Game of Thrones
| Game of Thrones | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Genre | |
| Created by | |
| Based on |
A Song of Ice and Fire by George R. R. Martin |
| Directed by | see List of Game of Thrones directors |
| Starring | see List of Game of Thrones characters |
| Theme music composer | Ramin Djawadi |
| Opening theme | "Main Title" |
| Composer(s) | Ramin Djawadi |
| Country of origin | United States |
| Original language(s) | English |
| No. of seasons | 6 |
| No. of episodes | 60 (list of episodes) |
| Production | |
| Executive producer(s) |
|
| Location(s) |
|
| Running time | 50–69 minutes |
| Release | |
| Original network | HBO |
| Picture format | 1080i (16:9 HDTV) |
| Audio format | Dolby Digital 5.1 |
| Original release | April 17, 2011 – present |
| Chronology | |
| Related shows |
After the Thrones Thronecast |
| External links | |
| Website | |
| Production website | |
Game of Thrones is an American fantasy drama television series created by David Benioff and D. B. Weiss. It is an adaptation of A Song of Ice and Fire, George R. R. Martin's series of fantasy novels, the first of which is A Game of Thrones. It is filmed at Titanic Studios in Belfast, on location in the United Kingdom, and in Croatia, Iceland, Malta, Morocco, Spain, and the United States. The series premiered on HBO in the United States on April 17, 2011, and its sixth season ended on June 26, 2016. The series was renewed for a seventh season, scheduled to premiere in mid-2017, with a total of seven episodes[1] and will conclude with its eighth season in 2018.[2]
Set on the fictional continents of Westeros and Essos, it has several plot lines and a large ensemble cast. The first story arc follows a dynastic conflict among competing claimants for succession to the Iron Throne of the Seven Kingdoms, with other noble families fighting for independence from the throne. The second covers attempts to reclaim the throne by the exiled last scion of the realm's deposed ruling dynasty; the third chronicles the threat of the impending winter and the legendary creatures and fierce peoples of the North.
Game of Thrones has attracted record viewership on HBO and has a broad, active, international fan base. It has been acclaimed by critics, particularly for its acting, complex characters, story, scope, and production values, although its frequent use of nudity and violence (including sexual violence) has attracted criticism. The series has received 38 Primetime Emmy Awards, including Outstanding Drama Series in 2015 and 2016, more than any other primetime scripted television series. Its other awards and nominations include three Hugo Awards for Best Dramatic Presentation (2012–2014), a 2011 Peabody Award, and three nominations for the Golden Globe Award for Best Television Series – Drama (2012 and 2015–2016). Of the ensemble cast, Peter Dinklage has won two Primetime Emmy Awards for Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Drama Series (2011 and 2015) and the Golden Globe Award for Best Supporting Actor – Series, Miniseries or Television Film (2012) for his performance as Tyrion Lannister. Lena Headey, Emilia Clarke, Kit Harington, Maisie Williams, Diana Rigg, and Max von Sydow have also received Primetime Emmy Award nominations for their performances in the series.
Background

Setting
Game of Thrones is roughly based on the storylines of A Song of Ice and Fire,[3][4] set in the fictional Seven Kingdoms of Westeros and the continent of Essos. The series chronicles the violent dynastic struggles among the realm's noble families for the Iron Throne, while other families fight for independence from it. It opens with additional threats in the icy North and Essos in the east.[5]
Showrunner David Benioff jokingly suggested "The Sopranos in Middle-earth" as Game of Thrones' tagline, referring to its intrigue-filled plot and dark tone in a fantasy setting of magic and dragons.[6] In a 2012 study of deaths per episode, it ranked second out of 40 recent U.S. TV drama series (with an average of 14).[7]
Themes
The series is generally praised for what is perceived as a sort of medieval realism.[8][9] George R.R. Martin set out to make the story feel more like historical fiction than contemporary fantasy, with less emphasis on magic and sorcery and more on battles, political intrigue, and the characters.[10] Believing that magic should be used moderately in the epic fantasy genre.[11][12] Benioff said, "George brought a measure of harsh realism to high fantasy. He introduced gray tones into a black-and-white universe."[12]
A common theme in the fantasy genre is the battle between good and evil, which Martin says is not mirroring the real world.[13] Just like people's capacity for good and for evil in real life, Martin explores the questions of redemption and character change.[14] The show allows the audience to view different characters from their perspective, unlike in many other fantasies, the supposed villains can provide their side of the story.[12][15]
Main characters are regularly killed off, and this has been credited with developing tension among viewers.[12] The series also reflect the substantial death rates in war.[16]
Inspirations and derivations
Although the first season is a faithful adaptation of the novel, later seasons have significant changes. According to David Benioff, the show is "about adapting the series as a whole and following the map George laid out for us and hitting the major milestones, but not necessarily each of the stops along the way".[17]
The novels and their adaptations base aspects of their settings, characters and plot on events in European history.[18] A principal inspiration for the novels is the English Wars of the Roses[19] (1455–85) between the houses of Lancaster and York, reflected in Martin's houses of Lannister and Stark. Most of Westeros is reminiscent of high medieval western Europe, with castles and knightly tournaments; the scheming Cersei evokes Isabella, the "she-wolf of France" (1295–1358).[18] Isabella and her family (particularly as portrayed in Maurice Druon's historical-novel series, The Accursed Kings) inspired Martin.[20] Other historical antecedents of series elements include Hadrian's Wall (which becomes Martin's Wall), the legend of Atlantis (ancient Valyria), Byzantine Greek fire ("wildfire"), Icelandic sagas of the Viking Age (the Ironborn), the Mongol hordes (the Dothraki), the Hundred Years' War (1337–1453) and the Italian Renaissance (c. 1400–1500).[18] The series' popularity has been attributed, in part, to Martin's skill at fusing these elements into a seamless, credible version of alternate history.[18]
Cast and characters

Game of Thrones has an ensemble cast estimated as the largest on television;[21] during its third season, 257 cast names were recorded.[22] In 2014, several actor contracts were renegotiated to include a seventh-season option, with raises which reportedly made them among the highest-paid performers on cable TV.[23] The main cast is listed below.[24]
Lord Eddard "Ned" Stark (Sean Bean) is the head of House Stark, whose members are involved in most of the series' plot lines. He and his wife, Catelyn Tully (Michelle Fairley), have five children: Robb (Richard Madden), the eldest, followed by Sansa (Sophie Turner), Arya (Maisie Williams), Bran (Isaac Hempstead-Wright) and Rickon (Art Parkinson), the youngest. Ned's illegitimate son Jon Snow (Kit Harington) and his friend, Samwell Tarly (John Bradley), serve in the Night's Watch under Lord Commander Jeor Mormont (James Cosmo). The Wildlings living north of the Wall include warriors Tormund Giantsbane (Kristofer Hivju) and Ygritte (Rose Leslie) and young Gilly (Hannah Murray).[25]
Others associated with House Stark include Ned's ward Theon Greyjoy (Alfie Allen), his vassal Roose Bolton (Michael McElhatton) and his bastard son, Ramsay Snow (Iwan Rheon). Robb falls in love with the healer Talisa Maegyr (Oona Chaplin), and Arya befriends blacksmith's apprentice Gendry (Joe Dempsie) and assassin Jaqen H'ghar (Tom Wlaschiha). The tall warrior Brienne of Tarth (Gwendoline Christie) serves Catelyn and, later, Sansa.[25]
In King's Landing, the capital, Ned's friend King Robert Baratheon (Mark Addy) shares a loveless marriage with Cersei Lannister (Lena Headey) – who has taken her twin, the Kingslayer Ser Jaime Lannister (Nikolaj Coster-Waldau), as her lover. She loathes her younger brother, the dwarf Tyrion Lannister (Peter Dinklage), who is attended by his mistress Shae (Sibel Kekilli) and the sellsword Bronn (Jerome Flynn). Cersei's father is Lord Tywin Lannister (Charles Dance). Cersei also has two young sons: Joffrey (Jack Gleeson) and Tommen (Dean-Charles Chapman). Joffrey is guarded by the scar-faced warrior, Sandor "the Hound" Clegane (Rory McCann).[25]
The king's Small Council of advisors includes crafty Master of Coin Lord Petyr "Littlefinger" Baelish (Aidan Gillen) and eunuch spymaster Lord Varys (Conleth Hill). Robert's brother, Stannis Baratheon (Stephen Dillane), is advised by foreign priestess Melisandre (Carice van Houten) and former smuggler Ser Davos Seaworth (Liam Cunningham). The wealthy Tyrell family is primarily represented at court by Margaery Tyrell (Natalie Dormer). The High Sparrow (Jonathan Pryce) is the capital's principal religious leader. In the southern principality of Dorne, Ellaria Sand (Indira Varma) seeks vengeance against the Lannisters.[25]
Across the Narrow Sea, siblings Viserys (Harry Lloyd) and Daenerys Targaryen (Emilia Clarke) – the exiled children of the last king of the original ruling dynasty, who was overthrown by Robert Baratheon – are running for their lives and trying to win back the throne. Daenerys has been married to Khal Drogo (Jason Momoa), the leader of the nomadic Dothraki. Her retinue includes exiled knight Ser Jorah Mormont (Iain Glen), her aide Missandei (Nathalie Emmanuel) and the sellsword Daario Naharis (Michiel Huisman).[25]
Production
Conception and development

In January 2006, George R. R. Martin's literary agent sent the first four books of A Song of Ice and Fire to David Benioff after a phone conversation.[26] Benioff read a few hundred pages of the first novel, A Game of Thrones, shared his enthusiasm with D. B. Weiss and suggested that they adapt Martin's novels into a television series; Weiss finished the first novel in "maybe 36 hours".[27] They pitched the series to HBO after a five-hour meeting with Martin (a veteran screenwriter) in a restaurant on Santa Monica Boulevard. According to Benioff, they won Martin over with their answer to his question, "Who is Jon Snow's mother?"[28] Asked about why they decided to turn the novels into an HBO show instead of a feature film, Benioff said that it would be impossible, considering that the scale of the novels is too big for a feature film and would mean dozen of characters would be discarded. Benioff also added, "a fantasy movie of this scope, financed by a major studio, would almost certainly need a PG-13 rating. That means no sex, no blood, no profanity. Fuck that."[12]
The series began development in January 2007.[3] HBO acquired the TV rights to the novels, and Benioff and Weiss were its executive producers. The intention was for each novel to yield a season's worth of episodes.[3] Initially, Benioff and Weiss were to write every episode except one per season which was reserved for Martin (who was co-executive producer).[3][29] Jane Espenson and Bryan Cogman were later added to write one episode apiece the first season.[5]
The first and second drafts of the pilot script by Benioff and Weiss were submitted in August 2007[30] and June 2008,[31] respectively. Although HBO liked both drafts,[31][32] a pilot was not ordered until November 2008;[33] the 2007–2008 Writers Guild of America strike may have delayed the process.[32] The pilot episode, "Winter Is Coming", was first shot in 2009; after a poor reception in a private viewing, HBO demanded an extensive re-shoot (about 90 percent of the episode, with cast and directorial changes).[28][34]
The pilot reportedly cost HBO $5–10 million,[35] and the first season's budget was estimated at $50–60 million.[36] In the second season, the show received a 15-percent budget increase for the climactic battle in "Blackwater" (which had an $8 million budget).[37][38] Between 2012 and 2015, the average budget per episode increased from $6 million[39] to "at least" $8 million.[40] The sixth-season budget was over $10 million per episode, for a season total of over $100 million and a series record.[41]
Casting
