Görlitz
| Görlitz | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
From top: View over Görlitz, inside Görlitz Department Store, Untermarkt (market square), Landeskrone (Sedło) mountain, Upper Lusatian Library of Sciences (Oberlausitzische Bibliothek der Wissenschaften) | |||||||
| |||||||
 Görlitz | |||||||
Location of Görlitz within Görlitz district 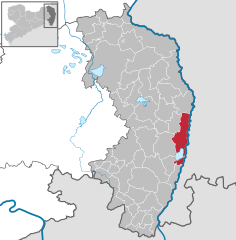
 | |||||||
| Coordinates: 51°09′10″N 14°59′14″E / 51.15278°N 14.98722°ECoordinates: 51°09′10″N 14°59′14″E / 51.15278°N 14.98722°E | |||||||
| Country | Germany | ||||||
| State | Saxony | ||||||
| District | Görlitz | ||||||
| Government | |||||||
| • Mayor | Siegfried Deinege | ||||||
| Area | |||||||
| • Total | 67.22 km2 (25.95 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population (2015-12-31)[1] | |||||||
| • Total | 55,255 | ||||||
| • Density | 820/km2 (2,100/sq mi) | ||||||
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | ||||||
| Postal codes | 02826–02828 | ||||||
| Dialling codes | 03581 | ||||||
| Vehicle registration | GR | ||||||
| Website |
www | ||||||
Görlitz ([ˈɡœɐ̯lɪts ]; Polish: Zgorzelec, Upper Sorbian: Zhorjelc, Lower Sorbian: Zgórjelc, Czech: Zhořelec) is a town in Germany and the capital of the district of Görlitz. It is the easternmost town in the country, located on the Lusatian Neisse River in the Bundesland (Federal State) of Saxony. It is opposite the Polish town of Zgorzelec, which was a part of Görlitz until 1945.
Görlitz is the second biggest town of Lusatia and the biggest of Upper Lusatia. It belonged to the Electorate of Saxony since 1635. In 1815, due to the partition of Saxony, some parts of Lusatia were integrated into the Prussian Province of Silesia, and later into the Province of Lower Silesia. Görlitz is the largest city of the former Province of Lower Silesia that lies west of the Oder-Neisse line and hence remains in Germany today. Thus it is both the most Silesian city, in terms of character, and the largest, in Germany today. This is not unjustified since the city adapted to a large extent to the rest of Silesia when it was part of it administratively. The city combines Lusatian and Silesian traditions as well as German and Sorbian culture.
Görlitz has a rich architectural heritage. Many movie-makers have used the various sites as backgrounds.[2]
History
Duchy of Poland 1002–1025
![]() Kingdom of Poland 1025–1031
Kingdom of Poland 1025–1031
![]() Margraviate of Meissen 1032–ca. 1072
Margraviate of Meissen 1032–ca. 1072
![]() Duchy of Bohemia ca. 1072–1198
Duchy of Bohemia ca. 1072–1198
![]() Kingdom of Bohemia 1198–1253
Kingdom of Bohemia 1198–1253
![]() Margraviate of Brandenburg 1253–1319
Margraviate of Brandenburg 1253–1319
![]() Duchy of Jawor 1319–1329
Duchy of Jawor 1319–1329
![]() Kingdom of Bohemia 1329–1466
Kingdom of Bohemia 1329–1466
![]() Kingdom of Hungary 1466–1490
Kingdom of Hungary 1466–1490
![]() Kingdom of Bohemia 1490–1635
Kingdom of Bohemia 1490–1635
![]() Electorate of Saxony 1635–1697
Electorate of Saxony 1635–1697
![]() Poland-Saxony 1697–1706
Poland-Saxony 1697–1706
![]() Electorate of Saxony 1706–1709
Electorate of Saxony 1706–1709
![]() Poland-Saxony 1709–1763
Poland-Saxony 1709–1763
![]() Electorate of Saxony 1763–1806
Electorate of Saxony 1763–1806
![]() Kingdom of Saxony 1806–1815
Kingdom of Saxony 1806–1815
![]() Kingdom of Prussia 1815–1871
Kingdom of Prussia 1815–1871
![]() German Empire 1871–1918
German Empire 1871–1918
![]() Weimar Republic 1918–1933
Weimar Republic 1918–1933
![]() Nazi Germany 1933–1945
Nazi Germany 1933–1945
![]() Allied-occupied Germany 1945–1949
Allied-occupied Germany 1945–1949
![]() East Germany 1949–1990
East Germany 1949–1990
![]() Germany 1990–present
Germany 1990–present
