International sanctions during the Ukrainian crisis
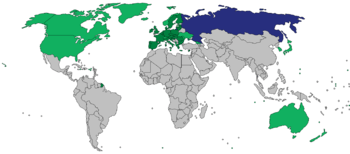
The Russian military intervention in Ukraine, which began in late February 2014, prompted a number of governments to apply sanctions against individuals, businesses and officials from Russia and Ukraine. Sanctions were approved by the United States, the European Union (EU) and other countries and international organisations. Russia has responded with sanctions against a number of countries, including a total ban on food imports from the EU, United States, Norway, Canada and Australia.
The sanctions have contributed to the collapse of the Russian ruble and the Russian financial crisis (2014–present).[1] They have also caused economic damage to a number of EU countries, with the total losses estimated at €100 billion.[2]
According to Ukrainian officials,[lower-alpha 1] the sanctions forced Russia to change its approach towards Ukraine and undermined the Russian military advances in the region.[3][4] Representatives of these countries say that they will lift sanctions against Russia only after Moscow fulfils the Minsk II agreements.[5][6][7]
Background
| Ukrainian crisis |
|---|
 |
| Main topics |
| Related topics |
|
|
In response to the Crimean crisis and the subsequent annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, some governments and international organisations, led by the United States and European Union, imposed sanctions on Russian individuals and businesses. As the unrest expanded into other parts of southern and eastern Ukraine, and later escalated into the ongoing war in the Donbass region, the scope of the sanctions increased. The Russian government responded in kind, with sanctions against some Canadian and American individuals and, in August 2014, with a total ban on food imports from the European Union, United States, Norway, Canada and Australia.
Sanctions against Russian and Ukrainian individuals, companies and officials
First round of sanctions: March/April 2014
On 6 March 2014, US president Barack Obama, invoking, inter alia, the International Emergency Economic Powers Act and the National Emergencies Act, signed an executive order that declared a national emergency and ordered sanctions, including travel bans and the freezing of their U.S. assets, against not-yet-specified individuals, later to be determined by the Secretary of the Treasury (in consultation with the Secretary of State) who had "asserted governmental authority in the Crimean region without the authorization of the Government of Ukraine" and whose actions were found, inter alia, to "undermine democratic processes and institutions in Ukraine".[8][9]
The US, the EU and Canada introduced the first round of specifically targeted sanctions on 17 March 2014,[10][11][12] the day after the Crimean referendum and a few hours before the Russian president Vladimir Putin, by signing a decree recognizing Crimea as an independent state, laid the groundwork for its annexation by Russia.
The principal EU sanction that day aimed to "prevent the entry into (…) their territories of the natural persons responsible for actions which undermine (…) the territorial integrity (…) of Ukraine, and of natural persons associated with them, as listed in the Annex".[10] The EU imposed its sanctions "in the absence of de-escalatory steps by the Russian Federation" in order to bring an end to the violence in eastern Ukraine. The EU at the same time clarified that the Union "remains ready to reverse its decisions and reengage with Russia when it starts contributing actively and without ambiguities to finding a solution to the Ukrainian crisis".[13] These 17 March sanctions were the most wide-ranging sanctions used against Russia since the 1991 fall of the Soviet Union.[14] Japan also announced sanctions against Russia. These included the suspension of talks regarding military matters, space, investment, and visa requirements.[15] A few days thereafter, the US government announced it was expanding the sanctions.[16]
On 19 March, Australia imposed sanctions against Russia after annexation of Crimea from Ukraine. The Australian government imposed targeted financial sanctions and travel bans on those who have been instrumental in the Russian threat to Ukraine's sovereignty.[17] The Australian sanctions were expanded on 21 May.[18]
