Krishnagiri district
| Krishnagiri District கிருஷ்ணகிரி மாவட்டம் | |
|---|---|
| District | |
 Location in Tamil Nadu, India | |
| Coordinates: 12°31′4.8″N 78°12′46.8″E / 12.518000°N 78.213000°ECoordinates: 12°31′4.8″N 78°12′46.8″E / 12.518000°N 78.213000°E | |
| Country |
|
| State | Tamil Nadu |
| Region | Tiruvannamalai |
| Headquarters | Krishnagiri |
| Talukas | Krishnagiri, Hosur, Pochampalli, Uthangarai and Denkanikottai |
| Government | |
| • Collector | T. P. Rajesh IAS |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 1,879,809 |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Tamil |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+5:30) |
| PIN | 635001 |
| Telephone code | 04343 |
| ISO 3166 code | ISO 3166-2:IN |
| Vehicle registration | TN 24, TN 70[1] |
| Largest city | Hosur |
| Central location: | 12°31′N 78°12′E / 12.517°N 78.200°E |
| Website |
krishnagiri |
Krishnagiri district is a district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India .This is a new district which craved out from Dharmapuri District by the year 2004. The municipal town of Krishnagiri is the district headquarters. In Tamil Nadu, e-Governance was first introduced at Krishnagiri district under the National e-Governance Project (NEGP) in revenue and social welfare departments on a pilot basis.[2][3] The district is one of the largest producers of Mangoes in India.[4] As of 2011, the district had a population of 1,879,809 with a sex-ratio of 958 females for every 1,000 males
Etymology
'Krishna' refers to 'black' and 'giri' refers to 'hill'. The area contains many granite hillocks hence the name 'Krishnagiri'. The region was under the rule of Krishna Deva Raya and hence it might also have been named after him.[5]
History

Krishnagiri district was formed as the 30th district of Tamil Nadu on February 9, 2004. Krishnagiri District was formed by carving out five taluks and ten blocks of the erstwhile Dharmapuri district.
District Administration
A district Collector heads the district administration. Krishnagiri district is divided into 2 divisions and 5 Taluks for the purpose of revenue administration. Revenue Divisional Officer heads the divisions and Tahsildar is the head of taluk level administration. Development administration in this district is coordinated by the panchayats (also called as blocks) for the rural areas. There are about 10 Panchayat Unions, 7 Town Panchayats, 352 Village Panchayats and 874 Revenue Villages in this district. Krishnagiri district comprises two revenue divisions Krishnagiri and Hosur. There are seven taluks namely Krishnagiri, Hosur, Pochampalli, Uthangarai, Shoolagiri, Bargur and Denkanikottai. There are 12 Panchayat Unions as follows: Kelamangalam, Thalli, Anchetti, Krishnagiri, Shoolagiri, Vepanapalli, Hosur, Kaveripattinam, Pochampalli, Mathur and Uthangarai.
Geography & Climate
Krishnagiri district covers an area of 5143 km². Krishnagiri district is bound by Vellore and Thiruvannamalai districts to the East, state of Karnataka to the west, state of Andhra Pradesh to the North and Dharmapuri District to the south. This district is elevated from 300m to 1400m above the mean sea level. It is located between 11° 12' N and 12° 49' N latitude, 77° 27' E to 78° 38' E longitude.
| Taluk H.Q | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) |
|---|---|---|
| Krishnagiri Taluk | 12o32’44” | 78o13’36” |
| Pochampalli Taluk | 12o20’ | 78o22’ |
| Uthangarai Taluk | 12o15’ | 78o33’ |
| Hosur Taluk | 12o48’ | 77o50’23” |
| Denkanikottai Taluk | 12o02’ | 77o47’ |
It basically has a mountainous terrain. The flatlands are irrigated by the South Pennar River. The eastern part of the district experiences hot climate and the western part contrastingly has a pleasant climate. The average rainfall is 830 mm per annum. March - June is the summer season. July - November is the Rainy Season and during December - February winter prevails.
| Year | Rain fall (in mm) |
|---|---|
| 2001–2002 | 825.700 |
| 2002–2003 | 521.600 |
| 2003–2004 | 1075.600 |
| 2004–2005 | 230.620 |
| 2005–2006 | 1262.800 |
Net Cultivated, Irrigated, Double, Multiple Cropped, Cultivable Wasteland, Water land and Forest
| Classification | Geo. | Extent (Ha) |
|---|---|---|
| Forest | 202409 | 39% |
| Banner and uncultivable waste | 24194 | 5% |
| Land put to non agricultural uses | 21466 | 4% |
| Cultivable waste | 6341 | 1% |
| Permanent pastures and other grassing lands | 7378 | 1% |
Transportation
The following major roads pass through Krishnagiri
Highways
| Start/End Point | NH No. | Kilometers |
|---|---|---|
| Kanniyakumari–Varanasi | 7 | 2460 |
| Krishnagiri–Ranipet | 46 | 144 |
| Pondicherry–Krishnagiri | 66 | 214 |
| Krishnagiri–Madanapalli | 219 | 175 |
| Sarjapur–Bagalur–Hosur | 207 | 40 |
Railways
Salem -Dharmapuri- Bengaluru broad gauge line runs through Hosur. salem-Erode-Jolaarpettai brode gauge line runs through Samalpatti
Public Amenities
Irrigation

