Heidelberg
| Heidelberg | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
| ||
 Heidelberg | ||
| Coordinates: 49°25′N 08°43′E / 49.417°N 8.717°ECoordinates: 49°25′N 08°43′E / 49.417°N 8.717°E | ||
| Country | Germany | |
| State | Baden-Württemberg | |
| Admin. region | Karlsruhe | |
| District | Urban district | |
| Government | ||
| • Lord Mayor | Dr. Eckart Würzner (Ind.) | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 108.83 km2 (42.02 sq mi) | |
| Population (2015-12-31)[1] | ||
| • Total | 156,267 | |
| • Density | 1,400/km2 (3,700/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | |
| Postal codes | 69115–69126 | |
| Dialling codes | 06221 | |
| Vehicle registration | HD | |
| Website | heidelberg.de | |
Heidelberg (German pronunciation: [ˈhaɪdl̩bɛʁk]) is a city situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. The fifth-largest town in the State of Baden-Württemberg after Stuttgart, Karlsruhe, Mannheim and Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg is part of the densely populated Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region. In 2015, over 156,000 people lived in the city.
A former residence of the Electorate of the Palatinate, Heidelberg is the location of Heidelberg University, contemporary Germany's oldest and among its most reputable universities. Heidelberg is a popular tourist destination due to its romantic and picturesque cityscape, including Heidelberg Castle and the baroque style Old Town.
Geography

Heidelberg is in the Rhine Rift Valley, on the left bank of the lower part of the Neckar in a steep valley in the Odenwald. It is bordered by the Königsstuhl (568 m) and the Gaisberg (375 m) mountains. The Neckar here flows in an east-west direction. On the right bank of the river, the Heiligenberg mountain rises to a height of 445 meters. The Neckar flows into the Rhine approximately 22 kilometres north-west in Mannheim. Villages incorporated during the 20th century stretch from the Neckar Valley along the Bergstraße, a road running through the Odenwald hills.
Heidelberg is on European walking route E1 (Sweden-Umbria).



Flora and fauna
Since Heidelberg is among the warmest regions of Germany, plants atypical of the central-European climate flourish there, including almond and fig trees; there is also an olive tree in Gaisbergstraße. Alongside the Philosophenweg (Philosophers' Walk) on the opposite side of the Old Town, winegrowing was restarted in 2000.[2]
There is a wild population of African rose-ringed parakeets,[3] and a wild population of Siberian swan geese, which can be seen mainly on the islands in the Neckar near the district of Bergheim.
Administrative structures
Heidelberg is a unitary authority within the Regierungsbezirk Karlsruhe. The Rhein-Neckar-Kreis rural district surrounds it and has its seat in the town, although the town is not a part of the district. Heidelberg is a part of the Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region, often referred to as the Rhein-Neckar Triangle. This region consists of the southern part of the State of Hessen, the southern part of the State of Rhineland-Palatinate (Vorderpfalz), the administrative districts of Mannheim and Heidelberg, and the southern municipalities of the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis. The Rhein-Neckar Triangle became a European metropolitan area in 2005.
Heidelberg consists of 15 districts distributed in six sectors of the town. In the central area are Altstadt (the Old Town), Bergheim and Weststadt; in the north, Neuenheim and Handschuhsheim; in the east, Ziegelhausen and Schlierbach; in the south, Südstadt, Rohrbach, Emmertsgrund, and Boxberg; in the southwest, Kirchheim; in the west, Pfaffengrund, Wieblingen, and a new district, named Bahnstadt, is built on land in Weststadt and Wieblingen. The new district will have approximately 5,000–6,000 residents and employment for 7,000.
Neighbouring communes
The following towns and communes border the city of Heidelberg, beginning in the west and in a clockwise direction: Edingen-Neckarhausen, Dossenheim, Schriesheim, Wilhelmsfeld, Schönau, Neckargemünd, Bammental, Gaiberg, Leimen, Sandhausen, Oftersheim, Plankstadt, Eppelheim (all part of the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis) and Mannheim.
Climate
Heidelberg has an oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification Cfb), defined by the protected valley between the Pfälzerwald and the Odenwald. Year-round, the mild temperatures are determined by maritime air masses coming from the west. In contrast to the nearby Upper Rhine Plain, Heidelberg's position in the valley leads to more frequent easterly winds than average. The hillsides of the Odenwald favour clouding and precipitation. The warmest month is July, the coldest is January. Temperatures often rise beyond 30 °C (86 °F) in midsummer. According to the German Meteorological Service, Heidelberg was the warmest place in Germany in 2009.[4][5][6]

| Climate data for Heidelberg | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 3.8 (38.8) |
6.1 (43.0) |
10.9 (51.6) |
15.4 (59.7) |
19.9 (67.8) |
23 (73.4) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.1 (77.2) |
21.5 (70.7) |
15.3 (59.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
4.8 (40.6) |
15 (59.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.4 (36.3) |
3.7 (38.7) |
7.4 (45.3) |
11.2 (52.2) |
15.5 (59.9) |
18.1 (64.6) |
20.6 (69.1) |
20.1 (68.2) |
16.1 (61) |
11.5 (52.7) |
6.3 (43.3) |
3.3 (37.9) |
11.4 (52.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.4 (29.5) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
1.9 (35.4) |
4.9 (40.8) |
8.9 (48.0) |
12.2 (54.0) |
14 (57.2) |
13.8 (56.8) |
10.6 (51.1) |
6.7 (44.1) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
6.1 (42.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 56 (2.2) |
53 (2.1) |
53 (2.1) |
61 (2.4) |
79 (3.1) |
86 (3.4) |
71 (2.8) |
66 (2.6) |
53 (2.1) |
58 (2.3) |
66 (2.6) |
66 (2.6) |
770 (30.3) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 46 | 78 | 118 | 173 | 206 | 215 | 233 | 219 | 157 | 101 | 50 | 35 | 1,631 |
| Source #1: Intellicast[7] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Deutscher Wetterdienst[8] | |||||||||||||
History


