Classification of indigenous peoples of the Americas
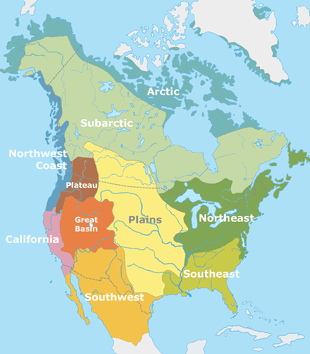
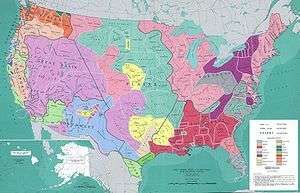
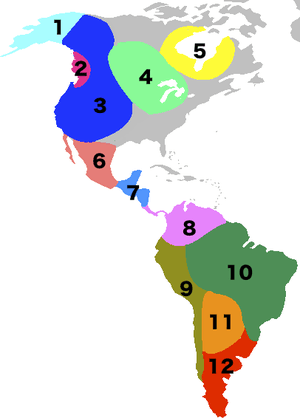
Classification of indigenous peoples of the Americas is based upon cultural regions, geography, and linguistics. Anthropologists have named various cultural regions, with fluid boundaries, that are generally agreed upon with some variation. These cultural regions are broadly based upon the locations of indigenous peoples of the Americas from early European and African contact beginning in the late 15th century. When indigenous peoples have been forcibly removed by nation-states, they retain their original geographic classification. Some groups span multiple cultural regions.
Canada, Greenland, United States, and northern Mexico
In the United States and Canada, ethnographers commonly classify indigenous peoples into ten geographical regions with shared cultural traits, called cultural areas.[1] Greenland is part of the Arctic region. Some scholars combine the Plateau and Great Basin regions into the Intermontane West, some separate Prairie peoples from Great Plains peoples, while some separate Great Lakes tribes from the Northeastern Woodlands.
Arctic
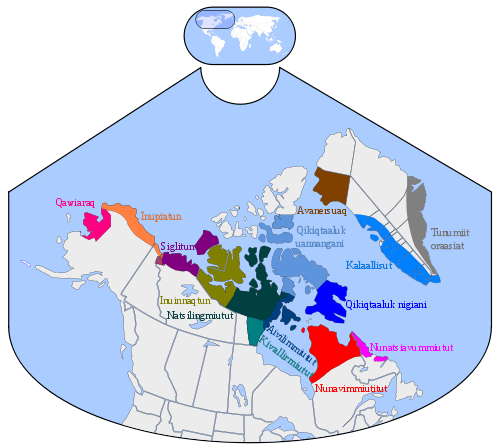
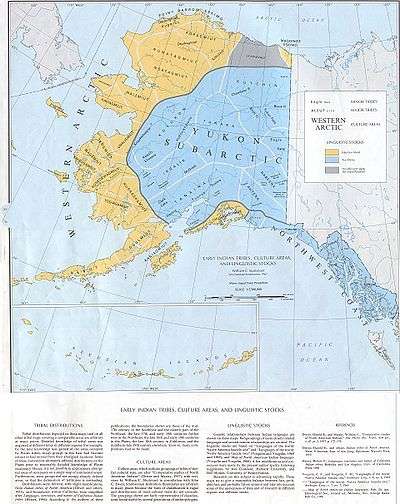
- Paleo-Eskimo, prehistoric cultures, Russia, Alaska, Canada, Greenland, 2500 BCE–1500 CE
- Arctic small tool tradition, prehistoric culture, 2500 BCE, Bering Strait
- Pre-Dorset, eastern Arctic, 2500–500 BCE
- Saqqaq culture, Greenland, 2500–800 BCE)
- Independence I, northeastern Canada and Greenland, 2400–1800 BCE
- Independence II culture, northeastern Canada and Greenland, 800–1 BCE)
- Groswater, Labrador and Nunavik, Canada
- Dorset culture, 500 BCE–1500 CE, Alaska, Canada
- Aleut (Unangan), Aleutian Islands of Alaska, and Kamchatka Krai, Russia
- Inuit, Russia, Alaska, Canada, Greenland
- Thule, proto-Inuit, Alaska, Canada, Greenland, 900–1500 CE
- Birnirk culture, prehistoric Inuit culture, Alaska, 500 CE–900 CE
- Greenlandic Inuit people, Greenland
- Kalaallit, west Greenland
- Avanersuarmiut (Inughuit), north Greenland
- Tunumiit, east Greenland
- Inuvialuit, western Canadian Arctic
- Iñupiat, north and northwest Alaska
- Thule, proto-Inuit, Alaska, Canada, Greenland, 900–1500 CE
- Yupik peoples (Yup'ik), Alaska and Russia
- Alutiiq people (Sugpiaq, Pacific Yupik), Alaska Peninsula, coastal and island areas of south central Alaska
- Central Alaskan Yup'ik people, west central Alaska
- Cup'ik, Hooper Bay and Chevak, Alaska
- Nunivak Cup'ig people (Cup'ig), Nunivak Island, Alaska
- Siberian Yupik people, Russian Far East and St. Lawrence Island, Alaska
Subarctic

- Ahtna (Ahtena, Nabesna)
- Anishinaabe - see also Northeastern Woodlands
- Atikamekw, Quebec
- Chipewyan, Alaskan interior, Western Canada
- Cree, Central and Eastern Canada, North Dakota
- Dakelh (Carrier), British Columbia
- Babine, British Columbia
- Wet'suwet'en, British Columbia
- Deg Hit’an (Deg Xinag, Degexit’an, Kaiyuhkhotana), Alaska
- Dena’ina (Dialects: Outer Inlet, Upper Inlet, Iliama, Inland Dena'ina, Kachemak Bay, Kenai Dena'ina, Susitna River), Alaska
- Dane-zaa (Beaver, Dunneza), Alberta, British Columbia
- Gwich'in (Kutchin, Loucheaux), Alaska, Yukon
- Hän, Alaska, Yukon
- Holikachuk, Alaska
- Innu (Montagnais), Labrador, Quebec
- Kaska (Nahane)
- Kolchan (Upper Kuskokwim)
- Koyukon, Alaska
- Naskapi
- Sekani
- Sahtú (North Slavey, Bearlake, Hare, Mountain), Northwest Territories
- Slavey (Dialects: Hay River, Simpson Providence, Liard, Fort Nelson)
- Tagish
- Tahltan
- Lower Tanana
- Middle Tanana
- Upper Tanana
- Tanacross
- Tasttine (Beaver)
- Tli Cho
- Inland Tlingit
- Tsetsaut (extinct)
- Tsilhqot'in (Chilcotin)
- Northern Tutchone
- Southern Tutchone
- Yellowknives
Pacific Northwest Coast
- Alsea
- Applegate
- Heiltsuk
- Nuxalk
- Tsleil-Waututh First Nation
- Chehalis (Upper and Lower), Washington
- Chehalis (BC), Fraser Valley
- Chemakum Washington (extinct)
- Chetco – see Tolowa
- Chinook Dialects: (Lower Chinook, Upper Chinook, Clackamas, Wasco)
- Clallam – see Klallam
- Clatsop
- Comox Vancouver Island/BC Georgia Strait
- Coos Hanis Oregon
- Lower Coquille (Miluk) Oregon
- Upper Coquille
- Cowichan Southern Vancouver Island/Georgia Strait
- Lower Cowlitz Washington
- Duwamish Washington
- Eyak Alaska
- Galice
- Gitxsan, British Columbia
- Haida (Dialects: Kaigani, Skidegate, Masset) BC & Alaska
- Haisla BC North/Central Coast
- Heiltsuk BC Central Coast
- Hoh Washington
- Kalapuya (Calapooia, Calapuya, Tfalatim, Yamel, Yaquina, Yoncalla), Oregon
- Central Kalapuya, Oregon
- Ahantchuyuk
- Mary's River
- Lakmiut
- Mohawk, Oregon
- Santiam
- North Kalapuya, Oregon
- South Kalapuya (Yonkalla, Yoncalla), Oregon
- Central Kalapuya, Oregon
- Klallam (Clallam, Dialects: Klallam (Lower Elwha), S'Klallam (Jamestown), S'Klallam (Port Gamble))
- Klickitat
- Kwalhioqua
- Kwakwaka'wakw (Kwakiutl)
- Koskimo
- 'Namgis
- Laich-kwil-tach (Euclataws or Yuculta)
- Kwalhioqua
- Lummi, Washington
- Makah, Washington
- Muckleshoot, Washington
- Musqueam, BC Lower Mainland (Vancouver)
- Nisga'a, British Columbia
- Nisqually - Washington
- Nooksack Washington
- Nisqually Washington
- Nuu-chah-nulth West Coast of Vancouver Island
- Nuxalk (Bella Coola) – BC Central Coast
- Oowekeno – see Wuikinuxv
- Pentlatch Vancouver Island/Georgia Strait (extinct)
- Puyallup Washington
- Quileute Washington
- Quinault Washington
- Rivers Inlet – see Wuikinuxv
- Rogue River or Upper Illinois (Chasta Costa), Oregon, California
- Saanich Southern Vancouver Island/Georgia Strait
- Samish, Washington
- Sauk-Suiattle, Washington
- Sechelt, BC Sunshine Coast/Georgia Strait (Shishalh)
- Shoalwater Bay Tribe, Washington
- Siletz, Oregon
- Siuslaw, Oregon
- Skagit
- Skokomish, Washington
- Sliammon, BC Sunshine Coast/Georgia Strait (Mainland Comox)
- Snohomish
- Snoqualmie
- Snuneymuxw (Nanaimo), Vancouver Island
- Songhees (Songish) Southern Vancouver Island/Strait of Juan de Fuca
- Sooke Southern Vancouver Island/Strait of Juan de Fuca
- Squamish , British Columbia
- Squaxin Island Tribe Washington
- Spokane Washington
- Stillaguamish Washington
- Sto:lo, BC Lower Mainland/Fraser Valley
- Squamish – see Skwxwu7mesh
- Suquamish Washington
- Swinomish Washington
- Tait
- Takelma Oregon
- Talio
- Tillamook (Nehalem) Oregon
- Tlatlasikoala
- Tlingit, Alaska
- Tolowa-Tututni, Northern California
- Tsimshian
- Tsleil-waututh (Burrard), British Columbia
- Tulalip, Washington
- Twana, Washington
- Tzouk-e (Sooke), Vancouver Island
- Lower Umpqua, Oregon
- Upper Umpqua, Oregon
- Upper Skagit Washington
- Wuikinuxv (Owekeeno), BC Central Coast
Northwest Plateau
add
Plateau tribes include the following:
Chinook peoples
Interior Salish
- Chelan
- Coeur d'Alene Tribe, ID, MT, WA
- Entiat, WA
- Flathead (Selisch or Salish), ID and MT
- Bitterroot Salish
- Kalispel (Pend d'Oreilles), MT and WA
- Lower Kalispel, WA
- Upper Kalispel, MT
- Methow, WA
- Nespelem, WA
- Nlaka'pamux (Thompson people), BC
- Nicola people (Thompson-Okanagan confederacy)
- Okanagan, BC and WA
- Secwepemc, BC (Shuswap people)
- Sinixt (Lakes), BC, ID, and WA
- Sinkiuse-Columbia, WA (extinct)
- Spokane people, WA
- St'at'imc, BC (Upper Lillooet)
- Lil'wat, BC (Lower Lillooet)
- In-SHUCK-ch, BC (Lower Lillooet)
- Wenatchi (Wenatchee)
- Sanpoil, WA
- Sinkayuse
Sahaptin people
- Upper Cowlitz or Taidnapam
- Kittitas (Upper Yakima)
- Klickitat Tribe, WA
- Nez Perce, ID
- Pshwanwapam (Pswanwapam)
- Skinpah (Skin)
- Tenino (Warmsprings)
- Tygh (Upper Deschutes), OR
- Umatilla, OR
- Walla Walla, WA
- Wanapum, WA
- Wauyukma
- Wyam (Lower Deschutes)
- Yakama, WA
Other or both
- Cayuse, OR
- Celilo (Wayampam)
- Cowlitz, WA
- Fort Klamath, OR
- Kalapuya, northwest OR
- Atfalati (Tualatin, northwest OR
- Mohawk River, northwest OR
- Santiam, northwest OR
- Yaquina, northwest OR
- Kutenai (Kootenai, Ktunaxa), BC, ID, and MT
- Lower Snake people: Chamnapam, Wauyukma, Naxiyampam
- Modoc, CA and OR
- Molala (Molale), OR
- Nicola Athapaskans (extinct), BC
- Palus (Palouse), ID, OR, and WA
- Upper Nisqually (Mishalpan)
Great Plains
Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains are often separated into Northern and Southern Plains tribes.
