Hydrothorax
| Hydrothorax | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | pulmonology |
| ICD-10 | J94.8 |
| ICD-9-CM | 511.8 |
| DiseasesDB | 10122 |
| MeSH | D006876 |
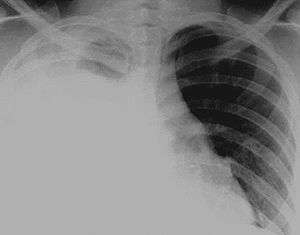
Hydrothorax is a type of pleural effusion in which serous fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity. This condition is most likely to develop secondary to congestive heart failure, but may rarely develop in patients with cirrhosis or ascites. Hepatic hydrothorax is often difficult to manage in end-stage liver failure and often fails to respond to therapy.
In similar pleural effusions, the fluid is blood in hemothorax (as in major chest injuries), pus in pyothorax (resulting from chest infections), and lymph in chylothorax (resulting from rupture of the thoracic duct).
Treatment
Treatment of hydrothorax is difficult for several reasons. The underlying condition needs to be corrected; however, often the source of the hydrothorax is end stage liver disease and correctable only by transplant. Chest tube placement should not occur. Other measures such as a TIPS procedure are more effective as they treat the etiology of the hydrothorax, but have complications such as worsened hepatic encephalopathy.