Kosovo Security Force
| Kosovo Security Force Albanian: Forcat e Armatosura të Kosovës Serbian: Косовске безбедносне снаге / Kosovske bezbednosne snage | |
|---|---|
|
Security Force Emblem | |
| Founded | January 21, 2009 |
| Headquarters | Pristina, Kosovo |
| Leadership | |
| Commander-in-Chief | Hashim Thaçi |
| Minister of the Kosovo Armed Force | Haki Demolli |
| Chief of Defense | Lt. Gen. Rrahman Rama |
| Manpower | |
| Military age | 18 |
| Fit for military service | 1,300,000 [1], age 15–49 |
| Active personnel | 4500 |
| Reserve personnel | 2000 |
| Expenditures | |
| Budget | €65,000,000(2015)[2] |
| Percent of GDP | 0.89% (2016) |
| Related articles | |
| History | Kosovo Protection Corps |
| Ranks | Kosovo military ranks |
The Kosovo Security Force or Kosovo Armed Force (abbreviated KSF or KAF; Albanian: Forcat e Armatosura të Kosovës, Serbian: Косовске безбедносне снаге / Kosovske bezbednosne snage), is an Army response force charged with conducting crisis response operations in Kosovo and abroad and civil protection operations in Kosovo. Its main tasks are operations in the areas of Search and Rescue, Explosive Ordnance Disposal, Firefighting, and Hazardous Material Disposal. However, it is also equipped with light weaponry, and the Kosovo government plans to transform it into an army. The Commander of the KSF is Lieutenant General Rrahman Rama.
In March 2008, the NATO-led Kosovo Force (KFOR) and the Kosovo Protection Corps (KPC) started preparations for the formation of the Kosovo Security Force. According to guidance laid out in the Ahtisaari Plan, the security force is permitted to carry light weapons and the Government of Kosovo and the international community planned to bring the force in line with NATO standards. The admission and the training of personnel began in early June, when NATO experts arrived in Kosovo to guide the process, and from early December 2008, enlisting of candidates between 18–30 years old began.
History

Following the Kosovo War in 1999, United Nations Security Council Resolution 1244 placed Kosovo under the authority of the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK), with security provided by the NATO-led Kosovo Force (KFOR). KFOR entered Kosovo on June 12, 1999 under a United Nations mandate, two days after the adoption of UN Security Council Resolution 1244.
Kosovo declared independence in February 2008. On 19 March 2008, United States President George W. Bush authorised military aid to Kosovo Security Force in another step to establish formal relations with Kosovo.[3]
On 4 January 2009, the names of those who were to be selected for the KSF from the KPC were announced. After being vetted by NATO, roughly 1,400 former members of the KPC were selected to serve as officers and rank and file members of the KSF.
On 21 January 2009, the Kosovo Security Force was officially launched. The KSF did not replace the Kosovo Protection Corps (KPC) which was disbanded several months later. KFOR was charged with mentoring the KSF and bringing the force to Full Operational Capability. As part of this effort, various nations that are part of KFOR have provided assistance to the force on a bilateral basis including uniforms which were supplied by the United States and vehicles which were donated by Germany. Mentoring efforts were meant to develop the KSF in line with NATO standards.[4][5][6] Additionally Italy, Portugal and other NATO members are to help the KSF by donations and training.[7][8] Slovenia donated €30,000 towards the establishment of the KSF.[6]
The following senior officers took their oaths on 16 June 2009, under the supervision of then KSF Commander Lieutenant-General Sylejman Selimi:[9]
- Major-General Rrahman Rama – KSF Deputy Commander and Commander of Land Force Command
- Major-General Kadri Kastrati – Director of Operations
- Brigadier-General Bashkim Jashari – General Inspectorate of KSF
- Brigadier-General Nazmi Brahimaj – Commander of Rapid Reaction Brigade
- Brigadier-General Zymer Halimi – Chief of Operations and Training Department
- Brigadier –General Imri Ilazi – Commander of Operations Support Brigade
- Brigadier-General Enver Cikaqi – Commander of Training and Doctrine Command
On 15 September 2009 the Kosovo Security Force officially began the work, with its initial operational capacities after an eight-month training with NATO instructors.[10]
In 2010, the KSF deployed to northern Albania on two separate occasions to perform flood relief operations in support of the Albanian domestic response.
On 22 November 2011, Lieutenant General Sylejman Selimi retired from the KSF and President Atifete Jahjaga appointed the former Director of Operations Major General Kadri Kastrati to succeed him as Commander of the force. President Jahjaga also promoted Kastrati to the rank of Lieutenant General.