- Anishinaabe (Anishinape, Anicinape, Neshnabé, Nishnaabe) (see also Subarctic, Northeastern Woodlands)
- Saulteaux (Nakawē), Manitoba, Minnesota and Ontario; later Alberta, British Columbia, Montana, Saskatchewan
- Odawa people (Ottawa), Ontario,[2] Michigan, later Oklahoma
- Potawatomi, Michigan,[2] Ontario, Indiana, Wisconsin, later Oklahoma
- Apache (see also Southwest)
- Lipan Apache, New Mexico, Texas
- Plains Apache (Kiowa Apache), Oklahoma
- Querecho Apache, Texas
- Arapaho (Arapahoe), formerly Colorado, currently Oklahoma and Wyoming
- Arikara (Arikaree, Arikari, Ree), North Dakota
- Atsina (Gros Ventre), Montana
- Blackfoot
- Kainai Nation (Káínaa, Blood), Alberta
- Northern Peigan (Aapátohsipikáni), Alberta
- Blackfeet, Southern Piegan (Aamsskáápipikani), Montana
- Siksika (Siksikáwa), Alberta
- Cheyenne, Montana, Oklahoma
- Suhtai, Montana, Oklahoma
- Comanche, Oklahoma, Texas
- Plains Cree, Montana
- Crow (Absaroka, Apsáalooke), Montana
- Escanjaques, Oklahoma
- Hidatsa, North Dakota
- Iowa (Ioway), Kansas, Nebraska, Oklahoma
- Kaw (Kansa, Kanza), Oklahoma
- Kiowa, Oklahoma
- Mandan, North Dakota
- Métis people (Canada), North Dakota, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta
- Missouri (Missouria), Oklahoma
- Omaha, Nebraska
- Osage, Oklahoma, formerly Arkansas, Missouri
- Otoe (Oto), Oklahoma
- Pawnee, Oklahoma
- Chaui, Oklahoma[3]
- Kitkehakhi, Oklahoma[3]
- Pitahawirata, Oklahoma[3]
- Skidi, Oklahoma[3]
- Ponca, Nebraska, Oklahoma
- Quapaw, formerly Arkansas, Oklahoma
- Sioux
- Dakota, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, South Dakota, Manitoba, Saskatchewan
- Lakota (Teton), Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Saskatchewan
- Nakoda (Stoney), Alberta
- Nakota, Assiniboine (Assiniboin), Montana, Saskatchewan
- Teyas, Texas
- Tonkawa, Oklahoma
- Tsuu T’ina, (Sarcee, Sarsi, Tsuut’ina), Alberta
- Wichita and Affiliated Tribes, Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas
Eastern Woodlands
Northeastern Woodlands
- Adena culture (1000–200 BCE) formerly Ohio, Indiana, West Virginia, Kentucky, New York, Pennsylvania and Maryland
- Abenaki (Tarrantine), Maine, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, Quebec, and Vermont
- Eastern Abenaki, Quebec, Maine, and New Hampshire[2]
- Western Abenaki: Quebec, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont[2]
- Anishinaabeg (Anishinape, Anicinape, Neshnabé, Nishnaabe) (see also Subarctic, Plains)
- Algonquin,[4] Quebec, Ontario
- Nipissing,[4] Ontario[2]
- Ojibwe (Chippewa, Ojibwa), Ontario, Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin[2]
- Mississaugas, Ontario
- Saulteaux (Nakawē), Ontario
- Odawa people (Ottawa), Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, Ontario;[2] later Oklahoma
- Potawatomi, Illinois, Indiana, Michigan,[2] Ontario, Wisconsin; later Kansas and Oklahoma
- Assateague, Maryland[5]
- Attawandaron (Neutral), Ontario[2]
- Beothuk, formerly Newfoundland[2]
- Chowanoke, North Carolina
- Choptank people, Maryland[5]
- Conoy, Virginia,[5] Maryland
- Fort Ancient culture (1000-1750 CE), formerly Ohio, Kentucky, Indiana and West Virginia
- Erie, Pennsylvania, New York[2]
- Etchemin, Maine
- Ho-Chunk (Winnebago), southern Wisconsin, northern Illinois,[2] later Iowa and Nebraska
- Honniasont, Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia
- Hopewell tradition, formerly Ohio, Illinois, and Kentucky, and Black River region, 200 BCE—500 CE
- Housatonic, Massachusetts, New York[6]
- Illinois Confederacy (Illiniwek), Illinois, Iowa, and Missouri[2]
- Meskwaki (Fox), Michigan,[2] now Iowa, Oklahoma
- Mitchigamea, formerly Illinois
- Iroquois Confederacy[4] (Haudenosaunee), Ontario, Quebec, and New York[2]
- Kickapoo, Michigan,[2] Illinois, Missouri, now Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, Mexico
- Laurentian (St. Lawrence Iroquoians), formerly New York, Ontario, and Quebec, 14th century—1580 CE
- Lenni Lenape (Delaware), Pennsylvania, Delaware, New Jersey, now Ontario and Oklahoma
- Munsee-speaking subgroups, formerly Long Island and southeastern New York[7]
- Canarsie (Canarsee), formerly Long Island New York[8]
- Esopus, formerly New York,[7] later Ontario and Wisconsin
- Hackensack, formerly New York[7]
- Haverstraw (Rumachenanck), New York[9]
- Kitchawank (Kichtawanks, Kichtawank), New York[9]
- Minisink, formerly New York[7]
- Navasink,[9] to the east along the north shore of New Jersey
- Raritan, formerly Westchester County, New York[9]
- Sinsink (Sintsink), Westchester County, New York[9]
- Siwanoy, Massachusetts[9]
- Tappan, formerly New York[10]
- Waoranecks[11]
- Wappinger (Wecquaesgeek, Nochpeem), formerly New York[6][12]
- Warranawankongs[11]
- Wiechquaeskeck, formerly New York[7]
- Unami-speaking subgroups
- Acquackanonk, Passaic River in northern New Jersey
- Okehocking, southeast Pennsylvania[11]
- Unalachtigo, Delaware, New Jersey
- Munsee-speaking subgroups, formerly Long Island and southeastern New York[7]
- Manahoac, Virginia[13]
- Mascouten, formerly Michigan[2]
- Massachusett, Massachusetts
- Ponkapoag, Massachusetts
- Menominee, Wisconsin[2]
- Mahican (Stockbridge Mahican[4]) Connecticut, Massachusetts, New York, and Vermont[2][6]
- Massachusett, Massachusetts[4][14]
- Meherrin, Virginia,[15] North Carolina
- Mi'kmaq (Micmac), New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Quebec,[2] and Maine
- Mohegan,[4] Connecticut
- Monacan, Virginia[16]
- Montaukett (Montauk),[4] New York
- Monyton (Monetons, Monekot, Moheton) (Siouan), West Virginia and Virginia
- Nansemond, Virginia
- Nanticoke, Delaware and Maryland[2]
- Narragansett, Rhode Island[4]
- Niantic, coastal Connecticut[4][14]
- Nipmuc (Nipmuck), Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island[14]
- Nottaway, Virginia,[15]
- Occaneechi (Occaneechee), Virginia[15][17][18]
- Passamaquoddy, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Quebec, and Maine[2]
- Patuxent, Maryland[5]
- Paugussett, Connecticut[4]
- Penobscot, Maine
- Pequot, Connecticut[4]
- Petun (Tionontate), Ontario[2]
- Piscataway, Maryland[5]
- Pocumtuc, western Massachusetts[14]
- Podunk, New York,[14] eastern Hartford County, Connecticut
- Powhatan Confederacy, Virginia[5]
- Appomattoc, Virginia
- Arrohateck, Virginia
- Chesapeake, Virginia
- Chesepian, Virginia
- Chickahominy, Virginia[15]
- Kiskiack, Virginia
- Mattaponi, Virginia
- Nansemond, Virginia[15]
- Paspahegh, Virginia
- Powhatan, Virginia
- Pamunkey, Virginia[15]
- Quinnipiac, Connecticut,[4] eastern New York, northern New Jersey
- Rappahannock, Virginia
- Sauk (Sac), Michigan,[2] now Iowa, Oklahoma
- Schaghticoke, western Connecticut[4]
- Shawnee, formerly Ohio,[2] Virginia, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, currently Oklahoma
- Shinnecock,[4] Long Island, New York[14]
- Stegarake, Virginia[13]
- Stuckanox (Stukanox), Virginia[15]
- Susquehannock, Maryland, Pennsylvania[2]
- Tauxenent (Doeg), Virginia[19]
- Tunxis (Massaco), Connecticut[4]
- Tuscarora, formerly North Carolina, Virginia, currently New York
- Tutelo (Nahyssan), Virginia[15][17]
- Unquachog (Poospatuck), Long Island, New York[14]
- Wabanaki, Maine, New Brunswick, Novia Scotia, Quebec[4]
- Wampanoag, Massachusetts[4]
- Wangunk, Mattabeset, Connecticut[4]
- Wenro, New York[2][4]
- Wicocomico, Maryland, Virginia
- Wolastoqiyik, Maliseet, Maine, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Quebec[2]
- Wyachtonok, Connecticut, New York[6]
- Wyandot (Huron), Ontario south of Georgian Bay, now Oklahoma, Kansas, Michigan, and Wendake, Quebec
Southeastern Woodlands
- Acolapissa (Colapissa), Louisiana and Mississippi[20]
- Ais, eastern coastal Florida[21]
- Alafay (Alafia, Pojoy, Pohoy, Costas Alafeyes, Alafaya Costas), Florida[22]