The Public Works Department and Panchayat union tanks, ponds and supply channels plays an important role in the irrigation of Krishnagiri district. But they have to be desilted and strengthened. New Check Dams and flood protection walls have to be constructed for water conservation.
Electricity
Street lighting in rural areas vested with the Panchayat Administration. The panchayats looks after the erection of new streetlights in the hamlets, payment of current consumption charges from the panchayat funds. Also the procurement of tube lights, sodium vapor lights and other electrical appliances are done by the connected panchayats itself. Now solar lights are also being utilized to cut down on consumption cost. Overall, 95% of the hamlets are covered under Rural Electrification. Generally the power supply position in Krishnagiri District is normal. But in some areas low voltage problem is felt, especially in the hamlets in ghat section. To minimize the current consumption charges in the panchayats, efforts were taken to utilize solar power lights as an alternate and renewable source in Krishnagiri district.
Education
There is a Community Polytechnic run by the Government in Krishnagiri district. Also, the TAHDCO (Tamil Nadu Adi Dravidar Housing Development Corporation) offers Nursing and Catering Training under Vocational Training courses through private training institutions to people belonging to SC / ST communities.To uplift the education of womechnology St.James Tailoring Institute is striving for the welfare of women in Krishnagiri town.This dress making technology gives self earning at home and makes women to get jobs in Ready made garment companies in Krishnagiri itself.
| Education centers | no. |
|---|---|
| Primary Schools | 988 |
| Middle schools | 107 |
| High schools | 113 |
| Hr. Sec. Schools | 72 |
| Industrial Training Institutions | 5 |
| Music school | 1 |
| Teachers Training School | 2 |
| Polytechnic | 4 |
| Engineering College | 5 |
| Arts & Science College | 8 |
Demographics