In early April, Albania, Iceland and Montenegro, as well as Ukraine, decided to follow the EU and impose the same restrictions and travel bans issued by the EU on 17 March.[19] Igor Lukšić, foreign minister of Montenegro, said that despite a "centuries old-tradition" of good ties with Russia, joining the EU in imposing sanctions had "always been the only reasonable choice".[20] Slightly earlier in March, Moldova had decided to follow the EU and impose the same set of sanctions against former president of Ukraine Viktor Yanukovych and a number of former Ukrainian officials, as announced by the EU on 5 March.[21] In response to the sanctions introduced by the United States and the EU, the State Duma (Russian parliament) unanimously passed a resolution asking for all members of the Duma to be included on the sanctions list.[22] The sanctions were expanded to include prominent Russian businessmen and women a few days later.[23]
Second round of sanctions: April 2014
On 28 April, the United States imposed a ban on business transactions within its territory on seven Russian officials, including Igor Sechin, executive chairman of the Russian state oil company Rosneft, and seventeen Russian companies.[24] On the same day, the European Union issued travel bans against a further fifteen individuals.[25] In connection with this, the EU issued a paper stating the aims of the sanctions. The EU states that their "sanctions are not punitive, but designed to bring about a change in policy or activity by the target country, entities or individuals. Measures are therefore always targeted at such policies or activities, the means to conduct them and those responsible for them. At the same time, the EU makes every effort to minimise adverse consequences for the civilian population or for legitimate activities".[26]
Third round of sanctions: 2014–present
In response to the escalating War in Donbass, on 17 July 2014 the United States extended its transactions ban to two major Russian energy firms, Rosneft and Novatek, and to two banks, Gazprombank and Vnesheconombank.[27] United States also urged EU leaders to join the Third Wave[28] leading EU to start drafting European Sanctions a day before.[29][30] On 25 July, the EU officially expanded its sanctions to an additional fifteen individuals and eighteen entities,[31] followed by an additional eight individuals and three entities on 30 July.[32] On 31 July 2014 the EU introduced the third round of sanctions which included an embargo on arms and related material, and embargo on dual-use goods and technology intended for military use or a military end user, a ban on imports of arms and related material, controls on export of equipment for the oil industry, and a restriction on the issuance of and trade in certain bonds, equity or similar financial instruments on a maturity greater than 90 days (On September 2014 lowered to 30 days) [33]
On 24 July 2014, Canada announced sanctions targeting Russian arms, energy and financial entities.[34]
On 5 August 2014, Japan decided to freeze the assets of "individuals and groups supporting the separation of Crimea from Ukraine" and restrict imports from Crimea. Japan will additionally freeze funds for new projects in Russia in line with the policy of the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development.[35]
On 8 August 2014 Australian prime minister Tony Abbott announced that Australia is "working towards" tougher sanctions against Russia, which should be implemented in the coming weeks.[36][37]
On 12 August 2014 Norway decided to adopt the tougher sanctions against Russia that were imposed by the EU and the United States on 12 August 2014. Although Norway is not a part of the EU, the Norwegian Foreign Minister Børge Brende said that it would impose restrictions similar to the EU's 1 August sanctions. Russian state-owned banks will be banned from taking long-term and mid-term loans, arms exports will be banned and supplies of equipment, technology and assistance to the Russian oil sector will be prohibited.[38]
On 14 August 2014 Switzerland expanded sanctions against Russia over its threat to Ukraine's sovereignty. Swiss government added 26 more Russians and pro-Russian Ukrainians to the list of sanctioned Russian citizens that was first announced after Russia's annexation of Crimea.[39] On 27 August 2014 Switzerland further expanded their sanctions against Russia. The Swiss government said it is expanding measures to prevent the circumvention of sanctions relating to the situation in Ukraine to include the third round of sanctions imposed by the EU in July. The Swiss government also stated that five Russian banks (Sberbank, VTB, Vnesheconombank, Gazprombank and Rosselkhoz) will require authorisation to issue long-term financial instruments in Switzerland.[40]
On 14 August 2014 Ukraine passed a law introducing Ukrainian sanctions against Russia.[41][42] The law includes 172 individuals and 65 entities in Russia and other countries for supporting and financing "terrorism" in Ukraine, though actual sanctions would need approval from Ukraine's National Security and Defense Council.
