Religion in Serbia
Religion in Serbia (2011)
Serbia has been traditionally a Christian country since the Christianization of Serbs by Byzantine Christian missionaries Cyril and Methodius in the 9th century. Therefore, the dominant confession is Eastern Orthodoxy of the Serbian Orthodox Church. During the Ottoman rule of the Balkans, Sunni Islam established itself in the territories of Serbia, mainly in southern regions of Sandžak, Preševo, and Bujanovac, as well as in the disputed territory of Kosovo and Metohija. Roman Catholicism has roots in the country since the presence of Hungarians in Vojvodina (mainly in the northern part of the province), while Protestantism arrived in the 18th and 19th century with the settlement of Slovaks in Vojvodina.
Demographics
| 1921[1] | 1991 | 2002[2] | 2011 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Orthodox Christians | 3,321,090 | 75.85 | 6,347,026 | 81.8 | 6,371,584 | 84.98 | 6,079,395 | 84.59 |
| Roman Catholics | 751,429 | 17.16 | 496,226 | 6.4 | 410,976 | 5.48 | 356,957 | 4.97 |
| Muslims | 97,672 | 2.23 | 224,120 | 2.89 | 239,658 | 3.2 | 222,829 | 3.1 |
| Protestants | no data | no data | 88,275 | 1.14 | 80,837 | 1.08 | 71,284 | 0.99 |
| Jews | 26,464 | 0.6 | 740 | 0.01 | 785 | 0.01 | 578 | 0.01 |
| Total | 4,378,595 | 100 | 7,759,571 | 100 | 7,498,001 | 100 | 7,186,862 | 100 |
Christianity
Orthodoxy

Most of the citizens of Serbia are adherents of the Serbian Orthodox Church, while the Romanian Orthodox Church is also present in parts of Vojvodina inhabited by ethnic Romanian minority. Besides Serbs, other Christians of the Orthodox Church include Montenegrins, Romanians, Macedonians, Bulgarians, Vlachs and majority of Roma people.
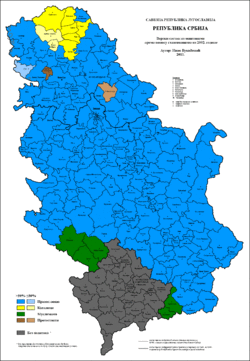
Orthodox Christianity predominates throughout most of Serbia, excluding several municipalities and cities near border with neighboring countries where adherents of Islam or Roman Catholicism are more numerous as well as excluding two predominantly Protestant municipalities in Vojvodina. Orthodoxy also predominates in most of the large cities of Serbia, excluding the cities of Subotica (which is mostly Catholic) and Novi Pazar (which is mostly Muslim).
The identity of ethnic Serbs was historically largely based on Orthodox Christianity and on the Serbian Orthodox Church, to the extent of the claims that those who are not its faithful are not Serbs. However, the conversion of the south Slavs from paganism to Christianity took place before the Great Schism, the split between the Greek East and the Latin West. After the Schism, generally speaking, those Christians who lived within the Orthodox sphere of influence became "Orthodox" and those who lived within the Catholic sphere of influence, under Rome as the patriarchal see of the West, became "Catholic." Some ethnologists consider that the distinct Serb and Croat identities relate to religion rather than ethnicity. With the arrival of the Ottoman Empire, some Serbs converted to Islam. This was particularly, but not wholly, so in Bosnia. The best known Muslim Serb is probably either Mehmed Paša Sokolović or Meša Selimović. Since the second half of the 19th century, some Serbs converted to Protestantism, while historically some Serbs also were Latin Rite Catholic (especially in Dalmatia) or Eastern Catholic.
Roman Catholicism