Nina Gold and Robert Sterne are the series' primary casting directors.[42] Through a process of auditions and readings, the main cast was assembled. The only exceptions were Peter Dinklage and Sean Bean, whom the writers wanted from the start; they were announced as joining the pilot in 2009.[43][44] Other actors signed for the pilot were Kit Harington as Jon Snow, Jack Gleeson as Joffrey Baratheon, Harry Lloyd as Viserys Targaryen and Mark Addy as Robert Baratheon.[44][45] Catelyn Stark was scheduled to be played by Jennifer Ehle, but the role was recast with Michelle Fairley.[46] Daenerys Targaryen was also recast, with Emilia Clarke replacing Tamzin Merchant.[47][48] The rest of the first season's cast was filled in the second half of 2009.[49]
Although many of the first-season cast were set to return, the producers had a large number of new characters to cast for the second season. Due to this, Benioff and Weiss postponed the introduction of several key characters and merged several characters into one or assigned plot functions to different characters.[21]
Writing

Game of Thrones used seven writers in six seasons. Series creators David Benioff and D. B. Weiss, the showrunners, write most of the episodes each season.[50]
A Song of Ice and Fire author George R. R. Martin wrote one episode in each of the first four seasons. Martin did not write an episode for the fifth or sixth seasons, since he wanted to focus on completing the sixth novel (The Winds of Winter).[51] Jane Espenson co-wrote one first-season episode as a freelance writer.[52]
Bryan Cogman, initially a script coordinator for the series,[52] was promoted to producer for the fifth season. Cogman, who wrote at least one episode for the first five seasons, is the only other writer in the writers' room with Benioff and Weiss. Before his promotion, Vanessa Taylor (a writer during the second and third seasons) worked closely with Benioff and Weiss. Dave Hill joined the writing staff for the fifth season after working as an assistant to Benioff and Weiss.[53] Although Martin is not in the writers' room, he reads the script outlines and makes comments.[50]
Benioff and Weiss sometimes assign characters to particular writers; for example, Cogman was assigned to Arya Stark for the fourth season. The writers spend several weeks writing a character outline, including what material from the novels to use and the overarching themes. After these individual outlines are complete, they spend another two to three weeks discussing each main character's individual arc and arranging them episode by episode.[50] A detailed outline is created, with each of the writers working on a portion to create a script for each episode. Cogman, who wrote two episodes for the fifth season, took a month and a half to complete both scripts. They are then read by Benioff and Weiss, who make notes, and parts of the script are rewritten. All ten episodes are written before filming begins, since they are filmed out of order with two units in different countries.[50]
Adaptation schedule
Benioff and Weiss intend to adapt the entire, still-incomplete A Song of Ice and Fire series of novels for television. After Game of Thrones began outpacing the published novels in the sixth season, the series was based on a plot outline of the future novels provided by Martin[54] and original content. In April 2016, the showrunners' plan was to shoot 13 more episodes after the sixth season: seven episodes in the seventh season and six episodes in the eighth.[55] Later that month, the series was renewed for a seventh season with a seven-episode order.[1][56] As of 2016, seven seasons have been ordered; six have been filmed, adapting the novels at a rate of about 48 seconds per page for the first three seasons.[57]
| Season | Ordered | Filming | First aired | Last aired | Novel(s) adapted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season 1 | March 2, 2010[58] | Second half of 2010 | April 17, 2011 | June 19, 2011 | A Game of Thrones |
| Season 2 | April 19, 2011[59] | Second half of 2011 | April 1, 2012 | June 3, 2012 | A Clash of Kings and some early chapters from A Storm of Swords[60] |
| Season 3 | April 10, 2012[61] | July – November, 2012 | March 31, 2013 | June 9, 2013 | About the first two-thirds of A Storm of Swords[62][63] |
| Season 4 | April 2, 2013[64] | July – November, 2013 | April 6, 2014 | June 15, 2014 | The remaining one-third of A Storm of Swords and some elements from A Feast for Crows and A Dance with Dragons[65] |
| Season 5 | April 8, 2014[66] | July – December, 2014 | April 12, 2015 | June 14, 2015 | A Feast for Crows, A Dance with Dragons and original content,[67] with some late chapters from A Storm of Swords[68] and elements from The Winds of Winter[69][70] |
| Season 6 | April 8, 2014[66] | July – December, 2015 | April 24, 2016 | June 26, 2016 | Original content and outlined from The Winds of Winter,[71][72] with some late elements from A Feast for Crows and A Dance with Dragons[73] |
| Season 7 | April 21, 2016[56] | August 2016 – February 2017[55] | Mid-2017[1] | Mid-2017[1] | Original content and outlined from The Winds of Winter and A Dream of Spring[72] |
The first two seasons adapted one novel each. For the later seasons, its creators see Game of Thrones as an adaptation of A Song of Ice and Fire as a whole rather than the individual novels;[74] this enables them to move events across novels, according to screen-adaptation requirements.[75]
Filming

Principal photography for the first season was scheduled to begin on July 26, 2010,[5] and the primary location was the Paint Hall Studios in Belfast, Northern Ireland.[76] Exterior scenes in Northern Ireland were filmed at Sandy Brae in the Mourne Mountains (standing in for Vaes Dothrak), Castle Ward (Winterfell), Saintfield Estates (the Winterfell godswood), Tollymore Forest (outdoor scenes), Cairncastle (the execution site), the Magheramorne quarry (Castle Black) and Shane's Castle (the tourney grounds).[77] Doune Castle in Stirling, Scotland, was also used in the original pilot episode for scenes at Winterfell.[78] The producers initially considered filming the whole series in Scotland, but decided on Northern Ireland because of the availability of studio space.[79]
The first season's southern scenes were filmed in Malta, a change in location from the pilot episode's Moroccan sets.[5] The city of Mdina was used for King's Landing. Filming was also done at Fort Manoel (representing the Sept of Baelor); at the Azure Window on the island of Gozo (the Dothraki wedding site) and at San Anton Palace, Fort Ricasoli, Fort St Angelo and St. Dominic monastery (all used for scenes in the Red Keep).[77]

Filming of the second season's southern scenes shifted from Malta to Croatia, where the city of Dubrovnik and nearby locations allowed exterior shots of a walled, coastal medieval city. The Walls of Dubrovnik and Fort Lovrijenac were used for scenes in King's Landing and the Red Keep. The island of Lokrum, the St. Dominic monastery in the coastal town of Trogir, the Rector's Palace in Dubrovnik, and the Dubac quarry (a few kilometers east) were used for scenes set in Qarth. Scenes set north of the Wall, in the Frostfangs and at the Fist of the First Men, were filmed in November 2011 in Iceland: on the Vatnajökull glacier near Smyrlabjörg, the Svínafellsjökull glacier near Skaftafell and the Mýrdalsjökull glacier near Vik on Höfðabrekkuheiði.[77][80]
Third-season production returned to Dubrovnik, with the Walls of Dubrovnik, Fort Lovrijenac and nearby locations again used for scenes in King's Landing and the Red Keep. Trsteno Arboretum, a new location, is the garden of the Tyrells in King's Landing. The third season also returned to Morocco (including the city of Essaouira) to film Daenerys' scenes in Essos.[81] Dimmuborgir and the Grjótagjá cave in Iceland were used as well.[80] One scene, with a live bear, was filmed in Los Angeles.[82] The production used three units (Dragon, Wolf and Raven) filming in parallel, six directing teams, 257 cast members and 703 crew members.[22]

The fourth season returned to Dubrovnik and included new locations, including Diocletian's Palace in Split, Klis Fortress north of Split, Perun quarry east of Split, the Mosor mountain range, and Baška Voda further south.[83] Thingvellir National Park in Iceland was used for the fight between Brienne and the Hound.[80] Filming took 136 days and ended on November 21, 2013.[84] The fifth season added Seville, Spain, used for scenes of Dorne.[85] The sixth season, which began filming in July 2015, returned to Spain and filmed in Girona and Peniscola.[86] Seventh-season production is scheduled to return to Spain, filming in Seville, Cáceres, Almodovar del Rio, Santiponce, Zumaia and Bermeo.[87]
Directing
Each ten-episode season of Game of Thrones has four to six directors, who usually direct back-to-back episodes. Alex Graves, David Nutter, and Alan Taylor have directed the most episodes of the series, with six each. Daniel Minahan directed five episodes, and Michelle MacLaren, Mark Mylod, Jeremy Podeswa, Alik Sakharov, and Miguel Sapochnik directed four each. Brian Kirk directed three episodes during the first season, and Tim Van Patten directed the series' first two episodes. Neil Marshall directed two episodes, both with large battle scenes: "Blackwater" and "The Watchers on the Wall". Other directors have been Jack Bender, David Petrarca, Daniel Sackheim and Michael Slovis. Matt Shakman will direct at least one episode of the upcoming seventh season.[88] David Benioff and D. B. Weiss have also directed one episode each.[89]
Technical aspects
Alik Sakharov was the pilot's cinematographer. The series has had a number of cinematographers,[90] and has received seven Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Cinematography for a Single-Camera Series nominations.[91]
Oral Norrey Ottey, Frances Parker, Martin Nicholson, Crispin Green, Tim Porter and Katie Weiland have edited the series for a varying number of episodes. Weiland received a Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Single-Camera Picture Editing for a Drama Series in 2015.[91]
Costumes



Michele Clapton was costume designer for Game of Thrones' first five seasons before she was replaced by April Ferry.[92] Clapton will return to the show as costume designer for the seventh season.[88]
The series' costumes are inspired by a number of cultures, including medieval Japan and Persia. Dothraki dress resembles that of the Bedouin (one was made out of fish skins to resemble dragon scales), and the Wildlings wear animal skins like the Inuit.[93] Wildling bone armor is made from molds of actual bones, and is assembled with string and latex resembling catgut.[94] Although the extras who play Wildlings and the Night's Watch often wear hats (normal in a cold climate), members of the principal cast usually do not so viewers can distinguish the main characters. Björk's Alexander McQueen high-neckline dresses inspired Margaery Tyrell's funnel-neck outfit, and prostitutes' dresses are designed for easy removal.[93] All clothing is aged for two weeks so it appears realistic on high-definition television.[94]
About two dozen wigs are used for the actresses. Made of human hair and up to 2 feet (61 cm) in length, they cost up to $7,000 each and are washed and styled like real hair. Applying the wigs is time-consuming; Emilia Clarke, for example, requires about two hours to style her brunette hair with a platinum-blonde wig and braids. Other actors, such as Jack Gleeson and Sophie Turner, receive frequent hair coloring. For characters such as Daenerys (Clarke) and her Dothraki, their hair, wigs and costumes are processed to appear as if they have not been washed for weeks.[93]
Makeup
For the first three seasons, Paul Engelen was Game of Thrones' main makeup designer and prosthetic makeup artist with Melissa Lackersteen, Conor O'Sullivan and Rob Trenton. At the beginning of the fourth season Engelen's team was replaced by Jane Walker and her crew, composed of Ann McEwan and Barrie and Sarah Gower.[91][95]
Visual effects
For the series' large number of visual effects, HBO hired British-based BlueBolt and Irish-based Screen Scene for season one. Most of the environment builds were done as 2.5D projections, giving viewers perspective while keeping the programming from being overwhelming.[96] In 2011 the season-one finale, "Fire and Blood", was nominated for a Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Special Visual Effects.[91]
Because the effects became more complex in subsequent seasons (including CGI creatures, fire, and water), German-based Pixomondo became the lead visual-effects producer; nine of its twelve facilities contributed to the project for season two, with Stuttgart the lead.[97][98] Scenes were also produced by British-based Peanut FX, Canadian-based Spin VFX, and U.S.-based Gradient Effects. "Valar Morghulis" and "Valar Dohaeris" earned Pixomondo Primetime Emmy Awards for Outstanding Special Visual Effects in 2012 and 2013, respectively.[91]