On 28 August 2014 Switzerland amended its sanctions to include the sanctions imposed by the EU in July.[40]
On 11 September 2014, US President Barack Obama said that the United States would join the EU in imposing tougher sanctions on Russia's financial, energy and defence sectors.[43] On 12 September 2014, the United States imposed sanctions on Russia's largest bank (Sberbank), a major arms maker and arctic (Rostec), deepwater and shale exploration by its biggest oil companies (Gazprom, Gazprom Neft, Lukoil, Surgutneftegas and Rosneft). Sberbank and Rostec will have limited ability to access the US debt markets. The sanction on the oil companies seek to ban co-operation with Russian oil firms on energy technology and services by companies including Exxon Mobil Corp. and BP Plc.[44]
On 24 September 2014, Japan imposed additional sanctions against Russia by banning the issuance of securities by five Russian banks (Sberbank, VTB, Gazprombank, Rosselkhozbank and development bank VEB) and also tightened restrictions on defence exports to Russia.[45]
On 3 October 2014, US Vice President Joe Biden said that "It was America's leadership and the president of the United States insisting, oft times almost having to embarrass Europe to stand up and take economic hits to impose costs"[46] and added that "And the results have been massive capital flight from Russia, a virtual freeze on foreign direct investment, a ruble at an all-time low against the dollar, and the Russian economy teetering on the brink of recession. We don't want Russia to collapse. We want Russia to succeed. But Putin has to make a choice. These asymmetrical advances on another country cannot be tolerated. The international system will collapse if they are."[47]
On 18 December 2014 the European Union banned some investments in Crimea, halting support for Russian Federation Black Sea oil and gas exploration and stopping European companies from purchasing real estate or companies in Crimea, or offering tourism services.[48] On 19 December 2014, US President Barack Obama imposed sanctions on Russian-occupied Crimea by executive order prohibiting exports of US goods and services to the region.[49]
On 27 January 2015 the new government of Greece under Alexis Tsipras were preparing to veto further European sanctions on Russia,[50] but agreed to extend the term of existing sanctions until further talks later in the year.[51] Some member countries, including Italy, Cyprus, Bulgaria, Luxembourg and Austria, were split on further sanctions, but have nominated to go down the sanctions route.[52] Notwithstanding, during the Foreign Affairs Council on 29 January 2015, a unanimous EU condemned "the indiscriminate shelling of residential areas, especially in Mariupol, and the escalation of fighting in the Donetsk and Luhansk regions." The foreign ministers of the EU added that "The Council expects Russia to exert its influence and to induce the separatists to fully live up to the commitments under the Minsk agreements. These include notably the cessation of hostilities and the withdrawal of heavy weapons from the security zone as urgent first steps." The EU agreed to extend existing restrictive measures and called for a proposal within a week on additional targeted sanctions, for a decision at the Foreign Affairs Council on 9 February.[53] On this date the Council adopted "additional listings concerning separatists in Eastern Ukraine and their supporters in Russia". These consist of an asset freeze and a travel ban on 19 persons and 9 entities involved in action against Ukraine's territorial integrity. To "give space for current diplomatic efforts", the Council put the entry into force of the measures on hold until Monday 16 February 2015, in relation to the Minsk summit taking place on 11 February.[54]
On February 16, 2015, the EU increased its sanction list to cover 151 individuals and 37 entities.[55] Australia indicated that it would follow the EU in a new round of sanctions. If the EU sanctioned new Russian and Ukrainian entities then Australia would keep their sanctions in line with the EU.
On February 18, 2015, Canada increased its sanctions list by 37 Russian citizens and 17 Russian entities. Rosneft and Anatoly Antonov, deputy minister of defense became sanctioned.[56][57] In June 2015 Canada added three individuals and 14 entities, including Gazprom.[58] Media suggested the sanctions were delayed because Gazprom was a main sponsor of the 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup then concluding in Canada.[59]
In June 2015, the G7 collectively extended sanctions already in place for an additional six months. On 21 December 2015, the EU extended economic sanctions against Russia until 31 July 2016.[60] France announced in January 2016 that it wants to lift the sanctions in this summer. Earlier, U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry mentioned the possible lifting of sanctions.[61]
In June 2016, the French Senate voted to urge its government to "gradually and partially" lift the EU sanctions on Russia, although the vote was non-binding.[62]
In September 2016, the EU extended its sanctions, for another 6 months, against Russian officials and pro-Moscow separatists in Ukraine.[63] An EU asset freeze on ex-Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych was upheld by the bloc's courts.[63]
Sanctions over Ukrainians held by Russia
In April 2016, Lithuania sanctioned 46 individuals who were involved in the detention and sentencing of Ukrainian citizens Nadiya Savchenko, Oleh Sentsov, and Olexandr Kolchenko. Lithuanian Foreign Minister Linas Linkevičius said that his country wanted to "focus attention on the unacceptable and cynical violations of international law and human rights in Russia. [...] It would be more effective if the blacklist became Europe-wide. We hope to start such a discussion."[64]
Sanctions against Crimea
The United States, Canada, the European Union and other European countries (including Ukraine) imposed economic sanctions specifically targeting Crimea. Sanctions prohibit the sale, supply, transfer, or export of goods and technology in several sectors, including services directly related to tourism and infrastructure. They list seven ports where cruise ships cannot dock.[65][66][67][68][69] Sanctions against Crimean individuals include travel bans and asset freezes. Visa and MasterCard have stopped service in Crimea between December 2014 and April 2015.[70]
Consequences and assessment

The sanctions introduced both by and against Russia slowed down the trade between Russia and EU, causing damage to both Russian and European economy.
Effect on Russia
The economic sanctions are generally believed to have helped weaken the Russian economy and to intensify the challenges that Russia was already facing.