On 9 July 2013 the Kosovo Security Forces reached Full Operational Capability (FOC) as determined by NATO.[11] While the general security situation has been improving on the ground, this lightly armed force responsible for civil protection operations and assisting civil authorities in responding to natural disasters and other emergencies has now trained to standards designated by NATO. The declaration of full operational capability on 9 July 2013 by the North Atlantic Council means that the KSF is fully capable of performing the tasks assigned to it within its mandate. The KSF will conduct non-military security functions that are not appropriate for the police. In more concrete terms, this force of approximately 2200 personnel will deal with search and rescue operations, explosive ordnance disposal, control and clearance of hazardous materials, fire-fighting and other humanitarian assistance tasks. Recruitment for the Kosovo Security Force started early 2009, once NATO had agreed (June 2008) to implement new tasks in addition to those agreed under UNSCR 1244. These new tasks included the standing down of the Kosovo Protection Corps, and the creation of the KSF and of a civilian structure to oversee it.
NATO's role in the creation of KSF has therefore been two-fold: helping with its formation – standing up, recruitment and training; and the establishment of a civilian-led organisation to supervise and control the KSF. One of the principal aims was to encourage all minorities to enroll, so special attention was given to carrying out the recruitment process in two languages – Albanian and Serbian. The result has been a professional, multi-ethnic, all-volunteer force, which should continue to remain a source of regional stability.Following the declaration of full operational capability, NATO will continue to support the development of the KSF through the NATO Liaison and Advisory Team (NLAT), consisting of a mix of approximately 30 military and civilian personnel that will help with the professional development of the KSF, providing advice and support in a variety of areas such as capacity-building and training and leadership.[12]
Kosovan Armed Forces
On 5 March 2014, Prime Minister Hashim Thaçi declared that the Kosovan government had decided to establish a Defence Ministry and by 2019, officially transform the Kosovo Security Forces into an Army which meets all the standards of NATO states with aim in joining the alliance in the future. The new Army will have a €98 Million annual budget and will be 5,000 strong with another 3,000 reservists, which will be composed of land forces, a national guard, logistics and training commands.[13][14][15] Kosovo's Security Forces Minister Agim Çeku stated that the Kosovo Armed Forces' mission will be "to protect the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Kosovo, its people and their property and protect the interests of the Kosovo Republic".[16] Kosovo's ambassador to Turkey, Avni Spahiu, stated that the "decision to establish an army has been taken in consultation with NATO and our partners... [and] the army will have a defensive character as Kosovo has no territorial aspirations".[17] On 28 May 2014, President Atifete Jahjaga told the United Nations Security Council that the creation of the Kosovan Armed Forces would be a long process, requiring the support and participation of all ethnic communities in Kosovo; she added that its purpose would be to contribute to overall security in the Balkans and called on all ethnic communities to take part in the process.[18] In November 2014, Agim Çeku stated that the Kosovo Army was running behind schedule "because of the delay in the constitution of the Kosovo parliament" but the decision to transform the Kosovo Security Force into an Army will be confirmed "at one of the first sessions upon its constitution"; he also noted that this transformation enjoys nationwide support and he doesn't expect any complaints from the political opposition.[19]
Mission statement
The Kosovo Security Force (KSF) is a new, professional, multi-ethnic, middel armed and uniformed Security Force that is subject to democratic, civilian control. Its mission is to conduct crisis response operations in Kosovo and abroad; civil protection operations within Kosovo; and to assist the civil authorities in responding to natural disasters and other emergencies.
Such duties will include search and rescue operations; explosive ordnance disposal (de-mining and UXO removal); the control and clearance of hazardous materials; fire-fighting; and other humanitarian assistance tasks. The KSF will represent and protect all the people of Kosovo.
Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force: Mission Statement
The Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force (MKSF) is responsible for exercising civilian control over the Kosovo Security Force (KSF), including management and administration. It comprises a mixture of civilian and KSF personnel and is accountable, through the Prime Minister, to the Kosovo Assembly.
The mission of the MKSF, which is also the highest level KSF Headquarters, is to formulate, implement, evaluate and develop the policies and activities of the KSF within a framework of democratic governance and in accordance with the Constitution and laws of the Republic of Kosovo.