Early history
Between 600,000 and 200,000 years ago, "Heidelberg Man" died at nearby Mauer. His jaw bone was discovered in 1907. Scientific dating determined his remains as the earliest evidence of human life in Europe. In the 5th century BC, a Celtic fortress of refuge and place of worship were built on the Heiligenberg, or "Mountain of Saints". Both places can still be identified. In 40 AD, a fort was built and occupied by the 24th Roman cohort and the 2nd Cyrenaican cohort (CCG XXIIII and CCH II CYR). The Romans built and maintained castra (permanent camps) and a signal tower on the bank of the Neckar. They built a wooden bridge based on stone pillars across it. The camp protected the first civilian settlements that developed. The Romans remained until 260 AD, when the camp was conquered by Germanic tribes.
Middle Ages
Modern Heidelberg can trace its beginnings to the fifth century. The village Bergheim ("Mountain Home") is first mentioned for that period in documents dated to 769 AD. Bergheim now lies in the middle of modern Heidelberg. The people gradually converted to Christianity. In 863 AD, the monastery of St. Michael was founded on the Heiligenberg inside the double rampart of the Celtic fortress. Around 1130, the Neuburg Monastery was founded in the Neckar valley. At the same time, the bishopric of Worms extended its influence into the valley, founding Schönau Abbey in 1142. Modern Heidelberg can trace its roots to this 12th-century monastery. The first reference to Heidelberg can be found in a document in Schönau Abbey dated to 1196. This is considered to be the town's founding date. In 1155, Heidelberg castle and its neighboring settlement were taken over by the house of Hohenstaufen. Conrad of Hohenstaufen became Count Palatine of the Rhine (German: Pfalzgraf bei Rhein). In 1195, the Electorate of the Palatinate passed to the House of Welf through marriage.

.jpg)
In 1214, Ludwig I, Duke of Bavaria acquired the Palatinate, as a consequence of which the castle came under his control. By 1303, another castle had been constructed for defense. In 1356, the Counts Palatine were granted far-reaching rights in the Golden Bull, in addition to becoming Electors. In 1386, Heidelberg University was founded by Rupert I, Elector Palatine.
Modern history
Heidelberg University played a leading part in the era of humanism and the Reformation, and the conflict between Lutheranism and Calvinism, in the 15th and 16th centuries. Heidelberg's library, founded in 1421, is the oldest existing public library in Germany. In April 1518, a few months after proclaiming his 95 Theses, Martin Luther was received in Heidelberg, to defend them. In 1537, the castle located higher up the mountain was destroyed by a gunpowder explosion. The duke's palace was built at the site of the lower castle.

Elector Frederick III, sovereign of the Electoral Palatinate from 1559 to 1576, commissioned the composition of a new Catechism for his territory. While the catechism's introduction credits the "entire theological faculty here" (at the University of Heidelberg) and "all the superintendents and prominent servants of the church" for the composition of the catechism, Zacharius Ursinus is commonly regarded as the catechism's principal author. Caspar Olevianus (1536–1587) was formerly asserted as a co-author of the document, though this theory has been largely discarded by modern scholarship. Johann Sylvan, Adam Neuser, Johannes Willing, Thomas Erastus, Michael Diller, Johannes Brunner, Tilemann Mumius, Petrus Macheropoeus, Johannes Eisenmenger, Immanuel Tremellius and Pierre Boquin are all likely to have contributed to the Catechism in some way. Frederick himself wrote the preface to the Catechism and closely oversaw its composition and publication. Frederick, who was officially Lutheran but had strong Reformed leanings, wanted to even out the religious situation of his highly Lutheran territory within the primarily Catholic Holy Roman Empire. The Council of Trent had just concluded with its conclusions and decrees against the Protestant faiths, and the Peace of Augsburg had only granted toleration for Lutheranism within the empire where the ruler was Lutheran. One of the aims of the catechism was to counteract the teachings of the Roman Catholic Church as well as Anabaptists and "strict" Gnesio-Lutherans like Tilemann Heshusius and Matthias Flacius, who were resisting Frederick's Reformed influences, particularly on the matter of Eucharist (the Lord's Supper). The Catechism-based each of its statements on biblical proof-texts, and Frederick himself would defend it as biblical, not reformed, at the 1566 Diet of Augsburg when he was called to answer to charges of violating the Peace of Augsburg. This was the Heidelberg Catechism, officially called the ″Catechism, or Christian Instruction, according to the Usages of the Churches and Schools of the Electoral Palatinate.″