- Amacano, Florida west coast[23]
- Apalachee, northwestern Florida[24]
- Atakapa (Attacapa), Louisiana west coast and Texas southwestern coast[24]
- Avoyel ("little Natchez"), Louisiana[16][20]
- Bayogoula, southeastern Louisiana[16][20]
- Biloxi, Mississippi[20][24]
- Caddo Confederacy, Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Texas[24][26]
- Adai (Adaizan, Adaizi, Adaise, Adahi, Adaes, Adees, Atayos), Louisiana and Texas[20]
- Cahinnio, southern Arkansas[26]
- Doustioni, north central Louisiana[26]
- Eyeish (Hais), eastern Texas[26]
- Hainai, eastern Texas[26]
- Hasinai, eastern Texas[26]
- Kadohadacho, northeastern Texas, southwestern Arkansas, northwestern Louisiana[26]
- Nabedache, eastern Texas[26]
- Nabiti, eastern Texas[26]
- Nacogdoche, eastern Texas[26]
- Nacono, eastern Texas[26]
- Nadaco, eastern Texas[26]
- Nanatsoho, northeastern Texas[26]
- Nasoni, eastern Texas[26]
- Natchitoches, Lower: central Louisiana, Upper: northeastern Texas[26]
- Neche, eastern Texas[26]
- Nechaui, eastern Texas[26]
- Ouachita, northern Louisiana[26]
- Tula, western Arkansas[26]
- Yatasi, northwestern Louisiana[26]
- Calusa, southwestern Florida[22][24]
- Cape Fear Indians, North Carolina southern coast[20]
- Catawba (Esaw, Usheree, Ushery, Yssa),[27] North Carolina, South Carolina[24]
- Chacato, Florida panhandle and southern Alabama[20]
- Chakchiuma, Alabama and Mississippi[24]
- Chatot people (Chacato, Chactoo), west Florida
- Chawasha (Washa), Louisiana[20]
- Cheraw (Chara, Charàh), North Carolina
- Cherokee, western North Carolina, eastern Tennessee, later Georgia, northwestern South Carolina, northern Alabama, Arkansas, Texas, Mexico, and currently North Carolina and Oklahoma[28]
- Chickanee (Chiquini), North Carolina
- Chickasaw, Alabama and Mississippi,[24] later Oklahoma[28]
- Chicora, coastal South Carolina[16]
- Chine, Florida
- Chisca (Cisca), southwestern Virginia, northern Florida[16]
- Chitimacha, Louisiana[24]
- Choctaw, Mississippi, Alabama,[24] and parts of Louisiana; later Oklahoma[28]
- Chowanoc (Chowanoke), North Carolina
- Coharie, North Carolina
- Congaree (Canggaree), South Carolina[20][29]
- Coree, North Carolina[16]
- Coharie, North Carolina
- Croatan, North Carolina
- Cusabo coastal South Carolina[24]
- Eno, North Carolina[20]
- Grigra (Gris), Mississippi[30]
- Guacata (Santalûces), eastern coastal Florida[22]
- Guacozo, Florida
- Guale (Cusabo, Iguaja, Ybaja), coastal Georgia[20][24]
- Guazoco, southwestern Florida coast[22]
- Houma, Louisiana and Mississippi[24]
- Jaega (Jobe), eastern coastal Florida[21]
- Jaupin (Weapemoc), North Carolina
- Jororo, Florida interior[22]
- Keyauwee, North Carolina[20]
- Koasati (Coushatta), formerly eastern Tennessee,[24] currently Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas
- Koroa, Mississippi[20]
- Luca, southwestern Florida coast[22]
- Lumbee, North Carolina
- Machapunga, North Carolina
- Matecumbe (Matacumbêses, Matacumbe, Matacombe), Florida Keys[22]
- Mayaca, Florida[22]
- Mayaimi (Mayami), interior Florida[21]
- Mayajuaca, Florida
- Mikasuki (Miccosukee), Florida
- Mobila (Mobile, Movila), northwestern Florida and southern Alabama[24]
- Mocoso, western Florida[21][22]
- Mougoulacha, Mississippi[16]
- Muscogee (Creek), Tennessee, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, Florida, later Oklahoma
- Abihka, Alabama,[25] later Oklahoma
- Alabama, formerly Alabama,[25] southwestern Tennessee, and northwestern Mississippi,[20][24] now Oklahoma and Texas
- Apalachicola, Creek Confederacy, Alabama, Florida, Georgia and South Carolina[25]
- Chiaha, Creek Confederacy, Alabama[25]
- Eufaula tribe, Georgia, later Oklahoma
- Hitchiti, Creek Confederacy, Georgia, Alabama, and Florida[20]
- Kialegee Tribal Town, Alabama, later Oklahoma
- Osochee (Osochi, Oswichee, Usachi, Oosécha), Creek Confederacy, Alabama[20][25]
- Talapoosa, Creek Confederacy, Alabama[25]
- Thlopthlocco Tribal Town, Alabama, Georgia, later Oklahoma
- Tukabatchee, Muscogee Creek Confederacy, Alabama[25]
- Naniaba, northwestern Florida and southern Alabama[24]
- Natchez, Louisiana and Mississippi[24] later Oklahoma
- Neusiok (Newasiwac, Neuse River Indians), North Carolina[20]
- Norwood culture, Apalachee region, Florida, c. 12,000 BCE — 4500 BCE
- Oconee, Georgia, Florida
- Ofo, Arkansas and Mississippi,[24] eastern Tennessee[20]
- Okchai (Ogchay), central Alabama[20]
- Okelousa, Louisiana[20]
- Opelousas, Louisiana[20]
- Pacara, Florida
- Pamlico, formerly North Carolina
- Pascagoula, Mississippi coast[16]
- Pee Dee (Pedee), South Carolina[20][31] and North Carolina
- Pensacola, Florida panhandle and southern Alabama[24]
- Potoskeet, North Carolina
- Quinipissa, southeastern Louisiana and Mississippi[25]
- Roanoke, North Carolina
- Saluda (Saludee, Saruti), South Carolina[20]
- Santee (Seretee, Sarati, Sati, Sattees), South Carolina (no relation to Santee Sioux), South Carolina[20]
- Santa Luces, Florida
- Saponi, North Carolina,[32] Virginia[15]
- Saura, North Carolina
- Sawokli (Sawakola, Sabacola, Sabacôla, Savacola), southern Alabama and Florida panhandle[20]
- Saxapahaw (Sissipahaw, Sissipahua, Shacioes), North Carolina[20]
- Secotan, North Carolina
- Seminole, Florida and Oklahoma[28]
- Sewee (Suye, Joye, Xoye, Soya), South Carolina coast[20]
- Shakori, North Carolina
- Shoccoree (Haw), North Carolina,[20] possibly Virginia
- Sissipahaw, North Carolina
- Sugeree (Sagarees, Sugaws, Sugar, Succa), North Carolina and South Carolina[20]
- Surruque, east central Florida[33]
- Suteree (Sitteree, Sutarees, Sataree), North Carolina
- Taensa, Mississippi[30]
- Tawasa, Alabama[34]
- Tequesta, southeastern coastal Florida[20][22]
- Timucua, Florida and Georgia[20][22][24]
- Acuera, central Florida[35]
- Agua Fresca (or Agua Dulce or Freshwater), interior northeast Florida[35]
- Arapaha, north central Florida and south central Georgia?[35]
- Cascangue, coastal southeast Georgia[35]
- Icafui (or Icafi), coastal southeast Georgia[35]
- Mocama (or Tacatacuru), coastal northeast Florida and coastal southeast Georgia[35]
- Northern Utina north central Florida[35]
- Ocale, central Florida[35]
- Oconi, interior southeast Georgia[35]
- Potano, north central Florida[35]
- Saturiwa, northeast Florida[35]
- Tacatacuru, coastal southeast Georgia[36]
- Tucururu (or Tucuru), central? Florida[35]
- Utina (or Eastern Utina), northeast central Florida[37]
- Yufera, coastal southeast Georgia[35]
- Yui (Ibi), coastal southeast Georgia[35]
- Yustaga, north central Florida[35]
- Tiou (Tioux), Mississippi[29]
- Tocaste, Florida[22]
- Tocobaga, Florida[20][22]
- Tohomé, northwestern Florida and southern Alabama[24]
- Tomahitan, eastern Tennessee
- Topachula, Florida
- Tunica, Arkansas and Mississippi[24]
- Utiza, Florida[21]
- Uzita, Tampa Bay, Florida[38]
- Vicela, Florida[21]
- Viscaynos, Florida
- Waccamaw, South Carolina
- Waccamaw Siouan, North Carolina
- Wateree (Guatari, Watterees), North Carolina[20]
- Waxhaw (Waxsaws, Wisack, Wisacky, Weesock, Flathead), North Carolina and South Carolina[20][31]
- Westo, Virginia and South Carolina,[16] extinct
- Winyaw, South Carolina coast[20]
- Woccon, North Carolina[20][31]
- Yamasee, Florida, Georgia[16]
- Yazoo, southeastern tip of Arkansas, eastern Louisiana, Mississippi[20][39]
- Yuchi (Euchee), central Tennessee,[20][24] then northwest Georgia, now Oklahoma
Great Basin
- Ahwahnechee, Yosemite Valley, California
- Bannock, Idaho[40]
- Southern Paiute, Arizona, Nevada, Utah
- Chemehuevi, southeastern California
- Kaibab, northwestern Arizona[41]
- Kaiparowtis, southwestern Utah[41]
- Moapa, southern Nevada[41]
- Panaca[41]
- Panguitch, Utah[41]
- Paranigets, southern Nevada[41]
- Shivwits, southwestern Utah[41]
- Southern Paiute, Arizona, Nevada, Utah
