Interest rate swap
An interest rate swap (IRS) is a liquid financial derivative instrument in which two parties agree to exchange interest rate cash flows, based on a specified notional amount from a fixed rate to a floating rate (or vice versa) or from one floating rate to another.[1] Interest rate swaps can be used for both hedging and speculating.
Structure
In an interest rate swap, each counterparty agrees to pay either a fixed or floating rate denominated in a particular currency to the other counterparty. The fixed or floating rate is multiplied by a notional principal amount (say, $1 million) and an accrual factor given by the appropriate day count convention. When both legs are in the same currency, this notional amount is typically not exchanged between counterparties, but is used only for calculating the size of cashflows to be exchanged. When the legs are in different currencies, the respective notional amounts are typically exchanged at the start and the end of the swap, which is called cross currency interest rate swap.
The most common interest rate swap involves counterparty A paying a fixed rate (the swap rate) to counterparty B while receiving a floating rate indexed to a reference rate like LIBOR, EURIBOR, or MIBOR. By market convention, the counterparty paying the fixed rate is the "payer" (while receiving the floating rate), and the counterparty receiving the fixed rate is the "receiver" (while paying the floating rate).
A pays fixed rate to B (A receives floating rate)
B pays floating rate to A (B receives fixed rate)
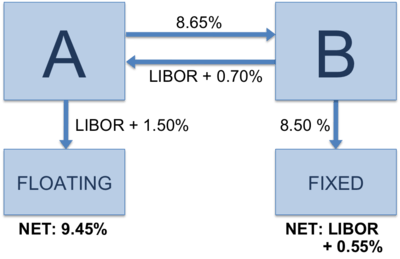
Currently, A borrows from Market @ LIBOR +1.5%. B borrows from Market @ 8.5%.
Consider the following swap in which Party A agrees to pay Party B periodic fixed interest rate payments of 8.65% in exchange for periodic variable interest rate payments of LIBOR + 70 bps (0.70%) in the same currency. Note that there is no exchange of the principal amounts and that the interest rates are on a "notional" (i.e., imaginary) principal amount. Also note that interest payments are settled in net; that is, Party A pays (LIBOR + 1.50%)+8.65% - (LIBOR+0.70%) = 9.45% net. The fixed rate (8.65% in this example) is referred to as the swap rate.[2]
At the point of initiation of the swap, the swap is priced so that it has a net present value of zero. If one party wants to pay 50 bps above the par swap rate, the other party has to pay approximately 50bps over LIBOR to compensate for this.
Types
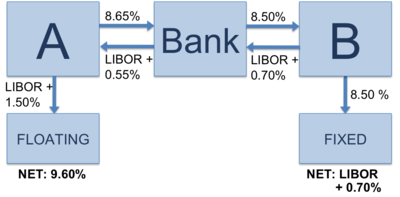
As OTC instruments, interest rate swaps can come in a number of varieties and can be structured to meet the specific needs of the counterparties. For example, the legs of the swap could be in same or different currencies; the notional of the swap could be amortized over time; reset dates (or fixing dates) of the floating rate could be irregular.
The interbank market, however, only has a few standardized types which are listed below. Each currency has its own standard market conventions regarding the frequency of payments, the day count conventions and the end-of-month rule.[3]
Fixed-for-floating rate swap, different currencies
For example, if a company has a $10 million fixed rate loan at 5.3% paid monthly and a floating rate investment of JPY 1.2 billion that returns JPY 1M Libor +50bps every month, and wants to lock in the profit in USD as they expect the JPY 1M Libor to go down or USDJPY to go up (JPY depreciate against USD), then they may enter into a fixed-for-floating swap in different currencies where the company pays floating JPY 1M Libor+50bps and receives 5.6% fixed rate, locking in 30bps profit against the interest rate and the FX exposure.
Floating-for-floating rate swap, same currency
Party P pays/receives floating interest in currency A indexed to X to receive/pay floating rate in currency A indexed to Y on a notional N for a tenure of T years. For example, you pay JPY 1M LIBOR monthly to receive JPY 1M TIBOR monthly on a notional JPY 1 billion for three years or you pay EUR 3M EURIBOR quarterly to receive EUR 6M EURIBOR semi-annually. The second example, where the indexes are the same type but with different tenors, are the most liquid and most commonly traded same currency floating-for-floating swaps..