In November 1619, the royal crown of Bohemia was offered to the Elector, Frederick V. (He was married to Elizabeth, eldest daughter of James VI and I of Scotland and England, respectively.) Frederick became known as the "Winter King", as he reigned for only one winter before the Imperial House of Habsburg regained the crown by force. His overthrow in 1621 marked the beginning of the Thirty Years' War. In 1622, after a siege of two months, the armies of the Catholic League, commanded by Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly, captured the town. Tilly gave the famous Bibliotheca Palatina from the Church of the Holy Spirit to the Pope as a present. The Catholic Bavarian branch of the House of Wittelsbach gained control over the Palatinate and the title of Prince-Elector. In 1648, at the end of the war, Frederick V's son Charles I Louis, Elector Palatine, was able to recover his titles and lands.
In late 1634 Imperialist forces attempted to take back the city, as the Swedish army had conquered it. They quickly took the city, but were unable to take the castle. As they prepared to blow up its fortifications with gunpowder the French army arrived, 30,000 men strong, led by Urbain de Maillé-Brézé, who had fought in many battles and participated in the Siege of La Rochelle (1627–1628), and Jacques-Nompar de Caumont, duc de La Force. They ended the siege and drove off the Catholic forces.[9]
To strengthen his dynasty, Charles I Louis arranged the marriage of his daughter Liselotte to Philip I, Duke of Orléans, brother of Louis XIV, king of France. In 1685, after the death of Charles Louis' son, Elector Charles II, Louis XIV laid claim to his sister-in-law's inheritance. The Germans rejected the claim, in part because of religious differences between local Protestants and the French Catholics, as the Protestant Reformation had divided the peoples of Europe. The War of the Grand Alliance ensued. In 1689, French troops took the town and castle, bringing nearly total destruction to the area in 1693. As a result of the destruction due to repeated French invasions related to the War of the Palatinate Succession coupled with severe winters, thousands of Protestant German Palatines emigrated from the lower Palatinate in the early 18th century. They fled to other European cities and especially to London (where the refugees were called "the poor Palatines"). In sympathy for the Protestants, in 1709–1710, Queen Anne's government arranged transport for nearly 6,000 Palatines to New York. Others were transported to Pennsylvania, and to South Carolina. They worked their passage and later settled in the English colonies there.
In 1720, after assigning a major church for exclusively Catholic use, religious conflicts with the mostly Protestant inhabitants of Heidelberg caused the Roman Catholic Prince-Elector Charles III Philip to transfer his residence to nearby Mannheim. The court remained there until the Elector Charles Theodore became Elector of Bavaria in 1777 and established his court in Munich. In 1742, Elector Charles Theodore began rebuilding the Palace. In 1764, a lightning bolt destroyed other palace buildings during reconstruction, causing the work to be discontinued.
1803 to 1933
Heidelberg fell to the Grand Duchy of Baden in 1803. Charles Frederick, Grand Duke of Baden, re-founded the university, named "Ruperto-Carola" after its two founders. Notable scholars soon earned it a reputation as a "royal residence of the intellect". In the 18th century, the town was rebuilt in the Baroque style on the old medieval layout.
In 1810, the French revolution refugee Count Charles Graimberg began to preserve the palace ruins and establish a historical collection. In 1815, the Emperor of Austria, the Emperor of Russia and the King of Prussia formed the "Holy Alliance" in Heidelberg. In 1848, the German National Assembly was held there. In 1849, during the Palatinate-Baden rebellion of the 1848 Revolutions, Heidelberg was the headquarters of a revolutionary army. It was defeated by a Prussian army near Waghaeusel. The city was occupied by Prussian troops until 1850. Between 1920 and 1933, Heidelberg University became a center of notable physicians Czerny, Erb, and Krehl; and humanists Rohde, Weber, and Gandolf.
Nazism and the World War II-period
During the Nazi period (1933–1945), Heidelberg was a stronghold of the NSDAP, (the National Socialist German Workers' Party) the strongest party in the elections before 1933 (the NSDAP obtained 30% at the communal elections of 1930[10]). The NSDAP received 45.9% of the votes in the German federal election of March 1933 (the national average was 43.9%).[11] Non-Aryan university staff were discriminated against. By 1939, one-third of the university's teaching staff had been forced out for racial and political reasons. The non-Aryan professors were ejected in 1933, within one month of Hitler's rise to power. The lists of those to be deported were prepared beforehand.
In 1934 and 1935, the Reichsarbeitsdienst (State Labor Service) and Heidelberg University students built the huge Thingstätte amphitheatre on the Heiligenberg north of the town, for Nazi Party and SS events. A few months later, the inauguration of the huge Ehrenfriedhof memorial cemetery completed the second and last NSDAP project in Heidelberg. This cemetery is on the southern side of the old part of town, a little south of the Königstuhl hilltop, and faces west towards France. During World War II and after, Wehrmacht soldiers were buried there.
During the Kristallnacht on November 9, 1938, Nazis burned down synagogues at two locations in the city. The next day, they started the systematic deportation of Jews, sending 150 to Dachau concentration camp. On October 22, 1940, during the "Wagner Buerckel event", the Nazis deported 6000 local Jews, including 281 from Heidelberg, to Camp Gurs concentration camp in France. Within a few months, as many as 1000 of them (201 from Heidelberg) died of hunger and disease.[12] Among the deportees from Heidelberg, the poet Alfred Mombert (1872–1942) left the camp in April 1941 thanks to the Swiss poet Hans Reinhart.[13] From 1942, the deportees who had survived internment in Gurs were deported to Eastern Europe, where most of them were murdered.
On March 29, 1945, German troops left the city after destroying three arches of the old bridge, Heidelberg's treasured river crossing. They also destroyed the more modern bridge downstream. The U.S. Army (63rd Infantry, 7th Army) entered the town on March 30, 1945. The civilian population surrendered without resistance.[14]
A popular belief is that Heidelberg escaped bombing in World War II because the U.S. Army wanted to use the city as a garrison after the war. As Heidelberg was neither an industrial center nor a transport hub, it did not present a target of opportunity. Other notable university towns, such as Tübingen and Göttingen, were spared bombing as well. Allied air raids focused extensively on the nearby industrial cities of Mannheim and Ludwigshafen.