As a small Sorbian village named Gorelic in the region of Upper Lusatia in the March of Lusatia of the Holy Roman Empire, it was temporarily conquered and held by the Kingdom of Poland during Bolesław I Chrobry's invasion of Lusatia between 1002 and 1031, after which the region fell back to the March of Lusatia under the counts of the Margraviate of Meissen. Around 1072 the village was assigned to the duchy of Bohemia. The date of the town's foundation is unknown. However, Goreliz was first mentioned in a document from the King of Germany, and later Holy Roman Emperor, Henry IV in 1071. This document granted Görlitz to the Diocese of Meissen, then under Bishop Benno of Meissen. Currently, this document can be found in the Saxony State Archives in Dresden.[3] The origin of the name Görlitz is derived from the Slavic word for "burned land",[4] referring to the technique used to clear land for settlement. Zgorzelec and Czech Zhořelec have the same derivation. In the 13th century the village gradually became a town. Due to its location on the Via Regia, an ancient and medieval trade route, the settlement prospered.
In the following centuries Görlitz was a wealthy member of the Lusatian League, which consisted of Bautzen, Görlitz, Kamenz, Lauban, Löbau and Zittau. In 1352 during the reign of Casimir the Great, Lusatian German colonists from Görlitz founded the town of Gorlice in southern Poland near Kraków.

The Protestant Reformation came to Görlitz in the early 1520s and by the last half of the 16th century, it and the surrounding vicinity, became almost completely Lutheran.
After suffering for years in the Thirty Years' War, the region of Upper Lusatia (including Görlitz) was ceded to the Electorate of Saxony in 1635. After the Napoleonic Wars, the 1815 Congress of Vienna transferred the town from the Kingdom of Saxony to the Kingdom of Prussia. Görlitz was subsequently administered within the Province of Silesia, and, after World War I, the Province of Lower Silesia, until 1945.
Near the end of World War II, German troops destroyed all bridges crossing the Lusatian Neisse. The redrawing of boundaries in 1945—in particular the relocation of the German-Polish border to the present Oder-Neisse line—divided the town. The right bank became part of Poland and was renamed Zgorzelec by the Polish communist government in 1948, while the main portion on the left bank remained part of Germany, now within the state of Saxony. When the East German states were dissolved in 1952, Görlitz became part of the Dresden District, but the states were restored upon German reunification in 1990.
On 27 June 1994, the town became the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Görlitz, but it remains a Lutheran Protestant stronghold.
In 2002 Lake Berzdorf, located south of Görlitz, began to flood. The Altstadtbrücke (literally old town bridge) between Görlitz and sister city Zgorzelec was rebuilt between 2003 and 2004. It was officially opened on 20 October 2004. As soon as Poland signed the Schengen Agreement (20 December 2007), movement between the two banks of the river again became unrestricted, since border controls were eliminated. Indeed, the new pedestrian bridge fails to tell the traveller that they are leaving one country and entering another.
Whilst the town was always well preserved, it was notably grey and colourless under communist East German rule. Since reunification many buildings have been redecorated and is now more clearly "beautiful" even to the layman. It is a popular place to which the elderly of Germany retire, being quiet and relatively affordable by German standards. Its tourist potential is rapidly expanding, being very much an eastern counterpart to towns such as Heidelberg.
Culture

Today Görlitz and Zgorzelec, two towns on opposite banks of the narrow river, get along well. Two bridges have been rebuilt, a bus line connects the German and Polish parts of the town, and there is a common urban management, with annual joint sessions of both town councils.
