Kalmia latifolia
| Kalmia latifolia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Kalmia latifolia flowers | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Kalmia |
| Species: | K. latifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Kalmia latifolia L. | |
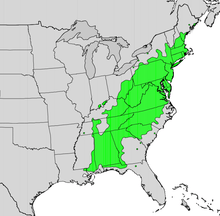 | |
Kalmia latifolia, commonly called mountain laurel,[1] calico-bush,[1] or spoonwood,[1] is a broadleaved evergreen shrub in the heather family, Ericaceae, that is native to the eastern United States. Its range stretches from southern Maine south to northern Florida, and west to Indiana and Louisiana. Mountain laurel is the state flower of Connecticut and Pennsylvania. It is the namesake of Laurel County in Kentucky and the city of Laurel, Mississippi (founded 1882).
Growth
It is an evergreen shrub growing to 3–9 m tall. The leaves are 3–12 cm long and 1–4 cm wide. Its flowers are round, ranging from light pink to white, and occur in clusters. There are several named cultivars today that have darker shades of pink, near red and maroon pigment. It blooms in May and June. All parts of the plant are poisonous. Roots are fibrous and matted.[2]
The plant is naturally found on rocky slopes and mountainous forest areas. It thrives in acidic soil, preferring a soil pH in the 4.5 to 5.5 range. The plant often grows in large thickets, covering great areas of forest floor. In the Appalachians, it can become tree-sized but is a shrub farther north.[2] The species is a frequent component of oak-heath forests.[3][4] In low, wet areas, it grows densely, but in dry uplands has a more sparse form.
Reproduction
Kalmia latifolia is notable for its unusual method of dispensing its pollen. As the flower grows, the filaments of its stamens are bent and brought into tension. When an insect lands on the flower, the tension is released, catapulting the pollen forcefully onto the insect.[5] Experiments have shown the flower capable of flinging its pollen up to 15 cm.[6] Physicist Lyman J. Briggs became fascinated with this phenomenon in the 1950s after his retirement from the National Bureau of Standards and conducted a series of experiments in order to explain it.[7]
Etymology
It is also known as Ivybush or spoonwood (because Native Americans used to make their spoons out of it) .
The plant was first recorded in America in 1624, but it was named after Pehr Kalm, who sent samples to Linnaeus in the 18th century.
Cultivation
The plant was originally brought to Europe as an ornamental plant during the 18th century. It is still widely grown for its attractive flowers and year round evergreen leaves. Elliptic, alternate, leathery, glossy evergreen leaves (to 5” long) are dark green above and yellow green beneath and reminiscent to the leaves of rhododendrons. All parts of this plant are toxic if ingested. Numerous cultivars have been selected with varying flower color. Many of the cultivars have originated from the Connecticut Experiment Station in Hamden and from the plant breeding of Dr. Richard Jaynes. Jaynes has numerous named varieties that he has created and is considered the world's authority on Kalmia latifolia.[8][9]
The cultivar 'Pink Charm'[10] has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.
Wood

The wood of the mountain laurel is heavy and strong but brittle, with a close, straight grain.[11] It has never been a viable commercial crop as it does not grow large enough,[12] yet it is suitable for wreaths, furniture, bowls and other household items.[11] It was used in the early 19th century in wooden-works clocks.[13] Root burls were used for pipe bowls in place of imported briar burls unattainable during World War II.[12] It can be used for handrails or guard rails.
Toxicity
Mountain laurel is poisonous to several different animals, including horses,[14] goats, cattle, deer,[15] monkeys, and humans,[16] due to grayanotoxin[17] and arbutin.[18] The green parts of the plant, flowers, twigs, and pollen are all toxic,[16] including food products made from them, such as toxic honey that may produce neurotoxic and gastrointestinal symptoms in humans eating more than a modest amount.[17] Fortunately the honey is sufficiently bitter to discourage most people from eating it, whereas it does not harm bees sufficiently to prevent its use as winter bee fodder. Symptoms of toxicity begin to appear about 6 hours following ingestion.[16] Symptoms include irregular or difficulty breathing, anorexia, repeated swallowing, profuse salivation, watering of the eyes and nose, cardiac distress, incoordination, depression, vomiting, frequent defecation, weakness, convulsions,[18] paralysis,[18] coma, and eventually death. Necropsy of animals who have died from spoonwood poisoning show gastrointestinal hemorrhage.[16]
Use by Native Americans
The Cherokee use the plant as an analgesic, placing an infusion of leaves put on scratches made over location of the pain.[19] They also rub the bristly edges of ten to twelve leaves" over the skin for rheumatism, crush the leaves to rub brier scratches, use an infusion as a wash "to get rid of pests", use a compound as a liniment, rub leaf ooze into the scratched skin of ball players to prevent cramps, and use a leaf salve for healing. They also use the wood for carving.[20]
The Hudson Bay Cree use a decoction of the leaves for diarrhea, but consider the plant to be poisonous.[21]
The Mahuna consider the plant to be poisonous, but regard it as forage for deer and use it as body deodorizer.[22]
Gallery
 K. latifolia leaves and early buds
K. latifolia leaves and early buds Flower buds
Flower buds Beginning to bloom
Beginning to bloom Full bloom
Full bloom Blooming and wilted flowers on the same flower head
Blooming and wilted flowers on the same flower head
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "Germplasm Resources Information Network: Kalmia latifolia".