The U.S. Army may have chosen Heidelberg as a garrison base because of its excellent infrastructure, including the Heidelberg-Mannheim Autobahn (motorway), which connected to the Mannheim-Darmstadt-Frankfurt Autobahn, and the U.S. Army installations in Mannheim and Frankfurt. The intact rail infrastructure was more important in the late 1940s and early 1950s when most heavy loads were still carried by train, not by lorry. Heidelberg had the untouched Wehrmacht barracks, the "Grossdeutschland Kaserne" which the US Army occupied soon after, renaming it the Campbell Barracks.
History after 1945
In 1945, the university was reopened relatively quickly on the initiative of a small group of professors, among whom were the anti-Nazi economist Alfred Weber and the philosopher Karl Jaspers.[15] The surgeon Karl Heinrich Bauer was nominated rector.
On December 9, 1945, US Army General George S. Patton had a car accident in the adjacent city of Mannheim and died in the Heidelberg US Army hospital on December 21, 1945. The funeral ceremony was held at the Heidelberg-Weststadt Christuskirche (Christ Church), and he was buried in the 3rd Army cemetery in Luxembourg.[16]
During the post-war military occupation, the U.S. Army used the Thingsstätte for cultural and religious events. Civilian use started in the early to mid-1980s for occasional concerts and other cultural events. Today, the celebrations on Hexennacht ("Witches' Night"), also called Walpurgis Night), the night of April 30, are a regular "underground" fixture at the Thingstätte. Thousands of mostly young people congregate there to drum, to breathe fire, and to juggle. The event has gained fame throughout the region, as well as a certain notoriety due to the amount of litter left behind.
Population
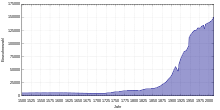
The population of the city of Heidelberg exceeded 100,000 for the first time in 1946. It is a city with an international population, including one of the largest American communities outside North America, but this is not analysed in the Heidelberg population statistics. At the end of December 2011, the city had 149,633 inhabitants with an official primary residence in Heidelberg (not including the soldiers and employees of the U.S. Army and their dependents, a total of about 20,000 people), a historic high.[17]
The following table shows the number of inhabitants within the boundaries of the city at the time. To 1833 they are mostly estimates, then census results or official updates of the statistical offices of the time or the city administration. The data refer from 1843 to the "local population", from 1925 to the resident population and since 1987 the "population at the site of their main dwelling." Prior to 1843 the population was determined by non-uniform collection procedures.
|
|
|
|
¹ Census results
With a fertility rate of 1.1 children per woman in the Stadtkreis (county), Heidelberg had the lowest fertility rate in Baden-Württemberg in 2008.
Politics
| Election | 2004[18] | 2009 | 2014[19] | |||
| Party | Votes | Seats | Votes | Seats | Votes | Seats |
| CDU | 25.9 % | 11 | 20.1% | 9 | 20.81% | 10 |
| SPD | 21.6% | 9 | 16.8% | 7 | 17.26% | 8 |
| Greens | - | - | 15.1% | 6 | 19.67% | 10 |
| Green Alternative List | 21.4% | 9 | 10.2% | 4 | 4.37% | 2 |
| FDP | 6.8% | 3 | 9.1% | 4 | 4.36% | 2 |
| Heidelberger | 10.6% | 4 | 8.6% | 3 | 8.10% | 4 |
| generation.hd | 3.2% | 1 | 5.8% | 2 | 5.05% | 2 |
| FWV | 4.5% | 2 | 5.8% | 2 | 3.34% | 2 |
| Bunte Linke | 3.1% | 1 | 5.4% | 2 | 3.75% | 2 |
| HD P. u. E. | - | - | 3.1% | 1 | 2.72% | 1 |
| The Left | – | – | – | – | 4.08% | 2 |
| AfD | – | – | – | – | 3.84% | 2 |
| Pirates | – | – | – | – | 2.64% | 1 |
| Others | 2.8% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 |
| Turnout | 50.5% | 48.8% | 51.29% | |||
Since 2006, the Oberbürgermeister (lord mayor) of Heidelberg has been the independent Eckart Würzner. From 1990 to 2006, the mayor was Beate Weber (SPD).
The council consists of 40 volunteer members with the mayor as chairman. The council is directly elected for a term of five years. The task of the council is to decide with the mayor presiding all the affairs of the city. The council controls the city administration and oversees the enforcement of its decisions.
Heidelberg has always been a stronghold of the Greens. For the municipal elections in 2009, they split into the Green Alternative List and Alliance 90/The Greens and each ran their own lists. Together they gained 10 seats to become the strongest force for the first time.
After the election, the deputies of the Alliance 90/The Greens formed a coalition with generation.HD. In September 2011 two members of the GAL Group joined the Alliance 90/The Greens, so now with generation.HD, they form the largest group in the council.
Cityscape
The old town



The "old town" (German: Altstadt), on the south bank of the Neckar, is long and narrow. It is dominated by the ruins of Heidelberg Castle, 80 metres above the Neckar on the steep wooded slopes of the Königstuhl (King's chair or throne) hill.
- The Main Street (Hauptstrasse), a mile-long pedestrian street, running the length of the old town.
- The old stone bridge was erected 1786–1788. A medieval bridge gate is on the side of the old town, and was originally part of the town wall. Baroque tower helmets were added as part of the erection of the stone bridge in 1788.
- The Church of the Holy Spirit (Heiliggeistkirche), a late Gothic church in the marketplace of the old town.
- The Karls‘ gate (Karlstor) is a triumphal arch in honour of the Prince Elector Karl Theodor, located at Heidelberg's east side. It was built 1775–1781 and designed by Nicolas de Pigage.
- The house Zum Ritter Sankt Georg (Knight St. George) is one of the few buildings to survive the War of Succession. Standing across from the Church of the Holy Spirit, it was built in the style of the late Renaissance. It is named after the sculpture at the top.
- The Marstall (Stables), a 16th-century building on the Neckar that has served several purposes through its history. It is now a cafeteria for the university.
Heidelberg Castle

The castle is a mix of styles from Gothic to Renaissance. Prince Elector Ruprecht III (1398–1410) erected the first building in the inner courtyard as a royal residence. The building was divided into a ground floor made of stone and framework upper levels. Another royal building is located opposite the Ruprecht Building: the Fountain Hall. Prince Elector Philipp (1476–1508) is said to have arranged the transfer of the hall's columns from a decayed palace of Charlemagne from Ingelheim to Heidelberg.
In the 16th and 17th centuries, the Prince Electors added two palace buildings and turned the fortress into a castle. The two dominant buildings at the eastern and northern side of the courtyard were erected during the rule of Ottheinrich (1556–1559) and Friedrich IV (1583–1610). Under Friedrich V (1613–1619), the main building of the west side was erected, the so-called "English Building".
The castle and its garden were destroyed several times during the Thirty Years' War and the Palatine War of Succession. As Prince Elector Karl Theodor tried to restore the castle, lightning struck in 1764, and ended all attempts at rebuilding. Later on, the castle was misused as a quarry; stones from the castle were taken to build new houses in Heidelberg. This was stopped in 1800 by Count Charles de Graimberg, who then began the process of preserving the castle.
Although the interior is in Gothic style, the King's Hall was not built until 1934. Today, the hall is used for festivities, e.g. dinner banquets, balls and theatre performances. During the Heidelberg Castle Festival in the summer, the courtyard is the site of open air musicals, operas, theatre performances, and classical concerts performed by the Heidelberg Philharmonics.
The castle is surrounded by a park, where the famous poet Johann von Goethe once walked. The Heidelberger Bergbahn funicular railway runs from Kornmakt to the summit of the Königstuhl via the castle.
Philosophers' Walk
On the northern side of the Neckar is located the Heiligenberg (Saints' Mountain), along the side of which runs the Philosophers' Walk (German: Philosophenweg), with scenic views of the old town and castle. Traditionally, Heidelberg's philosophers and university professors would walk and talk along the pathway. Farther up the mountain lie the ruined 11th-century Monastery of St. Michael, the smaller Monastery of St. Stephen, a Nazi-era amphitheater, the so-called Pagan's hole and the remains of an earthen Celtic hill fort from the 4th century BC.