A 2015 data analysis confirmed Russia’s entry into a recession, with negative GDP of -2.2% for the first quarter of 2015, as compared to the first quarter of 2014. Further, the combined effect of the sanctions and the rapid decline in oil prices in Q$2014 has caused significant downward pressure on the value of the ruble and flight of capital out of Russia. At the same time, the sanctions on access to financing have forced Russia to use part of its foreign exchange reserves to prop up the economy. These events forced the Central Bank of Russia to stop supporting the value of the ruble and increase interest rates.
Russia’s ban on western imports had the additional effect on these challenging events as the embargo led to higher food prices and further inflation in addition to the effects of decreased value of the ruble which had already raised the price of imported goods.[72]
Effect on US and EU countries
The losses of EU have been estimated as €100 billion,[2] with Italy in particular losing over €1.25 billion.[73] The German business sector, with around 30,000 workplaces depending on trade with Russia, also reported being affected by the sanctions.[74] The sanctions had an impact on numerous European market sectors, including energy, agriculture,[75] and aviation.[76] In March 2016, the Finnish farmers’ union MTK stated that the Russian sanctions and falling prices have put farmers under tremendous pressure. Finland’s Natural Resources Institute LUKE has estimated that last year farmers saw their incomes shrink by 40 percent compared to the previous year.[77]
In February 2015, Exxon Mobil reported losing about $1 billion due to sanctions.[78]
Opposition within Europe
Italy, Hungary, Greece, France, some German states, Cyprus and Slovakia are among the EU states most skeptical about the sanctions and have called for review of sanctions.[79] The Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orbán stated that Europe “shot itself in the foot” by introducing economic sanctions.[80] In the words of the Bulgarian Prime Minister Boiko Borisov: “I don’t know how Russia is affected by the sanctions, but Bulgaria is affected severely”;[81] Czech President Miloš Zeman [82] and Slovakian Prime Minister Robert Fico[83] also argued that the sanctions should be lifted.
The Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras said that Greece would seek to mend ties between Russia and EU through European institutions. Tsipras also said that Greece was not in favour of Western sanctions imposed on Russia, adding that it risked the start of another Cold War.[84][85]
A number of business figures in France and Germany have opposed the sanctions.[86][87][88] The German Economy Minister Sigmar Gabriel suggested that the Ukrainian crisis should be resolved by dialogue rather than economic confrontation,[89] later adding that the reinforcement of anti-Russian sanctions will “provoke an even more dangerous situation… in Europe”.[90]
Paolo Gentiloni, Italian Minister of Foreign Affairs, said that the sanctions “are not the solution to the conflict”.[91] Some companies, most notably Siemens Gas Turbine Technologies LLC, were reported to attempt bypassing the sanctions and exporting power generation turbines to the annexed Crimea.[92]
In August 2015, the British think tank Bow Group released a report on sanctions, calling for the removal of them. According to the report, the sanctions have had "adverse consequences for European and American businesses, and if they are prolonged... they can have even more deleterious effects in the future"; the potential cost of sanctions for the Western countries has been estimated as over $700 billion.[93]
Sanctions by Russia
Three days after the first sanctions against Russia, on 20 March 2014, the Russian Foreign Ministry published a list of reciprocal sanctions against certain American citizens, which consisted of ten names, including Speaker of the House of Representatives John Boehner, Senator John McCain, and two advisers to Barack Obama. The ministry said in the statement, "Treating our country in such way, as Washington could have already ascertained, is inappropriate and counterproductive", and reiterated that sanctions against Russia would have a boomerang effect.[94] On 24 March, Russia banned thirteen Canadian officials, including members of the Parliament of Canada, from entering the country.[95]
On 6 August 2014,[96] Putin signed a decree "On the use of specific economic measures", which mandated an effective embargo for a one-year period on imports of most of the agricultural products whose country of origin had either "adopted the decision on introduction of economic sanctions in respect of Russian legal and (or) physical entities, or joined same".[97][98] The next day, the Russian government ordinance was adopted and published with immediate effect,[99] which specified the banned items as well as the countries of provenance: the United States, the EU, Norway, Canada and Australia, including a ban on fruit, vegetables, meat, fish, milk and dairy imports. Prior to the embargo, food exports from the EU to Russia were worth around €11.8 billion, or 10% of the total EU exports to Russia. Food exports from the United States to Russia were worth around €972 million. Food exports from Canada were worth around €385 million.[100][101]
