow Advisory Circular 70-2[33] "Reporting of Laser Illumination of Aircraft".
UK laser operators report outdoor laser, searchlight or firework operations at least 28 days in advance, using the Notification Form found in annex A of the CAP 736 document.[31]
Regulatory and standards development
A key group inside the U.S. working on laser/aviation safety is the SAE G-10T, Laser Safety Hazards Subcommittee. It consists of laser safety experts and researchers, pilots and other interested parties representing military, commercial and private aviation, and laser users. Their recommendations have formed the basis of the FAA laser and bright light regulations and forms, as well as standards adopted in other countries and by the ICAO.
The ANSI Z136.6 standard is the "American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers Outdoors." [14] The Z136.6 committee has worked closely with SAE G-10T and others, to develop recommended safety procedures for outdoor laser use.
History
Until the early 1990s, laser and bright light aviation incidents were sporadic. In the U.S., NASA's Aviation Safety Reporting System showed only one or two incidents per year.[34] The SAE G-10T subcommittee began meeting around 1993 as the number of incidents grew. Almost all of the incidents were known or suspected to be due to outdoor laser displays. Almost all of the concern was over potential eye damage; at the time visual effects were felt to be a minor consequence.
In late 1995, a number of illumination incidents occurred in Las Vegas due to new outdoor laser displays. Although the displays had been approved by the FDA as eye-safe for their airport proximity, no one had realized that the glare/distraction hazard would adversely affect pilots. In December 1995 the FDA issued an emergency order shutting down the Las Vegas shows.
Within the SAE G-10T subcommittee, there was some consideration about cutting back or banning laser shows. However, it became apparent that there were a large number of non-entertainment laser users as well. The focus shifted to control of known laser users, whether shows or industry/research. New policies and procedures were developed, such as the FAA 7200 Chapter 29, and Advisory Circular 70-1. Although incidents continued to occur (from January 1996 to July 1999, the FAA's Western-Pacific Region identified more than 150 incidents in which low-flying aircraft were illuminated by lasers),[35] the situation seemed under control.
Then in late 2004 and early 2005, came a significant increase in reported incidents linked to laser pointers. The wave of incidents may have been triggered in part by "copycats" who read press accounts of laser pointer incidents. In one case, David Banach of New Jersey was charged under federal Patriot Act anti-terrorism laws, after he allegedly shone a laser pointer at aircraft.[36]
Responding to the incidents, the Congressional Research Service issued a study on the laser "threat to aviation safety and security."[18] Because there was no federal law specifically banning deliberate laser illumination of aircraft, Congressman Ric Keller introduced H.R. 1400, the "Securing Airplane Cockpits Against Lasers Act of 2005."[37] The bill was passed by the U.S. House and Senate, but did not go to conference and thus did not become law.[38] In 2007, Keller re-introduced the bill as H.R. 1615. Although passed by the House in May 2007, it was not acted on by the Senate before the end of the 110th Congress and never became law.[39]
On March 28, 2008, a "coordinated attack" took place using four green laser pointers aimed at six aircraft landing at the Sydney (New South Wales) Australia airport.[40][41] As a result of this attack plus others, a law was proposed in mid-April 2008 in NSW to ban possession of handheld lasers, even "harmless classroom pointers".[42][43] The Australian state of Victoria has reportedly had a similar ban since 1998, but press reports state that it is easy to buy lasers without a permit.[44]
On February 22, 2009, a dozen planes were targeted with green laser beams at Seattle-Tacoma International Airport.[45] An FAA spokeswoman said there were 148 laser attacks on aircraft in the U.S. from January 1, 2009 to February 23, 2009.[46]
During the July 2013 protests of the Morsi Presidency in Egypt and later celebration of his removal, thousands of protesters and revelers aimed laser pointers at government helicopters.[47][48]
On February 2016 a Virgin Atlantic flight from Heathrow to New York JFK Airport was forced to turn back when a laser beam was shone into the cockpit.[49] The incident led BALPA to call for lasers to be classified as offensive weapons.[50]
See also
References
- ↑ Safety in Aviation
- ↑ Eastern Region FAA Safety Team Laser Warning System Video(Updated: 8:26 am ET October 5, 2007)
- ↑ Helicopter Airborne Laser Positioning Systems (HALPS) (march 1990) NASA
- ↑ FAA press release: Laser Technology Will Make It Easier For Pilots To See Runway Markings
- 1 2 June 2004 FAA follow-up study: "The Effects of Laser Illumination on Operational and Visual Performance of Pilots During Final Approach", DOT/FAA/AM-04/9.