Heidelberg churches
There are many historical churches in Heidelberg and its surroundings. The Church of the Holy Spirit has been shared over the centuries since the Protestant Reformation by both Catholics and Protestants. It is one of the few buildings to survive the many wars during the past centuries. It was rebuilt after the French set fire to it in 1709 during the War of the Palatinian Succession. The church has remains of the tombs and epitaphs of the past Palatinate electors. This Church stands in the Marktplatz next to the seat of local government. In 1720, Karl III Philip, Elector Palatine came into conflict with the town's Protestants as a result of giving the Church of the Holy Spirit exclusively to the Catholics for their use. It had previously been split by a partition and used by both congregations. Due to pressure by the mostly Protestant powers of Prussia, Holland, and Sweden, Prince Karl III Philip gave way and repartitioned the church for joint use. In 1936 the separating wall was removed. The church is now exclusively used by Protestants. Furthermore, there is the Catholic Church of the Jesuits. Its construction began in 1712. It was completed with the addition of a bell tower from 1866–1872. The church is also home to the Museum für sakrale Kunst und Liturgie (Museum of Ecclesiastical Arts). The oldest church in Heidelberg is the St. Peter's Church (now Lutheran). It was built some time during the 12th century.
 The Church of the Jesuits
The Church of the Jesuits St. Peter's Church
St. Peter's Church- St. Bonifatius Church
Education
Universities and academia


Heidelberg is known for its institutions of higher education. The most famous of those is Heidelberg University. Founded in 1386, it is one of Europe's oldest institutions. In fact, Heidelberg is the oldest university town of today's Germany. Among the prominent thinkers associated with the institution are Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Karl Jaspers, Hans-Georg Gadamer, Jürgen Habermas, Karl-Otto Apel and Hannah Arendt. The campus is situated in two urban areas and several buildings. In numerous historical buildings in the old town there are the Faculties of the Humanities, the Social Science and the Faculty of Law. The school of applied sciences is located in the Science Tower in Wieblingen. The Faculties of Medicine and Natural Science are settled on the Neuenheimer Feld Campus.
Since 1904 there has been a College of Educational Science, the Pädagogische Hochschule Heidelberg; since 1979 there has been a college of Jewish Studies, the Hochschule für Jüdische Studien Heidelberg. It comprises nine branches specializing on both religion and Jewish culture. The Schiller International University, a private American university is also represented with a campus in Heidelberg offering several undergraduate and graduate programs in the fields of International Business and International Relations and Diplomacy.
Research

In addition to the research centers and institutes of the university, there are numerous research institutions situated in the city of Heidelberg. Among them are the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO), the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Max Planck Institute for Medical Research, Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Max Planck Institute for Comparative Public Law and International Law.
Schools

Heidelberg is home to 23 elementary schools. There are several institutions of secondary education, both public and private, representing all levels of the German school system. There are 14 Gymnasiums, with six of them private. With 52% of secondary students attending a Gymnasium, Heidelberg sits above the German average, perhaps because a large number of academics live in Heidelberg and its environs. They include the Kurfürst-Friedrich-Gymnasium (German Wikipedia), Bunsen-Gymnasium (German Wikipedia), the Helmholtz-Gymnasium (German Wikipedia), the Hölderlin-Gymnasium and the Elisabeth-von-Thadden-Schule. Then there are seven Realschule, ten Hauptschule and nine vocational schools (the so-called Berufsschule). In addition, there are several folk high schools with different specialisations.[20] Heidelberg International School serves the local expatriate community.
Economy
Tourism
In 2004, 81.8% of people worked for service industries, including tourism. As a relic of the period of Romanticism, Heidelberg has been labeled a "Romantic town". This is used to attract more than 3.5 million visitors every year. Many events are organized to attract visitors.
Industry
Only 18% of employment is provided by industry. Printing and publishing are important enterprises; nearby Walldorf is a center of the IT industry and SAP World Headquarters. Noted pen manufacturer Lamy has its headquarters and factory in Heidelberg-Wieblingen. Heidelberger Druckmaschinen has its headquarters here; its factory is located in Walldorf. Soft-drink company Wild-Werke, manufacturer of the Capri-Sonne (Capri-Sun in the U.S.) is located nearby in Eppelheim. Heidelberg is also home to the headquarters of HeidelbergCement, the world's second largest cement producer. The Company has its roots in the suburb of Leimen where one of its cement plants is still located. With its long Hauptstrasse, Heidelberg is a shopping destination for people from the surrounding smaller towns.

