For Want of a Nail (novel)
|
1997 Greenhill Books edition of For Want of a Nail | |
| Author | Robert Sobel |
|---|---|
| Country | United States |
| Language | English |
| Genre | Alternate history novel |
| Publisher | Macmillan Publishers |
Publication date | 1973 |
| Media type | Print (hardcover and paperback) |
| Pages | 441 |
| ISBN | 1-85367-281-5 |
| OCLC | 36877367 |
| 973 21 | |
| LC Class | E46 .S62 1997 |
For Want of a Nail: If Burgoyne Had Won at Saratoga is an alternate history novel published in 1973 by the American business historian Robert Sobel. The novel depicts an alternate world where the American Revolution was unsuccessful. Although it is fiction, the novel takes the form of a work of nonfiction, specifically an undergraduate-level history of North America from 1763 to 1971. The fictional history includes a full scholarly apparatus, including a bibliography of 475 works and 860 footnotes citing imaginary books and articles; three appendices listing the leaders of the Confederation of North America, the United States of Mexico and Kramer Associates; an index; a contemporary map of the alternate North America; and a preface thanking imaginary people for their assistance with the book. The book also includes a critique of itself by Professor Frank Dana, an imaginary Mexican historian with two books listed in the bibliography.
Background
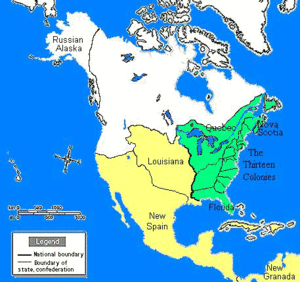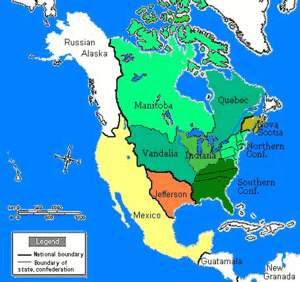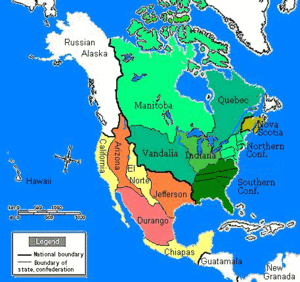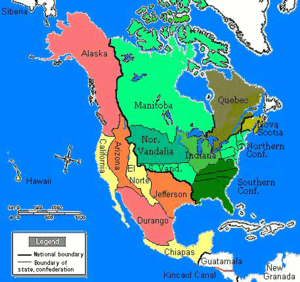
In the alternate world it describes, For Want of a Nail is a history of North America written by Robert Sobel, a business historian. North America is divided between two nations: the Confederation of North America (CNA), a union of British colonies that remains nominally associated with the United British Empire; and the United States of Mexico (USM), a bilingual nation resulting from an influx of expatriate American rebels to colonial Mexico. Other major powers include the United British Empire itself; the German Empire, which dominates much of Europe and the Middle East; the Japanese Empire, which dominates eastern Asia; and Kramer Associates (KA), a vast global corporation that arose in the USM but is now based in Taiwan. All of these powers are engaged in a nuclear arms race that was initiated by Kramer Associates' detonation of an atomic bomb in 1962.
Plot

For Want of a Nail opens in 1763, following the end of the Seven Years' War. Attempts by the British government to impose direct taxation on the American colonies provokes resistance by the colonists, which flares into open rebellion in 1775. After driving British troops from Boston and declaring independence, the American rebels suffer a series of reversals, losing control of New York City, Albany and Philadelphia by the end of 1777. (As indicated by the book's subtitle, the point of divergence from actual history occurs in October 1777, when British General John Burgoyne defeats American Generals Horatio Gates and Benedict Arnold at the Battle of Saratoga.) Conciliationists gain control of the Continental Congress in 1778, and negotiate a truce with the British, returning the colonies to British control.
Parliament passes a bill in 1780 reorganizing the North American colonies into the Confederation of North America (CNA), granting greater autonomy to the colonists. Nevertheless, many former rebels refuse to submit to British rule, and an exodus of pro-independence colonists to the Texas region of colonial Mexico takes place. The expatriate ex-Patriots in Texas organize themselves as the State of Jefferson, after the author of the Declaration of Independence (who was hanged in London for treason after the rebellion failed). Mexico gains its independence from Spain in 1805 and immediately descends into chaos and civil war. The Jeffersonians eventually become involved, and a Jeffersonian army under Andrew Jackson captures Mexico City in 1817. By 1819, Jackson manages to engineer the merger of Jefferson and Mexico as the United States of Mexico (USM), and in 1821 he wins election as the new country's first President.