Floating-for-floating rate swaps are used to hedge against or speculate on the spread between the two indexes. For example, if a company has a floating rate loan at JPY 1M LIBOR and the company has an investment that returns JPY 1M TIBOR + 30bps and currently the JPY 1M TIBOR = JPY 1M LIBOR + 10bps. At the moment, this company has a net profit of 40bps. If the company thinks JPY 1M TIBOR is going to come down (relative to the LIBOR) or JPY 1M LIBOR is going to increase in the future (relative to the TIBOR) and wants to insulate from this risk, they can enter into a float-float swap in same currency where they pay, say, JPY TIBOR + 30bps and receive JPY LIBOR + 35bps. With this, they have effectively locked in a 35bps profit instead of running with a current 40bps gain and index risk. The 5bps difference (w.r.t. the current rate difference) comes from the swap cost which includes the market expectations of the future rate difference between these two indices and the bid-offer spread, which is the swap commission for the dealer.
Floating-for-floating rate swaps are also seen where both sides reference the same index, but on different payment dates, or use different business day conventions. This can be vital for asset-liability management. An example would be swapping 3M LIBOR being paid with prior non-business day convention, quarterly on JAJO (i.e., Jan, Apr, Jul, Oct) 30, into FMAN (i.e., Feb, May, Aug, Nov) 28 modified following.
Fixed-for-fixed rate swap, different currencies
Party P pays/receives fixed interest in currency A to receive/pay fixed rate in currency B for a term of T years. For example, you pay JPY 1.6% on a JPY notional of 1.2 billion and receive USD 5.36% on the USD equivalent notional of $10 million at an initial exchange rate of USDJPY 120.
Floating-for-floating rate swap, different currencies
Party P pays/receives floating interest in currency A indexed to X to receive/pay floating rate in currency B indexed to Y on a notional N at an initial exchange rate of FX for a tenure of T years. The notional is usually exchanged at the start and at the end of the swap. This is the most liquid type of swap with different currencies. For example, you pay floating USD 3M LIBOR on the USD notional 10 million quarterly to receive JPY 3M TIBOR quarterly on a JPY notional 1.2 billion (at an initial exchange rate of USDJPY 120) for 4 years; at the start you receive the notional in USD and pay the notional in JPY and at the end you pay back the same USD notional (10 million) and receive back the same JPY notional (1.2 billion).
For example, consider a U.S. company operating in Japan that needs JPY 10 billion to fund its Japanese growth. The easiest way to do this is to issue debt in Japan, but this may be expensive if the company is new in the Japanese market and lacking a good reputation among the Japanese investors. Additionally, the company may not have the appropriate debt issuance program in Japan or may lack a sophisticated treasury operation in Japan. The company could issue USD debt and convert to JPY on the FX market. This option solves the first problem, but it introduces two new risks:
- FX risk: If this USDJPY spot goes up at the maturity of the debt, then when the company converts the JPY to USD to pay back its matured debt, it receives less USD and suffers a loss.
- USD–JPY interest rate risk: If JPY rates come down, the return on the investment in Japan may also go down, introducing interest rate risk.
The FX risk can be hedged with long-dated FX forward contracts, but this introduces yet another risk where the implied rate from the FX spot and the FX forward is a fixed but the JPY investment returns a floating rate. Although there are several alternatives to hedge both exposures effectively without introducing new risks, the easiest and most cost-effective alternative is to use a floating-for-floating swap in different currencies.
Other variations
A number of other far less common variations are possible. Mostly tweaks are made to ensure that a bond is hedged "perfectly", so that all the interest payments received are exactly offset, which can lead to swaps where the principal is paid on one or more legs, rather than just interest (for example to hedge a coupon strip), or where the balance of the swap is automatically adjusted to match that of a prepaying bond like residential mortgage-backed securities.
Uses
Interest rate swaps are used to hedge against or speculate on changes in interest rates.
Speculation
Interest rate swaps are also used speculatively by hedge funds or other investors who expect a change in interest rates or the relationships between them. Traditionally, fixed income investors who expected rates to fall would purchase cash bonds, whose value increased as rates fell. Today, investors with a similar view could enter a floating-for-fixed interest rate swap; as rates fall, investors would pay a lower floating rate in exchange for the same fixed rate.
Interest rate swaps are also popular for the arbitrage opportunities they provide. Varying levels of creditworthiness means that there is often a positive quality spread differential that allows both parties to benefit from an interest rate swap.
The interest rate swap market in USD is closely linked to the Eurodollar futures market which trades among others at the Chicago Mercantile Exchange.