- Coso People, of Coso Rock Art District in the Coso Range, Mojave Desert California
- Fremont culture (400 CE–1300 CE), formerly Utah[42]
- Kawaiisu, southern inland California[40]
- Mono, southeastern California
- Eastern Mono, southeastern California
- Western Mono or Owens Valley Paiute, eastern California and Nevada[40]
- Northern Paiute, eastern California, Nevada, Oregon, southwestern Idaho[40]
- Kucadikadi, Mono Lake Paiute, Mono Lake, California
- Guchundeka', Kuccuntikka, Buffalo Eaters[43][44]
- Tukkutikka, Tukudeka, Mountain Sheep Eaters, joined the Northern Shoshone[44]
- Boho'inee', Pohoini, Pohogwe, Sage Grass people, Sagebrush Butte People[43][44][45]
- Northern Shoshone, Idaho[40]
- Agaideka, Salmon Eaters, Lemhi, Snake River and Lemhi River Valley[45][45][46]
- Doyahinee', Mountain people[43]
- Kammedeka, Kammitikka, Jack Rabbit Eaters, Snake River, Great Salt Lake[45]
- Hukundüka, Porcupine Grass Seed Eaters, Wild Wheat Eaters, possibly synonymous with Kammitikka[45][47]
- Tukudeka, Dukundeka', Sheep Eaters (Mountain Sheep Eaters), Sawtooth Range, Idaho[45][46]
- Yahandeka, Yakandika, Groundhog Eaters, lower Boise, Payette, and Wiser Rivers[45][46]
-
- Kuyatikka, Kuyudikka, Bitterroot Eaters, Halleck, Mary's River, Clover Valley, Smith Creek Valley, Nevada[47]
- Mahaguadüka, Mentzelia Seed Eaters, Ruby Valley, Nevada[47]
- Painkwitikka, Penkwitikka, Fish Eaters, Cache Valley, Idaho and Utah[47]
- Pasiatikka, Redtop Grass Eaters, Deep Creek Gosiute, Deep Creek Valley, Antelope Valley[47]
- Tipatikka, Pinenut Eaters, northernmost band[47]
- Tsaiduka, Tule Eaters, Railroad Valley, Nevada[47]
- Tsogwiyuyugi, Elko, Nevada[47]
- Waitikka, Ricegrass Eaters, Ione Valley, Nevada[47]
- Watatikka, Ryegrass Seed Eaters, Ruby Valley, Nevada[47]
- Wiyimpihtikka, Buffalo Berry Eaters[47]
- Timbisha or Panamint or Koso, southeastern California
- Ute, Colorado, Utah, northern New Mexico[40]
- Capote, southeastern Colorado and New Mexico[48]
- Moanunts, Salina, Utah[49]
- Muache, south and central Colorado[48]
- Pahvant, western Utah[49]
- Sanpits, central Utah[49]
- Timpanogots, north central Utah[49]
- Uintah, Utah[48]
- Uncompahgre or Taviwach, central and northern Colorado[48]
- Weeminuche, western Colorado, eastern Utah, northwestern New Mexico[48]
- White River Utes (Parusanuch and Yampa), Colorado and eastern Utah[48]
- Washo, Nevada and California[50]
California
Nota bene: The California cultural area does not exactly conform to the state of California's boundaries, and many tribes on the eastern border with Nevada are classified as Great Basin tribes and some tribes on the Oregon border are classified as Plateau tribes.[51]
- Achomawi, Achumawi, Pit River tribe, northeastern California[52]
- Atsugewi, northeastern California[52]
- Cahuilla, southern California[52]
- Chumash, coastal southern California[52]
- Chilula, northwestern California[52]
- Chimariko, extinct, northwestern California[53]
- Cupeño, southern California[52]
- Eel River Athapaskan peoples
- Esselen, west-central California[52]
- Hupa, northwestern California[52]
- Juaneño, Acjachemem, southwestern California
- Karok, northwestern California[52]
- Kato, Cahto, northwestern California[52]
- Kitanemuk, south-central California[52]
- Konkow, northern-central California[52]
- Kumeyaay, Diegueño, Kumiai
- La Jolla Complex, southern California, c. 6050–1000 BCE
- Luiseño, southwestern California[52]
- Maidu, northeastern California[52]
- Konkow, northern California
- Mechoopda, northern California
- Nisenan, Southern Maidu, northern California
- Miwok, Me-wuk, central California[52]
- Coast Miwok, west-central California[52]
- Lake Miwok, west-central California[52]
- Valley and Sierra Miwok
- Monache, Western Mono, central California[52]
- Nisenan, eastern-central California[52]
- Nomlaki, northwestern California[52]
- Ohlone, Costanoan, west-central California[52]
- Patwin, central California[52]
- Suisun, Southern Patwin, central California
- Pauma Complex, southern California, c. 6050 — 1000 BCE
- Pomo, northwestern and central-western California[52]
- Salinan, coastal central California[52]
- Antoniaño[56]
- Migueleño
- Serrano, southern California[52]
- Shasta northwestern California[52]
- Konomihu, northwestern California
- Okwanuchu, northwestern California
- Tataviam, Allilik (Fernandeño), southern California[52]
- Tolowa, northwestern California[52]
- Tongva, Gabrieleño, Fernandeño, San Clemente tribe, coastal southern California[52]
- Tubatulabal, south-central California[52]
- Wappo, north-central California[52]
- Whilkut, northwestern California[52]
- Wintu, northwestern California[52]
- Wiyot, northwestern California[52]
- Yana, northern-central California[52]
- Yokuts, central and southern California[52]
- Chukchansi, Foothill Yokuts, central California[52]
- Northern Valley Yokuts, central California[52]
- Tachi tribe, Southern Valley Yokuts, south-central California[52]
- Yuki, Ukomno'm, northwestern California[52]
- Huchnom, northwestern California[57]
- Yurok, northwestern California[52]
Southwest
This region is also called Oasisamerica and includes parts of what is now Arizona, Southern Colorado, New Mexico, Western Texas, Southern Utah, Chihuahua, and Sonora
- Ak Chin, Arizona
- Southern Athabaskan
- Chiricahua Apache, New Mexico and Oklahoma
- Jicarilla Apache, New Mexico
- Lipan Apache, Texas
- Mescalero Apache, New Mexico
- Navajo (Navaho, Diné), Arizona and New Mexico
- San Carlos Apache, Arizona
- Tonto Apache, Arizona
- Western Apache (Coyotero Apache), Arizona
- White Mountain Apache, Arizona
- Aranama (Hanáma, Hanáme, Chaimamé, Chariname, Xaraname, Taraname)
- Coahuiltecan, Texas, northern Mexico
- Cocopa, Arizona, northern Mexico
- Comecrudo Texas, northern Mexico
- Cotoname (Carrizo de Camargo)
- Genízaro Arizona, New Mexico
- Halchidhoma, Arizona and California
- Hualapai, Arizona
- Havasupai, Arizona
- Hohokam, formerly Arizona
- Karankawa, Texas
- Kavelchadhom
- La Junta, Texas, Chihuahua
- Mamulique, Texas, northern Mexico
- Manso, Texas, Chihuahua
- Maricopa, Arizona
- Mojave, Arizona, California, and Nevada
- Pima, Arizona
- Pima Bajo
- Pueblo peoples, Arizona, New Mexico, Western Texas
- Ancestral Pueblo, formerly Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, Utah
- Hopi-Tewa (Arizona Tewa, Hano), Arizona, joined the Hopi during the Pueblo Revolt
- Hopi, Arizona
- Keres people, New Mexico
- Acoma Pueblo, New Mexico
- Cochiti Pueblo, New Mexico
- Kewa Pueblo (formerly Santo Domingo Pueblo), New Mexico
- Laguna Pueblo, New Mexico
- San Felipe Pueblo, New Mexico
- Santa Ana Pueblo, New Mexico
- Zia Pueblo, New Mexico
- Tewa people, New Mexico
- Nambé Pueblo, New Mexico
- Ohkay Owingeh (formerly San Juan Pueblo), New Mexico
- Pojoaque Pueblo, New Mexico
- San Ildefonso Pueblo, New Mexico
- Tesuque Pueblo, New Mexico
- Santa Clara Pueblo, New Mexico
- Tiwa people, New Mexico
- Isleta Pueblo, New Mexico
- Picuris Pueblo, New Mexico
- Sandia Pueblo, New Mexico
- Taos Pueblo, New Mexico
- Ysleta del Sur Pueblo (Tigua Pueblo), Texas
- Piro Pueblo, New Mexico
- Towa people
- Jemez Pueblo (Walatowa), New Mexico
- Pecos (Ciquique) Pueblo, New Mexico
- Zuni people (Ashiwi), New Mexico
- Quechan (Yuma), Arizona and California
- Quems
- Solano, Coahuila, Texas
- Tamique
- Toboso
- Tohono O'odham, Arizona and Mexico
- Qahatika, Arizona
- Tompiro
- Ubate
- Walapai, Arizona
- Yaqui (Yoreme), Arizona, Sonora
- Yavapai, Arizona
- Tolkapaya (Western Yavapai), Arizona
- Yavapé (Northwestern Yavapai), Arizona
- Kwevkapaya (Southeastern Yavapai), Arizona
- Wipukpa (Northeastern Yavapai), Arizona
Mexico and Mesoamerica
The regions of Oasisamerica, Aridoamerica, and Mesoamerica span multiple countries and overlap.