The town has a rich architectural heritage (Gothic, Renaissance, Baroque, Historicist, Art Nouveau). One example of this rich architectural heritage is the Schönhof, which is one of the oldest civic renaissance buildings in Germany. Another medieval heritage is a model of the Holy Sepulchre (de) which was constructed in the late 15th Century.
In 2006 the twin city Görlitz/Zgorzelec applied to be the European City of Culture 2010 for an award. It was hoped that the concept of Polish-German cooperation would be sufficient to convince the jury, but Essen won the award. Görlitz was placed second. As a result of the campaign Görlitz was renamed City of Culture in order to further German-Polish relations and to attract tourists from all over the world.
As Görlitz was part of Silesia from 1815 onward, it has a Silesian Museum dedicated to the region (Schlesisches Museum zu Görlitz) and even holds a Silesian Music festival (Schlesisches Musikfest). In addition, Görlitz is the seat of the Silesia Youth Group (Schlesische Jugend). There is also a newspaper in Görlitz called the Lower Silesian Kurier (Niederschlesischer Kurier).

Transport
Görlitz station is on the Berlin – Görlitz and the Dresden – Görlitz lines of Deutsche Bahn. The station also provides an international connection to Wrocław, Poland.
Local public transport is provided by:
- The Verkehrsgesellschaft Görlitz (VGG) provides public transport service in the city, including the Görlitz tramway and bus services.[5]
- The Polnische Verkehrsgesellschaft (PKS) provides bus service over the river between Görlitz and its sister city, Zgorzelec.[6]
Film location
Due to the historical parts of the city, many movie-makers have used the various sites as backgrounds. Quentin Tarantino shot the movie-in-a-movie Stolz der Nation (Pride of the Nation) for Inglourious Basterds (which incidentally purports to be Sicily) on the Untermarkt and Obermarkt in Görlitz' oldest parts of the city. Other films shot in Görlitz include the 2013 war drama The Book Thief and the teen years in The Reader. Görlitz was used as the primary shooting location for the Wes Anderson film The Grand Budapest Hotel, with Görlitz standing in for a resort in the fictional Eastern European country of Zubrowka. A vacant department store in the city was redecorated to serve as the hotel itself.[7]
International relations
Twin towns—Sister cities
Being the easternmost town in the country, Görlitz has formed a "Compass Alliance" (Zipfelbund) with the northernmost, westernmost and southernmost towns, List, Selfkant and Oberstdorf respectively. They always participate in the German Unity Day celebrations to represent the modern limits of Germany.
People
- Jakob Böhme (1575–1624), mystic and theologian
- Johann Gottlob Harrer; (1703–1755), composer
- Johann Carl Gehler; (1732–1796) physician, anatomist and mineralogist
- Johann Christoph Brotze (1742–1823), educator
- Gustavus Adolphus Neumann (1807–1886), publisher
- Richard Foerster (classical scholar) (1843–1922), classical scholar
- Pavle Jurišić Šturm (1848–1922), Serbian Army general

- Alfred Wagenknecht; (1881–1956) American Marxist politician.