Personnel

Any citizen of Kosovo over the age of 18 is eligible to serve in the Kosovo Security Force.[20] Active members of the Kosovo Security Force are not legally allowed to run for, or serve in the Assembly of Kosovo.[21] The membership of the Kosovo Security Force is required to reflect the ethnic composition of the country.[22] Members of the Security Force are protected from discrimination on the basis of gender or ethnicity.[23]
The Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force has taken active steps to recruit women into the Security Force. As of 2015, women make up 8.52% of the uniformed service members of the Security Force and 32% of the Ministry as a whole.[24] Of the 203 women in uniform in the Security Force, 21 are officers; the highest ranking woman in the Security Force is a Colonel.[25]
Ethnic Minorities
Ethnic minorities of Kosovo are encouraged to enroll in the Kosovo Security Force with the Republic of Kosovo's Constitution requiring the intergeneration of ethnic-minority communities into the Kosovo Security Force. In April 2013, 179 (8.2%) of the Kosovo Security Force's military personnel came from minority backgrounds with the rest being ethnic Albanians.[26] In May 2014, Kosovar President Atifete Jahjaga noted to the United Nations Security Council that 9% of the KSF were from minority communities.[18] In April 2015, it was reported that there were 42 Serbs currently serving in the Kosovo Security Force.[27]
| Ethnicity | Amount |
|---|---|
| Turks | 54 |
| Bosniaks | 49 |
| Ashkali | 30 |
| Egyptians | 20 |
| Serbs | 16 |
| Croats | 5 |
| Romani | 3 |
| Gorani | 2 |
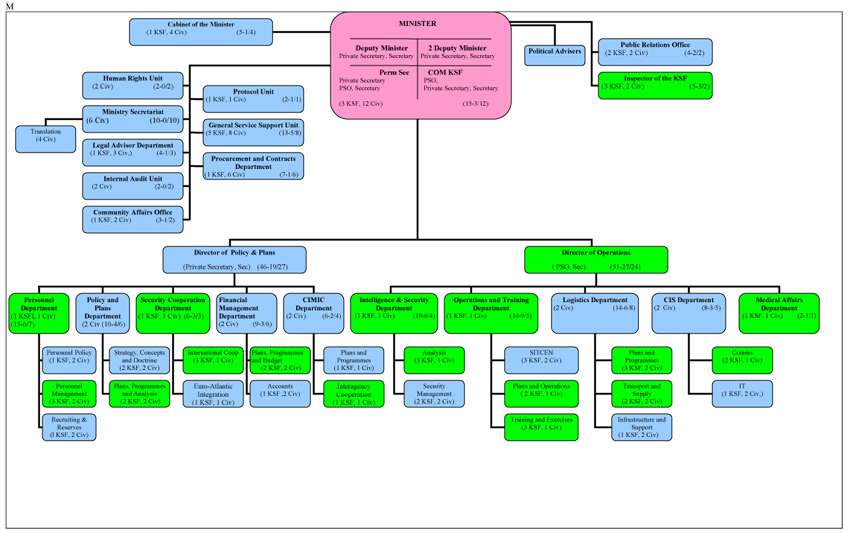
Structure
Military rank insignias
| Generals | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 | |
| radhë | Gjenerallejtënant | Gjeneralmajor | Gjeneralbrigade |
| rank | Lieutenant General | Major General | Brigadier General |
| Staff Officers | Officers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| radhë | Kolonel | Nënkolonel | Major | Kapiten | Toger | Nëntoger |
| rank | Colonel | Lieutenant Colonel | Major | Captain | First Lieutenant | Second Lieutenant |
| Non-Commissioned Officers | Enlisted Men | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| radhë | Rreshter Major | Rreshter i parë | Kapter | Rreshter | Tetar | Ushtar |
| rank | Sergeant Major | First Sergeant | Staff Sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Private |
Weapons and equipment
Firearms
| Picture | Weapon | Cartridge | Country Manufactured | Notes | Citation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assault Rifles | |||||||
 |
H&K G36 | 5.56×45mm NATO | |
Standard Service Rifle | [28] | ||
 |
M4 carbine | 5.56×45mm NATO | |
[29] | |||
| Pistols | |||||||
 |
Glock 17 | 9×19mm Parabellum | |
standard side arm | [28] | ||
| Submachine guns | |||||||
 |
H&K MP5 | 9×19mm Parabellum | |
Several Variants | |||
| M84 | 9×19mm | |
Serval Variants | ||||
| Grenade Launchers | |||||||
| |
H&K AG36 | 40×46mm grenade | |
Attaches to rifle | |||
| M72 Law | 66mm missle | |
Anti Tank Launcher | ||||
Vehicles
| Name | Country Manufactured | Number | Notes | Picture | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armored vehicles | |||||||
| Otokar Cobra | |
[30][31] |  | ||||
| Humvee | |
||||||
| Mercedes-Benz Wolf | |
||||||
| Unimog | |
||||||
| Iveco | |
||||||
| Land Rover | |
||||||
| Land Rover Defender | |
||||||
| Achleitner | |
||||||
| MB Man | |
||||||
| Jeep | |
||||||
| Trucks | |||||||
| Iveco Trakker | |
 | |||||
| Mercedes-Benz NG 1017A | |
 | |||||
| Otokar Cobra 2 | |
||||||
References
- ↑ "The World Factbook". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ Telegrafi. "Buxheti i ministrive për vitin 2011". Portali Telegrafi. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ Bush OKs supplying arms to Kosovo, AFP, March 19, 2008.