- ↑ "Luminous efficacy at HyperPhysics".
- ↑ Laser experts on the SAE G-10T Laser Safety Hazards Subcommittee considered whether pilots at night have primarily scotopic (night) vision or photopic (color) vision. One difference is that scotopic vision shifts towards the blue-green (roughly 450-550 nm, with a peak at 507 nm) compared with photopic vision which is more green-yellow (roughly 500-600 nm, with a peak at 555 nm). The subcommittee decided that because most nighttime cockpits have color displays and lights, the pilots' color vision is activated, which means their vision is more photopic than scotopic. Source: Verbal communication from Greg Makhov of Lighting Systems Design Inc. in Orlando, an SAE G-10T member who was in on this debate. This is confirmed since the FAA uses photopic data for its laser-aviation safety calculations. FAA Advisory Circular 70-1, Table 5, which lists visual color correction factors, uses data from the CIE normalized efficiency photopic visual function curve for a standard observer. http://forms.faa.gov/forms/faa7140-1%20appendix.pdf[]
- ↑ FAA AC-70-1, Table 5, shows these calculations, which are summarized here using the exact Visual Correction Factor for the wavelengths under consideration (FAA only gives ranges). Light at 555 nm appears brightest to the eye, so it has a VCF of 100% (1.0). Since light at 532 nm appears only 88% as bright (based on the CIE normalized efficiency photopic visual function curve for a standard observer), its VCF is 0.88. Light at 514 nm has a VCF of 0.585, and light at 488 nm has a VCF of 0.194. Now let's look at our two lasers. We have a 10-watt YAG emitting 10 watts of 532 nm light. The visually corrected power is 10W * 0.88VCF = 8.8 visually corrected watts. The 18-watt argon has 10 watts of 514 nm light (10W * 0.585VCF = 5.85 visually corrected watts) plus 8 watts of 488 nm light (8W * 0.194VCF = 1.55 visually corrected watts). Add the two argon outputs and you get a total of 5.85 + 1.55 = 7.40 visually corrected watts. This is how a 10-watt YAG beam can appear brighter to the eye than an 18-watt argon beam – all other factors such as beam divergence being equal.
- ↑ “Laser Pointers: Their Potential Affects [sic] on Vision and Aviation Safety”, Van B. Nakagawara, DOT/FAA/AM-01/7, April 2001.
- ↑ August 2003 FAA study: "The Effects of Laser Illumination on Operational and Visual Performance of Pilots Conducting Terminal Operations", DOT/FAA/AM-03/12.
- ↑ The laser effects and ranges shown in the graphic are based on consensus developed by the aviation advisory group SAE G-10T Laser Safety Hazards Subcommittee as published in SAE Aerospace Recommended Practice document 5293 (ARP5293) "Safety Considerations for Lasers Projected in the Navigable Airspace." These recommendations were adopted by the U.S. FAA, and are incorporated into FAA Order 7400.2, Procedures for Handling Airspace Matters, Part 6: Miscellaneous Procedures, Chapter 29: Outdoor Laser Operations. See for example the FAA's Laser Free, Critical, Sensitive and Normal Flight Zone power levels. The SAE G-10T recommendations also were adopted by ANSI Z136.6, "Safe Use of Lasers Outdoors". The photographs in the graphic are from the FAA and demonstrate visual effects of laser light in an aircraft simulator. Note that effects and hazards of lasers at close range (within a room or a few dozen feet) cannot always be extrapolated for distances of hundreds or thousands of feet. At long range, the beam spread is sufficient that it is possible to illuminate an aircraft cockpit with a laser pointer, even momentarily, with sufficient power to cause visual effects such as distraction, glare and flashblindness. This is amply illustrated by the many laser-aircraft incidents which have been reported in the press.
- ↑ This calculation is based upon determining when the irradiance of the laser just falls below the light levels of the ANSI nominal ocular hazard (eye hazard), the FAA Sensitive Flight Zone (flash blindness), Critical Flight Zone (glare) and Laser Free Zone (distraction).