Roads
The A 5 autobahn runs through the western outskirts of Heidelberg, connecting the region to Frankfurt am Main in the north and Karlsruhe to the south. The A 656 commences just west of the city, connecting Heidelberg with Mannheim. Both highways meet at Heidelberg autobahn intersection in the city of Heidelberg, and the A 656 connects to the A 6 at the Mannheim autobahn intersection, which connects to the east towards Stuttgart.
Furthermore, the B 3 (Frankfurt–Karlsruhe) runs north–south through the town, and the B 37 (Mannheim–Eberbach) runs east–west. Both meet in the city center at the Bismarckplatz. The B 535 begin in the south of Heidelberg and runs to Schwetzingen.
Tourist roads
Heidelberg is located on four tourist roads: Bergstraße, Bertha Benz Memorial Route, Castle Road, and Straße der Demokratie (Road of Democracy).
Railways
Heidelberg Central Station (Hauptbahnhof) is on the Rhine Valley Railway and is served by Intercity-Express, Euro City trains. This station is served by the RheinNeckar S-Bahn.
Public transport


The main transport hub of Heidelberg is the Bismarckplatz. Several main thoroughfares of the city intersect here and one of the longest pedestrian streets in Europe, the Hauptstraße (main street) runs from here through the entire old town of Heidelberg. Heidelberg Central Station was nearby for many years, which was a combined terminal and through station. In 1955, it was moved about 1.5 km further to the west, which removed the necessity for trains continuing to the south or from the south to the north to reverse. The new central station became the second major transport hub of Heidelberg.
Heidelberg has had a public transport service since 1883, when horse-drawn trams were established. Due to the rapidly rising patronage it was decided on 20 December 1901 to convert the Heidelberg tramway network to electrical operation. On 16 March 1902, the first electric tram ran on Rohrbacher Straße, sharing use of the suburban tracks built by the Deutsche Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft in 1901 between Heidelberg and Wiesloch. Until the 1950s, the tram network was expanded a bit at a time. The rapidly growing popularity of car transport presented the operator of the trams with increasingly difficult problems and the tram network was gradually dismantled. It was not until 10 December 2006 that the network was extended again with the opening of a new tram line from Kirchheim. Tram and bus services are now operated by Rhein-Neckar-Verkehr (RNV). Since 1989, all fares are set under a uniform scheme by the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Neckar (Rhine-Neckar Transport Association, VRN). Carsharing increasingly provides a complement to public transport. More than 50 car-sharing stations are available to users in 12 of the 14 districts of Heidelberg offering a total of more than 100 cars.

Since 14 December 2003, Heidelberg has been connected to the network of the Rhine-Neckar S-Bahn, which opens up the entire Rhine-Neckar region, with lines connecting with the Palatinate, the Saarland and southern Hesse.
The Heidelberger Bergbahn (Heidelberg Mountain Railway) has run since 2005 with new cars on the lower part from Kornmarkt to Molkenkur and historic cars built in 1907 on the upper section of the funicular from Molkenkur to Königstuhl. It is one of the most popular means to reach Heidelberg Castle. The first plans for the funicular were drawn up in 1873. Due to a lack of funds was the first section of the funicular was not opened until 1890. In 2004, the upper section of the funicular was listed as part of the heritage of the state of Baden-Württemberg.
United States military installations
During World War II, Heidelberg was one of the few major cities in Germany not significantly damaged by Allied bombing. Situated in the American Zone of Germany, Heidelberg became the headquarters of the American forces in Europe. Several military installations remain, including Campbell Barracks, the former Wehrmacht Grossdeutschland-Kaserne, where headquarters for several units are located. These include US Army, Europe (USAREUR) and NATO's Component Command-Land Headquarters. (Until 2004, this was designated Joint Headquarters Centre, and before that, LANDCENT).

Campbell Barracks and Mark Twain Village are both in Südstadt; Patton Barracks is in nearby Kirchheim. Nachrichten Kaserne in Rohrbach is home to the former Heidelberg Army Hospital, now designated the Heidelberg Health Center. Patrick Henry Village, the largest U.S. military housing area in the Heidelberg area, is west of Kirchheim. These installations, including Tompkins Barracks and Kilbourne Kaserne in nearby Schwetzingen, plus the Germersheim Depot, used to make up the U.S. Army Garrison Heidelberg. Tompkins Barracks is home to U.S. Army Installation Management Command Europe Region. The Heidelberg U.S. Army Air Field (Heidelberg AAF) was converted to an heliport (mostly Blackhawk Helicopters) after the NATO Kosovo campaign.
The children of United States Department of Defense employees based in Heidelberg tend to attend on-base schools operated by the DODDS-E (Department of Defense Dependents Schools – Europe). There are three schools of this kind: Heidelberg High School in Mark Twain Village (Mark Twain Elementary School closed at the completion of the 2010–2011 school year), and Heidelberg Middle School and Patrick Henry Elementary in Patrick Henry Village.[21]
On October 19, 2009 the U.S. Army announced that it will be building new headquarters for USAREUR in Wiesbaden. The move from Heidelberg will take place in 2012 and 2013, and will be completed by 2014.[22] By 2015 all United States forces will have moved out of Heidelberg. The barracks and the housing areas will be handed over to the German state for conversion to civilian use.
Culture
Events

