Formica lugubris
| Formica lugubris | |
|---|---|
 | |
| F. lugubris worker form Russia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Formicinae |
| Tribe: | Formicini |
| Genus: | Formica |
| Species: | F. lugubris |
| Binomial name | |
| Formica lugubris Zetterstedt, 1838 | |
Formica lugubris, also known as the hairy wood ant is common in the forests of the United Kingdom.[2][3][4] [5] Similar to other species of wood ants (genus Formica), Formica lugubris can be identified by a fringe of hairs that reaches down to their eyes. They can reach sizes of up to 12 mm long, and they live in massive colonies. Colonies consist of workers and queen ants, all of which are carnivores.[2][6]
Behavior

Formica lugubris are carnivorous ants that consume a variety of different foods.[2] Red wood ants prey on pestiferous insects and forest defoliators like spruce budworms.[4] They live in massive nests that can contain up to half a million colony members. They form large, domed nests on southerly facing slopes in relatively open woodland. The nests have several mechanisms for keeping the internal temperature stable. The southerly orientation captures sunlight; the nest is flattened on the south side to present a greater surface area to the sun and in spring, large numbers of workers can be seen sunbathing on the nest. When warm they will go into the nest to release their heat inside.[6]
Each ant is able to recognize other members of their colony by a specific odor they all carry on them.[5] Different odors allow them to also recognize other insects and ants from other colonies.[5] When these ants encounter outside species of ants and insects, they may become shocked and engage in combat.[5] Ants from outside species or colonies are usually considered intruders and are seized and dragged in to the nest.[5] Combat between ants is common and almost always ends with death of one ant.[5] When red wood ants encounter members of different colonies similar responses are made. The ants are at first startled and enter an upright body position with their mouths open.[5] This is their way of showing threatening behavior.[5] When in contact, members of the same colony are not threatened by each other and do not show signs of aggression. Workers are able to release pheromones that can alarm others of danger nearby; this is another way these ants use odors to communicate.[6] These ants prefer to mate during the month of June.[6] Sexually aroused female ants release a pheromone that will attract a male. They will both fly off into the forest and mate on the ground, usually where there are no other worker ants around.[6] Not every ant can reproduce; reproductive males and females are larger than worker ants and have wings.[6] This is to prevent competition when mating. After mating, the male will die and the female will lose her wings and start a new colony.[6] Fertilized queens can take over the colonies of brown ants. The queen lands on a brown ant nest, find and sting the brown ant queen to death and take her place. Her eggs are cared for by the brown ant workers and her children replace them over time.[7]
Location
Hairy wood ants are found primarily in conifer and mixed conifer forests in Northern Europe and parts of Asia north of the Himalayan-Tibetan barrier.[2] A nest of Formica lugubris was established near Quebec in 1971 to evaluate its potential as a biological control. By 2005, this single nest had grown to over 100 nests.[4]
Habitat

This ant does not have many natural predators, but its habitat is being destroyed by urban and industrial development.[2] Also a change in agriculture to a more intensive system of farming, and the lack of traditional woodland management is diminishing their habitat.[2] The main issue is when the woodland canopy becomes too dense, it can shade out the ant nests which prefer lots of sunlight, and woodland glades can be encroached upon by woodland and so there is a loss sunlight to the woodland floor, which can also decimate their nests gradually over time [2] As a part of the UK biodiversity action plan, red wood ant preservation attempts are occurring. Colonies can be found in mixed conifer and deciduous woodland, and play a big role in the forest ecosystem. Each colony can reach up about three million ants and live in above ground nests. Nest size can range from as small as 10 cm to over 100 cm in height and up to 192 cm in width.[4] Size of the nest does not necessarily mean the nest is newer. Small nests can continue to thrive for years at a time.[4] Nests are normally located in sunny areas and near woodland rides and glades.[2] In areas where many colonies exist, linked trails can allow a super colony to form.[4] Nests are created are above ground and shaped in a dome.[3] They are made with plant material and soil debris.[3] The majority of the nest is created with organic matter.[3] Although the nests are made above ground, tunnels are created so that ants can reach to depths of 25–30 cm.[3] Ants change the area where they live by re-locating forests litter and animals living there.[3] These nests also provide a home to 43 different species of organisms.[3]
Threats
This ant does not have many natural predators, but its habitat is being destroyed by urban and industrial development.[2] Change in agriculture and forestry is ruining their habitat.[2] Another issue is when plants take over an area, which causes loss of sunny areas in the forest where ants create their mounds.[2] Attempts to preserve the red wood ants are a part of the UK biodiversity plan.
References
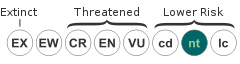
- ↑ Social Insects Specialist Group (1996). "Formica lugubris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 1996: e.T8643A12924499. Retrieved 16 June 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Pinchen, Bryan. "Hairy wood ant (Formica lugubris)". Arkive. Retrieved 11 April 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Korganova, G.A; Rakhleeva (17 May 2006). "Testate amoebae (Testacea) in a Formica lugubris nest: fauna composition and structure". Entomological Review. 85 (2): 189–200. doi:10.1134/s0013873806110133.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Storer, A. J.; Jurgensen, M. F.; Risch, A. C.; Delisle, J.; Hyslop, M. D. (2008). "The fate of an intentional introduction of Formica lugubris to North America from Europe". Journal of Applied Entomology. 132 (4): 276–280. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0418.2008.01275.x. ISSN 0931-2048.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Moli, F.; Parmigiani (1982). "Intraspecific combat in the red wood ant". Aggressive Behavior. 8: 145–148. doi:10.1002/1098-2337(1982)8:2<145::aid-ab2480080214>3.0.co;2-l.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Walter, F; Fletcher (1993). "Identification of the sex pheromone of an ant, Formica ugubris (Hymenoptera, Formicidae)". Naturwissenschaften. 80: 30–34. doi:10.1007/BF01139755.
- ↑ David Attenborough (2005) Life in the Undergrowth
External links
 Media related to Formica lugubris at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Formica lugubris at Wikimedia Commons