Russia had previously taken a position that it would not engage in "tit-for-tat" sanctions, but, announcing the embargo, Russian Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev said, "There is nothing good in sanctions and it was not an easy decision to take, but we had to do it." He indicated that sanctions relating to the transport manufacturing sector were also being considered. United States Treasury spokesperson David Cohen said that sanctions affecting access to food were "not something that the US and its allies would ever do".[102]
On the same day, Russia announced a ban on the use of its airspace by Ukrainian aircraft.[100]
In January 2015, it became clear that Russian authorities would not allow a Member of the European Parliament, Lithuanian MEP Gabrielius Landsbergis, make a visit to Moscow due to political reasons.[103]
In March 2015, Latvian MEP Sandra Kalniete and Speaker of the Polish Senate Bogdan Borusewicz were both denied entry into Russia under the existing sanctions regime, and were thus unable to attend the funeral of murdered opposition politician Boris Nemtsov.[104]
After a member of the German Bundestag was denied entry into Russia in May 2015, Russia released a blacklist to European Union governments of 89 politicians and officials from the EU who are not allowed entry into Russia under the present sanctions regime. Russia asked for the blacklist to not be made public.[105] The list is said to include eight Swedes, as well as two MPs and two MEPs from the Netherlands.[106] Finland's national broadcaster Yle published a leaked German version of the list.[107][108]
In response to this publication, British politician Malcolm Rifkind (whose name was included on the Russian list) commented: "It shows we are making an impact because they wouldn’t have reacted unless they felt very sore at what had happened. Once sanctions were extended, they've had a major impact on the Russian economy. This has happened at a time when the oil price has collapsed and therefore a main source of revenue for Mr Putin has disappeared. That’s pretty important when it comes to his attempts to build up his military might and to force his neighbours to do what they’re told." He added, “If there had to be such a ban, I am rather proud to be on it – I’d be rather miffed if I wasn’t.”[109] Another person on the list, Swedish MEP Gunnar Hökmark, remarked that he was proud to be on the list and said "a regime that does this does it because it is afraid, and at heart it is weak".[110]
In reply to the Russian entry ban on European politicians, a spokesperson from the EU said "The list with 89 names has now been shared by the Russian authorities. We don't have any other information on legal basis, criteria and process of this decision. We consider this measure as totally arbitrary and unjustified, especially in the absence of any further clarification and transparency."[111]
In addition, Russian President Vladimir Putin has signed an order extending the embargo on the same countries sanctioned in 2014 till August 5, 2016.
List of sanctioned individuals
Sanctioned individuals include notable and high-level central government personnel on all sides. In addition, companies suggested for possible involvement in the controversial issues have also been sanctioned.
See also
- Cold War II
- List of companies that applied sanctions during the Crimean crisis
- Russian financial crisis (2014–present)
- Magnitsky Act
- Autarky
Notes
- ↑ Liubov Nepop, the Head of the Ukrainian Mission to the EU, and Petro Poroshenko, the president of Ukraine
References
- ↑ "Russia’s rouble crisis poses threat to nine countries relying on remittances". The Guardian. 18 January 2015.
- 1 2 "Russian sanctions to 'cost Europe €100bn'". Newsweek. 19 June 2015.
- ↑ "When the sanctions regime appeared to cost almost nothing to EU trade volume... together with Ukrainian resistance, it forced Russia to change its approach towards Ukraine... So far, an approach comprised of EU unity and strong solidarity with Ukraine, as well as resistance and reforms implementation, has proved to be the most efficient way to stop Russian military advances." -- Liubov Nepop, the Head of the Ukrainian Mission to the EU (source)
- ↑ "... sanctions and heroism of our warriors are the key elements of deterring the Russian aggression" --the president of Ukraine Petro Poroshenko (source)
- ↑ "Obama calls on NATO, EU to boost support for Ukraine". Unian.info. 8 July 2016.
- ↑ "Austrian foreign minister calls for improving relationship with Moscow". Reuters. 19 June 2016.
- ↑ "Sanctions to be lifted from Russia after implementation of Minsk Agreements – Nuland". Interfax-Ukraine. 18 May 2016.
- ↑ Executive Order -- Blocking Property of Certain Persons Contributing to the Situation in Ukraine The White House, 6 March 2014.
- ↑ Holland, Steve (6 March 2014). "UPDATE 4-Obama warns on Crimea, orders sanctions over Russian moves in Ukraine". Reuters. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- 1 2 "COUNCIL DECISION 2014/145/CFSP of 17 March 2014 concerning restrictive measures in respect of actions undermining or threatening the territorial integrity, sovereignty and independence of Ukraine" (PDF). Official Journal of the European Union. 17 March 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ "U.S. and Europe Step Up Sanctions on Russian Officials". New York Times. 17 March 2014. Retrieved 18 January 2015.