For season four, HBO added German-based Mackevision to the project.[99] The season-four finale, "The Children", won the 2014 Emmy Award for Visual Effects. Additional producers for season four included Canadian-based Rodeo FX, German-based Scanline VFX and U.S.-based BAKED FX. The muscle and wing movements of the adolescent dragons in seasons four and five were based largely on those of a chicken. Pixomondo retained a team of 22 to 30 people which focused on visualizing Daenerys Targaryen's dragons, with the average production time per season of 20 to 22 weeks.[100] For the fifth season, HBO added Canadian-based Image Engine and U.S.-based Crazy Horse Effects to its list of main visual-effects producers.[101][102]
Sound
Unusual for a television series, the sound team receives a rough cut of a full season and approaches it as a ten-hour feature film. Although seasons one and two had different sound teams, one team has been in charge of sound since then.[103] For the show's blood-and-gore sounds, the team often uses a shammy. For dragon screams, mating tortoises and dolphin, seal, lion and bird sounds have been used.[104]
Title sequence
The series' title sequence was created by production studio Elastic for HBO. Creative director Angus Wall and his collaborators received the 2011 Primetime Emmy Award for Main Title Design for the sequence,[105] which depicts a three-dimensional map of the series' fictional world. The map is projected on the inside of a sphere which is centrally lit by a small sun in an armillary sphere.[106] As the camera moves across the map, focusing on the locations of the episode's events, clockwork mechanisms intertwine and allow buildings and other structures to emerge from the map. Accompanied by the title music, the names of the principal cast and creative staff appear. The sequence concludes after about 90 seconds with the title card and brief opening credits indicating the episode's writer(s) and director. Its composition changes as the story progresses, with new locations replacing those featuring less prominently or not at all.[106][107][108]
Music

The music for the series was composed by Ramin Djawadi. The first season's soundtrack, written in about ten weeks before the show's premiere,[109] was published by Varèse Sarabande in June 2011.[110] Soundtrack albums for subsequent seasons have been released, with tracks by the National, the Hold Steady and Sigur Rós.[111] Djawadi has composed themes for each of the major house and also for some of the main characters.[112] The themes may evolve over time, as Daenerys Targaryen theme started small and then became more powerful after each season. Her theme started first with a single instrument, a cello. But Djawadi later incorporated more instruments for it.[112]
Language
The Westerosi characters of Game of Thrones speak British English, often (but not consistently) with the accent of the English region corresponding to the character's Westerosi region; Eddard Stark (Warden of the North) speaks in actor Sean Bean's native northern accent, and the southern lord Tywin Lannister speaks with a southern accent. Characters foreign to Westeros often have a non-British accent.[113]
Although English is the common language of Westeros, the producers charged linguist David J. Peterson with constructing Dothraki and Valyrian languages based on the few words in the novels;[114] Dothraki and Valyrian dialogue is subtitled in English. According to the BBC, during the series these fictional languages have been heard by more people than the Welsh, Irish and Scots Gaelic languages combined.[115]
Effect on location
Game of Thrones is funded by Northern Ireland Screen, a UK government agency financed by Invest NI and the European Regional Development Fund.[116] As of April 2013, Northern Ireland Screen gave the show £9.25 million ($14.37 million); according to government estimates, this has benefited the Northern Ireland economy by £65 million ($100.95 million).[117]
Tourism Ireland has a Game of Thrones-themed marketing campaign similar to New Zealand's Tolkien-related advertising.[118] Invest NI and the Northern Ireland Tourist Board also expect the series to generate tourism revenue.[117] According to Arlene Foster, the series has given Northern Ireland the most non-political publicity in its history.[119] The production of Game of Thrones and other TV series also boosted Northern Ireland's creative industries, contributing to an estimated 12.4-percent growth in arts, entertainment and recreation jobs between 2008 and 2013 (compared with 4.3 percent in the rest of the UK during the same period).[120]
Tourism organizations elsewhere reported increases in bookings after their locations appeared in Game of Thrones. In 2012, bookings through LateRooms.com increased by 28 percent in Dubrovnik and 13 percent in Iceland. The following year, bookings doubled in Ouarzazate, Morocco (the location of Daenerys' season-three scenes).[121]
Availability
Broadcast
Game of Thrones is broadcast by HBO in the United States and by its local subsidiaries or other pay television services in other countries, at the same time as in the U.S. or weeks (or months) later. The series' broadcast in China on CCTV, begun in 2014, was heavily edited to remove scenes of sex and violence in accordance with a Chinese practice of censoring Western TV series to prevent what the People's Daily calls "negative effects and hidden security dangers". This resulted in viewer complaints about the incoherence of what remained.[122] Broadcasters carrying Game of Thrones include Showcase in Australia; HBO Canada, Super Écran and Showcase in Canada; SoHo and Prime in New Zealand, and Sky Atlantic in the United Kingdom and Ireland.[123]
Home video
The ten episodes of the first season of Game of Thrones were released as a DVD and Blu-ray box set on March 6, 2012. The box set includes extra background and behind-the-scenes material but no deleted scenes, since nearly all the footage shot for the first season was used in the show.[124] The box set sold over 350,000 copies in the first week after release, the largest first-week DVD sales ever for an HBO series, and the series set an HBO-series record for digital-download sales.[125] A collector's-edition box set was released in November 2012, combining the DVD and Blu-ray versions of the first season with the first episode of season two. A paperweight in the shape of a dragon egg is included in the set.[126]
DVD-Blu-ray box sets and digital downloads of the second season became available on February 19, 2013.[127] First-day sales broke HBO records, with 241,000 box sets sold and 355,000 episodes downloaded.[128] The third season was made available for purchase as a digital download on the Australian iTunes Store, parallel to the U.S. premiere, and was released on DVD and Blu-ray in region 1 on February 18, 2014.[129][130] The fourth season was released on DVD and Blu-ray on February 17, 2015,[131] and the fifth season on March 15, 2016.[132] The sixth season was released on Blu-ray and DVD on November 15, 2016.[133]
Copyright infringement
Game of Thrones has been widely pirated, primarily outside the U.S.[134] According to the file-sharing news website TorrentFreak, Game of Thrones has been the most-pirated TV series each year since 2012.[135][136][137][138] Illegal downloads increased to about seven million in the first quarter of 2015, up 45 percent from 2014.[134] An unnamed episode was downloaded about 4,280,000 times through public BitTorrent trackers in 2012, roughly equal to its number of broadcast viewers.[139][140] Piracy rates were particularly high in Australia,[141] and U.S. Ambassador to Australia Jeff Bleich issued a statement condemning Australian piracy of the series in 2013.[142]
Delays in availability apart from HBO and its affiliates[143] before 2015 and the cost of subscriptions to these services have been cited as causes of the series' illegal distribution. According to TorrentFreak, a subscription to a service for Game of Thrones would cost up to $25 per month in the United States, up to £26 per episode in the UK and up to $52 per episode in Australia.[144]
For "combating piracy", HBO said in 2013 that it intended to make its content more widely available within a week of the U.S. premiere (including HBO Go).[145] In 2015, the fifth season was simulcast to 170 countries and to HBO Now users.[134] On April 11, the day before the season premiere, screener copies of the first four episodes of the fifth season leaked to a number of file-sharing websites.[146] Within a day of the leak, the files were downloaded over 800,000 times;[147] in one week the illegal downloads reached 32 million, with the season-five premiere alone ("The Wars to Come") pirated 13 million times.[148] The season-five finale ("Mother's Mercy") was the most simultaneously shared file in the history of the BitTorrent filesharing protocol, with over 250,000 simultaneous sharers and over 1.5 million downloads in eight hours.[149] For the sixth season, HBO did not send screeners to the press to prevent the spread of unlicensed copies and possible spoilers.[150]
Observers, including series director David Petrarca[151] and Time Warner CEO Jeff Bewkes, said that illegal downloads did not hurt the series' prospects; it benefited from "buzz" and social commentary, and the high piracy rate did not significantly translate to lost subscriptions. According to Polygon, HBO's relaxed attitude towards piracy and the sharing of login credentials amounted to a premium-television "free-to-play" model.[152] At a 2015 Oxford Union debate, series co-creator David Benioff said that he was just glad that people watched the show; illegally downloaded copies of the show sometimes interested viewers enough to buy a copy of the show, especially in countries where the show was not televised. Co-creator D. B. Weiss had mixed feelings, saying that the show was expensive to produce and "if it doesn't make the money back, then it ceases to exist". However, he was pleased that so many people "enjoy the show so much they can't wait to get their hands on it."[153] In 2015, Guinness World Records called Game of Thrones the most-pirated television program.[154]
IMAX
Beginning on January 23, 2015, the last two episodes of season four were shown in 205 IMAX theaters across the United States; Game of Thrones is the first TV series shown in this format.[155] The show earned $686,000 at the box office on its opening day[156] and $1.5 million during its opening weekend;[157] the week-long release grossed $1,896,092.[158]
Reception and achievements
Game of Thrones was highly anticipated by fans before its premiere,[159][160] and has become a critical and commercial success. According to The Guardian, by 2014 it was "the biggest drama" and "the most talked about show" on television.[8]
Cultural influence
Although Game of Thrones was dismissed by some critics before it began,[8] its success has been credited with an increase in the popularity of fantasy themes. On the eve of the second season's premiere, a CNN.com blog post by Joel Williams read, "After this weekend, you may be hard pressed to find someone who isn't a fan of some form of epic fantasy" and cited Ian Bogost as saying that the series continues a trend of successful screen adaptations beginning with Peter Jackson's 2001 The Lord of the Rings film trilogy and the Harry Potter films establishing fantasy as a mass-market genre; they are "gateway drugs to fantasy fan culture".[161] Its success in the face of its genre was attributed by writers to a longing for escapism in popular culture, frequent female nudity and a skill in balancing lighthearted and serious topics (dragons and politics, for example) which provided it with a prestige enjoyed by conventional, top-tier drama series.[8]
The series' popularity increased sales of the A Song of Ice and Fire novels (republished in tie-in editions), which remained at the top of bestseller lists for months. According to The Daily Beast, Game of Thrones was a favorite of sitcom writers and the series has been referred to in other TV series.[162] With other fantasy series, it has been cited for an increase in the purchase (and abandonment) of huskies and other wolf-like dogs.[163]
