Oil production and smuggling in ISIL
Oil production and smuggling is the major revenue maker for the self-declared state of Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL/ISIS),[1][2] its product being termed "the 'black gold' feeding the 'black flag'".[2] Oil extracted from fields controlled by ISIL is mainly distributed within most its territory, but also smuggled to surrounding states at below market prices.
While oil products, petrol and mazout, are the backbone of the economy of ISIL-controlled areas with mazout being the power source for generators for electricity,[2] not all energy production is provided by oil. Hydroelectric power plants have been captured in northern Syria, so the Tabqa Dam, the Baath Dam, and, from 2012-2015, the Tishrin Dam.[3] Some electric power has been sold back to the Syrian government.[4] The Syrian government is also reported to send technicians to support and maintain ISIL-controlled gas power plants, and, in return, receives electricity.[5]
Oil as a source of revenue for ISIL
Estimates of the income ISIL derives from its oil operations vary. In 2014, Dubai-based energy analysts put the combined oil revenue from ISIL's Iraqi-Syrian production as high as US$3 million per day.[6] An estimate from October 2015 indicates the production to be about 34,000-40,000 bpd that is sold at US$20–45 at the wellhead generating an income of US$1.5 million per day.[2] Another 2015 estimate sets the monthly income as high as US$40 million.[7] Various other reports indicated in 2015 that ISIS obtained 1.1 to 1.5 million dollars a day from selling of oil and its products.[8][9][10] These estimates, however, may have to be revised due to increased air strikes targeting oil production and distribution at the end of 2015.[11] Thus an estimate for March 2016 was a monthly income of about US$20 million.[12]
Oil fields under ISIS control
In 2013 ISIL moved operations from the north of Syria to its east in recognition of the importance of the oil fields for its operations, among the fields in the Deir Ezzor region such as the al-Omar, the Deiro and the al-Tanak fields, and outside this region, the al-Jabsah fields and al Tabqa fields.[13] Deir Ezzor oil field is located in Deir ez-Zor province that produces 34,000-40,000 barrels a day. al-Omar and al-Tanak are top producing and beneficial oil fields. Quality of Petroleum determine price of each barrel and is sold at the wellhead 25 to 45 dollars.[10] al-Omar is an extensive oil and its oil is sold 45 dollars a barrel.[8][9][10]
In Iraq ISIL conquered the Ajil and Allas oil fields in northern Iraq during the Mosul campaign in 2014. These areas were later recaptured by the Iraq army.[2] Also, in north of Iraq, Qayyarah oil filed, controls by ISIS and produces 8,000 barrels a day of heavy crude oil.[8] Ajil in north of Tikrit and Himiran are important ISIS-controlled oil field in Iraq.[14] ISIL has been able recruit engineers and expert personnel to manage the oil production sites. Oil production is centrally controlled by the top leadership. Until his death in May 2015, Abu Sayyaf had been the "emir" or top official for oil production[2] controlling oil production from 200-plus wells.[11]
At the end of September 2016, Rudaw (a Kurdish media organization) reported that ISIL no longer controlled any Iraqi oil after Shargat and Qayyarah had been recaptured by the Iraqi army.[15]
Local distribution
ISIL makes its money at the pump where it sells its products to usually independent traders from Syria and Iraq.[13] In addition, ISIL taxes oil in the distribution system.[11] It has been estimated that there is a fleet of about 1,000 delivery trucks.[7] Oil is brought to local refineries to produce petrol and mazout.[13] Many "refineries" are just rudimentary furnaces spread along the roadsides.[16] Most of these oil products are sold within ISIL-controlled areas in Syria and Iraq by traders. Rebel-held areas in northern Syria are also receiving oil from ISIL.[13]
ISIS has several markets in Iraqi and Syrian towns and provinces. Some of the largest ISIS oil market are Manbij, Al-Bab, and Al-Qa'im.[8]
Oil smuggling