British local authorities
In June 1988 the Audit Commission was tipped off by someone working on the swaps desk of Goldman Sachs that the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham had a massive exposure to interest rate swaps. When the commission contacted the council, the chief executive told them not to worry as "everybody knows that interest rates are going to fall"; the treasurer thought the interest rate swaps were a "nice little earner". The Commission's Controller, Howard Davies, realised that the council had put all of its positions on interest rates going down and ordered an investigation.
By January 1989 the Commission obtained legal opinions from two Queen's Counsel. Although they did not agree, the commission preferred the opinion which made it ultra vires for councils to engage in interest rate swaps. Moreover, interest rates had increased from 8% to 15%. The auditor and the commission then went to court and had the contracts declared illegal (appeals all the way up to the House of Lords failed in Hazell v Hammersmith and Fulham LBC); the five banks involved lost millions of pounds. Many other local authorities had been engaging in interest rate swaps in the 1980s.[4] This resulted in several cases in which the banks generally lost their claims for compound interest on debts to councils, finalised in Westdeutsche Landesbank Girozentrale v Islington London Borough Council.[5]
Valuation and pricing
The valuation of vanilla swaps was often done using the so-called textbook formulas using a unique curve in each currency. Some early literature described some incoherence introduced by that approach and multiple banks were using different techniques to reduce them. It became even more apparent with the 2007–2012 global financial crisis that the approach was not appropriate. The now-standard pricing framework is the multi-curves framework.
The present value of a plain vanilla (i.e., fixed rate for floating rate) swap can be computed by determining the present value (PV) of the fixed leg and the floating leg.
The value of the fixed leg is given by the present value of the fixed coupon payments known at the start of the swap, i.e.
where C is the swap rate, n is the number of fixed payments, N is the notional amount, is the accrual factor according to the day count convention for the fixed rate period and is the discount factor for the payment time .
The value of the floating leg is given by the present value of the floating coupon payments determined at the agreed dates of each payment. However, at the start of the swap, only the actual payment rates of the fixed leg are known in the future, whereas the forward rates are unknown. The forward rate for each floating payment date is calculated using the forward curves. The forward rate for the period with accrual factor is given by
where I is the market index, such as USD LIBOR, and is the discount factor associated to the relevant forward curve. The value of the floating leg is given by the following:
where m is the number of floating payments, is the accrual factor according to the floating leg day count convention.
In the event that
,
this formula simplifies to
on the reset dates, since the summation in telescopes to the first and last terms only. On reset dates, the value of an off-the-run swap (old issue) is given by
where is the value of hypothetical bond that mimics the fixed leg of the swap with a unit principal payable at expiry. On non-reset dates the swap value becomes
where is the nearest reset date. The fixed rate offered in the swap is the rate which values the fixed rates payments at the same PV as the variable rate payments using today's forward rates, i.e.:
Therefore, at the time the contract is entered into, there is no advantage to either party, i.e.,
Thus, the swap requires no upfront payment from either party.
During the life of the swap the same valuation technique is used, but since, over time, both the discounting factors and the forward rates change, the PV of the swap will deviate from its initial value. Therefore, the swap will be an asset to one party and a liability to the other. The way these changes in value are reported is the subject of IAS 39 for jurisdictions following IFRS, and FAS 133 for U.S. GAAP. Swaps are marked to market by debt security traders to visualize their inventory at a certain time.
Risks
Interest rate swaps expose users to many different types of financial risk[7]
Predominantly they expose the user to market risks. The value of an interest rate swap will change as market interest rates rise and fall. In market terminology this is often referred to as delta risk. Other specific types of market risk that interest rate swaps have exposure to are basis risks (where various IBOR tenor indexes can deviate from one another) and reset risks (where the publication of specific tenor IBOR indexes are subject to daily fluctuation). Interest rate swaps also exhibit gamma risk whereby their delta risk increases or decreases as market interest rates fluctuate.
Uncollateralised interest rate swaps (that are those executed bilaterally without a credit support annex (CSA) in place) expose the trading counterparties to funding risks and credit risks. Funding risks because the value of the swap might deviate to become so negative that it is unaffordable and cannot be funded. Credit risks because the respective counterparty, for whom the value of the swap is positive, will be concerned about the opposing counterparty defaulting on its obligations.
Collateralised interest rate swaps expose the users to collateral risks. Depending upon the terms of the CSA, the type of posted collateral that is permitted might become more or less expensive due to other extraneous market movements. Credit and funding risks still exist for collateralised trades but to a much lesser extent.