Aridoamerica
.svg.png)
- Acaxee
- Chichimeca
- Cochimí, Baja California[58]
- Garza, Texas, northern Mexico
- Guachimontone
- Guamare
- Guaycura, Baja California
- Guarijío, Huarijío, Chihuahua, Sonora[58]
- Huichol[58] (Wixáritari), Nayarit, Jalisco, Zacatecas, and Durango
- Kiliwa, Baja California
- Mayo,[58] Sonora and Sinaloa
- Monqui, Baja California
- Paipai, Akwa'ala, Kw'al, Baja California[59]
- Opata
- Otomi, central Mexico
- Patiri, southeastern Texas
- Pericúe, Baja California
- Pima Bajo[58]
- Purépecha[58]
- Seri[58]
- Tarahumara[58]
- Tepecano
- Tepehuán[58]
- Terocodame, Texas and Mexico
- Codam
- Hieroquodame
- Oodame
- Perocodame
- Teroodame
- Teuchitlan tradition
- Western Mexico shaft tomb tradition
- Yaqui,[58] Sonora and now southern Arizona
- Zacateco
Mesoamerica
- Nahua, Guatemala and Mexico
- Cora people
- Huastec
- Huave (Wabi), Juchitán District, Oaxaca
- Lenca
- Maya, Belize, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Mexico
- Itzá, Petén Department, Guatemala
- Lacandon
- Mopan, Belize, Guatemala
- Yucatec (Maya proper)
- Achi, Guatemala
- Akatek, Guatemala
- Ch'ol
- Ch'orti', southeastern Guatemala, northwestern Honduras, and northern El Salvador
- Ixil, El Quiché, Guatemala
- Jacaltec (Jakaltek), northwestern Guatemala
- K'iche' (Quiché), El Salvador and Guatemala
- Kaqchikel
- Kekchi
- Mam
- Poqomam
- Tojolabales
- Tzotzil
- Tzeltal
- Tz'utujil
- Mazatec
- Mixtec
- Olmec
- Otomi
- Pipil
- Purépecha, also known as Tarascan
- Tlapanec
- Xinca
- Zapotec
- Toltec (900-1168 CE), Tula, Hildago
Circum-Caribbean
Partially organized per Handbook of South American Indians.[60]
Caribbean
Anthropologist Julian Steward defined the Antilles cultural area, which includes all of the Antilles and Bahamas, except for Trinidad and Tobago.[60]
- Arawak
- Caquetio, Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao, and Venezuela
- Carib, Lesser Antilles
- Garifuna ("Black Carib"), Originally Dominica and Saint Vincent, currently Belize, Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua
- Ciboney, Greater Antilles, c. 1000 — 300 BCE[61]
- Guanahatabey (Guanajatabey), Cuba, 1000 BCE
- Ciguayo, Hispaniola
- Garifuna ("Black Carib"), Originally Dominica and Saint Vincent, currently Belize, Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua
- Ortoiroid, c. 5500 — 200 BCE[62]
- Saladoid culture, 500 BCE—545 CE[62]
Central America
The Central American culture area includes part of El Salvador, most of Honduras, all of Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama, and some peoples on or near the Pacific coasts of Colombia and Ecuador.[60]
- Bagaces, Costa Rica
- Bokota, Panama
- Boruca, Costa Rica
- Bribri, Costa Rica
- Cabécar, Costa Rica
- Cacaopera (Matagalpa, Ulua), formerly El Salvador[63]
- Cayada, Ecuador
- Changuena, Panama
- Embera-Wounaan (Chocó, Wounaan), Colombia, Panama
- Choluteca, Honduras
- Coiba, Costa Rica
- Coito, Costa Rica
- Corobici, Costa Rica
- Desaguadero, Costa Rica
- Dorasque, Panama
- Guatuso, Costa Rica
- Guaymí, Panama
- Movere, Panama
- Murire, Panama
- Guetar, Costa Rica
- Kuna (Guna), Panama and Columbia
- Lenca, Honduras and El Salvador
- Mangue, Nicaragua
- Maribichocoa, Honduras and Nicaragua
- Miskito, Hondrus, Nicaragua
- Nagrandah, Nicaragua
- Ngöbe Buglé, Bocas del Toro, Panama
- Nicarao, Nicaragua
- Nicoya, Costa Rica
- Orotiña, Costa Rica
- Paparo, Panama
- Paya, Honduras
- Pech, northeastern Honduras
- Piria, Nicaragua
- Poton, Honduras and El Salvador
- Quepo, Costa Rica
- Rama, Nicaragua
- Sigua, Panama
- Subtiaba, Nicaragua
- Suerre, Costa Rica
- Sumo (Mayagna), Honduras and Nicaragua
- Terraba (Naso, Teribe, Tjër Di), Panama
- Tojar, Panama
- Tolupan (Jicaque), Honduras
- Ulva, El Salvador, Honduras and Nicaragua
- Voto, Costa Rica
- Yasika, Nicaragua
Colombia and Venezuela
The Colombia and Venezuela culture area includes most of Colombia and Venezuela. Southern Colombia is in the Andean culture area, as are some peoples of central and northeastern Colombia, who are surrounded by peoples of the Colombia and Venezuela culture. Eastern Venezuela is in the Guianas culture area, and southeastern Colombia and southwestern Venezuela are in the Amazonia culture area.[60]
- Abibe, northwestern Colombia
- Aburrá, central Colombia
- Achagua (Axagua), eastern Colombia, western Venezuela
- Agual, western Colombia
- Amaní, central Colombia
- Ancerma, western Colombia
- Andaqui (Andaki), Huila Department, Colombia
- Andoque, Andoke, southeastern Colombia
- Antiochia, Colombia
- Arbi, western Colombia
- Arma, western Colombia
- Atunceta, western Colombia
- Auracana, northeastern Colombia
- Buriticá, western Colombia
- Caquetio, western Venezuela
- Calamari, northwestern Colombia
- Calima culture, western Colombia, 200 BCE–400 CE
- Caramanta, western Columbia
- Carate, northeastern Colombia
- Carare, northeastern Colombia
- Carex, northwestern Colombia
- Cari, western Colombia
- Carrapa, western Colombia
- Cartama, western Colombia
- Cauca, western Colombia
- Corbago, northeastern Colombia
- Cosina, northeastern Colombia
- Catio, northwestern Colombia
- Cenú, northwestern Colombia
- Cenufaná, northwestern Colombia
- Chanco, western Colombia
- Coanoa, northeastern Colombia
- Cuiba, east Colombia west Venezuela
- Cuica, western Venezuela
- Cumanagoto, eastern Venezuela
- Evéjito, western Colombia
- Fincenú, northwestern Colombia
- Gorrón, western Colombia
- Guahibo (Guajibo), eastern Colombia, southern Venezuela
- Guambía, western Colombia
- Guanes, Colombia, pre-Columbian culture
- Guanebucan, northeastern Colombia
- Guazuzú, northwestern Colombia
- Hiwi, western Colombia, eastern Venezuela
- Jamundí, western Colombia
- Kari'ña, eastern Venezuela
- Kogi, northern Colombia
- Lile, western Colombia
- Lache, central Colombia
- Mariche, central Venezuela
- Maco (Mako, Itoto, Wotuja, or Jojod), northeastern Colombia and western Venezuela
- Mompox, northwestern Colombia
- Motilone, northeastern Colombia and western Venezuela
- Naura, central Colombia
- Nauracota, central Colombia
- Noanamá (Waunana, Huaunana, Woun Meu), northwestern Colombia and Panama
- Nutabé, northwestern Colombia
- Opón, northeastern Colombia
- Pacabueye, northwestern Colombia
- Pancenú, northwestern Colombia
- Patángoro, central Colombia
- Paucura, western Colombia
- Pemed, northwestern Colombia
- Pequi people, western Colombia
- Piaroa, Colombia and Venezuela
- Picara, western Colombia
- Pozo, western Colombia
- Pumé (Yaruro), Venezuela
- Quimbaya, central Colombia, 4th–7th centuries CE
- Quinchia, western Colombia
- Sutagao, central Colombian
- Tahamí, northwestern Colombia
- Tairona, northern Colombia, pre-Columbian culture, 1st–11th centuries CE
- Tamalameque, northwestern Colombia
- Mariche, central Venezuela
- Timba, western Colombia
- Timote, western Venezuela
- Tinigua, Caquetá Department, Colombia
- Tolú, northwestern Colombia
- Toro, western Colombia
- Tupe, northeastern Colombia
- Turbaco people, northwestern Colombia
- Urabá, northwestern Colombia
- Urezo, northwestern Colombia
- U'wa, eastern Colombia, western Venezuela
- Waikerí, eastern Venezuela
- Wayuu (Wayu, Wayúu, Guajiro, Wahiro), northeastern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela
- Xiriguana, northeastern Colombia
- Yamicí, northwestern Colombia
- Yapel, northwestern Colombia
- Yarigui, northeastern Colombia
- Yukpa, Yuko, northeastern Colombia
- Zamyrua, northeastern Colombia
- Zendagua, northwestern Colombia
- Zenú, northwestern Colombia, pre-Columbian culture, 200 BCE–1600 CE
- Zopia, western Colombia
Guianas


This region includes northern parts Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, Venezuela, and parts of the Amazonas, Amapá, Pará, and Roraima States in Brazil.