Oil smuggling to areas outside of Syria is profitable and brings contraband to Turkey, Jordan, Iraq and Iran.[17] A network to smuggle oil had been in place since at least the 1990s when Saddam Hussein evaded sanctions and smuggled oil out of Iraq.[16] A report by The Guardian in 2014 suggested that corruption and bribery facilitated transport of oil from ISIL-controlled areas into surrounding areas.[17]
In 2014 it was reported that the U.S. government had put diplomatic pressure on Turkey and the Kurdish government to take more steps to curtail smuggling.[18]
In November 2015 the Russian Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev indicated to have information that some Turkish officials have a "direct financial interest" in the oil trade with ISIL,[19] an assertion rejected by Turkish Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdoğan.[20] Vladimir Putin indicated that the extent of the oil smuggling had reached commercial-scale with trucks operating day and night as a "living oil pipe".[21] Officials from the US, however, responded that in their view only a small amount of oil is smuggled into Turkey and that this is economically insignificant.[22] According to Adam Szubin, acting U.S. Under Secretary of the Treasury for Terrorism and Financial Intelligence, most of the oil that leaves ISIL-controlled areas is going to places that are under control of the Syrian government.[23]
Subsequently, Turkey has been further implicated as an important recipient of smuggled oil. Thus, in January 2016 the Israeli Defence minister alleged Turkey buys oil from ISIS[24] In March 2016, an RT documentary presented documents left by retreating ISIL operatives and witness reports that also suggested a link between ISIL's oil production and support by Turkey that, in turn, benefits from cheap oil.[25]
Arab media accused Israel of being a major buyer of oil smuggled out of the ISIL-held Syrian and Iraqi territories.[26] According to this conspiracy theory, oil is smuggled to Zakhu where Israeli and Turkish dealers would determine the price, the oil is then sent as Kurdish oil to Silopi, Turkey, and transported to Turkish ports (such as Ceyhan) and shipped to Israel.[26]
Ways of smuggling
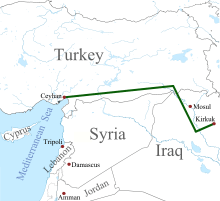
ISIL transfers oil in different ways out of its territory. Oil can be trucked to Turkey, refined there and be used in Turkey or transported to tankers at the ports of Ceyhan or Dortyol.[27] Oil may be sold to middlemen in northern Iraq who then mix it with legitimate oil that enters through one of many feeders the Kirkuk-Ceyhan pipeline.[27] At the end of the pipeline it is difficult to determine if some ISIS oil is present in the mix that is supposed to come from Kurdish fields.[27]
Another way of smuggling is the transport of oil to Jordan. Smugglers goes south through Al Anbar province towards Jordan.[8] In fact, Al Anbar known as a major smuggling hub in Iraq.[14] Sami Khalaf, an oil smuggler and former Iraqi intelligence officer under Saddam Hussein, said that: "We buy an oil tanker carrying around 26 to 28 tonnes [of oil] for $4,200. We sell it in Jordan for $15,000. Each smuggler takes around eight tankers a week." Also, he added: "smugglers typically paid corrupt border officials $650 to pass through each checkpoint."[14]
ISIL oil production as a military target
While degrading oil operations is an obvious target for military operations, the United States is reported to have refrained from using this approach out of concerns for civilian casualties and destabilizing the life of a 10 million population that depends on oil from ISIL production.[7][13][16] Also, rebel-held areas supported by the U.S. depend on ISIL oil for sustenance.[13] Further, direct hits on oil fields could lead to a natural disaster and make future use difficult.[28]
.jpg)
Bloomberg Business reported in the fall of 2014 that U.S. airstrikes had significantly reduced ISIL oil business.[18] However, by early October 2015, Financial Times reported that only 196 of 10,600 air strikes by U.S. led coalition forces were conducted against oil infrastructure since August 2014 and that ISIL continued a very profitable oil business generating about $1.5 million per day.[2] In late 2015 a U.S. spokesman conceded that the effectiveness of past air strikes against oil-related targets had been grossly overestimated while the importance of oil production as a revenue maker had been underestimated.[16]