Game of Thrones has added to the popular vocabulary. The first season's frequent scenes in which characters explain their motives (or background) while having sex with prostitutes gave rise to the word "sexposition" for providing exposition with sex and nudity.[164] "Dothraki", the series' nomadic horsemen, was ranked fourth in a September 2012 Global Language Monitor list of words from television most used on the Internet.[165] After the second season the media began using "Game of Thrones" as a figure of speech or comparison for situations of intense conflict and deceit, such as the court battle about U.S. healthcare legislation,[166] the Syrian civil war[167] and power struggles in the Chinese government.[168]
"Khaleesi" has increased in popularity as a name for baby girls in the United States. In the novels and the TV series, the word means "queen" in Dothraki and is a title held by Daenerys Targaryen.[169]
Critical response
 | ||||||||||||||
|
Game of Thrones has received broad critical acclaim, although the series' frequent use of nudity and violence has been criticized. Its seasons have appeared on annual "best of" lists published by the Washington Post (2011), TIME (2011 and 2012) and The Hollywood Reporter (2012).[176][177][178] Seasons two through five received a Metacritic rating of 90 or higher: "universal acclaim", according to the website. Its six seasons average a 94-percent "Fresh" rating on Rotten Tomatoes; the first season was rated 90 percent,[170] the second 96 percent,[171] the third 97 percent,[172] the fourth 96 percent,[173] the fifth 95 percent[174] and the sixth season 94 percent.[175]
The performances of the large, predominantly British and Irish cast have also been praised. American actor Peter Dinklage's "charming, morally ambiguous, and self-aware"[179] Tyrion, who earned him Emmy and Golden Globe awards, was noted. "In many ways, Game of Thrones belongs to Dinklage", wrote Mary McNamara of the L.A. Times before Tyrion became the series' central figure in season two.[180][181] Several critics highlighted performances by actresses[180] and children.[182] Fourteen-year-old Maisie Williams, noted in the first season for her debut as Arya Stark, was singled out for her season-two work with veteran actor Charles Dance (Tywin Lannister).[183]
First-season reviewers noted its production values, fully realized world and compelling characters.[184] According to Variety, "There may be no show more profitable to its network than 'Game of Thrones' is to HBO. Fully produced by the pay cabler and already a global phenomenon after only one season, the fantasy skein was a gamble that has paid off handsomely".[185]
The second season was also well received by critics. Entertainment Weekly praised its "vivid, vital, and just plain fun" storytelling[186] and, according to the Hollywood Reporter, the show made a "strong case for being one of TV's best series"; its seriousness made it the only drama comparable to Mad Men or Breaking Bad.[187] The New York Times gave the series a mixed review, criticizing its number of characters, their lack of complexity and a meandering plot.[188]
The third season was very well received by critics, with Metacritic giving it a score of 91 out of 100 (indicating "universal acclaim").[189] It has a rating of 97 percent on Rotten Tomatoes, with an average score of 8.4 out of 10 based on 44 reviews.[172] The fourth season was also praised; Metacritic gave it a score of 94 out of 100 based on 29 reviews, again indicating "universal acclaim".[190] All episodes had positive reviews of 91 percent or higher on Rotten Tomatoes, and a 97-percent rating (based on 50 reviews) for the season as a whole.[173] The fifth season, based on the first four episodes, was also well received by critics and has a score of 91 out of 100 (based on 29 reviews) on Metacritic.[191] On Rotten Tomatoes, it has a rating of 95 percent and an average score of 8.6 out of 10 (based on 52 reviews).[174] The sixth season, based on the first episode, was praised by critics. It has a score of 73 out of 100 (based on nine reviews) on Metacritic, indicating "generally favorable reviews".[192] The season has a rating of 94 percent on Rotten Tomatoes, with an average score of 8.4 out of 10 based on 30 reviews.[175]
Sex and violence
Despite its otherwise enthusiastic reception by critics, Game of Thrones has been criticized for the amount of female nudity, violence, and sexual violence against women it depicts, and for the manner in which it depicts these themes. The Atlantic called the series' "tendency to ramp up the sex, violence, and—especially—sexual violence" of the source material "the defining weakness" of the adaptation.[193]
The amount of sex and nudity in the series, especially in scenes that are incidental to the plot, was the focus of much of the criticism aimed at the series in its first and second seasons. Stephen Dillane, who portrays Stannis Baratheon, likened the series' frequent explicit scenes to "German porn from the 1970s".[194] Charlie Anders wrote in io9 that while the first season was replete with light-hearted "sexposition", the second season appeared to focus on distasteful, exploitative, and dehumanizing sex with little informational content.[195] According to the Washington Post's Anna Holmes, the nude scenes appeared to be aimed mainly at titillating heterosexual men, right down to the Brazilian waxes sported by the women in the series' faux-medieval setting, which made these scenes alienating to other viewers.[196] The Huffington Post's Maureen Ryan likewise noted that Game of Thrones mostly presented women naked, rather than men, and that the excess of "random boobage" undercut any aspirations the series might have to address the oppression of women in a feudal society.[197] Saturday Night Live parodied this aspect of the adaptation in a sketch that portrayed the series as retaining a thirteen-year-old boy as a consultant whose main concern was showing as many breasts as possible.[195][198]
In the third season, which saw Theon Greyjoy lengthily tortured and eventually emasculated, the series was also criticized for its use of torture.[199] New York magazine called the scene "torture porn."[200] Madeleine Davies of Jezebel agreed, saying, "it's not uncommon that Game of Thrones gets accused of being torture porn — senseless, objectifying violence combined with senseless, objectifying sexual imagery." According to Davies, although the series' violence tended to serve a narrative purpose, Theon's torture in "The Bear and the Maiden Fair" was excessive.[201]
A scene in the fourth season's episode "Breaker of Chains", in which Jaime Lannister rapes his sister and lover Cersei, triggered a broad public discussion about the series' depiction of sexual violence against women. According to Dave Itzkoff of the New York Times, the scene caused outrage, in part because of comments by director Alex Graves that the scene became "consensual by the end". Itzkoff also wrote that critics fear that "rape has become so pervasive in the drama that it is almost background noise: a routine and unshocking occurrence".[202] Sonia Saraiya of The A.V. Club wrote that the series' choice to portray this sexual act, and a similar one between Daenerys Targaryen and Khal Drogo in the first season – both described as consensual in the source novels – as a rape appeared to be an act of "exploitation for shock value".[203] George R. R. Martin responded that rape and sexual violence are common in war, and that omitting them from the narrative would have undermined one of his novels' themes: that "the true horrors of human history derive not from orcs and Dark Lords, but from ourselves."[202]
In the fifth season's episode "Unbowed, Unbent, Unbroken", Sansa Stark is raped by Ramsay Bolton. Most reviewers, including those from Vanity Fair, Salon, The Atlantic, and The Daily Beast, found the scene gratuitous and artistically unnecessary.[193][204][205][206] For example, Joanna Robinson, writing for Vanity Fair, said that the scene "undercuts all the agency that's been growing in Sansa since the end of last season."[207] In contrast, Sara Stewart of The New York Post wondered why viewers were not similarly upset about the many background and minor characters who'd undergone similar or worse treatment.[208] In response to the scene, pop culture website The Mary Sue announced that it would cease coverage of the series because of the repeated use of rape as a plot device.[209] and U.S. senator Claire McCaskill said that she would no longer watch it.[210]
Fandom

A Song of Ice and Fire and Game of Thrones have a broad, active international fan base. In 2012 Vulture.com ranked the series' fans as the most devoted in popular culture, more so than Lady Gaga's, Justin Bieber's, Harry Potter's or Star Wars'.[211] Fans include Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom, U.S. president Barack Obama,[212][213] former British prime minister David Cameron,[214] Australian prime minister Julia Gillard[215][216] and Dutch foreign minister Frans Timmermans, who framed European politics in quotes from Martin's novels in a 2013 speech.[217]
BBC News said in 2013 that "the passion and the extreme devotion of fans" had created a phenomenon unlike anything related to other popular TV series, manifesting itself in fan fiction,[218] Game of Thrones-themed burlesque routines and parents naming their children after series characters; writers quoted attributed this success to the rich detail, moral ambiguity, sexual explicitness and epic scale of the series and novels.[219] The previous year, "Arya" was the fastest-rising girl's name in the U.S. after it jumped in popularity from 711th to 413th place.[220]
In 2013 about 58 percent of series viewers were male and 42 percent female, and the average male viewer was 41 years old.[221][222] According to SBS Broadcasting Group marketing director Helen Kellie, Game of Thrones has a high fan-engagement rate; 5.5 percent of the series' 2.9 million Facebook fans talked online about the series in 2012, compared to 1.8 percent of the more than ten million fans of True Blood (HBO's other fantasy series).[223] Vulture.com cited Westeros.org and WinterIsComing.net (news and discussion forums), ToweroftheHand.com (which organizes communal readings of the novels) and Podcastoficeandfire.com as fan sites dedicated to the TV and novel series;[211] and podcasts cover Game of Thrones.[224]
Awards and accolades
Game of Thrones has won dozens of awards since it debuted as a series, including 38 Primetime Emmy Awards,[91] 5 Screen Actors Guild Award, and a Peabody Award.[225] It holds the Emmy-award record for a scripted television series, ahead of Frasier (which received 37).[226] In 2013 the Writers Guild of America listed Game of Thrones as the 40th "best written" series in television history.[227] In 2015 The Hollywood Reporter placed it at number four on there "best TV shows ever" list,[228] while in 2016 the show was placed seventh on Empire's "The 50 best TV shows ever".[229] The same year Rolling Stone named it the twelfth "greatest TV Show of all time".[230]
The 2011 first season received 13 nominations (including Outstanding Drama Series), and won for Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Drama Series (given to Peter Dinklage for his portrayal of Tyrion Lannister) and Outstanding Main Title Design. Other nominations included Outstanding Directing ("Winter Is Coming") and Outstanding Writing ("Baelor").[91] Dinklage was also named Best Supporting Actor at the Golden Globe, Satellite and Scream Awards.[231][232][233] In 2012, the second season received six Creative Arts Emmy Awards from 11 nominations, including Outstanding Drama Series and Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Drama Series (Dinklage).[91]
The 2013 third season received 16 Emmy nominations, including Outstanding Drama Series, Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Drama Series (Dinklage), Outstanding Supporting Actress in a Drama Series (Emilia Clarke), Outstanding Guest Actress in a Drama Series (Diana Rigg) and Outstanding Writing ("The Rains of Castamere"), winning two Creative Arts Emmys.[91] In 2014 the fourth season received four Creative Arts Emmys from 19 nominations, which included Outstanding Drama Series, Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Drama Series (Dinklage), Outstanding Supporting Actress in a Drama Series (Lena Headey), Outstanding Guest Actress in a Drama Series (Rigg), Outstanding Directing ("The Watchers on the Wall") and Outstanding Writing ("The Children").[91]