- Emil Jannings (1884–1950), first actor to win the Academy Award for Best Actor
- Arthur Pohl; (1900–1970), set designer, director and screenwriter
- Olivier Messiaen (1908–1992), musician, professor of harmony at the Paris Conservatoire
- Werner Finck; (1902–1978), comedian, actor and writer
- Oskar Morgenstern (1902–1977), economist
- Hans Georg Dehmelt (born 1922), co-recipient of 1989 Nobel Prize in Physics
- Reinhart Koselleck (1923–2006), historian
- Giorgio Zur; (born 1930) Catholic Archbishop and Apostolic Nuncio in Austria
- Hanna von Hoerner (1942–2014), astrophysicist
- Hans-Jürgen Dörner (born 1951), football player and coach
- Torsten Gütschow (born 1962), football player
- Jens Jeremies (born 1974), football player
- Michael Ballack (born 1976), football player
- Lars Kaufmann (born 1982), handball player
Climate
| Climate data for Görlitz (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 1.8 (35.2) |
3.1 (37.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
13.5 (56.3) |
18.7 (65.7) |
21.2 (70.2) |
23.7 (74.7) |
23.4 (74.1) |
18.4 (65.1) |
13.1 (55.6) |
6.5 (43.7) |
2.6 (36.7) |
12.8 (55.05) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −3.2 (26.2) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
0.5 (32.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
8.1 (46.6) |
11.1 (52) |
13.1 (55.6) |
12.8 (55) |
9.6 (49.3) |
5.7 (42.3) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
4.87 (40.77) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 45.7 (1.799) |
37.3 (1.469) |
49.2 (1.937) |
40.0 (1.575) |
57.6 (2.268) |
65.8 (2.591) |
86.6 (3.409) |
80.0 (3.15) |
53.4 (2.102) |
40.3 (1.587) |
49.2 (1.937) |
50.7 (1.996) |
655.8 (25.82) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 62.8 | 78.8 | 120.9 | 179.2 | 223.6 | 210.5 | 228.2 | 220.3 | 152.7 | 124.9 | 62.9 | 50.1 | 1,714.9 |
| Source: Météoclimat | |||||||||||||
Gallery
 St. Peter and Paul church and the river Lusatian Neisse in Görlitz
St. Peter and Paul church and the river Lusatian Neisse in Görlitz Interior of St. Peter and Paul with its famous "Sonnenorgel" (English: sun organ).
Interior of St. Peter and Paul with its famous "Sonnenorgel" (English: sun organ). The Schönhof, the oldest Renaissance building in Görlitz.
The Schönhof, the oldest Renaissance building in Görlitz. Interior of the Görlitzer Warenhaus department store
Interior of the Görlitzer Warenhaus department store_02_ies.jpg) View over Obermarkt taken from Reichenbacher Turm
View over Obermarkt taken from Reichenbacher Turm Old town hall
Old town hall New town hall
New town hall Reichenbacher Turm
Reichenbacher Turm Typical Gründerzeit buildings in Görlitz
Typical Gründerzeit buildings in Görlitz The Landeskrone
The Landeskrone View over Görlitz old town
View over Görlitz old town Panorama over Zgorzelec taken from Görlitz
Panorama over Zgorzelec taken from Görlitz Former East German rail exit stamp from Görlitz.
Former East German rail exit stamp from Görlitz.
See also
References
- ↑ "Aktuelle Einwohnerzahlen nach Gemeinden 2015] (Einwohnerzahlen auf Grundlage des Zensus 2011)" (PDF). Statistisches Landesamt des Freistaates Sachsen (in German). July 2016.
- ↑ http://www.morgenpost.de/reise/kleine-fluchten/article206737371/Hier-dreht-sich-alles-um-das-Drehen.html
- ↑ Görlitz and Diocese of Miessen
- ↑ "Placenames of the World" by Adrian Room, McFarland Pub. 2003 page 140
- ↑ "Willkommen" (in German). Verkehrsgesellschaft Görlitz GmbH. Retrieved 2015-02-20.
- ↑ "Informacje bieżące" [Current Information] (in Polish). Polnische Verkehrsgesellschaft (Polish Transport Company). Archived from the original on 2012-03-10. Retrieved 2010-06-23.
- ↑ http://www.avclub.com/article/wes-andersons-new-movie-has-a-distributor-plot-95750
- ↑ "Städtepartnerschaften" (in German). Stadt Görlitz. Retrieved 2015-01-05.
- ↑ "Wiesbaden's international city relations". Retrieved 24 December 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Görlitz. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Görlitz. |
-
 Görlitz travel guide from Wikivoyage
Görlitz travel guide from Wikivoyage - Official website
- DW-World 'trial living' report.
- DW-World A New Yorker in Görlitz. Begins at 26:13.
- "Görlitz/Zgorzelec – Urban development from 12th to 21st century" on YouTube
- (Polish) Zgorzelice in the Geographical Dictionary of the Kingdom of Poland (1895)

.jpg)
_01_ies.jpg)