When in May 2015 U.S. forces conducted a raid that killed Abu Sayyaf, detailed records of the oil operation of ISIL were obtained.[11] The recognition of the significance of oil for ISIL and insights into its operations led to a new focus in air strikes.[11] Thus, on 21 October 2015 the U.S. launched operation Operation Tidal Wave II in reference to Operation Tidal Wave in WWII in a renewed effort to reduce the ability of ISIL to fund itself through oil production.[1][29]
After the November 2015 Paris attacks the French Defence Minister Jean-Yves Le Drian indicated that degradation of oil production as the "lifeblood" of ISIL is at the center of military strategy.[5] U.S. forces claimed to have destroyed at 116 fuel trucks near Deir ez-Zor by mid-November,[30] while Russian airstrikes hit about 1,000 oil tankers.[31] In an effort to reduce revenue for ISIL more oil tankers were destroyed later in the month.[32] Prior to targeted air raids, smuggling trucks had sometimes waited for weeks in queues near the oil fields to buy crude.[8] The defense ministry of Moscow released satellite images showing columns of waiting trucks near the border of Turkey.[33] After Russian air attacks against smuggling trucks, ISIS changed its system to prevent the formation of long queues.[8]
A report at the end of December 2015 indicated that ISIL was starting to have financial problems due to lower oil revenues resulting in lower salaries for foreign fighters and higher prices for electricity and oil in Raqqa.[34] A shortage of oil within ISIL-controlled territories has resulted in energy shortages with less electricity and water becoming available.[11] Also, smuggling of oil has decreased as it has become more dangerous and less lucrative.[11]
A 2016 analysis of ISIL's response to the air strikes on the oil infrastructure indicated the development of multiple tiny makeshift refineries in oil fields under their control.[12] These micro-refineries consist of a pit to store crude and a portable metal furnace to distill it into fuel.[12] The operation is dirty and relatively inefficient but harder to destroy. According to Stratfor income from oil has declined to about $20 million a month (March 2016).[12]
2015 Production rate and price in the ISIS-controlled oil fields
Below table shows oil production amount and price in important ISIS-controlled oil fields (December 2015).[8]
| Oil fields | Production rate (barrels per day) | Price of each barrel |
|---|---|---|
| al-Tanak | 11,000-12,000 | $40 |
| al-Omar | 6,000-9,000 | $45 |
| al-Jabseh | 2,500-3,000 | $30 |
| al-Tabqa | 1,500-1,800 | $20 |
| al-Kharata | 1,000 | $30 |
| al-Shoula | 650-800 | $30 |
| Deiro | 600-1,000 | $30 |
| al-Taim | 400-600 | $40 |
| al-Rashid | 200-300 | $25 |
See also
References
- 1 2 Jenny Cosgrove (10 November 2015). "US Air Force pledges to 'degrade' ISIS oil cash". CNBC. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Erika Solomon; Guy Chazan; Sam Jones (14 October 2015). "Isis Inc: how oil fuels the jihadi terrorists". Financial Times. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ↑ Harry Istepanian (22 September 2014). "Iraq's electricity: from crisis to ISIS". Power Engineering International. Retrieved 18 November 2015.
- ↑ Fisher, Max (12 June 2014). "How ISIS is exploiting the economics of Syria's civil war". Vox. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- 1 2 Keiligh Baker (19 November 2015). "Putin hits ISIS where it hurts: Russia hits more than 200 targets in 24 hours as Moscow aims to cut off jihadists' income by taking out refinery and oil trucks". Daily Mail. Retrieved 19 November 2015.
- ↑ Karen Leigh (2 August 2014). "ISIS Makes Up To $3 Million a Day Selling Oil, Say Analysts". ABC news. Retrieved 8 October 2014.
- 1 2 3 "US airstrikes destroy more than 100 ISIS oil trucks in Syria". RT. 16 November 2015. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Solomon, Erika; Kwong, Robin; Bernard, Steven (11 December 2015). "Inside Isis Inc: The journey of a barrel of oil". Financial Times. Retrieved 27 December 2015.