The 2015 fifth season won the most Primetime Emmy Awards for a series in a year (12 awards from 24 nominations), including Outstanding Drama Series; other wins included Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Drama Series (Dinklage), Outstanding Directing ("Mother's Mercy") and Outstanding Writing ("Mother's Mercy"), and eight were Creative Arts Emmy Awards.[234] In 2016, the sixth season received the most nominations for the 68th Primetime Emmy Awards (23). It won for Outstanding Drama Series, Outstanding Directing ("Battle of the Bastards"), Outstanding Writing ("Battle of the Bastards"), and nine Creative Arts Emmys. Nominations included Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Drama Series (Dinklage and Kit Harington), Outstanding Supporting Actress in a Drama Series (Clarke, Headey and Maisie Williams), Outstanding Guest Actor in a Drama Series (Max von Sydow) and Outstanding Directing ("The Door").[235]
Viewer numbers
The first season averaged 2.5 million viewers for its first Sunday-night screenings and a gross audience (including repeats and on-demand viewings) of 9.3 million viewers per episode.[236] For its second season, the series had an average gross audience of 11.6 million viewers.[237] The third season was seen by 14.2 million viewers, making Game of Thrones the second-most-viewed HBO series (after The Sopranos).[238][239] For the fourth season, HBO said that its average gross audience of 18.4 million viewers (later adjusted to 18.6 million) had passed The Sopranos for the record.[240][241] By the sixth season the average per-episode gross viewing figure had increased to over 25 million, with nearly 40 percent of viewers watching on HBO digital platforms.[242] The series set records on pay-television channels in the United Kingdom (with a 2016 average audience of more than five million on all platforms)[243] and Australia (with a cumulative average audience of 1.2 million).[244]
The following graph indicates first-airing viewer numbers:
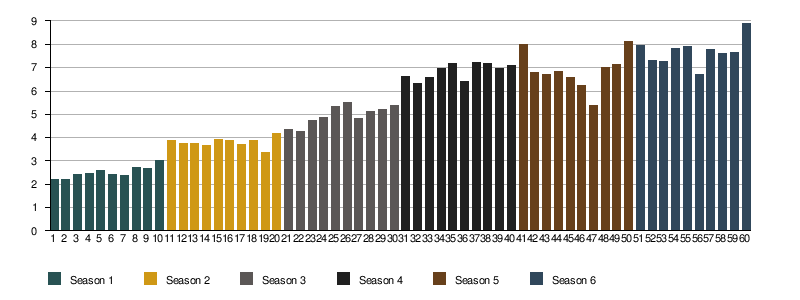
| Season | Ep. 1 | Ep. 2 | Ep. 3 | Ep. 4 | Ep. 5 | Ep. 6 | Ep. 7 | Ep. 8 | Ep. 9 | Ep. 10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season 1 | 2.22 | 2.20 | 2.44 | 2.45 | 2.58 | 2.44 | 2.40 | 2.72 | 2.66 | 3.04 | 2.52[245] |
| Season 2 | 3.86 | 3.76 | 3.77 | 3.65 | 3.90 | 3.88 | 3.69 | 3.86 | 3.38 | 4.20 | 3.80[245] |
| Season 3 | 4.37 | 4.27 | 4.72 | 4.87 | 5.35 | 5.50 | 4.84 | 5.13 | 5.22 | 5.39 | 4.97[246] |
| Season 4 | 6.64 | 6.31 | 6.59 | 6.95 | 7.16 | 6.40 | 7.20 | 7.17 | 6.95 | 7.09 | 6.84[247] |
| Season 5 | 8.00 | 6.81 | 6.71 | 6.82 | 6.56 | 6.24 | 5.40 | 7.01 | 7.14 | 8.11 | 6.88[248] |
| Season 6 | 7.94 | 7.29 | 7.28 | 7.82 | 7.89 | 6.71 | 7.80 | 7.60 | 7.66 | 8.89 | 7.69[249] |
Other media and products
Video games
The series has inspired four video games based on the TV series and novels. The strategy game Game of Thrones Ascent ties into the HBO series, making characters and settings available to players as they appear on television.[250]
Merchandise and exhibition

HBO has licensed a variety of merchandise based on Game of Thrones, including games, replica weapons and armor, jewelry, bobblehead dolls by Funko, beer by Ommegang and apparel.[251] High-end merchandise includes a $10,500 Ulysse Nardin wristwatch[252] and a $30,000 resin replica of the Iron Throne.[253] In 2013 and 2014, a traveling exhibition of costumes, props, armor and weapons from the series visited major cities in Europe and the Americas.[254]
Accompanying material
Thronecast: The Official Guide to Game of Thrones, a series of podcasts presented by Geoff Lloyd and produced by Koink, has been released on the Sky Atlantic website and the UK iTunes store during the series' run; a new podcast, with analysis and cast interviews, is released after each episode.[255] In 2014 and 2015 HBO commissioned Catch the Throne, two rap albums about the series.[256][257]
A companion book, Inside HBO's Game of Thrones (ISBN 978-1-4521-1010-3) by series writer Bryan Cogman, was published on September 27, 2012. The 192-page book, illustrated with concept art and behind-the-scenes photographs, covers the creation of the series' first two seasons and its principal characters and families.[258]
After the Thrones is a live aftershow in which hosts Andy Greenwald and Chris Ryan discuss episodes of the series. It airs on HBO Now the Monday after each sixth-season episode.[259] The Game of Thrones Live Concert Experience, a 28-city orchestral tour which will perform the series' soundtrack with composer Ramin Djawadi, is scheduled to begin February 15, 2017 in Kansas City, Missouri.[260]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Hibberd, James (July 18, 2016). "Game of Thrones: HBO announces summer return, 7 episodes". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved July 18, 2016.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones to end after season eight in 2018". BBC News. July 30, 2016. Archived from the original on August 3, 2016. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Fleming, Michael (January 16, 2007). "HBO turns Fire into fantasy series". Variety. Archived from the original on May 16, 2012. Retrieved March 2, 2010.
- ↑ Cogman, Bryan (November 6, 2014). Inside HBO's Game of Thrones. Orion. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-4732-1040-0. Retrieved November 6, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Martin, George R. R. (July 16, 2010). "From HBO". Not a Blog. Archived from the original on March 7, 2016. Retrieved March 14, 2013.
- ↑ Kachka, Boris (May 18, 2008). "Dungeon Master: David Benioff". New York. Archived from the original on May 3, 2016. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- ↑ O'Connell, Michael (May 22, 2012). "'Game of Thrones' Topped by 'Spartacus: Vengeance' as TV's Deadliest Series". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on June 29, 2016. Retrieved May 23, 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 Hughes, Sarah (March 22, 2014). "'Sopranos meets Middle-earth': how Game of Thrones took over our world". The Guardian. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved March 22, 2014.
- ↑ Orr, David (August 12, 2011). "Dragons Ascendant: George R. R. Martin and the Rise of Fantasy". The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 5, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ Richards, Linda (January 2001). "January interview: George R.R. Martin". January Magazine. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ Itzkoff, Dave (April 1, 2011). "His Beautiful Dark Twisted Fantasy: George R. R. Martin Talks Game of Thrones". The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Cogman, Bryan (November 6, 2014). Inside HBO's Game of Thrones. Orion. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-4732-1040-0. Retrieved November 6, 2016.
- ↑ Gevers, Nick (December 2000). "Sunsets of High Renown – An Interview with George R. R. Martin". Infinity Plus. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ "The battle between good and evil reigns – Martin talks about new series Game of Thrones". The Guardian. June 11, 2011. Archived from the original on April 5, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ Baum, Michele Dula (April 11, 2001). "A Song of Ice and Fire – Author George R.R. Martin's fantastic kingdoms". CNN. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ Kirschling, Gregory (November 27, 2007). "George R.R. Martin answers your questions". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (March 17, 2015). "Game of Thrones showrunners answer burning season 5 questions". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved March 18, 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Holland, Tom (March 24, 2013). "Game of Thrones is more brutally realistic than most historical novels". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on June 29, 2013. Retrieved March 24, 2013.
- ↑ Orr, David (August 12, 2011). "Dragons Ascendant: George R. R. Martin and the Rise of Fantasy". The New York Times. Archived from the original on July 22, 2016. Retrieved March 24, 2013.
Martin's books are essentially the War of the Roses with magic
- ↑ Milne, Ben (April 4, 2014). "Game of Thrones: The cult French novel that inspired George RR Martin". BBC News Magazine. Archived from the original on July 21, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- 1 2 Hibberd, James (May 29, 2012). "'Game of Thrones' scoop: Season 3 character list revealed – EXCLUSIVE". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on January 5, 2015. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
- 1 2 "Season 3: by the Numbers". Making Game of Thrones. November 2, 2012. Archived from the original on March 6, 2013. Retrieved November 3, 2012.
- ↑ Belloni, Matthew; Goldberg, Lesley (October 30, 2014). "'Game of Thrones' Cast Signs for Season 7 with Big Raises". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on August 13, 2016. Retrieved October 31, 2014.
- ↑ "More Details on the Return of Game of Thrones" (Press release). HBO (via ComingSoon.net). Archived from the original on October 27, 2014. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Game of Thrones: Cast". HBO. Retrieved May 18, 2015.
- ↑ Cogman, Bryan (November 6, 2014). Inside HBO's Game of Thrones. Gollancz. ASIN B00P187U0Y.
- ↑ Mitchell, Elvis (May 8, 2013). "UpClose: Game of Thrones with David Benioff and D. B. Weiss (FULL LENGTH)". KCRW. Retrieved May 15, 2013. At about 2:50.
- 1 2 Birnbaum, Debra (April 15, 2015). "'Game of Thrones' Creators: We Know How It's Going to End". Variety. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016.
- ↑ Benioff, David; D. Weiss (November 19, 2008). "Hello from Benioff and Weiss". A Song of Ice and Fire. Westeros. Archived from the original on September 18, 2013.
- ↑ Hudson, Laura (August 14, 2007). "Talking with George R. R. Martin Part 2". Publishers Weekly. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- 1 2 Martin, George R. R. (June 13, 2008). "Ice & Fire on HBO". Not a Blog.
- 1 2 Kirschling, Gregory (November 27, 2007). "George R.R. Martin answers your questions". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on October 17, 2014. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- ↑ Hibberd, Jame (November 11, 2008). "HBO orders fantasy pilot Thrones". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on October 16, 2014. Retrieved June 5, 2012.
- ↑ Robinson, Joanna (February 3, 2016). "Game of Thrones Show-Runners Get Extremely Candid About Their Original "Piece of Sh—t" Pilot". Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on April 17, 2016.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (January 14, 2010). "HBO: 'Game of Thrones' dailies 'look fantastic'". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on June 2, 2012. Retrieved July 24, 2010.
- ↑ Goldberg, Lesley (April 14, 2011). "'Game of Thrones' by The Numbers". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 14, 2011.
- ↑ Pallotta, Frank (April 7, 2012). "How HBO Let Game of Thrones Make an $8 Million Episode". Slate. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved March 14, 2015.
- ↑ "This Week's Cover: 'Game of Thrones,' the battle to make season 2 epic". Entertainment Weekly. March 14, 2012. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved March 18, 2012.
- ↑ Gornstein, Leslie (May 28, 2012). "Holy Flaming Warships! How Expensive Is Game of Thrones, Anyway?". E!. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved March 14, 2015.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (March 2015). "'Game of Thrones': EW spends 240 hours in Westeros". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 1, 2015.
- ↑ Lee, Ben (March 30, 2016). "Game of Thrones season 6 costs A LOT per episode: The HBO fantasy epic's massive budget is revealed". Digital Spy. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ↑ Barraclough, Leo (April 15, 2016). "'Game of Thrones' Casting Director Nina Gold to Receive BAFTA Award". Variety. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved March 18, 2016.
- ↑ Andreeva, Nellie (May 5, 2009). "Two will play HBO's 'Game'". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on May 9, 2009. Retrieved May 12, 2009.
- 1 2 Kit, Borys; Andreeva, Nellie (July 19, 2009). "Sean Bean ascends to "Game of Thrones"". Reuters. Archived from the original on November 6, 2015. Retrieved July 20, 2009.
- ↑ Martin, George R. R. (July 19, 2009). "A Casting We Will Go". Not A Blog. LiveJournal. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved July 20, 2009.
- ↑ Sepinwall, Alan (March 19, 2010). "'Game of Thrones' recasting: Ehle out, Fairley in". HitFix. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved February 24, 2013.
- ↑ Ryan, Maureen (May 21, 2010). "Exclusive: 'Game of Thrones' recasts noble role". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved February 24, 2013.