- ↑ "Sanctions List". Prime Minister of Canada Stephen Harper. 17 March 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ "EU sanctions against Russia over Ukraine crisis". European External Action Service. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ↑ Katakey, Rakteem (25 March 2014). "Russian Oil Seen Heading East Not West in Crimea Spat". Bloomberg L.P. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ↑ "Japan imposes sanctions against Russia over Crimea independence". Fox News. Associated Press. 18 March 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ "US imposes second wave of sanctions on Russia". jnmjournal.com. 20 March 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ "Australia imposes sanctions on Russians after annexation of Crimea from Ukraine". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 2014-03-19. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ Minister for Foreign Affairs (Australia) (21 May 2014). "Further sanctions to support Ukraine". Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ↑ "Declaration by the High Representative on behalf of the European Union on the alignment of certain third countries with the Council Decision 2014/145/CFSPconcerning restrictive measures in respect of actions undermining or threatening the territorial integrity, sovereignty and independence of Ukraine" (PDF). Council of the European Union. 11 April 2014. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
- ↑ Rettman, Andrew (17 December 2014). "Montenegro-EU talks advance in Russia's shadow". EUobserver. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ↑ "Moldova joined EU sanctions against former Ukrainian officials". Teleradio Moldova. 20 March 2014. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ↑ "All Russian MPs volunteer to be subject to US, EU sanctions". 2014-03-18. Retrieved 20 March 2014.
- ↑ "U.S. levels new sanctions against Russian officials, companies". Haaretz. 28 April 2014.
- ↑ "EU strengthens sanctions against actions undermining Ukraine's territorial integrity". International Trade Compliance. 28 April 2014.
- ↑ "EU restrictive measures" (PDF). Council of the European Union. 29 April 2014. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
- ↑ "Third Wave of Sanctions Slams Russian Stocks". Moscow Times. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ Marchak, Daria (15 July 2014). "EU Readies Russia Sanctions Amid U.S. Pressure on Ukraine". Bloomberg L.P.
- ↑ "EU summit: Leaked draft of new Russia sanctions". Financial Times. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ "EU Draft Urges Deeper Sanctions Against Russia". International Business Times UK. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ "restrictive measures in respect of actions undermining or threatening the territorial integrity, sovereignty and independence of Ukraine".
- ↑ "Council Decision 2014/508/CFSP of 30 July 2014 amending Decision 2014/145/CFSP concerning restrictive measures in respect of actions undermining or threatening the territorial integrity, sovereignty and independence of Ukraine".
- ↑ http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=OJ:JOL_2014_229_R_0001&from=EN COUNCIL REGULATION (EU) No 833/2014
- ↑ "Ukraine crisis: U.S., EU, Canada announce new sanctions against Russia". cbc.ca. Thomson Reuters. 29 July 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ "Japan Formally OKs Additional Russia Sanctions". ABC News. 5 August 2014. Archived from the original on 2014-08-06.
- ↑ Rosie Lewis (8 August 2014). "Australia 'working towards' tougher sanctions against Russia: Abbott". The Australian. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ "Prime Minister Tony Abbott arrives in Netherlands, flags tougher sanctions against Russia over MH17". ABC News. 11 August 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ Saleha Mohsin (12 August 2014). "Norway 'Ready to Act' as Putin Sanctions Spark Fallout Probe". Bloomberg L.P. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ Switzerland Expands Sanctions Against Russia Over Ukraine Crisis RFERL: Switzerland Expands Sanctions Against Russia Over Ukraine Crisis
- 1 2 https://www.news.admin.ch/message/index.html?lang=en&msg-id=54221 Situation in Ukraine: Federal Council decides on further measures to prevent the circumvention of international sanctions
- ↑ RFE/RL (14 August 2014). "Ukraine Passes Law On Russia Sanctions, Gas Pipelines". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ "Ukraine approves law on sanctions against Russia". Reuters. 14 August 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ Lamarque, Kevin (11 September 2014). "Obama says U.S. to outline new Russia sanctions on Friday". Reuters. Retrieved 12 September 2014.
- ↑ Arshad, Mohammed (12 September 2014). "U.S. steps up sanctions on Russia over Ukraine". Reuters. Retrieved 12 September 2014.
- ↑ Takahashi, Maiko (25 September 2014). "U.S. Japan Steps Up Russia Sanctions, Protests Island Visit". Bloomberg.
- ↑ "Biden says US 'embarrassed' EU into sanctioning Russia over Ukraine". RT. 4 October 2014.