- Acawai (6N 60W)
- Acokwa (3N 53W)
- Acuria (Akurio, Akuriyo), 5N 55W, Suriname
- Akawaio, Roraima, Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela
- Amariba (2N 60W)
- Amicuana (2N 53W)
- Apalaí (Apalai), Amapá, Brazil
- Apirua (3N 53W)
- Apurui (3N 53W)
- Aracaret (4N 53W)
- Aramagoto (2N 54W)
- Aramisho (2N 54W)
- Arebato (7N 65W)
- Arekena (2N 67W)
- Arhuaco, northeastern Colombia
- Arigua
- Arinagoto (4N 63W)
- Arua (1N 50W)
- Aruacay, Venezuela
- Atorai (2N 59W)
- Atroahy (1S 62W)
- Auaké, Brazil and Guyana
- Baniwa (Baniva) (3N 68W), Brazil, Colombia and Venezuela
- Baraüana (1N 65W)
- Bonari (3S 58W)
- Baré (3N 67W)
- Caberre (4N 71 W)
- Cadupinago
- Cariaya (1S 63 W)
- Carib (Kalinago), Venezuela
- Carinepagoto, Trinidad
- Chaguan, Venezuela
- Chaima, Venezuela
- Cuaga, Venezuela
- Cuacua, Venezuela
- Cumanagoto, Venezuela
- Guayano, Venezuela
- Guinau (4N 65W)
- Hixkaryána, Amazonas, Brazil
- Inao (4N 65W)
- Ingarikó, Brazil, Guyana and Venezuela
- Jaoi (Yao), Guyana, Trinidad and Venezuela
- Kali'na, Brazil, Guyana, French Guiana, Suriname, Venezuela
- Lokono (Arawak, Locono), Guyana, Trinidad, Venezuela
- Macapa (2N 59W)
- Macushi, Brazil and Guyana
- Maipure (4N 67W)
- Maopityan (2N 59W)
- Mapoyo (Mapoye), Venezuela
- Marawan (3N 52W)
- Mariusa, Venezuela
- Marourioux (3N 53W)
- Nepuyo (Nepoye), Guyana, Trinidad and Venezuela
- Orealla, Guyana
- Palengue, Venezuela
- Palikur, Brazil, French Guiana
- Parauana (2N 63W)
- Parauien (3S 60W)
- Pareco, Venezuela
- Paria, Venezuela
- Patamona, Roraima, Brazil
- Pauishana (2N 62W)
- Pemon (Arecuna), Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela
- Piapoco (3N 70W)
- Piaroa, Venezuela
- Pino (3N 54W)
- Piritú, Venezuela
- Purui (2N 52W)
- Saliba (Sáliva), Venezuela
- Sanumá, Venezuela, Brazil
- Shebayo, Trinidad
- Sikiana (Chikena, Xikiyana), Brazil, Suriname
- Tagare, Venezuela
- Tamanaco, Venezuela
- Tarumá (3S 60W)
- Tibitibi, Venezuela
- Tiriyó (Tarëno), Brazil, Suriname
- Tocoyen (3N 53W)
- Tumuza, Venezuela
- Wai-Wai, Amazonas, Brazil and Guyana
- Wapishana, Brazil and Guyana
- Warao (Warrau), Guyana and Venezuela
- Wayana (Oyana), Pará, Brazil
- Ya̧nomamö (Yanomami), Venezuela and Amazonas, Brazil
- Ye'kuana, Venezuela, Brazil
Eastern Brazil
This region includes parts of the Ceará, Goiás, Espírito Santo, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Pará, and Santa Catarina states of Brazil
- Apinajé (Apinaye Caroyo),[4] Rio Araguiaia
- Apurinã (Popũkare), Amazonas and Acre
- Arara, Pará
- Atikum, Bahia and Pernambuco
- Bororo (Borôro),[4] Mato Grosso
- Botocudo (Lakiãnõ)
- Carijo Guarani[4]
- East Brazilian Tradition, Precolumbian culture[4]
- Guató (Guato), Mato Grosso
- Kadiwéu (Guaicuru),[4] Mato Grosso do Sul
- Karajá (Iny, Javaé),[4] Goiás, Mato Grosso, Pará, and Tocantins
- Kaxixó, Minas Gerais
- Kayapo (Cayapo, Mebêngôkre),[4] Mato Grosso and Pará
- Laklãnõ,[4] Santa Catarina
- Mehim (Krahô, Crahao),[4] Rio Tocantins
- Ofayé, Mato Grosso do Sul
- Parakatêjê (Gavião),[4] Pará
- Pataxó, Bahia
- Potiguara (Pitigoares),[4] Ceará
- Tabajara, Ceará
- Tupiniquim, Espírito Santo
- Umutina (Barbados)[4]
- Xakriabá (Chakriaba, Chikriaba, or Shacriaba), Minas Gerais
- Xavánte (Shavante),[4] Mato Grosso
- Xerénte (Sherente),[4] Goiás
- Xucuru, Pernambuco
Andes
.svg.png)
- Andean Hunting-Collecting Tradition, Argentina, 11,000–4,000 CE
- Awa-Kwaiker, northern Ecuador, southern Colombia
- Aymara, Bolivia,[64] Chile, Peru
- Callawalla (Callahuaya), Bolivia[64]
- Cañari, Ecuador
- Capulí culture, Ecuador, 800—1500 CE
- Cerro Narrio (Chaullabamba) (Precolumbian culture)
- Chachapoyas, Amazonas, Peru
- Chachilla (Cayapas)
- Chanka (Chanca), Peru
- Chavín, northern Peru, 900–200 BCE
- Chincha people, Peru (Precolumbian culture)
- Chipaya, Oruro Department, Bolivia[64]
- Chuquibamba culture (Precolumbian culture)
- Conchucos
- Diaguita
- Guangaia (Precolumbian culture)
- Ichuña microlithic tradition (Precolumbian culture)
- Inca Empire (Inka), based in Peru
- Jama-Coaque (Precolumbian culture)
- Killke culture, Peru, 900–1200 CE
- Kogi
- Kolla (Colla), Argentina, Bolivia, Chile
- La Tolita (Precolumbian culture)
- Las Vegas culture, coastal Ecuador, 8000 BCE–4600 BCE
- Lauricocha culture, Peru, 8000–2500 BCE
- Lima culture, Peru, 100–650 CE
- Maina, Ecuador, Peru
- Manteño-Huancavilca (Precolumbian culture)
- Milagro (Precolumbian culture)
- Mollo culture, Bolivia, 1000–1500 CE
- Muisca, Colombian highlands (Precolumbian culture)
- Pachacama (Precolumbian culture)
- Paez (Nasa culture), Colombian highlands (Precolumbian culture)
- Panzaleo (Precolumbian culture)
- Pasto
- Pijao, Colombia
- Quechua (Kichua, Kichwa), Bolivia[64]
- Quitu culture, 2000 BCE—1550 CE
- Salinar (Precolumbian culture)
- Saraguro
- Tiwanaku culture (Tiahuanaco), 400-1000 CE, Bolivia
- Tsáchila (Colorado), Ecuador
- Tuza-Piartal (Precolumbian culture)
- Uru, Bolivia,[64] Peru
- Uru-Murato, Bolivia
- Wari culture, central coast and highlands of Peru, 500–1000 CE
- Pocra culture, Ayacucho Province, Peru, 500–1000 CE
Pacific lowlands
- Amotape complex, northern coastal Peru, 9,000–7,1000 BCE
- Atacameño (Atacama, Likan Antaí), Chile
- Awá, Colombia and Ecuador
- Bara, Colombia
- Cara culture, coastal Ecuador, 500 BCE-1550 CE
- Bahía, Ecuador, 500 BCE–500 CE
- Casma culture, coastal Peru, 1000–1400 CE
- Chancay, central coastal Peru, 1000–1450 CE
- Chango, coastal Peru, northern Chile
- Chimú, north coastal Peru, 1000–1450 CE
- Cupisnique (Precolumbian culture), 1000-200 BCE, coastal Peru
- Lambayeque (Sican culture), north coastal Peru, 750–1375 CE
- Machalilla culture, coastal Ecuador, 1500–1100 BCE
- Manteño civilization, western Ecuador, 850–1600 CE
- Moche (Mochica), north coastal Peru, 1-750 CE
- Nazca culture (Nasca), south coastal Peru, 1-700 CE
- Norte Chico civilization (Precolumbian culture), coastal Peru
- Paiján culture, northern coastal Peru, 8,700–5,900 BCE
- Paracas, south coastal Peru, 600-175 BCE
- Recuay culture, Peru (Precolumbian culture)
- Tallán (Precolumbian culture), north coastal Peru
- Valdivia culture, Ecuador, 3500–1800 BCE
- Virú culture, Piura Region, Peru, 200 BCE–300 CE
- Wari culture (Huari culture), Peru, 500–1000 CE
- Yukpa (Yuko), Colombia
- Yurutí, Colombia
Amazon
Northwestern Amazon
This region includes Amazonas in Brazil; the Amazonas and Putumayo Departments in Colombia; Cotopaxi, Los Rios, Morona-Santiago, Napo, and Pastaza Provinces and the Oriente Region in Ecuador; and the Loreto Region in Peru.
- Arabela, Loreto Region, Peru
- Arapaso (Arapaco), Amazonas, Brazil
- Baniwa
- Barbudo, Loreto Region, Peru
- Bora, Loreto Region, Peru
- Candoshi-Shapra (Chapras), Loreto Region, Peru
- Carútana (Arara), Amazonas, Brazil
- Chayahuita (Chaywita) Loreto Region, Peru
- Cocama, Loreto Region, Peru
- Cofán (Cofan), Putumayo Department, Colombia and Ecuador
- Cubeo (Kobeua), Amazonas, Brazil and Colombia
- Dâw, Rio Negro, Brazil
- Flecheiro
- Huaorani (Waorani, Waodani, Waos), Ecuador
- Hupda (Hup), Brazil, Colombia
- Jibito, Loreto Region, Peru
- Jivaroan peoples, Ecuador and Peru
- Kachá (Shimaco, Urarina), Loreto Region, Peru
- Kamsá (Sebondoy), Putumayo Department, Colombia
- Kanamarí, Amazonas, Brazil
- Kichua (Quichua)
- Cañari Kichua (Canari)
- Canelo Kichua (Canelos-Quichua), Pataza Province, Ecuador
- Chimborazo Kichua
- Cholos cuencanos
- Napo Runa (Napo Kichua, Quijos-Quichua, Napo-Quichua), Ecuador and Peru
- Saraguro
- Sarayacu Kichua, Pastaza Province, Ecuador
- Korubu, Amazonas, Brazil
- Kugapakori-Nahua
- Macaguaje (Majaguaje), Río Caquetá, Colombia
- Machiguenga, Peru
- Marubo
- Matsés (Mayoruna, Maxuruna), Brazil and Peru
- Mayoruna (Maxuruna)
- Miriti, Amazonas Department, Colombia
- Murato, Loreto Region, Peru
- Mura, Amazonas, Brazil
- Pirahã (Mura-pirarrã), Amazonas, Brazil
- Nukak (Nukak-Makú), eastern Colombia
- Ocaina, Loreto Region, Peru
- Omagua (Cambeba, Kambeba, Umana), Amazonas, Brazil
- Orejón (Orejon), Napo Province, Ecuador
- Panoan, western Brazil, Bolivia, Peru
- Sharpas
- Siona (Sioni), Amazonas Department, Colombia
- Siriano, Brazil, Colombia
- Siusi, Amazonas, Brazil
- Tariano (Tariana), Amazonas, Brazil
- Tsohom Djapá
- Tukano (Tucano), Brazil, Colombia
- Waikino (Vaikino), Amazonas, Brazil
- Waimiri-Atroari (Kinja, Uaimiri-Atroari), Amazonas and Roraima, Brazil
- Wanano (Unana, Vanana), Amazonas, Brazil
- Witoto
- Murui Witoto, Loreto Region, Peru
- Yagua (Yahua), Loreta Region, Peru
- Yaminahua (Jaminawa, Yamanawa, Yaminawá), Pando Department, Bolivia[64]
- Yora
- Záparo (Zaparo), Pastaza Province, Ecuador
- Zuruahã (Suruahá, Suruwaha), Amazonas, Brazil
Eastern Amazon
This region includes Amazonas, Maranhão, and parts of Pará States in Brazil.