Throughout the year there are different regular festivals and events hosted and organized in Heidelberg. In February, the Ball der Vampire (Ball of the Vampires)[23] is arranged and Fasching, the equivalent of Mardis Gras or Carnival in some German regions, with a giant vampire-themed costume party at the local castle or city hall is celebrated. In March or April the Heidelberger Frühling (Heidelberg Spring), the Classic Music Festival and the international Easter egg market are conducted. During the last weekend of April there is an annually organized half marathon. In the summertime there are the Frühlingsmesse on the Messeplatz (May) and Illumination of the castle and bridge with lights and fireworks take place. In September, on the last Saturday the Old Town Autumn Festival is held.[24] It includes a Medieval Market, an arts and crafts market, a flea market, and music from Samba to Rock. During October or November there are the Heidelberger Theater Days and a jazz festival. Every year in November the International Filmfestival Mannheim-Heidelberg take place in the city, too. The festival presents arthouse films of international newcomer directors and is held jointly by both of the cities.[25] During Christmas there is a Christmas market throughout the oldest part of the city. A famous gift is the chocolate called Heidelberger Studentenkuss (student kiss).
Cinemas
The Karlstorkino offers an arthouse program, rare classics and feature films. Here, most films are shown in original version. The Harmonie Lux has had a rather mainstream Hollywood program before its closing in 2014, whilst the small independent cinemas Gloria & Gloriette as well as Kamera also show arthouse films, mostly in German versions. Plans for a new Luxor-Kino in the new district Bahnstadt, featuring both blockbusters and arthouse films, have been in the works since 2013 and the construction began in July, 2015.[26]
Museums and exhibitions
Among the most prominent museums of Heidelberg are for instance the Carl Bosch Museum which shows life and work of chemist and Nobel Prize-winner Carl Bosch. Then there is the Documentation and Culture Centre of German Sinti and Roma (Dokumentations- und Kulturzentrum Deutscher Sini und Roma) describing the Nazi genocide of the Sinti and Roma peoples. The German Packing Museum (Deutsches Verpackungsmuseum) gives an overview on the history of packing and wrapping goods whereas the German Pharmacy Museum (Deutsches Apothekenmuseum) which is located in the castle illustrates the story of Pharmacy in Germany. The Kurpfälzisches Museum (Palatinate Museum) offers a great art collection and some Roman archeological artifacts from the region. In the honour of Friedrich Ebert one established the President Friedrich Ebert Memorial which remembers the life of Germany's first democratic head of state. Besides, there are guided tours in most of the historical monuments of Heidelberg, as well as organized tourist tours through the city available in several languages.
Heidelberg Romanticism

Heidelberg was the centre of the epoch of Romantik (Romanticism) in Germany. The phase after Jena Romanticism is often called Heidelberg Romanticism (see also Berlin Romanticism). There was a famous circle of poets (the Heidelberg Romantics), such as Joseph von Eichendorff, Johann Joseph von Görres, Ludwig Achim von Arnim, and Clemens Brentano. A relic of Romanticism is the Philosophers' Walk (German: Philosophenweg), a scenic walking path on the nearby Heiligenberg, overlooking Heidelberg.
The Romantik epoch of German philosophy and literature, was described as a movement against classical and realistic theories of literature, a contrast to the rationality of the Age of Enlightenment. It elevated medievalism and elements of art and narrative perceived to be from the medieval period. It also emphasized folk art, nature and an epistemology based on nature, which included human activity conditioned by nature in the form of language, custom and usage.
Old Heidelberg
In 1901 Wilhelm Meyer-Förster wrote the play Old Heidelberg which was followed by a large number of film adaptations. It was the basis for Sigmund Romberg's 1924 operetta The Student Prince which was itself turned into a film of the same title.
I Lost My Heart in Heidelberg
The 1925 song "I Lost My Heart in Heidelberg" composed by Fred Raymond was a major hit and inspired a stage musical and two films. It remains the theme song of Heidelberg.
Sport
Heidelberg is one of the centres of Rugby union in Germany, along with Hanover. In 2008–09, four out of nine clubs in the Rugby-Bundesliga were from Heidelberg, these being RG Heidelberg, SC Neuenheim, Heidelberger RK and TSV Handschuhsheim. Heidelberger TV has a rugby department. Rugby League Deutschland has two teams based in Heidelberg, Heidelberg Sharks formed in 2005 and Rohrbach Hornets formed in 2007.
The city is also home to the USC Heidelberg, which won 9 German Basketball Championships and remains the second most successful team in the history of German professional basketball. Today, the club plays in Germany's second division ProA. It is primarily known for its youth department which developed several members of Germany's senior national basketball team.
Further, Germany's oldest tennis club, which was founded in the year 1890, is located in Heidelberg.
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Heidelberg is twinned (städtepartnerschaft) with:[27]
|
In popular culture
Heidelberg features in the 1968 film The Girl on a Motorcycle, the university being the ultimate destination of Marianne Faithfull's character. Heidelberg is the home of a professional Quidditch team operating within the fictional Harry Potter universe: the Heidelberg Harriers have been described as “fiercer than a dragon and twice as clever”.[30] Heidelberg is the residence of fictional character Nina Fortner/Anna Liebert in the anime/manga series Monster, by Naoki Urasawa. Further, its castle forms the setting for the beginning of Mark Twain's story The Awful German Language. The city also features during a mission in the Electronic Arts strategy game Red Alert 3. Heidelberg also features in Somerset Maugham's Of Human Bondage and its film versions. Also, "Morris from America" takes places in Heidelberg.
Notable inhabitants