- 1 2 Keeler, Harriet L. (1900). Our Native Trees and How to Identify Them. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 186–189.
- ↑ The Natural Communities of Virginia Classification of Ecological Community Groups (Version 2.3), Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation, 2010
- ↑ Schafale, M. P. and A. S. Weakley. 1990. Classification of the natural communities of North Carolina: third approximation. North Carolina Natural Heritage Program, North Carolina Division of Parks and Recreation.
- ↑ McNabb, W. Henry. "Kalmia latifolia L." (PDF). United States Forest Service. United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ Nimmo, John R.; Hermann, Paula M.; Kirkham, M. B.; Landa, Edward R. (2014). "Pollen Dispersal by Catapult: Experiments of Lyman J. Briggs on the Flower of Mountain Laurel". Physics in Perspective. 16 (3): 383. doi:10.1007/s00016-014-0141-9. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ Nimmo, John R.; Hermann, Paula M.; Kirkham, M. B.; Landa, Edward R. (2014). "Pollen Dispersal by Catapult: Experiments of Lyman J. Briggs on the Flower of Mountain Laurel". Physics in Perspective. 16 (3): 371–389. doi:10.1007/s00016-014-0141-9. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ Shreet, Sharon (April–May 1996). "Mountain Laurel". Flower and Garden Magazine.
- ↑ Jaynes, Richard A. (1997). Kalmia: Mountain Laurel and Related Species. Portland, OR: Timber Press. ISBN 0-88192-367-2.
- ↑ "RHS Plant Selector - Kalmia latifolia 'Pink Charm'". Retrieved 15 July 2013.
- 1 2 "Species: Kalmia latifolia". Fire Effects Information Service. United States Forest Service. Retrieved Oct 3, 2011.
- 1 2 "Mountain Laurel". Wood Magazine.com. Retrieved Oct 3, 2011.
- ↑ Galbraith, Gene (September 12, 2006). "The legacy of the Ogee Clock". Retrieved October 3, 2011.
- ↑ "Mountain Laurel". ASPCA. Retrieved Oct 3, 2011.
- ↑ Horton, Jenner L.; Edge, W.Daniel (July 1994). "Deer-resistant Ornamental Plants" (PDF). Oregon State University Extension. Retrieved Oct 3, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 "Kalmia latifolia". University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine. Retrieved Oct 3, 2011.
- 1 2 "Grayanotoxin". Bad Bug Book. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. May 4, 2009. Retrieved Oct 7, 2011.
- 1 2 3 Russell, Alice B.; Hardin, James W.; Grand, Larry; Fraser, Angela. "Poisonous Plants: Kalmia latifolia". Poisonous Plants of North Carolina. North Carolina State University. Retrieved Oct 3, 2011.
- ↑ Taylor, Linda Averill 1940 Plants Used As Curatives by Certain Southeastern Tribes. Cambridge, MA. Botanical Museum of Harvard University (p. 48)
- ↑ Hamel, Paul B. and Mary U. Chiltoskey 1975 Cherokee Plants and Their Uses -- A 400 Year History. Sylva, N.C. Herald Publishing Co. (p. 42)
- ↑ Holmes, E.M. 1884 Medicinal Plants Used by Cree Indians, Hudson's Bay Territory. The Pharmaceutical Journal and Transactions 15:302-304 (p. 303)
- ↑ Romero, John Bruno 1954 The Botanical Lore of the California Indians. New York. Vantage Press, Inc. (p. 52)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kalmia latifolia. |
- USDA Plant Profile: Kalmia latifolia
- Connecticut Botanical Society Profile: Kalmia latifolia
- Kalmia latifolia images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu