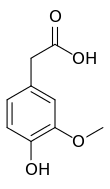
Homovanillic acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid | |||
| Other names
2-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 306-08-1 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:545959 | ||
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1562 | ||
| ChemSpider | 1675 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.616 | ||
| KEGG | C05582 | ||
| MeSH | Homovanillic+acid | ||
| PubChem | 1738 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C9H10O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 182.18 g·mol−1 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Homovanillic acid (HOC6H3(OCH3)CH2COOH; synonyms: 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid; HVA; 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzeneacetic acid; 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylacetic acid) is a major catecholamine metabolite and is produced by the consecutive action of monoamine oxidase and catechol-O-methyl transferase on dopamine.[1] It is used as a reagent to detect oxidative enzymes, and is associated with dopamine levels in the brain.
In psychiatry and neuroscience, brain and cerebrospinal fluid levels of HVA are measured as a marker of metabolic stress caused by 2-deoxy-D-glucose.[2] HVA presence supports a diagnosis of neuroblastoma and malignant pheochromocytoma.
Fasting plasma levels of HVA are known to be higher in females than in males. This does not seem to be influenced by adult hormonal changes, as the pattern is retained in the elderly and post-menopausal as well as transsexuals according to their genetic sex, both before and during cross-sex hormone administration. Differences in HVA have also been correlated to tobacco usage, with smokers showing significantly lower amounts of plasma HVA.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Lambert, G.W.; Eisenhofer, G.; Jennings, G.L.; Esler, M.D. "Regional homovanillic acid production in humans". Life Sciences. 53 (1): 63–75. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(93)90612-7.
- ↑ Marcelis M, Suckling J, Hofman P, Woodruff P, Bullmore E, van Os J (September 2006). "Evidence that brain tissue volumes are associated with HVA reactivity to metabolic stress in schizophrenia". Schizophr. Res. 86 (1–3): 45–53. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2006.05.001. PMID 16806836.
- ↑ Giltay E, Kho K, Blandjaar B, Verbeek M, Geurtz P, Geleijnse J, Gooren L (July 2005). "The sex difference of plasma homovanillic acid is unaffected by cross-sex hormone administration in transsexual subjects". J Endocrinol. 187 (1): 109–16. doi:10.1677/joe.1.06307. PMID 16214946.