- 1 2 Staff writers (18 December 2015). "Russia unveils schemes of Islamic State's oil supplies to Turkey to UN". TASS. Retrieved 27 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 Solomon, Erika; Chazan, Guy; Jones, Sam (14 October 2015). "Jihadis' oil operation forces even their enemies to trade with them". Financial Times. Retrieved 28 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Van Heuvelen B and staff (28 December 2015). "Armed with intel, U.S. strikes curtail IS oil sector". Iraq Oil Report. Retrieved 29 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Joby Warrick (7 July 2016). "Satellite photos show Islamic State installing hundreds of makeshift oil refineries to offset losses from airstrikes". Washington Post. Retrieved 13 July 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Financial Times: Inside Isis Inc: The journey of a barrel of oil
- 1 2 3 Hawramy, Fazel; Mohammad, Shalaw; Harding, Luke (19 November 2014). "Inside Islamic State's oil empire: how captured oilfields fuel Isis insurgency". Theguardian. Retrieved 27 December 2015.
- ↑ "ISIS no longer controls any Iraqi oil". Rudaw Media Network. September 27, 2016. Retrieved October 8, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Cam Simpson; Matthew Philips (19 November 2015). "Why ISIS has all the money it needs". Bloomberg Business. Retrieved 19 November 2015.
- 1 2 Fazel Hawramy; Shalaw Mohammed; Luke Harding (19 November 2014). "Inside Islamic State's oil empire: how captured oilfields fuel Isis insurgency". The Guardian. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- 1 2 Matthew Philips (14 October 2014). "Islamic State Loses Its Oil Business". Bloomberg Business. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ↑ "Ankara defends ISIS, Turkish officials have financial interest in oil trade with group - PM Medvedev". RT. 25 November 2015. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ↑ Anna Smolchenko; Fulya Ozerkan (26 November 2015). "Russia targets Turkish economy over downed plane". Yahoo News. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ "'Commercial scale' oil smuggling into Turkey becomes priority target of anti-ISIS strikes". RT. 27 November 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- ↑ "IS oil smuggling to Turkey insignificant: US official". Middle East Eye. 5 December 2015. Retrieved 7 December 2015.
- ↑ "Syria's Assad buying 'a great deal' of ISIS oil, US official says". Fox News. 11 December 2015. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- ↑ "Israeli defence minister accuses Turkey of buying IS oil". BBC. 26 January 2016. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ↑ "ISIS, oil & Turkey: What RT found in Syrian town liberated from jihadists by Kurds (EXCLUSIVE)". RT. 24 March 2016. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- 1 2 "Israel has become the main buyer for oil from ISIS controlled territory, reports "al-Araby al-Jadeed."". Globes. 11 November 2015. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- 1 2 3 Erin Banco (29 March 2016). "How ISIS Oil Ended Up On US Streets". IBTimes. Retrieved 13 July 2016.
- ↑ "How ISIS steals oil to stay in power". PBS. 19 October 2015. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- ↑ Martin Matyshak (13 November 2015). "With ISIS Making Millions, U.S. Boosts Its Attacks on Oil Fields". The Fiscal Times. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- ↑ "Media Manipulation: US Shows Footage of Russian Airstrike against ISIS as Its Own". Global Research. 22 November 2015. Retrieved 23 November 2015.
- ↑ "Russian airstrikes destroy 472 terrorist targets in Syria in 48 hours, 1,000 oil tankers in 5 days". RT. 23 November 2015. Retrieved 23 November 2015.
- ↑ Lizzie Dearden (24 November 2015). "Isis in Syria: US air strikes destroys 283 oil tankers used for smuggling to fund terror group". The Independent. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ↑ Brooks-Pollock, Tom (4 December 2015). "Russia unveils 'proof' Turkey's Erdogan is smuggling Isis oil across border from Syria". Independent. Retrieved 27 December 2015.
- ↑ "Höhere Steuern, niedrigere Gehälter: Terror-Staat IS kämpft gegen die Pleite" (in German). Focus. 27 December 2015. Retrieved 27 December 2015.