- Amanayé (Ararandeura), Brazil
- Araweté (Araueté, Bïde), Pará, Brazil
- Awá (Guajá), Brazil
- Ch'unchu, Peru
- Ge
- Guajajára (Guajajara), Maranhão, Brazil
- Guarani, Paraguay
- Ka'apor, Maranhão, Brazil
- Kuruaya, Pará, Brazil
- Marajoara, Precolumbian culture, Pará, Brazil
- Panará, Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil
- Parakanã (Paracana)
- Suruí do Pará, Pará, Brazil
- Tembé (Tembe)
- Turiwára (Turiwara)
- Wayampi
- Zo'é people, Pará, Brazil
Southern Amazon
This region includes southern Brazil (Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, parts of Pará, and Rondônia) and Eastern Bolivia (Beni Department).
- Apiacá (Apiaká), Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil[65]
- Assuriní do Toncantins (Tocantin)
- Aweti (Aueto), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Bakairí (Bakairi)
- Chácobo (Chacobo), northwest Beni Department, Bolivia[64]
- Chiquitano (Chiquito, Tarapecosi), Brazil and Santa Cruz, Bolivia[64]
- Cinta Larga, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Enawene Nawe, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Gavião of Rondônia
- Guarayu (Guarayo), Bolivia[64]
- Ikpeng (Xicao), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Itene, Beni Department, Bolivia[64]
- Irántxe (Iranche)
- Juma (Kagwahiva), Rondônia, Brazil
- Jurúna (Yaruna, Juruna, Yudjá), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kaiabi (Caiabi, Cajabi, Kajabi, Kayabi), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kalapálo (Kalapalo), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kamayurá (Camayura), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kanoê (Kapixaná), Rondônia, Brazil
- Karipuná (Caripuna)
- Karitiâna (Caritiana), Brazil
- Kayapo, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kuikuro, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Matipu, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Mehináku (Mehinacu, Mehinako), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Moxo (Mojo), Bolivia
- Nahukuá (Nahuqua), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Nambikuára (Nambicuara, Nambikwara), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Pacahuara (Pacaguara, Pacawara), northwest Beni Department, Bolivia[64]
- Pacajá (Pacaja)
- Panará, Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil
- Parecís (Paressi)
- Rikbaktsa (Erikbaksa), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Rio Pardo people, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Sateré-Mawé (Maue), Brazil
- Suyá (Kisedje), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Tacana (Takana), Beni and Madre de Dios Rivers, Bolivia[64]
- Tapajó (Tapajo)
- Tapirapé (Tapirape)
- Tenharim
- Terena, Mato Gross and Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil
- Trumai, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Tsimané (Chimané, Mosetén, Pano), Beni Department, Bolivia[64]
- Uru-Eu-Wau-Wau, Rondônia, Brazil
- Wari' (Pacanawa, Waricaca'), Rondônia, Brazil
- Wauja (Waurá, Waura), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Wuy jugu (Mundurucu, Munduruku)
- Yawalapiti (Iaualapiti), Mato Grosso, Brazil
Southwestern Amazon
This region includes the Cuzco, Huánuco Junín, Loreto, Madre de Dios, and Ucayali Regions of eastern Peru, parts of Acre, Amazonas, and Rondônia, Brazil, and parts of the La Paz and Beni Departments of Bolivia.
- Aguano (Santacrucino, Uguano), Peru
- Aikanã, Rondônia, Brazil
- Akuntsu, Rondônia, Brazil
- Amahuaca, Brazil, Peru
- Asháninka (Campa, Chuncha), Acre, Brazil and Junín, Pasco, Huánuco, and Ucayali, Peru
- Banawá (Jafí, Kitiya), Amazonas, Brazil
- Cashibo (Carapache), Huánuco Region, Peru
- Conibo (Shipibo-Conibo), Peru and Amazonas, Brazil
- Ese Ejja (Chama), Beni Department, Bolivia[64]
- Harakmbut, Madre de Dios, Peru
- Amarakaeri, Madre de Dios Region, Peru
- Kareneri, Madre de Dios Region, Peru
- Huachipaeri, Madre de Dios Region, Peru
- Amarakaeri, Madre de Dios Region, Peru
- Hi-Merimã, Himarimã, Amazonas, Brazil
- Jamamadi, Acre and Amazonas, Brazil
- Kaxinawá (Cashinahua, Huni Kuin), Peru and Acre, Brazil
- Kulina (Culina), Peru
- Kwaza (Coaiá, Koaiá), Rondônia, Brazil
- Latundê, Rondônia, Brazil
- Machinere, Bolivia[64] and Peru
- Mashco-Piro, Peru
- Matís (Matis), Brazil
- Matsés (Mayoruna, Maxuruna), Brazil, Peru
- Parintintin (Kagwahiva’nga), Brazil
- Shipibo, Loreto Region, Peru
- Sirionó (Chori, Miá), Beni and Santa Cruz Departments, Bolivia
- Ticuna (Tucuna), Brazil, Colombia, Peru
- Toromono (Toromona), La Paz Department, Bolivia[64]
- Yanesha' (Amuesha), Cusco Region, Peru
- Yawanawa (Jaminawá, Marinawá, Xixinawá), Acre, Brazil; Madre de Dios, Peru; and Bolivia
- Yine (Contaquiro, Simiranch, Simirinche), Cuzco Region, Peru
- Yuqui (Bia, Yuki), Cochabamba Department, Bolivia[64]
- Yuracaré (Yura), Beni and Cochabamba Departments, Bolivia[64]
Gran Chaco

- Abipón, Argentina, historic group
- Angaite (Angate), northwestern Paraguay
- Ayoreo[67] (Ayoré, Moro, Morotoco, Pyeta, Yovia,[64] Zamuco), Bolivia and Paraguay
- Chamacoco (Zamuko),[67] Paraguay
- Chané, Argentina and Bolivia
- Chiquitano (Chiquito, Tarapecosi), eastern Bolivia
- Chorote (Choroti,[67] Iyo'wujwa,[64] Iyojwa'ja Chorote, Manjuy), Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay
- Guana[67] (Kaskihá), Paraguay
- Guaraní,[67] Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay
- Guaycuru peoples, Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay
- Kaiwá,[67] Argentina and Brazil
- Lengua people (Enxet),[67] Paraguay
- North Lengua (Eenthlit, Enlhet, Maskoy), Paraguay
- South Lengua, Paraguay
- Lulé (Pelé, Tonocoté), Argentina
- Maká[67] (Towolhi), Paraguay
- Nivaclé (Ashlushlay,[67] Chulupí, Chulupe, Guentusé), Argentina and Paraguay
- Sanapaná[67] (Quiativis), Paraguay
- Vilela, Argentina
- Wichí (Mataco),[67] Argentina and Tarija Department, Bolivia[64]
Southern Cone
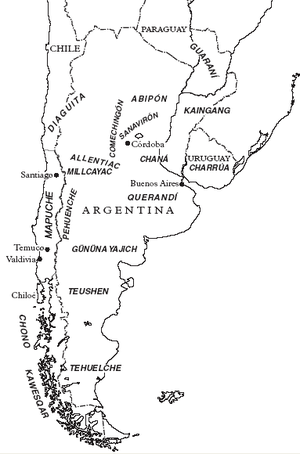
- Aché, southeastern Paraguay
- Alacaluf (Kaweshkar, Halakwulup), Chile
- Chaná (extinct), formerly Uruguay
- Chandule (Chandri)
- Charrúa, southern Brazil and Uruguay
- Chono (Precolumbian culture), formerly Chiloé Archipelago, Chile
- Comechingon (Henia-Camiare), Argentina
- Haush (Manek'enk, Mánekenk, Aush), Tierra del Fuego
- Het (Querandí) (extinct), formerly Argentinian Pampas
- Huarpe (Warpes), Strait of Magellan, Argentina, Chile
- Allentiac (Alyentiyak)
- Millcayac (Milykayak)
- Oico
- Mapuche (Araucanian), southwestern Argentina and Chile
- Mbeguá (extinct), formerly Paraná River, Argentina
- Minuane (extinct), formerly Uruguay
- Puelche (Guennaken, Pamba) (extinct), Argentinian and Chilean Andes[68]
- Tehuelche, Patagonia
- Künün-a-Güna (Gennakenk, Gennaken)
- Küwach-a-Güna
- Mecharnúekenk
- Aónikenk (Zuidelijke Tehuelche)
- Teushen (Tehues), extinct, formerly Tierra del Fuego
- Selk'nam (Ona), Tierra del Fuego
- Yaghan (Yamana), Tierra del Fuego
- Yaro (Jaro)
Languages
Indigenous languages of the Americas (or Amerindian Languages) are spoken by indigenous peoples from the southern tip of South America to Alaska and Greenland, encompassing the land masses which constitute the Americas. These indigenous languages consist of dozens of distinct language families as well as many language isolates and unclassified languages. Many proposals to group these into higher-level families have been made. According to UNESCO, most of the indigenous American languages in North America are critically endangered and many of them are already extinct.[69]
Genetic classification
4. North Amerindian |
The haplogroup most commonly associated with Indigenous Americans is Haplogroup Q1a3a (Y-DNA).[70] Y-DNA, like (mtDNA), differs from other nuclear chromosomes in that the majority of the Y chromosome is unique and does not recombine during meiosis. This has the effect that the historical pattern of mutations can easily be studied.[71] The pattern indicates Indigenous Amerindians experienced two very distinctive genetic episodes; first with the initial-peopling of the Americas, and secondly with European colonization of the Americas.[72][73] The former is the determinant factor for the number of gene lineages and founding haplotypes present in today's Indigenous Amerindian populations.[72]
Human settlement of the Americas occurred in stages from the Bering sea coast line, with an initial 20,000-year layover on Beringia for the founding population.[74][75] The micro-satellite diversity and distributions of the Y lineage specific to South America indicates that certain Amerindian populations have been isolated since the initial colonization of the region.[76] The Na-Dené, Inuit and Indigenous Alaskan populations exhibit haplogroup Q (Y-DNA) mutations, however are distinct from other indigenous Amerindians with various mtDNA mutations.[77][78][79] This suggests that the earliest migrants into the northern extremes of North America and Greenland derived from later populations.[80]
See also
- "Information About California Tribes" Northern California Indian Development Council
- Indigenous languages of the Americas
- List of pre-Columbian cultures
- List of traditional territories of the indigenous peoples of North America
- Population history of indigenous peoples of the Americas
- Aaron Carapella's maps of indigenous tribes of North America
Notes
- ↑ "Culture Areas Index". the Canadian Museum of Civilization.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Sturtevant and Trigger ix
- 1 2 3 4 "Preamble." Constitution of the Pawnee Nation of Oklahoma .Retrieved 5 Dec 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 "Cultural Thesaurus". National Museum of the American Indian. Accessed 8 April 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sturtevant and Trigger 241
- 1 2 3 4 Sturtevant and Trigger 198
- 1 2 3 4 5 Goddard 72
- ↑ Goddard 72 and 237
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Goddard 237
- ↑ Goddard 72, 237–238
- 1 2 3 Goddard 238
- ↑ Goddard 72 and 238
- 1 2 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 290
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Sturtevant and Trigger 161
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 293
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 81-82
- 1 2 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 291
- ↑ Sturtevant and Trigger 96
- ↑ Sturtevant and Trigger 255
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 69
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 205
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 214
- ↑ Sturtevant and Fogelson, 673
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Sturtevant and Fogelson, ix
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 374
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Sturtevant, 617
- ↑ Folgelson, ed. (2004), p. 315
- 1 2 3 4 Frank, Andrew K. Indian Removal. Oklahoma Historical Society's Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture. Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- 1 2 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 188
- 1 2 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 598-9
- 1 2 3 Sturtevant and Fogelson, 302
- ↑ Haliwa-Saponi Tribe. . Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- ↑ Hann 1993
- ↑ Sturtevant and Fogelson, 78, 668
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Hann 1996, 5-13
- ↑ Milanich 1999, p. 49.