- ↑ Martin, George R. R. (May 21, 2010). "A New Daenerys". Not A Blog. LiveJournal. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved February 24, 2013.
- ↑ Ryan, Maureen (October 13, 2009). "The 'Games' afoot: HBO's 'Game of Thrones' gears up". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on August 17, 2016. Retrieved August 29, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Collins, Sean T. (April 2, 2015). "Blood Caffeine Sex Magic: How 'Game of Thrones' Gets Written". Observer. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 15, 2015.
- ↑ Karmali, Luke (March 30, 2015). "George R. R. Martin Not Writing Game of Thrones Season 6 Episode". IGN. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 15, 2015.
- 1 2 Ryan, Maureen (March 16, 2010). "HBO's 'Game of Thrones': The 'Buffy' and 'Battlestar' connection". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 15, 2015.
- ↑ "The Surprising Connection Between Game of Thrones and Monty Python". Vanity Fair. March 24, 2014. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved September 7, 2014.
- ↑ Robinson, Joanna (March 22, 2015). "Game of Thrones Creators Confirm the Show Will Spoil the Books". Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on June 21, 2016. Retrieved March 23, 2015.
- 1 2 Birnbaum, Debra (April 14, 2016). "'Game of Thrones' Creators Mull Shorter Final Seasons (EXCLUSIVE)". Variety. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 28, 2016.
- 1 2 Andreeva, Nellie (April 21, 2016). "'Game Of Thrones' Picked Up For Season 7, 'Veep' & 'Silicon Valley' Also Renewed By HBO". Deadline. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 21, 2016.
- ↑ Scott, Patrick (April 6, 2014). "Game of Thrones: how does the TV series compare to the books?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ↑ Ryan, Maureen (March 2, 2010). "HBO picks up 'Game of Thrones'; first picture, cast list". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 15, 2012.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (April 19, 2011). "HBO renews 'Game of Thrones' for second season!". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved July 19, 2015.
- ↑ Anders, Charlie Jane (June 5, 2012). "10 Best Changes Game of Thrones Made to A Clash of Kings". Gizmodo. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved January 3, 2016.
- ↑ O'Connell, Michael (April 10, 2012). "'Game of Thrones' Renewed for Season 3". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved July 19, 2015.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (March 30, 2012). "'Game of Thrones' showrunners on season 2, splitting Book 3 and their hope for a 70-hour epic". Entertainment Weekly. p. 3. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ↑ Schwartz, Terri (May 12, 2014). "'Game of Thrones' Season 4: Writer Bryan Cogman breaks down Tyrion's trial, book deviations and that White Walker scene". Zap2it. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 17, 2015.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (April 2, 2013). "'Game of Thrones' renewed for season 4". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on October 9, 2014. Retrieved April 2, 2013.
- ↑ Vineyard, Jennifer (June 11, 2013). "What Will Happen in Season 4 of Game of Thrones?". Vulture. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved February 7, 2014.
- 1 2 Goldman, Eric (April 8, 2014). "Game of Thrones Renewed for Season 5 and Season 6". IGN. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 8, 2014.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones Season 5: Inside the Episode #9 (HBO)". YouTube. June 7, 2015. Retrieved June 9, 2015.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (June 18, 2014). "'Game of Thrones' showrunners talk season 5: 'There will be Dorne'". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on January 12, 2015. Retrieved June 18, 2014.
- ↑ Kain, Erik (April 12, 2015). "Why Season 5 Of 'Game Of Thrones' Is The Most Important Yet For HBO". Forbes. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 13, 2015.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones Episodes: EP510: Mother's Mercy". Westeros.org. Retrieved June 18, 2015.
- ↑ Noble, Matt (August 18, 2015). "'Game of Thrones' director Jeremy Podeswa dishes Jon Snow death, teases season six (Exclusive Video)". GoldDerby. Archived from the original on April 3, 2016. Retrieved August 21, 2015.
- 1 2 Hibberd, James (May 24, 2016). "George R. R. Martin revealed 3 huge shocks to Game of Thrones producers". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 24, 2016.
- ↑ Vineyard, Jennifer (May 5, 2016). "Why It's a Misconception That Game of Thrones Has Gone 'Off-Book'". Vulture. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 24, 2016.
- ↑ Collins, Sean T. (March 20, 2013). "Q&A: 'Game of Thrones' Insider Bryan Cogman on the Biggest Season Yet". Rolling Stone. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved March 24, 2013.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (March 30, 2012). "'Game of Thrones' showrunners on season 2, splitting Book 3 and their hope for a 70-hour epic". Entertainment Weekly. p. 2. Archived from the original on January 12, 2015. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ↑ "HBO to film TV pilot in Belfast, Northern Ireland" (Press release). Northern Ireland Executive. April 21, 2009. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- 1 2 3 Roberts, Josh (April 1, 2012). "Where HBO's hit 'Game of Thrones' was filmed". USA Today. Archived from the original on April 1, 2012. Retrieved March 8, 2013.
- ↑ "Medieval keep becomes film set". BBC News. October 23, 2009. Archived from the original on August 11, 2016. Retrieved April 11, 2012.
- ↑ Miller, Phil (June 17, 2013). "Beaten in Game of Thrones: why Scotland lost £160m chance to host TV series". The Herald. Archived from the original on May 29, 2015. Retrieved June 17, 2013.
- 1 2 3 Smith, Oliver (June 7, 2016). "Iceland's most spectacular Game of Thrones filming locations". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on August 26, 2016.
- ↑ Phelan, Jessica (April 29, 2014). "The 7 kingdoms in 'Game of Thrones' are actually these 5 real-world places". Salon. Archived from the original on June 17, 2016. Retrieved August 23, 2014.
- ↑ Schwartz, Terri (January 28, 2013). "'Game of Thrones' casts a bear and shoots in Los Angeles for major Season 3 scene". Zap2it. Archived from the original on January 30, 2013. Retrieved March 8, 2013.
- ↑ "New set photos from Klis and Dubrovnik". WinterIsComing.net. September 18, 2013. Archived from the original on December 24, 2013. Retrieved September 19, 2013.
- ↑ "That's a wrap! Season 4 filming is complete". WinterIsComing.net. November 21, 2013. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved November 26, 2013.
- ↑ Burgen, Stephen (July 6, 2014). "Game of Thrones fifth series: more than 10,000 Spaniards apply to be extras". The Guardian. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (June 3, 2015). "Game of Thrones returning to Spain for season 6". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on May 30, 2016. Retrieved June 3, 2015.
- ↑ "EMMY®- AND GOLDEN GLOBE-WINNING HBO SERIES GAME OF THRONES TO BEGIN PRODUCTION ON SEASON SEVEN THIS SUMMER" (Press release). HBO. July 18, 2016. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved August 31, 2016.
- 1 2 Hibberd, James (June 29, 2016). "Game of Thrones season 7 directors revealed". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Cast & Crew". HBO. Retrieved December 28, 2015.
- ↑ "ALIK SAKHAROV ASC". Cinematographers. Retrieved August 29, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Game of Thrones". Emmys.com. Retrieved February 21, 2016.
- ↑ Ginsberg, Merle (June 19, 2015). "'Game of Thrones' Season 6 Adds New Costume Designer". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved December 13, 2015.
- 1 2 3 Wischhover, Cheryl (June 4, 2012). "Game of Thrones' Hair and Wardrobe Secrets Revealed". Fashionista. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved June 6, 2012.
- 1 2 Snead, Elizabeth (June 11, 2012). "'Game of Thrones' Designer Michelle Clapton's Secret Source for Wildling Bones: eBay". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ↑ Elio (September 16, 2012). "Game of Thrones Wins Big at Creative Arts Emmys". Westeros.org. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved February 21, 2016.
- ↑ Elio (June 22, 2011). "Interview with VFX Producer Lucy Ainsworth-Taylor". Westeros.org. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved August 18, 2014.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season 2". Pixomondo. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved August 19, 2014.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season 3". Pixomondo. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved August 19, 2014.
- ↑ "Mackevision erhält Emmy-Nominierung für visuelle Effekte in "Game of Thrones" – Pressemeldung" (PDF) (in German). Mackevision. July 10, 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 21, 2014. Retrieved August 19, 2014.
- ↑ Johnson, Thomas (March 19, 2015). "How 'Game of Thrones' creates its dragons". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 12, 2015.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones". Image Engine. Retrieved May 18, 2015.
- ↑ "Current Projects". Crazy Horse Effects. Retrieved May 18, 2015.
- ↑ Andersen, Asbjoern (August 6, 2014). "This is how the fantastical sound of Game Of Thrones is made". A Sound Effect. Retrieved August 6, 2014.
- ↑ Calautti, Katie (June 12, 2014). "Game of Thrones: The Secrets Behind All the Stabbings, Screams, and Sex Scenes". Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on May 6, 2016. Retrieved August 6, 2014.
- ↑ Fernandez, Sofia M. (September 10, 2011). "Emmys 2011: 'Game of Thrones' Title Sequence Gives Series Its First Emmy". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved June 1, 2013.
- 1 2 Perkins, Will (May 11, 2011). "Game of Thrones (2011)". Art of the Title. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved June 1, 2013.
- ↑ Axelrod, John (March 30, 2013). "How The Innovative Game Of Thrones Opening Credits Were Built". Forbes. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 18, 2015.
- ↑ Appelo, Tim (April 19, 2011). "Secrets Behind 'Game of Thrones' Opening Credits (Video)". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 18, 2015.
- ↑ Ryan, Maureen (February 2, 2011). "'Game of Thrones' Changes Its Tune, Hires New Composer". AOL TV. Archived from the original on February 2, 2011. Retrieved July 20, 2011.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones Soundtrack Details". Film Music Reporter. May 31, 2011. Archived from the original on July 25, 2016. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
- ↑ "Ramin Djawadi Biography". Retrieved August 29, 2016.
- 1 2 Vineyard, Jennifer (July 21, 2016). "Game of Thrones Composer Ramin Djawadi on the Show's Key Musical Elements, and That Godfather-esque Finale Tune". Vulture. Retrieved November 6, 2016.
- ↑ Read, Max (May 6, 2013). "What Is Going on With the Accents in Game of Thrones?". Gawker. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 8, 2013.
- ↑ Martin, Denise (April 23, 2013). "Learn to Speak Dothraki and Valyrian From the Man Who Invented Them for Game of Thrones". Vulture. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Can you speak Dothraki?". BBC Radio 4's Today programme. May 9, 2013. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 10, 2013.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones season 3 to film in Northern Ireland". Northern Ireland Screen. April 12, 2012. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 12, 2012.
- 1 2 Bradley, Una (April 12, 2013). "The 'Game of Thrones' tourists: How much is the hit HBO fantasy series worth to its home, Northern Ireland?". The Irish Times. Archived from the original on May 8, 2013. Retrieved April 12, 2013.
- ↑ Shankman, Samantha. "Will Game of Thrones make Ireland the next New Zealand?". Quartz. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ↑ McAdam, Noel (May 16, 2012). "Game of Thrones pumped £43m into Northern Ireland's economy, and more could be on the way". The Belfast Telegraph. Retrieved May 16, 2012.
- ↑ Pym, Hugh (May 11, 2014). "Game of Thrones boost to economy in Northern Ireland". BBC News. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 11, 2014.
- ↑ Adam, Shabana (April 17, 2013). "Travel News: Game of Thrones Sparks Big Boosts in Hotel Bookings to Filming Locations". Female First. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2013.