- ↑ "Lt. Gen. Selimi appointed as Chief of Staff of KSF" newkosovoareport.com 20 December 2009. Link accessed 21-01-09
- ↑ "Kosovo's security force launched" news.bbc.co.uk 21 January 2009. Link Retrieved 21-01-09
- 1 2 "Kosovo: Security or militarisation?" b92.net 21 January 2009. Link retrieved 21-01-09
- ↑ "Italy to support the establishment of Kosovo armed forces" newkosovoareport.com 24 December 2008. Link accessed 21-01-09
- ↑ "Portugal to assist the establishment of Kosovo Army" newkosovoareport.com 20 December 2008. Link accessed 21-01-09
- ↑ Ministry Press Release, 16 June 2009, Pristina
- ↑ "FSK nis zyrtarisht punën" (in Albanian). Pristina, Kosovo: Gazeta Express. September 18, 2009. Retrieved September 18, 2009.
- ↑ "NATO Secretary General statement on Kosovo Security Force reaching Full Operational Capability".
- ↑ "The Kosovo Security Force now self-sustainable".
- ↑ "Kosovo to create national army of 5,000 soldiers". Reuters. 4 March 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- ↑ "Kosovo to Have Army by 2019". noinvite.com. 5 March 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- ↑ "Kosovo to build its first national army". Euronews. 4 March 2014. Retrieved 11 March 2014.
- ↑ "Kosovo to Have Armed Forces by 2019". Balkan Insight. 4 March 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ↑ "Kosovo to form army 15 yrs after war, Serbia reacts". Turkish Weekly. 11 March 2014. Retrieved 11 March 2014.
- 1 2 "Kosovo precedent created new hotspots". B92. 28 May 2014. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- ↑ "Kosovo will soon have its army". B92. 26 November 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ↑ Article 13, Section 13.1, The Law on the Kosovo Security Force, No. Law No. 03/L-046 of 13 March 2008. Retrieved on 7 July 2016.
- ↑ Article 73 of the Constitution of Kosovo Section 1(2), Constitution of Kosovo (April 9, 2008). Retrieved on 7 July 2016.
- ↑ Article 126 of the Constitution of Kosovo Section 4, Constitution of Kosovo (April 9, 2008). Retrieved on 7 July 2016.
- ↑ Article 3, Section 3(a), Law on Service in the Kosovo Security Force, No. Law No. 03/L-082 of 13 June 2008 (in English). Retrieved on 7 July 2016.
- ↑ Annual Report 2015 (PDF) (Report). Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force. December 2015. p. 20. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- ↑ Status of Female – Member of Kosovo Security Force (PDF) (Report). Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force. October 2015. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- 1 2 "Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force Newsletter" (PDF) (Press release). Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force. April 2013. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- ↑ "Serb Wears Kosovo Uniform with Pride". Balkan Insight. 10 April 2015. Retrieved 14 April 2015.
- 1 2 "FSK Blen Armët e Para" [FSK Money Buys Weapons]. Gazeta Express (in Albanian). Kosovo: MediaWorks. 10 February 2010. Archived from the original on 13 February 2010.
- ↑ "Contract Awards Notice 21700/16/030/115" (PDF). Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force. 9 June 2016. Retrieved 26 July 2016.
- ↑ http://www.telegrafi.com/lajme/turqia-kosova-duhet-te-kete-ushtri-2-28950.html Turkey: Kosovo, Should have Military like every region state
- ↑ "43 members of the First Battalion of RRB completed two –months training with armored vehicle "KOBRA"" (Press release). Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force. 24 June 2016. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
External links
- Ministry for the Kosovo Security Force
- PDF document of the Law of the Kosovo Security Force
- KSF Cleans terrain from mines