- ↑ Biden, Joe (3 October 2014). "Remarks by the Vice President at the John F. Kennedy Forum". www.whitehouse.gov. The White House - President Barack Obama. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ↑ Adrian Croft; Robin Emmott (18 December 2014). "EU bans investment in Crimea, targets oil sector, cruises". Reuters. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ "US slaps trade ban on Crimea over Russia 'occupation'". Channel NewsAsia. AFP/fl. 20 December 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ James G Neuger (27 January 2015). "Greece's Coming Clash in Europe Starts With Russia Sanctions". Bloomberg.com. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ↑ Robin Emmott; Pavel Polityuk (29 January 2015). "EU wins Greek backing to extend Russia sanctions, delays decision on new steps". Reuters. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ↑ Adrian Croft (26 January 2015). "EU hawks lead calls for tougher sanctions on Russia". Reuters. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ↑ "Foreign Affairs Council, 29/01/2015". Council of the European Union. 29 January 2015. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ↑ "Main results of the Foreign Affairs Council". Council of the European Union. 9 February 2015. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ↑ "New EU Sanctions Hit 2 Russian Deputy DMs". Defense News. 16 February 2015. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ "Expanded Sanctions List". pm.gc.ca. 17 February 2015.
- ↑ "Ukraine conflict: Russia rebuffs new Canadian sanctions as 'awkward'". CBC News. 18 February 2015.
- ↑ "Expanded Sanctions List". pm.gc.ca. 29 June 2015.
- ↑ Berthiaume, Lee (8 July 2015). "Russian sponsor of FIFA world cup sanctioned as tournament ended". Ottawa Citizen. Retrieved 8 July 2015.
- ↑ "Russia: EU prolongs economic sanctions by six months". Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ "France Hopes To See Russia Sanctions Lifted 'This Summer': French Economy Minister". NDTV.com. 24 January 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ "French Senate Urges Government To Lift Sanctions On Russia". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 9 June 2016.
- 1 2 Norman, Laurence (September 11, 2016). EU Extends Sanctions on Russian Officials Over Ukraine Crisis. The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved: October 5, 2016.
- ↑ Sytas, Andrius (12 April 2016). "Lithuania blacklists 46 for their role in Savchenko trial". Reuters.
- ↑ "EU sanctions add to Putin's Crimea headache". EUobserver.com. EUobserver. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- ↑ "Obama authorizes 'economic embargo' on Russia's Crimea". RT.com. TV-Novosti. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- ↑ "Special Economic Measures (Ukraine) Regulations". Canadian Justice Laws Website. 17 March 2014. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- ↑ "Australia and sanctions - Consolidated List - Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade". Dfat.gov.au. 25 March 2015. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ↑ "Declaration by the High Representative on behalf of the European Union on the alignment of certain third countries with the Council Decision 2014/145/CFSPconcerning restrictive measures in respect of actions undermining or threatening the territorial integrity, sovereignty and independence of Ukraine" (PDF). European Union. 11 April 2014. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ↑ "Visa and MasterCard resume operations in Crimea". RT.com. TV-Novosti. 30 April 2015. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ↑ Golubkova, Katya; Baczynska, Gabriela (10 December 2014). "Rouble fall, sanctions hurt Russia's economy: Medvedev". Reuters. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ↑ http://www.nato.int/docu/review/2015/Also-in-2015/sanctions-after-crimea-have-they-worked/EN/
- ↑ "Russians Live Without Parmesan as Italy Pays Sanctions Price". Bloomberg. 19 June 2015.
- ↑ "German businesses suffer fallout as Russia sanctions bite". Financial Times. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ "EU agro-business suffers from Russian Embargo". New Europe. 22 June 2015.
- ↑ "Russia Sanctions Stall Europe's Business Aviation Market". Aviation Week. 5 May 2015.
- ↑ "Tractors roll into Helsinki for massive farmers' demo". Yle Uutiset. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ "Here's What Exxon Lost From Russia Sanctions". Forbes. 27 February 2015.
- ↑ "Italy, Hungary say no automatic renewal of Russia sanctions". Reuters. 14 March 2016.
- ↑ Gergely Szakacs (15 August 2014). "Europe 'shot itself in foot' with Russia sanctions: Hungary PM". Reuters. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ "Bulgaria says it is suffering from EU sanctions on Russia". Mail Online. 4 December 2014. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ Prague Post: Zeman apprears on Russian TV to blast sanctions
- ↑ "Slovak PM slams sanctions on Russia, threatens to veto new ones". Reuters. 31 August 2014.
- ↑ "Tsipras: Greece will seek to mend ties between Russia & EU through European institutions". RT. 8 April 2015. Retrieved 15 August 2015.
- ↑ "Greece's Tsipras meets Putin in Moscow - as it happened". The Guardian. 8 April 2015. Retrieved 15 August 2015.