According to 2011 census, Krishnagiri district had a population of 1,879,809 with a sex-ratio of 963 females for every 1,000 males, much above the national average of 929.[6] A total of 217,323 were under the age of six, constituting 112,832 males and 104,491 females. Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes accounted for 14.22% and 1.19% of the population respectively. The average literacy of the district was 63.2%, compared to the national average of 72.99%.[6] The district had a total of 448,053 households. There were a total of 877,779 workers, comprising 218,600 cultivators, 197,369 main agricultural labourers, 15,237 in house hold industries, 310,795 other workers, 135,778 marginal workers, 17,438 marginal cultivators, 65,959 marginal agricultural labourers, 6,681 marginal workers in household industries and 45,700 other marginal workers.[7] Tamil is the official and majorly spoken language while Telugu and Kannada urdu also spoken in parts of the district . Hinduism is the major religion followed by Islam and Christian minorities.
Economy
Agriculture
The important crops of Krishnagiri District are Paddy, Maize, Ragi, Banana, Sugarcane, Cotton, Tamarind, Coconut, Mango, Groundnut, Vegetables and Flowers. The district has an excellent scope for agri business. Regional Agricultural Research Center of Tamil Nadu Agricultural University is functioning efficiently at Paiyur in Kaveripattinam union since 1973. This center is functioning in 18.5 hec. of land. It helps the peasants to develop and adopt the modern technique of cultivation. It has developed hybrid seeds by research which yields more tonnage and good quality. Krishnagiri district is famous for Mangoes. Krishangiri district is also famous for the Granite Industry with quarries and processing units spread around the district. Hosur, one of the most industrialized places in the state is located in this district. With 40% share, the district is the top producer of Ragi in Tamil Nadu.[8]
| production | area(hectares) |
|---|---|
| Paddy | 20,687 |
| Ragii | 48,944 |
| other minor crops | 11,937 |
| Pulses | 48,749 |
| Sugarcane | 50,000 |
| Mangoes | 30,017 |
| Coconut | 13,192 |
| Tamarind | 1,362 |
| Other Crops | 43,199 |
Mining and Forestry based activities
In Krishnagiri district, quarry leases are being granted for granite in Patta lands and rough stone and earth quarry leases are being granted in Government and patta lands under Tamil Nadu Minor Mineral Concession Rules 1959. Public works Department (WRO wing) is operating sand quarry in riverbeds. A state owned corporation called Tamil Nadu Metals and Mineral Ltd is also earning quarry / Mining grants etc. in Government lands. The total mineral revenue realized during the year 2006-07 is Rs. 7.45 crores. It is ascertained that nearly 7,000 workers are being engaged in quarry activities. As Krishnagiri District has 2,02,409 hectares of forest land which constitutes 39% of the total geographical area, there are abundant produce from the forest areas. Bamboo products, honey collection and tamarind production are the forestry land activities found in Anchetty, Denkanikotta, Thally and Berigai areas. This has generated employment opportunities to thousands of rural people in these areas.
Animal Husbandry and Fisheries
Fisheries
Details about the revenue in Fisheries up to 15.07.2007
| Name of the Reservoir | Target(MT) | Achievement | Revenue Collection (Rs) | Fishermen benefited / Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Krishnagiri Dam | 51.0 | 6.810 | 4844 | 23/4844 |
| Pambaru Dam | 30 | 2.018 | 13570 | 16/13570 |
| Kelavarppalli Dam | 29.0 | 15.110 | 95387 | 30/95387 |
| Barur Lake | 284.0 | 17.600 | 124600 | 37/124600 |
| Chinnaru Dam | 6.8 | 0.931 | 10410 | 5/10410 |
| Mayil Ravanan Lake | 3.0 | 0.164 | 820 | 1/820 |
| Ramanayakan Lake | 4.0 | 0.273 | 2305 | 1/2305 |
| paraiyur lake | 2.0 | 0.216 | 1869 | 1/1260 |
Animal Husbandry
In Krishnagiri District the annual income in the Animal Husbandry Sector as follows for the year 2006-07.
| Classification | Income received |
|---|---|
| Milk | 24,94,926 |
| Egg | 3,88,192 |
| Pork | 1,54,496 |
| Sale of livestocks | 4,21,578 |
| Miscellaneous | 13,55,244 |
| Artificial Insemination | 5,79,898 |
| LN 2 (Liquid Nitrogen) | 1,27,819 |
| Total income | 55,22,153 |
Gallery
-
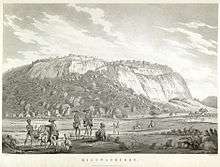
"Kistnagherry" fort painting by Alexander Allan -

An old photo of Hosur -
._Between_1790_and_1792.jpg)
”Anchettidurgam” painting by Sir Alexander Allan -

”Rayakottai fort” painting by Thomas Daniel
file:25-1524.jpg|
See also
References
- ↑ www.tn.gov.in
- ↑ "e-Governance in Pilot Basis". TNeGA.
- ↑ "CM to inaugurate e-Governance scheme in Krishnagiri". The Hindu. Sep 23, 2010.
- ↑ "Arab political world's uncertainty shakes Mango export of India". BBC. Retrieved November 14, 2011.
- ↑ "Krishnagiri Etymology". District Admin., Krishnagiri.
- 1 2 "Census Info 2011 Final population totals". Office of The Registrar General and Census Commissioner, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. 2013. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ↑ "Census Info 2011 Final population totals - Krishnagiri district". Office of The Registrar General and Census Commissioner, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. 2013. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ↑ http://www.tn.gov.in/deptst/agriculture.pdf
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Krishnagiri district. |
