Hayoceros
| Hayoceros Temporal range: Mid Pleistocene | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Antilocapridae |
| Genus: | †Hayoceros Skinner, 1942 |
| Species | |
| |
Hayoceros is an extinct genus of the artiodactyl family Antilocapridae, endemic to North America during the Early Pleistocene epoch (1.8 mya—300,000 years ago), existing for approximately 1.5 million years.[1]
Taxonomy
Hayoceros was named by Skinner (1942) and named as a subgenus of Tetrameryx by Frick 1937; raised to genus level. It was assigned to Antilocapridae by Skinner (1942) and Carroll (1988).[2][3]
Morphology
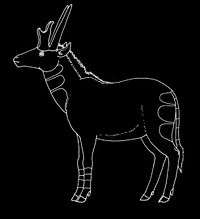
It was about 1.8 metres (5.9 ft) in body length, and, in most respects, resembled modern pronghorns. However, in addition to the pair of forked horns located above the eyes, as in modern pronghorns, it also possessed a second, longer and unforked, pair on the back of the skull. Most likely, males used these to fight in a fashion similar to modern pronghorns, locking horns and then pushing until the opponent gave in.[4]
References
- ↑ PaleoBiology Database: Dinictis, basic info
- ↑ M. F. Skinner. 1942. The fauna of Papago Springs Cave, Arizona, and a study of Stockeros; with three new antilocaprines from Nebraska and Arizona. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 80(6):143-220
- ↑ R. L. Carroll. 1988. Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York 1-698
- ↑ Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 280. ISBN 1-84028-152-9.