Hindgut
| Hindgut | |
|---|---|
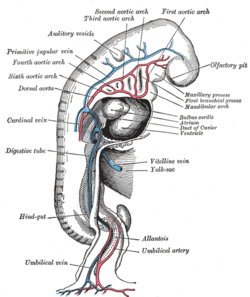 Profile view of a human embryo estimated at twenty or twenty-one days old. (Hindgut labeled at lower left.) | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 10 |
| Precursor | Mesenchyme |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | metenteron |
| TE | E5.4.9.0.2.0.1 |
| FMA | 45618 |
The hindgut (or epigaster) is the posterior (caudal) part of the alimentary canal. In mammals, it includes the distal third of the transverse colon and the splenic flexure, the descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum. In zoology, the term hindgut refers also to the cecum and ascending colon.
Blood flow
Arterial supply is by the Inferior mesenteric artery, and venous drainage is to the portal venous system. Lymphatic drainage is to the chyle cistern.
Autonomic innervation
The hindgut is innervated via the inferior mesenteric plexus. Sympathetic innervation is from the Lumbar splanchnic nerves (L1-L2), parasympathetic innervation is from S2-S4.
Additional images
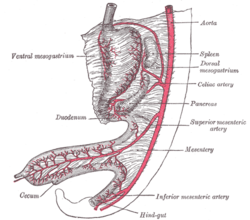 Abdominal part of digestive tube and its attachment to the primitive or common mesentery. Human embryo of six weeks.
Abdominal part of digestive tube and its attachment to the primitive or common mesentery. Human embryo of six weeks.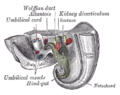 Tail end of human embryo twenty-five to twenty-nine days old.
Tail end of human embryo twenty-five to twenty-nine days old._-_ZooKeys-241-077-g006.jpeg) Metenteron in the milliped Illacme plenipes.
Metenteron in the milliped Illacme plenipes.
See also
External links
- digest-035—Embryo Images at University of North Carolina
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.