Due to regulations set out in the Basel III Regulatory Frameworks trading interest rate derivatives commands a capital usage. Dependent upon their specific nature interest rate swaps might command more capital usage and this can deviate with market movements. Thus capital risks are another concern for users.
Reputation risks also exist. The mis-selling of swaps, over-exposure of municipalities to derivative contracts, and IBOR manipulation are examples of high-profile cases where trading interest rate swaps has led to a loss of reputation and fines by regulators.
Hedging interest rate swaps can be complicated and relies on numerical processes of well designed risk models to suggest reliable benchmark trades that mitigate all market risks. The other, aforementioned risks must be hedged using other systematic processes.[7]
Market-Making
The market-making of IRSs is an involved process involving multiple tasks; curve construction with reference to interbank markets, individual derivative contract pricing, risk management of credit, cash and capital. The cross disciplines required include quantitative analysis and mathematical expertise, disciplined and organized approach towards profits and losses, and coherent psychological and subjective assessment of financial market information and price-taker analysis. The time sensitive nature of markets also creates a pressurized environment. Many tools and techniques have been designed to improve efficiency of market-making in a drive to efficiency and consistency.[7]
Market size
On its December 2014 statistics release, the Bank for International Settlements reported that interest rate swaps were the largest component of the global OTC derivative market representing 60% of it, with the notional amount outstanding in OTC interest rate swaps of $381 trillion, and the gross market value of $14 trillion.[8]
Interest rate swaps can be traded as an index through the FTSE MTIRS Index.
See also
- Swap rate
- Interest rate cap and floor
- Equity swap
- Total return swap
- Inflation derivative
- Eurodollar
- Constant maturity swap
- FTSE MTIRS Index
References
- ↑ "Interest Rate Swap". Glossary. ISDA.
- ↑ "Interest Rate Swap" by Fiona Maclachlan, The Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- ↑ "Interest Rate Instruments and Market Conventions Guide" Quantitative Research, OpenGamma, 2012.
- ↑ Duncan Campbell-Smith, "Follow the Money: The Audit Commission, Public Money, and the Management of Public Services 1983-2008", Allen Lane, 2008, chapter 6 passim.
- ↑ [1996] UKHL 12, [1996] AC 669
- ↑ "Understanding interest rate swap math & pricing" (PDF). California Debt and Investment Advisory Commission. January 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-27.
- 1 2 3 The Pricing and Hedging of Interest Rate Derivatives: A Practical Guide to Swaps, J H M Darbyshire, 2016, ISBN 978-0995455511
- ↑ "OTC derivatives statistics at end-December 2014" (PDF). Bank for International Settlements.
- Pricing and Hedging Swaps, Miron P. & Swannell P., Euromoney books 1991
Most recent literature on the evolution of the swaps market to incorporate credit and collateral risks.
- The Pricing and Trading of Interest Rate Derivatives: A Practical Guide to Swaps, J H M Darbyshire, 2016
Early literature on the incoherence of the one curve pricing approach.
- Interest rate parity, money market basis swaps and cross-currency basis swaps, Tuckman B. and Porfirio P., Fixed income liquid markets research, Lehman Brothers, 2003.
- Cross currency swap valuation, Boenkost W. and Schmidt W., Working Paper 2, HfB - Business School of Finance & Management, 2004. SSRN preprint.
- The Irony in the Derivatives Discounting, Henrard M., Wilmott Magazine, pp. 92–98, July 2007. SSRN preprint.
Multi-curves framework:
- A multi-quality model of interest rates, Kijima M., Tanaka K., and Wong T., Quantitative Finance, pages 133-145, 2009.
- Two Curves, One Price: Pricing & Hedging Interest Rate Derivatives Decoupling Forwarding and Discounting Yield Curves, Bianchetti M., Risk Magazine, August 2010. SSRN preprint.
- The Irony in the Derivatives Discounting Part II: The Crisis, Henrard M., Wilmott Journal, Vol. 2, pp. 301–316, 2010. SSRN preprint.
External links
- Understanding Derivatives: Markets and Infrastructure Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, Financial Markets Group
- Bank for International Settlements - Semiannual OTC derivatives statistics
- Glossary - Interest rate swap glossary
- Investopedia - Spreadlock - An interest rate swap future (not an option)
- Basic Fixed Income Derivative Hedging - Article on Financial-edu.com.
- Hussman Funds - Freight Trains and Steep Curves
- Interest Rate Swap Calculator
- Historical LIBOR Swaps data
- "All about money rates in the world: Real estate interest rates", WorldwideInterestRates.com