- ↑ Blum, Jeremy (April 30, 2014). "Game of Thrones premieres on CCTV, viewers call it an edited 'mess'". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 4, 2014.
- ↑ "International Game of Thrones airings". WinterIsComing.net. August 2, 2011. Archived from the original on August 2, 2011. Retrieved October 2, 2011.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (November 30, 2011). "'Game of Thrones' scoop: DVD release date, details, photos". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on October 17, 2014. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ↑ Richwine, Lisa (March 16, 2012). "'Game of Thrones' rules HBO's DVD sales". Reuters. Archived from the original on October 18, 2014. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: The Complete First Season Premium Edition Gift Box [8 Discs] [Blu-ray/DVD] (Blu-ray Disc)". Best Buy. November 20, 2012. Archived from the original on April 25, 2016. Retrieved April 19, 2016.
- ↑ "'Game of Thrones' season 2 DVD date and extras revealed". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on July 4, 2014. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (February 22, 2013). "'Game of Thrones' early DVD sales breaking HBO records". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on October 30, 2014. Retrieved February 23, 2013.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones season 3 on iTunes Australian Store". iTunes. Retrieved March 31, 2013.
- ↑ Lambert, David (June 24, 2013). "Game of Thrones – 2014 Release Date, Package Art for 'The Complete 3rd Season', on DVD, Blu". TVShowsOnDVD.com. Archived from the original on September 9, 2016. Retrieved June 25, 2013.
- ↑ Lambert, David (July 16, 2014). "Game of Thrones – 'The Complete 4th Season' Press Release: Date, Art, Cost, Extras". TVShowsOnDVD.com. Archived from the original on September 8, 2016. Retrieved July 16, 2014.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season 5 [Blu-ray + Digital HD]". Amazon. Archived from the original on May 16, 2016. Retrieved October 18, 2015.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: The Complete Sixth Season [Blu-ray]". Amazon. Archived from the original on August 14, 2016. Retrieved August 29, 2016.
- 1 2 3 Jarvey, Natalie (April 9, 2015). "'Game of Thrones' Piracy Soars Ahead of Season 5 Premiere". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on June 29, 2016. Retrieved April 10, 2015.
- ↑ Greenberg, Andy (May 9, 2012). "HBO's 'Game Of Thrones' On Track To Be Crowned Most Pirated Show Of 2012". Forbes. Archived from the original on July 2, 2016. Retrieved May 9, 2012.
- ↑ "'Game of Thrones' Most Pirated TV-Show of 2013". TorrentFreak. December 25, 2013. Archived from the original on June 25, 2016. Retrieved December 28, 2013.
- ↑ Williams, Rhiannon (April 8, 2014). "Game of Thrones still most pirated TV show". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on May 4, 2016. Retrieved June 23, 2014.
- ↑ Kamen, Matt (December 28, 2015). "Game of Thrones tops 2015's piracy charts". Wired. Archived from the original on March 10, 2016. Retrieved December 28, 2015.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones tops TV show internet piracy chart". BBC News. December 24, 2012. Archived from the original on July 20, 2016. Retrieved January 4, 2013.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones Most Pirated TV-Show of 2012". TorrentFreak. December 23, 2012. Archived from the original on June 17, 2016. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
- ↑ "Who's Pirating Game of Thrones, And Why?". TorrentFreak. May 20, 2012. Archived from the original on August 2, 2016. Retrieved March 31, 2013.
- ↑ Piotrowski, Daniel (April 25, 2013). "US ambassador Jeffrey Bleich pleads: Australia, stop pirating Game of Thrones". The Age. Archived from the original on January 25, 2015. Retrieved April 25, 2013.
- ↑ Kain, Erik (May 10, 2012). "International Audiences Have Few Choices To Legally Watch HBO's 'Game Of Thrones'". Forbes. Archived from the original on May 8, 2016. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ↑ "Why People Pirate Game of Thrones, a Global Cost Breakdown". TorrentFreak. April 13, 2014. Archived from the original on July 10, 2016. Retrieved April 15, 2014.
- ↑ Pinchefsky, Carol (March 3, 2013). "How HBO Is Protecting 'Game of Thrones' from Online Piracy in 2013". Forbes. Archived from the original on March 7, 2016. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
- ↑ "Nearly Half of Game of Thrones Season 5 Just Leaked". Gizmodo. Archived from the original on June 26, 2016.
- ↑ Steinberg, Joseph (April 12, 2015). "Nearly Half Of 'Game of Thrones' Upcoming Season Leaks Online – Was HBO Hacked?". Forbes. Archived from the original on April 12, 2016. Retrieved April 12, 2015.
- ↑ Denham, Jess (April 23, 2015). "Game of Thrones season 5 breaks piracy record with 32m illegal downloads". The Independent. Archived from the original on March 7, 2016. Retrieved May 12, 2015.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones Season Finale breaks Piracy Records". TorrentFreak. June 15, 2015. Archived from the original on August 11, 2016. Retrieved June 15, 2015.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (March 2, 2016). "Game of Thrones lockdown: HBO won't send press any season 6 episodes". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on April 15, 2016. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- ↑ "Downloads don't matter". The Sydney Morning Herald. Australian Associated Press. February 26, 2013. Archived from the original on March 18, 2016. Retrieved March 2, 2013.
- ↑ Kuchera, Ben (April 21, 2014). "Game of Thrones is the first 'free-to-play' TV show, and gaming is racing to catch up". Polygon. Archived from the original on March 8, 2016. Retrieved April 21, 2014.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones at the Oxford Union – Full Address". YouTube. Retrieved June 15, 2015.
- ↑ Lynch, Kevin (August 31, 2015). "Maisie Williams overjoyed as Game of Thrones marches into Guinness World Records 2016". Guinness World Records. Archived from the original on June 3, 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (January 6, 2015). "'Game of Thrones' coming to IMAX: First TV series released in format". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on January 23, 2015. Retrieved January 22, 2015.
- ↑ Khatchatourian, Maane (January 31, 2015). "Box Office: 'Game of Thrones' Eyes $2 Million in Imax Debut". Variety. Archived from the original on August 28, 2016. Retrieved February 1, 2015.
- ↑ Mendelson, Scott (February 1, 2015). "Box Office: 'American Sniper' Sets Super Bowl Record, 'Game Of Thrones' Scores IMAX Touchdown". Forbes. Archived from the original on April 21, 2016. Retrieved February 1, 2015.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones (IMAX) (2015)". Box Office Mojo. Internet Movie Database. February 6, 2015. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved April 12, 2016.
- ↑ Gregory, Mathilda (July 23, 2010). "Is A Game of Thrones the most eagerly anticipated TV show ever?". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on November 20, 2011. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- ↑ Colins, Scott (August 8, 2010). "With 'Game of Thrones,' HBO is playing for another 'True Blood'". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved March 13, 2013.
- ↑ Williams, Joel (March 30, 2012). "Mainstream finally believes fantasy fans". CNN. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 5, 2012.
- ↑ Lacob, Jace (September 21, 2012). "'Game of Thrones': 'Modern Family,' 'Parks and Rec' Writers on Why They Love the HBO Drama". The Daily Beast. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved September 27, 2012.
- ↑ O'Brian, Liam (December 26, 2012). "Game of Thrones inspired Huskie craze goes cold as owners give up on dogs". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved March 10, 2013.
- ↑ Hann, Michael (March 11, 2012). "How 'sexposition' fleshes out the story". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on March 28, 2013. Retrieved March 29, 2012.
- ↑ Steinmetz, Kate (September 25, 2012). "And the Top TV Words of the Year Are ...". Time. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved September 27, 2012.
- ↑ Brescia, Ray (July 6, 2012). "Game of Robes: Why Conservatives May Ultimately Praise the Roberts Switch on Health Care Reform". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved July 7, 2012.
- ↑ Varsavsky, Martin (July 4, 2012). "The Game of Thrones Around Us". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved July 7, 2012.
- ↑ Garnaut, John (July 1, 2012). "Strongmen of China playing a risky game of thrones". The Age. Melbourne. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved July 7, 2012.
- ↑ O'Neil, Lauren (April 11, 2014). "There are now more babies named 'Khaleesi' than 'Betsy' or 'Nadine' in the U.S.". CBC News. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 27, 2016.
- 1 2 "Game of Thrones: Season 1 (2011)". Rotten Tomatoes. Retrieved August 27, 2015.
- 1 2 "Game of Thrones: Season 2 (2012)". Rotten Tomatoes. Retrieved August 27, 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Game of Thrones: Season 3 (2013)". Rotten Tomatoes. Retrieved August 27, 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Game of Thrones: Season 4". Rotten Tomatoes. Retrieved August 27, 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Game of Thrones: Season 5 (2015)". Rotten Tomatoes. Retrieved August 27, 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Game of Thrones: Season 6 (2016)". Rotten Tomatoes. Retrieved April 25, 2016.
- ↑ "Thrones lands on tons of top TV shows of 2011 lists". WinterIsComing.net. December 23, 2011. Archived from the original on March 5, 2013. Retrieved December 23, 2011.
- ↑ Martin, George R. R. (December 21, 2011). "Plaudits for GAME OF THRONES". Not A Blog. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved December 23, 2011.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: The best of 2012". WinterIsComing.net. December 27, 2012. Archived from the original on April 11, 2014. Retrieved January 4, 2013.
- ↑ Gilbert, Matthew (April 15, 2011). "Fantasy comes true with HBO's 'Game of Thrones'". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- 1 2 McNamara, Mary (April 15, 2011). "Swords, sex and struggles". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- ↑ Paskin, Willa (March 29, 2012). "Bloody, bloody "Game of Thrones"". Salon. Archived from the original on March 29, 2012. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- ↑ Roush, Matt (April 15, 2011). "Roush Review: Grim Thrones Is a Crowning Achievement". TV Guide. Archived from the original on August 21, 2014. Retrieved May 11, 2011.
- ↑ "The Tywin and Arya Show". Rolling Stone. May 15, 2012. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- ↑ Tucker, Ken (April 14, 2011). "Game of Thrones (2011)". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on October 17, 2014. Retrieved May 11, 2011.
- ↑ Levine, Stuart (December 27, 2011). "Cablers hit highs, lows, PR hurdles in 2011". Variety. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved December 31, 2011.
- ↑ Tucker, Ken (March 21, 2012). "TV Review: Game Of Thrones (2012)". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on October 27, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2012.
- ↑ Goodman, Tim (March 27, 2012). "'Game of Thrones' Season 2: TV Review". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on February 3, 2015. Retrieved March 28, 2012.
- ↑ Genzlinger, Neil (March 29, 2012). "Uneasy Lies the Head That Steals a Crown: 'Game of Thrones' on HBO". The New York Times. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved March 29, 2012.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season 3". Metacritic. Retrieved March 28, 2013.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season 4". Metacritic. Retrieved April 8, 2014.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season 5". Metacritic. Retrieved April 11, 2015.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season 6". Metacritic. Retrieved April 28, 2016.
- 1 2 Kornhaber, Spencer; Orr, Christopher; Sullivan, Amy (May 17, 2015). "Game of Thrones: A Pointless Horror and a Ridiculous Fight". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 18, 2015.
- ↑ Frost, Caroline (January 14, 2014). "'Game of Thrones' Star Stephen Dillane Admits the Nudity Is Like 'German Porn from the 1970s'". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved January 16, 2014.