- ↑ BBC: Police fight back on laser threat
- 1 2 3 ANSI Z136.6 Standard, "Safe Use of Lasers Outdoors"
- 1 2 NASA’s “Use Policy for Outdoor Lasers” archived from the original
- ↑ "Laser pointers banned after attacks", Reuters article dated April 21, 2008
- ↑ “Safety Recommendations of Laser Pointers”, by Rockwell Laser Industries and the (U.S.) National Institutes of Occupational Safety & Health archived from the original
- 1 2 3 CRS Report for Congress - Lasers Aimed at Aircraft Cockpits:Background and Possible Options to Address the Threat to Aviation Safety and Security - Bart Elias (January 26, 2005)Order Code:RS22033
- ↑ "HB 2164" (PDF). Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- 1 2 FAA Order 7400.2, Procedures for Handling Airspace Matters, Part 6, Chapter 29, Section 4: "Issuance of Notices to Airmen (NOTAM)
- ↑ SAE Standards for Works in Progress, ARP5598, Laser Visual Interference - Pilot Operational Procedures
- 1 2 3 "Laser Illuminations: Last Line of Defense - The Pilot!" by Capt. C.W. "Bill" Connor, Ph.D., Air Line Pilot, April 2005, p. 21
- ↑ Sample page provided by Google Book Search, from Weapons of Mass Casualties and Terrorism Response by Charles Edward Stewart, Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 2006.
- ↑ "Aircrew laser eye protection visors", Opt. Eng. Vol. 44, 084303, August 29, 2005, referenced from SPIE Digital Library online
- ↑ "Military hazard software gauges human thresholds" by Hassaun Jones-Bey, LaserFocusWorld magazine, September 1, 2000
- ↑ "Active laser protection system", U.S. Patent 7202852, retrieved from freepatentsonline.com
- ↑ "Stowable laser eye protection", U.S. Patent 7344260, retrieved from freepatentsonline.com
- ↑ Laser event and laser exposure recorder from OPTRA, Inc.
- ↑ FAA Order 7400.2, Procedures for Handling Airspace Matters, Part 6. Miscellaneous Procedures, Chapter 29. Outdoor Laser Operations
- ↑ FAA Order 7400.2, Procedures for Handling Airspace Matters, Part 6. Miscellaneous Procedures, Chapter 30. High Intensity Light Operations
- 1 2 CAP736: Guide for the Operation of Lasers,Searchlights and Fireworks in the United Kingdom Airspace (www.caa.co.uk)
- ↑ FAA Advisory Circular 70-1 Subject:Outdoor Laser Operations (12/30/04)
- ↑ FAA Advisory Circular 70-2 Subject:Reporting of Laser Illumination of Aircraft (January 11, 2005)
- ↑ A sampling of NASA ASRS laser incident reports can be done by searching for the term "laser".
- ↑ (PDF) https://web.archive.org/web/20130626225239/http://www.hf.faa.gov/docs/508/docs/cami/0107.pdf. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 26, 2013. Retrieved February 19, 2016. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ USATODAY.com - N.J. man charged with aiming laser at aircraft: By Alan Levin (Posted 1/4/2005 12:41 PM)
- ↑ U.S. Congressman Ric Keller: 8th District Of Florida:Committee Passes Keller Pilot Protection Bill (Washington, September 29, 2005)
- ↑ H.R. 1400 (109th): Securing Aircraft Cockpits Against Lasers Act of 2005 (GovTrack.us)
- ↑ H.R. 1615: Securing Aircraft Cockpits Against Lasers Act of 2007 (GovTrack.us)
- ↑ "City's worst laser attacks on aircraft", Frank Walker, March 30, 2008, smh.com.au
- ↑ Laser 'cluster' attacks Sydney planes | Herald Sun (March 29, 2008 10:37pm)
- ↑ Backlash over ban on laser pointers - National - smh.com.au (Jordan Baker Chief Police Reporter April 22, 2008)
- ↑ Australia Takes On Laser Lunatics(April 21, 2008, 10:52 am By Mike Nizza)- The Lede - New York Times Blog
- ↑ Laser pointers ban spread (April 22, 2008 12:00am) Herald Sun
- ↑ The Seattle Times - Someone shining laser at planes landing at Sea-Tac.
- ↑ CNN.com - Pilots landing at Seattle-Tacoma airport report lasers
- ↑ "Euphoric Egyptians light up helicopter with laser beams - BBC News". Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ↑ "Egypt crisis: Why are Cairo protesters using laser pens? - BBC News". Bbc.co.uk. 2013-07-04. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ↑ "Virgin Atlantic flight back in UK after 'laser incident' - BBC News". Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ↑ Press Association (15 February 2016). "Virgin Atlantic laser incident: pilots' union demands action". The Guardian. Retrieved 15 February 2016.