- ↑ Milanich 1996, p. 46.
- ↑ Hann 2003:11
- ↑ Sturtevant and Fogelson, 190
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 D'Azevedo, ix
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Pritzker, 230
- ↑ D'Azevedo, 161-2
- 1 2 3 Loether, Christopher. "Shoshones". Encyclopedia of the Great Plains. Retrieved 20 Oct 2013.
- 1 2 3 Shimkin 335
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Murphy and Murphy 306
- 1 2 3 Murphy and Murphy 287
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Thomas, Pendleton, and Cappannari 280–283
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 D'Azevedo, 339
- 1 2 3 4 D'Azevedo, 340
- ↑ Nicholas, Walter S. "A Short History of Johnsondale". RRanch.org. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ↑ Pritzker 112
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 Heizer ix
- ↑ Heizer 205-7
- ↑ Heizer 190
- ↑ Heizer 593
- ↑ Heizer 769
- ↑ Heizer 249
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Mexico: Map". Ethnologue. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ↑ "Paipai Language (Akwa'ala)". Native Languages of the Americas. Retrieved 10 Sept 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 Steward, Julian H. (1948) Editor. Handbook of South American Indians. Volume 4 The Circum-Caribbean Tribes. Smithsonian Institution Bureau of American Ethnology Bulletin 143.
- ↑ "Aboriginal Roots of Cuban Culture". (retrieved 9 July 2011)
- 1 2 3 4 "Prehistory of the Caribbean Culture Area". Southeast Archaeological Center. (retrieved 9 July 2011)
- ↑ "Cacaopera". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. (retrieved 1 Dec 2011)
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "Languages of Bolivia". Ethnologue. Retrieved 23 Oct 2012.
- ↑ "Apiaká: Introduction". Instituto Socioambiental: Povos Indígenas no Brasil. Retrieved 28 March 2012
- ↑ "Huachipaeri". Ethnologue. Retrieved 18 Feb 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "Cultural Thesaurus". National Museum of the American Indian. (retrieved 18 Feb 2011)
- ↑ "Puelche". Encyclopedia Brittanica. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
- ↑ Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (Ed.). (2005). Ethnologue: Languages of the world (15th ed.). Dallas, TX: SIL International. ISBN 1-55671-159-X. (Online version: http://www.ethnologue.com).
- ↑ "Y-Chromosome Evidence for Differing Ancient Demographic Histories in the Americas" (PDF). Department of Biology, University College, London; Departamento de Gene´tica, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil; Instituto Venezolano de Investigaciones Cientı´ficas, Caracas, Venezuela; Departamento de Gene´tica, Universidade Federal do Parana´, Curitiba, Brazil; 5Department of Anthropology, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque; 6Laboratorio de Gene´tica Humana, Universidad de los Andes, Bogota´; Victoria Hospital, Prince Albert, Canada; Subassembly of Medical Sciences, Mongolian Academy of Sciences, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia; Laboratorio de Gene´tica Molecular, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia, Medellı´n, Colombia; Université de Montréal. University College London 73:524–539. 2003. Retrieved 2010-01-22.
- ↑ Orgel L (2004). "Prebiotic chemistry and the origin of the RNA world" (PDF). Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 39 (2): 99–123. doi:10.1080/10409230490460765. PMID 15217990. Retrieved 2010-01-19.
- 1 2 Wendy Tymchuk, Senior Technical Editor (2008). "Learn about Y-DNA Haplogroup Q" (Verbal tutorial possible). Genebase Systems. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
Haplogroups are defined by unique mutation events such as single nucleotide polymorphisms, or SNPs. These SNPs mark the branch of a haplogroup, and indicate that all descendents of that haplogroup at one time shared a common ancestor. The Y-DNA SNP mutations were passed from father to son over thousands of years. Over time, additional SNPs occur within a haplogroup, leading to new lineages. These new lineages are considered subclades of the haplogroup. Each time a new mutation occurs, there is a new branch in the haplogroup, and therefore a new subclade. Haplogroup Q, possibly the youngest of the 20 Y-chromosome haplogroups, originated with the SNP mutation M242 in a man from Haplogroup P that likely lived in Siberia approximately 15,000 to 20,000 years before present
- ↑ Wells, Spencer; Read, Mark (2002). The Journey of Man – A Genetic Odyssey (Digitised online by Google books). Random House. ISBN 0-8129-7146-9. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ↑ "First Americans Endured 20,000-Year Layover – Jennifer Viegas, Discovery News". Retrieved 2009-11-18.
Archaeological evidence, in fact, recognizes that people started to leave Beringia for the New World around 40,000 years ago, but rapid expansion into North America didn't occur until about 15,000 years ago, when the ice had literally broken
page 2 Archived March 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. - ↑ Than, Ker (2008). "New World Settlers Took 20,000-Year Pit Stop". National Geographic Society. Retrieved 2010-01-23.
Over time descendants developed a unique culture—one that was different from the original migrants' way of life in Asia but which contained seeds of the new cultures that would eventually appear throughout the Americas
- ↑ "Summary of knowledge on the subclades of Haplogroup Q". Genebase Systems. 2009. Archived from the original on 2011-05-10. Retrieved 2009-11-22.
- ↑ Ruhlen M (November 1998). "The origin of the Na-Dene". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (23): 13994–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.23.13994. PMC 25007
 . PMID 9811914.
. PMID 9811914. - ↑ Zegura SL, Karafet TM, Zhivotovsky LA, Hammer MF; Karafet; Zhivotovsky; Hammer (January 2004). "High-resolution SNPs and microsatellite haplotypes point to a single, recent entry of Native American Y chromosomes into the Americas". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 21 (1): 164–75. doi:10.1093/molbev/msh009. PMID 14595095.
- ↑ Juliette Saillard, Peter Forster, Niels Lynnerup1, Hans-Jürgen Bandelt and Søren Nørby (2000). "mtDNA Variation among Greenland Eskimos. The Edge of the Beringian Expansion". Laboratory of Biological Anthropology, Institute of Forensic Medicine, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research,University of Cambridge, Cambridge, University of Hamburg, Hamburg. Retrieved 2009-11-22.
The relatively lower coalescence time of the entire haplogroup A2 including the shared sub-arctic branches A2b (Siberians and Inuit) and A2a (Eskimos and Na-Dené) is probably due to secondary expansions of haplogroup A2 from the Beringia area, which would have averaged the overall internal variation of haplogroup A2 in North America.
- ↑ A. Torroni; T. G. Schurr; C. C. Yang; EJE. Szathmary; R. C. Williams; M. S. Schanfield; G. A. Troup; W. C. Knowler; D. N. Lawrence; K. M. Weiss; D. C. Wallace. "Native American Mitochondrial DNA Analysis Indicates That the Amerind and the Nadene Populations Were Founded by Two Independent Migrations". Center for Genetics and Molecular Medicine and Departments of Biochemistry and Anthropology, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Genetics Society of America. Vol 130, 153-162. Retrieved 2009-11-28.
The divergence time for the Nadene portion of the HaeIII np 663 lineage was about 6,000-10,000 years. Hence, the ancestral Nadene migrated from Asia independently and considerably more recently than the progenitors of the Amerinds
References
- D'Azevedo, Warren L., volume editor. Handbook of North American Indians, Volume 11: Great Basin. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution, 1986. ISBN 978-0-16-004581-3.
- Hann, John H. "The Mayaca and Jororo and Missions to Them", in McEwan, Bonnie G. ed. The Spanish Missions of "La Florida". Gainesville, Florida: University Press of Florida. 1993. ISBN 0-8130-1232-5.
- Hann, John H. A History of the Timucua Indians and Missions. Gainesville, Florida: University Press of Florida, 1996. ISBN 0-8130-1424-7.
- Hann, John H. (2003). Indians of Central and South Florida: 1513-1763. University Press of Florida. ISBN 0-8130-2645-8.
- Heizer, Robert F., volume editor. Handbook of North American Indians, Volume 8: California. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution, 1978. ISBN 978-0-16-004574-5.
- Milanich, Jerald (1999). The Timucua. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-21864-5. Retrieved June 11, 2010.
- Pritzker, Barry M. A Native American Encyclopedia: History, Culture, and Peoples. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. ISBN 978-0-19-513877-1.
- Steward, Julian H., editor. Handbook of South American Indians, Volume 4: The Circum-Caribbean Tribes. Smithsonian Institution, 1948.
- Sturtevant, William C., general editor and Bruce G. Trigger, volume editor. Handbook of North American Indians: Northeast. Volume 15. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1978. ASIN B000NOYRRA.
- Sturtevant, William C., general editor and Raymond D. Fogelson, volume editor. Handbook of North American Indians: Southeast. Volume 14. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution, 2004. ISBN 0-16-072300-0.
.svg.png)