- ↑ "Industry urges Merkel to back down on Moscow sanctions - The Sunday Times". Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ WSJ Staff. "Total CEO Christophe de Margerie's Speech About Russian Sanctions". WSJ. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ Reuters Editorial (26 September 2014). "UniCredit says sanctions hurting Europe more than Russia: Czech media". Reuters. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ Reuters: German economy minister rejects tougher sanctions on Russia
- ↑ More Anti-Russian Sanctions Will Ultimately Cripple Europe – German Vice-Chancellor
- ↑ "Paolo Gentiloni; dalla Russia alla Libia, per orientarci nelle crisi "la bussola sarà l'interesse nazionale"". L'Huffington Post. 2 December 2014. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
- ↑ "https://meduza.io/en/news/2015/06/30/siemens-to-bypass-sanctions-and-work-in-crimea". meduza.io. Retrieved 2015-06-30. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ The Sanctions On Russia — The Bow Group
- ↑ Sanctions tit-for-tat: Moscow strikes back against US officials RT
- ↑ Steven Chase (24 March 2014). "Russia imposes sanctions on 13 Canadians, including MPs". The Globe and Mail. Toronto. Retrieved 20 April 2014.
- ↑ Putin bans agricultural imports from sanctioning countries for 1 year RT, 6 August 2014.
- ↑ "Western food imports off the menu as Russia hits back over Ukraine sanctions". The Guardian. 7 August 2014.
- ↑ "Указ Президента РФ от 6 августа 2014 г. N 560 "О применении отдельных специальных экономических мер в целях обеспечения безопасности Российской Федерации"" [Presidential Decree of August 6, 2014 N 560 "On the application of certain special economic measures to ensure the security of the Russian Federation"]. garant.ru (in Russian). 7 August 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ "О мерах по реализации Указа Президента России "О применении отдельных специальных экономических мер в целях обеспечения безопасности Российской Федерации"" [On measures to implement the Decree of the President of Russia "On the application of certain special economic measures in order to ensure the security of the Russian Federation"]. government.ru (in Russian). 7 August 2014. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- 1 2 "Russia hits West with food import ban in sanctions row". BBC News. 7 August 2014.
- ↑ Payton, Laura (7 August 2014). "Russia sanctions: Vladimir Putin retaliates, sanctions Canada". CBC News.
- ↑ "Russia threatens to go beyond food sanctions". Financial Times. 7 August 2014.
- ↑ Rettman, Andrew (23 January 2015). "Russia suspends official EU parliament visits". Euobserver. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ↑ "Russia bars two EU politicians from Nemtsov funeral". Reuters. 2015-03-03. Retrieved 2015-03-04.
- ↑ "Russia releases 89-name EU travel blacklist". Yahoo News. Agence France-Presse. 2015-05-29. Retrieved 2015-05-30.
- ↑ "Eight Swedes on Russia's blacklist". Radio Sweden. 2015-05-29. Retrieved 2015-05-30.
- ↑ "Russische "Visasperrliste" vom RAM am 27.5. an EU-Delegation Moskau übergeben" [Russian visa bans] (PDF) (in German). Yle. 26 May 2015.
- ↑ "European Union anger at Russian travel blacklist". BBC News. 30 May 2015.
- ↑ Khomami, Nadia (31 May 2015). "Russian entry ban on politicians shows EU sanctions are working, says Rifkind". United Kingdom: The Guardian. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ↑ Granlund, John; Eriksson, Niklas (29 May 2015). "Gunnar Hökmark: En rädd regim gör så här" (in Swedish). Aftonbladet. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ↑ Fox, Emily (31 May 2015). "EU reacts with FURY over Russia's 'blacklist' as MP claims Putin sanctions ARE working". www
.express . United Kingdom: Express. Retrieved 1 June 2015. External link in.co .uk |website=(help)
Further reading
- Bond, Ian, Christian Odendahl and J. Rankin. "Frozen: The politics and economics of sanctions against Russia." Sentre for European Reform (2015). online
- Gilligan, Emma. "Smart Sanctions against Russia: Human Rights, Magnitsky and the Ukrainian Crisis." Demokratizatsiya: The Journal of Post-Soviet Democratization 24.2 (2016): 257-277. online
- Wang, Wan. "Impact of western sanctions on Russia in the Ukraine crisis." Journal of Politics & Law 8 (2015): 1+ online. a pro-Russian analysis by a Chinese academic.
External links
- Ukrainian crisis: sanctions and reactions, Information Telegraph Agency of Russia (owned by the Government of Russia)
- Ukraine and Russia Sanctions, United States Department of State
- EU sanctions against Russia over Ukraine crisis, European Union
- Overview of the European Council policy on sanctions, European Council (European Union)