- 1 2 Anders, Charlie Jane (May 2, 2012). "Is Game of Thrones' gratuitous sex worse than the gratuitous violence?". io9. Archived from the original on September 11, 2015. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ↑ Holmes, Anna (April 26, 2012). "Skin is wearing thin on HBO's 'Game of Thrones'". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ↑ Ryan, Maureen (May 29, 2011). "'Game of Thrones' Season 1, Episode 7 Recap". AOL TV. Archived from the original on May 2, 2012. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ↑ Toder, Matt (April 15, 2012). "SNL Explains the Nudity in Game of Thrones". Gawker. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ↑ Orr, Christopher (May 13, 2013). "Game of Thrones' Worst Scene Yet?". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- ↑ David, Allison P. (May 12, 2014). "Game of Thrones Couple of the Week: Tyrion and Shae Are Never Getting Back Together". New York. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved July 17, 2015.
- ↑ Davis, Madeleine (May 13, 2013). "Game of Boners: This Is Torture Porn". Jezebel. Retrieved May 17, 2013.
- 1 2 Itzkoff, Dave (May 2, 2014). "For 'Game of Thrones,' Rising Unease Over Rape's Recurring Role". The New York Times. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 4, 2014.
- ↑ Saraiya, Sonia (April 20, 2014). "Rape of Thrones Why are the Game Of Thrones showrunners rewriting the books into misogyny?". The A.V. Club. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 21, 2014.
- ↑ Silman, Anna (May 18, 2015). "Here's why people are so upset about the latest "Game of Thrones" rape: "So cheap, such an obvious choice, I felt offended as a fan"". Salon. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved June 26, 2015.
- ↑ Runcie, Charlotte (May 17, 2015). "Game of Thrones: Unbowed, Unbent, Unbroken, season 5 episode 6, review: 'raw emotion'". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 18, 2015.
- ↑ Leon, Melissa (May 19, 2015). "The Rape of Sansa Stark: 'Game of Thrones' Goes Off-Book and Enrages Its Female Fans". The Daily Beast. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 20, 2015.
- ↑ Robinson, Joanna (May 17, 2015). "Game of Thrones Absolutely Did Not Need to Go There with Sansa Stark". Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 18, 2015.
- ↑ Stewart, Sara (May 19, 2015). "It's a Stark reality: Outrage over Sansa rape scene misses the point". New York Post. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2015.
- ↑ Pantozzi, Jill (May 18, 2015). "We Will No Longer Be Promoting HBO's Game of Thrones". The Mary Sue. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 20, 2015.
- ↑ "'Gratuitous and disgusting': Senator leads boycott of Game of Thrones over shocking rape scene of Sansa Stark but actress playing her says she 'kinda loved it'". Daily Mail. May 20, 2015. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved May 20, 2015.
- 1 2 "The 25 Most Devoted Fan Bases". Vulture. October 15, 2012. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved October 17, 2012.
- ↑ Shear, Michael (December 29, 2013). "Obama's TV Picks". The New York Times. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved December 29, 2013.
- ↑ Ghahremani, Tanya (December 30, 2013). "President Obama 'Really Likes' Game of Thrones, In Case You Were Wondering". Complex. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved December 30, 2013.
- ↑ Armstrong, Victoria (April 7, 2015). "David Cameron admits he is a 'Throney' and 'huge fan' on Game of Thrones studio tour". Daily Express. Retrieved April 10, 2015.
- ↑ Taylor, Lenore (May 30, 2013). "Julia Gillard reveals Game of Thrones addiction". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on July 16, 2013. Retrieved May 30, 2013.
- ↑ Gillard, Julia (April 7, 2014). "Game of Thrones has parallels with my time as Australian prime minister". The Guardian. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved April 7, 2014.
- ↑ Luoma, Sarah (May 31, 2013). "Dutch foreign minister uses 'Game of Thrones' as political analogy". Digital Spy. Archived from the original on October 19, 2014. Retrieved November 2, 2016.
- ↑ Templeton, Molly (June 16, 2013). "The best (and the weirdest) of "Game of Thrones" fanfiction". Salon. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved July 6, 2013.
- ↑ de Castella, Tom (March 22, 2013). "Game of Thrones: Why does it inspire such devotion among fans?". BBC News Magazine. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved March 23, 2013.
- ↑ Carlson, Adam (May 10, 2013). "'Game of Thrones' domination is nearly complete: 'Arya' is the fastest-rising name for baby girls". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on October 19, 2014. Retrieved May 10, 2013.
- ↑ Hibberd, James (March 31, 2013). "HBO: 'Game of Thrones' piracy is a compliment". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on October 28, 2014. Retrieved April 3, 2013.
- ↑ Watercutter, Angela (June 3, 2013). "Yes, Women Really Do Like Game of Thrones (We Have Proof)". Wired. Archived from the original on March 21, 2014. Retrieved June 6, 2013.
- ↑ Kellie, Helen (October 26, 2012). "Social is coming of age in the marketing mix – a TV perspective". Marketing magazine. Archived from the original on December 6, 2014. Retrieved October 29, 2012.
- ↑ Nguyen, Nicole (May 3, 2013). "In the Game of Thrones, These Podcasts Play to Win". Geeksugar. Archived from the original on June 23, 2014. Retrieved May 4, 2013.
- ↑ "Complete List of Recipients of the 71st Annual Peabody Awards". Peabody Awards. Retrieved November 5, 2016.
- ↑ Dockterman, Eliana (September 18, 2016). "Game of Thrones Now Has the Most Emmy Wins Ever". Time. Retrieved September 19, 2016.
- ↑ "'101 Best Written TV Series Of All Time' From WGA/TV Guide: Complete List". Deadline.com. June 2, 2013. Archived from the original on June 3, 2013. Retrieved November 5, 2016.
- ↑ "Hollywood's 100 Favorite TV Shows". The Hollywood Reporter. Retrieved November 5, 2016.
- ↑ "The 50 Greatest TV Shows of All Time". Empire. Retrieved November 5, 2016.
- ↑ "100 Greatest TV Shows of All Time". Rolling Stone. Retrieved November 5, 2016.
- ↑ "Golden Globes 2012: The Winners List". The Hollywood Reporter. January 15, 2012. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved August 29, 2016.
- ↑ West, Kelly (June 19, 2011). "The 2011 Scream Awards Winners: Vampires, Wizards And Swans". Cinemablend. Archived from the original on August 29, 2012. Retrieved August 29, 2016.
- ↑ "2011 Winners". International Press Academy. June 19, 2011. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved August 29, 2016.
- ↑ Prudom, Laura (September 20, 2015). "'Game of Thrones' Sets Record for Most Emmy Wins in a Year". Variety. Archived from the original on September 1, 2016. Retrieved September 21, 2015.
- ↑ Prudom, Laura (July 14, 2016). "'Game of Thrones' Rules 2016 Emmy Race With 23 Nominations". Variety. Archived from the original on August 30, 2016. Retrieved July 14, 2016.
- ↑ Thomas, June (March 29, 2012). "How Much Gold Is Game of Thrones Worth". Slate. Archived from the original on May 8, 2016. Retrieved June 5, 2014.
- ↑ "HBO Renews 'Game of Thrones' for Fourth Season" (Press release). HBO. April 2, 2013. Retrieved August 23, 2014.
- ↑ Ritter, Dan (August 7, 2013). "Game of Thrones is Time Warner's Cash Cow". Wall Street Cheat Sheet. Archived from the original on October 20, 2014. Retrieved August 8, 2013.
- ↑ Adalian, Josef (June 8, 2013). "For HBO, Game of Thrones Ratings Second Only to The Sopranos". Vulture. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved June 6, 2013.
- ↑ Fienberg, Daniel (June 5, 2014). "'Game of Thrones' has become more popular than 'The Sopranos' sorta kinda". HitFix. Archived from the original on June 3, 2016. Retrieved June 5, 2014.
- ↑ Sinha-Roy, Piya (June 16, 2014). "'Game of Thrones' draws 7.1 million viewers for blood-filled finale". Reuters. Archived from the original on October 20, 2015. Retrieved July 13, 2014.
- ↑ Shepherd, Jack (July 19, 2016). "Game of Thrones season 6 ratings: Show brought in 25.1 million viewers on average per episode". The Independent. Archived from the original on August 19, 2016. Retrieved July 22, 2016.
- ↑ Plunkett, John (July 6, 2016). "Game of Thrones most popular Sky series ever with 5m viewers". The Guardian. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved July 6, 2016.
- ↑ Idato, Michael (June 29, 2016). "Game of Thrones season six finale sets Australian audience record for Foxtel". The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on October 20, 2016. Retrieved July 6, 2016.
- 1 2 "Game of Thrones: Season Two Ratings". TV Series Finale. June 11, 2012. Archived from the original on September 1, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2016.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season Three Ratings". TV Series Finale. June 12, 2013. Archived from the original on September 1, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2016.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season Four Ratings". TV Series Finale. June 18, 2014. Archived from the original on September 1, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2016.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season Five Ratings". TV Series Finale. June 16, 2015. Archived from the original on September 1, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2016.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones: Season Six Ratings". TV Series Finale. June 28, 2015. Archived from the original on September 1, 2016. Retrieved April 24, 2016.
- ↑ Fahey, Mike (April 22, 2013). "Game of Thrones: Ascent is More Up-to-Date With the Show Than You Are". Kotaku. Archived from the original on August 24, 2016. Retrieved April 23, 2013.
- ↑ Sacco, Dominic (June 11, 2013). "Brand Profiles: Game of Thrones". Licensing.biz. Archived from the original on April 29, 2016. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Miller, Julie (May 9, 2013). ""Is the $10,500 Game of Thrones Watch Blood-Resistant?" and Our Other Most Pressing Concerns About the Official "Night's" Timepiece". Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on December 21, 2014. Retrieved May 10, 2013.
- ↑ Miller, Julie (June 5, 2012). "The Pros and Cons of Owning a $30,000 Game of Thrones Replica Throne". Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on November 29, 2014. Retrieved May 10, 2013.
- ↑ "Exhibition". HBO. Retrieved February 19, 2013.
- ↑ "Thronecast: The Official Fan Show for Game of Thrones on Sky Atlantic HD". iTunes Store. April 18, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ↑ Whelan, Robbie (March 4, 2014). "Unlikely Mix: Rappers, Dragons and Fantasy: HBO Hires Hip-Hop, Latin-Music Artists to Promote 'Game of Thrones'". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on June 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2014.
- ↑ Joyce, Colin (March 7, 2015). "Snoop Dogg, Talib Kweli, Mastodon, More To Appear On 'Game of Thrones' Mixtape". Spin. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ↑ Edwards, Richard (September 21, 2012). "Inside HBO's Game Of Thrones by Bryan Cogman REVIEW". SFX. Archived from the original on October 20, 2014. Retrieved September 27, 2012.
- ↑ Snierson, Dan (April 4, 2016). "HBO orders Game of Thrones weekly after-show from Bill Simmons". Entertainment Weekly. Archived from the original on May 6, 2016. Retrieved April 5, 2016.
- ↑ "Game of Thrones concert experience hits the road in 2017". The Guardian. August 8, 2016. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. Retrieved August 9, 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Game of Thrones. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Game of Thrones |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Game of Thrones tourism. |
- Game of Thrones – official website
- Game of Thrones – official UK website
- Game of Thrones at the Internet Movie Database
- Game of Thrones Viewers Guide at HBO.com
- Making Game of Thrones Blog