.jpg)
- Ernst Albrecht (1930–2014), politician (CDU), Minister-president of Lower Saxony, father of Ursula von der Leyen
- Jill Asemota, German-Nigerian model
- Jackson Browne (born 1948) Singer-songwriter and musician born here
- Petar Beron (1799–1871), Bulgarian educator
- Robert Bunsen (1811-1899), German chemist
- Antje Duvekot (born 1976), singer-songwriter
- Hans-Georg Gadamer (1900–2002), German philosopher
- Michael Fassbender (born 1977), German-Irish actor born here
- Ian Harding (born 1986), German actor
- Harald zur Hausen (born 1936), virologist, Nobel Laureate
- Dietmar Hopp (born 1940), software entrepreneur SAP
- Muhammad Iqbal (1877–1938), Pakistani Poet, Philosopher
- Wolfgang Ketterle (born 1957), physicist, professor at MIT, Nobel Laureate
- Paul Kirchhof (born 1943), former Judge in the Federal Constitutional Court of Germany (Bundesverfassungsgericht)
- Hans Kroh (1907–1967), German officer in Wehrmacht and Bundeswehr
- Karl A. Lamers (born 1951), politician, former President of the NATO Parliamentary Assembly
- Ananda Mahidol (1925–1946), King of Thailand
- Heinrich Neal (1870–1940), German composer, directed the Heidelberg Conservatory of Music
- Vasil Radoslavov (1854–1929), Bulgarian Prime Minister
- José Rizal (1861–1896), National Hero of the Philippines
- Christiane Schmidtmer (1939–2003), Hollywood actress and model
- Bernd Schmitt (born 1957) Marketing professor at Columbia University
- Klaus Schütz (1926-2012), German politician (SPD)
- Silvia Renate Sommerlath (born 1943), Queen of Sweden
- Albert Speer (1905–1981), German architect and Third Reich minister
- Ferdinand Thomas (1913–1944), Resistance fighter
- Ernst Jünger (1895-1998), German author, officer, botanist and entomologist, famous for his World War I memoir Storm of Steel.
Notable people who died in Heidelberg
- Robert Bunsen (1811–1899), German chemist
- Alexandru Ioan Cuza (3 May 1873), Prince of Moldavia, Prince of Wallachia and later domnitor (ruler) of the Romanian Principalities
- Walther Dahl, (1916-1985), GermanLuftwaffe ace
- Konstantin Hierl, leader of the Reichsarbeitsdienst (24 February 1875 – 23 September 1955)
- George S. Patton (1885–1945), US Army general
- Christiane Schmidtmer (1939–2003) German actress
- Felix Heinrich Wankel (1902–1988), mechanical engineer and inventor of the Wankel engine
Gallery
|
See also
Notes
- ↑ "Gemeinden in Deutschland nach Fläche, Bevölkerung und Postleitzahl am 30.09.2016". Statistisches Bundesamt (in German). 2016.
- ↑ "Heidelberg-Rohrbach: Wein, Reben und Winzer". Hilfe-hd.de. Retrieved 2012-11-08.
- ↑ Stefanie Wegener: Verbreitung und Arealnutzung der Halsbandsittiche (Psittacula krameri) in Heidelberg, published by: Ornithologische Gesellschaft Baden-Württemberg e. V., Ornithol. Jh. Bad.-Württ. 23: 39–55 (2007)
- ↑ Mechthild Henneke: Wetterextreme in Deutschland 2009. In: Südkurier, 28. April 2010
- ↑ Kreisbeschreibung Bd. 1, S. 54ff
- ↑ www.klimadiagramme.de
- ↑ "Heidelberg historic weather averages". Intellicast. Retrieved October 21, 2009.
- ↑ "Deutscher Wetterdienst - weather and climate, 1981-2010". Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ↑ Helfferich, Tryntje, The Thirty Years War: A Documentary History (Cambridge, 2009), pp. 289-90.
- ↑ Cser 2007, pp. 209–10)
- ↑ Cser 2007, p. 229)
- ↑ Cser 2007, pp. 246–8
- ↑ "Alfred Mombert". Badische Landesbibliothek (in German).
- ↑ Fink, Oliver (2005). Kleine Heidelberger Stadtgeschichte. ISBN 978-3-7917-1971-9.
- ↑ Remy 2002, p. 240
- ↑ George S. Patton#Accident and death
- ↑ "Population of city of Heidelberg" (in German). Statistical office of the state of Baden-Württemberg. Retrieved 25 July 2012.
- ↑ After the 2004 election, there were several changes the parties/groups Heidelberg
- ↑ "Ergebnis Gemeinderatswahl 2014". Stadt Heidelberg. Retrieved 23 June 2014.
- ↑ Archived September 27, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Our Districts and Schools Dependents Schools Europe website, accessed: April 19, 2009
- ↑ Heidelberg, Mannheim to close by 2015, HeraldPost Vol. 35 No. 38, accessed: October 22, 2011.
- ↑ Archived October 30, 2010, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Veranstaltungen in Heidelberg: Heidelberg aktuell - Home". Heidelberg-aktuell.de. Retrieved 2012-11-08. http://www.heidelberg-event.com/events/heidelberger-herbst/?lang=en. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ "Internationales FilmFestival Mannheim-Heidelberg |". Mannheim-filmfestival.com. 2012-10-18. Retrieved 2012-11-08.
- ↑ Heidelberg-Bahnstadt: Spatenstich: Baubeginn für den Luxor Filmpalast | Heidelberg
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Partnerstädte" (official website) (in German). Heidelberg, Germany: Stadt Heidelberg. Retrieved 2015-02-04.
- ↑ heidelberg.de - Cambridge
- ↑ "Mostar Gradovi prijatelji" [Mostar Twin Towns]. Grad Mostar [Mostar Official City Website] (in Macedonian). Archived from the original on 2013-10-30. Retrieved 2013-12-19. However, according to Heidelberg's website, there is no partnership with Mostar!
- ↑ Whisp, Kennilworthy (2001). Quidditch Through the Ages. WhizzHard Books. pp. 31–46. ISBN 1-55192-454-4.
References
- Cser, Andreas (2007). Kleine Geschichte der Stadt Heidelberg und ihrer Universität [Short history of the city of Heidelberg and its University] (in German). Karlsruhe: Verlag G. Braun. ISBN 978-3-7650-8337-2.
- Remy, Steven P. (2002). The Heidelberg Myth: The Nazification and Denazification of a German University. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-00933-9.
Further reading
- "Heidelberg", The Rhine from Rotterdam to Constance, Leipsic: Karl Baedeker, 1882, OCLC 7416969
- "Heidelberg", The Encyclopaedia Britannica (11th ed.), New York: Encyclopaedia Britannica, 1910, OCLC 14782424
- "Heidelberg", The Rhine, including the Black Forest & the Vosges, Leipzig: Karl Baedeker, 1911, OCLC 21888483
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Heidelberg. |
-
 Heidelberg travel guide from Wikivoyage
Heidelberg travel guide from Wikivoyage  "Heidelberg". Encyclopædia Britannica. 13 (11th ed.). 1911.
"Heidelberg". Encyclopædia Britannica. 13 (11th ed.). 1911.- Official site of Heidelberg, a small English section is available
- Audio Tour in the Castle of Heidelberg
- U.S. Army Garrison Heidelberg homepage
- Heidelberg American High School, The official site of Heidelberg American High School
 |
Mannheim | Darmstadt, Frankfurt | Aschaffenburg, Würzburg |  |
| Kaiserslautern | |
Odenwald | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Speyer, Landau | Karlsruhe, Stuttgart | Heilbronn, Schwäbisch Hall |