Roman Catholicism is present mostly in the northern part of Vojvodina, notably in the municipalities with Hungarian ethnic majority (Bačka Topola, Mali Iđoš, Kanjiža, Senta, Ada, Čoka) and in the multi-ethnic city of Subotica and multi-ethnic municipality of Bečej. It is represented mainly by the following ethnic groups: Hungarians, Croats, Bunjevci, Germans, Slovenes, Czechs, etc. A smaller number of Roma people, Slovaks and Serbs are also Catholic. The ethnic Rusyns and a smaller part of the ethnic Ukrainians are primarily Eastern Rite Catholics.
Protestantism
The largest percentage of the Protestant Christians in Serbia on municipal level is in the municipalities of Bački Petrovac and Kovačica, where the absolute or relative majority of the population are ethnic Slovaks (most of whom are adherents of Protestant Christianity). Some members of other ethnic groups (especially Serbs in absolute terms and Hungarians and Germans in proportional terms) are also adherents of various forms of Protestant Christianity.
There are various neo-Protestant groups in the country, including Methodists, Seventh-day Adventists, Evangelical Baptists (Nazarene), and others. Many of these groups are situated in the culturally diverse province of Vojvodina. Prior to end of World War II number of Protestants in the region was larger.
According to the 2002 census, the largest Protestant communities were recorded in the municipalities of Kovačica (12,350) and Bački Petrovac (9,613), as well as in the second largest Serbian city Novi Sad (9,428), which is predominately Orthodox. While Protestants from Kovačica and Bački Petrovac are mostly Slovaks, services in most of the Protestant churches in Novi Sad are performed in the Serbian language.[3]
Protestantism (mostly in its Nazarene form) started to spread among Serbs in Vojvodina in the last decades of the 19th century. Although, percentage of Protestants among Serbs is not large, it is the only religious form besides Orthodoxy, which is today widely spread among Serbs.
Islam

Islam is mostly present in the southwest of Serbia in the region of Sandžak or Raška (notably in the city of Novi Pazar and municipalities of Tutin and Sjenica), as well as in parts of southern Serbia (municipalities of Preševo and Bujanovac). Ethnic groups whose members are mostly adherents of Islam are: Bosniaks, Muslims by nationality, Albanians, and Gorani. A significant number of Roma people are also adherents of Islam.
Adherents belong to one of the two following communities - Islamic Community of Serbia or the Islamic Community in Serbia.
Judaism

As of 2011, out of 787 declared Jews in Serbia 578 stated their religion as Judaism, mostly in the cities of Belgrade (286), Novi Sad (84), Subotica (75) and Pančevo (31).[4] The only remaining functioning synagogue in Serbia is the Belgrade Synagogue. There are also small numbers of Jews in Zrenjanin and Sombor, with isolated families scattered throughout the rest of Serbia.
Irreligion
About 1.1% of Serbian population is atheist. Religiosity was lowest in Novi Beograd, with 3.5% of population being atheists (compare to whole Belgrade's and Novi Sad's 1.5%) and highest in rural parts of the country, where atheism in most municipacities went below 0.01%.[5]
In a 2009 Gallup poll, 44% of respondents in Serbia answered 'no' to the question "Is religion an important part of your daily life?"[6]
Role of the religion in public life
Freedom of religion is a right defined by the Constitution of Serbia, which also defines all religious communities as equal in front of the law and separate from the state.
Public schools allow religious teaching in cooperation with religious communities having agreements with the state, but attendance is not mandated. Religion classes (Serbian: verska nastava) are organized in public elementary and secondary schools, most commonly coordinated with the Serbian Orthodox Church, but also with the Roman Catholic Church and Islamic community.
The public holidays in Serbia also include the religious festivals of Orthodox Christmas and Orthodox Easter, as well as Saint Sava Day which is a working holiday and is celebrated as a Day of Spirituality as well as Day of Education. Believers of other faiths are legally allowed to celebrate their religious holidays.
See also
References
- ↑ Demographic growth and ethnographic changes in Serbia
- ↑ Book 3 Page 13
- ↑ "Mapa verskih zajednica Novog Sada" (PDF). Ehons.org. Retrieved 2013-10-07.
- ↑ http://pod2.stat.gov.rs/ObjavljenePublikacije/Popis2011/Knjiga4_Veroispovest.pdf
- ↑ Book 3 Pages 13-16
- ↑ "Gallup Global Reports". Gallup.com. Retrieved 2013-10-07.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Religion in Serbia. |