In the outside world, there are other consequences. The French Revolution fails, but an alternate version of the Napoleonic War still occurs in Europe during the nineteenth century, due to the avaricious nature of Regent Marie Antoinette, ruling France for her son King Louis XVII and the Bourbon ascendancy continues until the brief reign of Louis XXI, at which point France becomes a republic, albeit in the late nineteenth century, much as in our world. Anglo-French enmities are not resolved until the mid-twentieth century in this world. Germany's reunification occurs earlier, the Ottoman Empire falls apart later than in our world, Japan still industrialises but the Russian Revolution doesn't occur in 1917 because the Tsarist Empire disintegrated after a devastating defeat at the hands of the USM, which gives Alaska to the USM and a satellite republic in Siberia.
Despite the exodus of dissatisfied rebels, the population of the CNA continues to grow. Industrialization takes root in the Northern Confederation (a union of the New England and mid-Atlantic colonies), while the invention of the cotton gin brings prosperity and widespread slavery to the Southern Confederation (a union of the southern colonies). After a series of calamities (and the abolition of slavery in the Southern Confederation due to economic reasons) in the 1830s, the CNA wins approval from the British government to reform itself as a unified nation.
After clashing with each other in the Rocky Mountain War (1845–1855), the CNA and USM go their separate ways. The CNA becomes increasingly isolationist, and though a prosperous industrialized nation, suffers recurring bouts of internal civil strife. However, its parliamentary democracy stabilizes into a two party democracy- initially a CNA Liberal Party and rural populist Conservative Party, but the latter is displaced by a social democratic "People's Coalition." As in our world, multicultural diversity occurs due to immigrant exodus from the ongoing turmoil in nineteenth century Europe. The USM gives rise to a monopolistic corporation called Kramer Associates and enters into a period of imperialistic expansion and dictatorship in the late 19th century that sees it conquer Central America, part of South America, Alaska, Hawaii and Siberia. A clash between the Mexican government and Kramer Associates in the 1920s and 1930s results in the latter relocating to the Philippines in 1936.
Global War breaks out in 1939 pitting the British, French and Japanese against the Germans and Mexicans, with the CNA remaining neutral due to economic machinations from Kramer Associates. The war dies down (though it doesn't officially end) in 1948, with the Germans in control of Europe (apart from the United Kingdom) and the Middle East, the Japanese in control of China, Siberia and the western Pacific, Kramer Associates relocated to Taiwan, and the USM suffering a social breakdown and renewed dictatorship. Kramer Associates detonates an atomic bomb in June 1962, which plunges the world into an alternate-universe nuclear arms race. The British detonate their own bomb in 1964, the Germans do so in 1965, and the CNA in 1966. Attempts by the USM to acquire an atomic bomb remain unsuccessful as of 1971, as do global disarmament talks due to Anglo-German mutual mistrust.
Writing and publication
Sobel wrote the book in the summer of 1971, to keep himself occupied in between book contracts. Sobel's original title for the book was Scorpions in a Bottle, but his agent persuaded him to change it. The inspiration to write a counterfactual history came from Jeff Weinper, a former student of Sobel's who later died in Vietnam. Another aim of the book was to spoof the growing trend in academic history for heavily footnote-laden, unreadably dense prose (the more outrageous the assertion made in the text, the denser the footnotes). Each chapter was written in the style of a different academic historian, and the final critique by Frank Dana was based on the savage reviews commonplace in historical journals. Sobel took the names of historical characters and academic historians from friends and from current and former students.
A hardcover edition of For Want of a Nail was published in March 1973 by the Macmillan Company. The book was reviewed in several newspapers and in Time and was nominated for a Pulitzer Prize. For Want of a Nail was eventually republished in hardcover in 1997 by Greenhill Books of Great Britain, a publisher of military histories, after Greenhill's publisher heard about the book from the editor of the Military Book Club at a lunch in New York. Also in 1997, Sobel was awarded a Special Achievement Sidewise Award for Alternate History for the book. A softcover edition was published by Greenhill Books in 2002.
Publication history
- Macmillan Company, March 1973 (hardcover). LCCN 72084742
- Greenhill Books, September 1997 (hardcover). ISBN 1-85367-281-5
- Greenhill Books, August 2002 (softcover). ISBN 1-85367-504-0
Literary significance and criticism
When it first appeared in 1973, For Want of a Nail was unique: a book-length history of an alternate world. Over two hundred years' worth of people, places, economics, finance, technology, politics and war was spelled out.
Despite being nominated for a Pulitzer Prize, the book gained little notice from Sobel's fellow historians. Alternate history was considered a subgenre of science fiction, so it was from fans of science fiction that the book gained its initial audience, and For Want of a Nail gained the status of a classic work of alternate history.
The first critique of For Want of a Nail was that provided in the book's final section by imaginary USM historian Frank Dana. Among the other complaints in his scathing review, Dana decries the book's anti-Mexican bias. He traces this bias back to Sobel's central thesis that the North American Rebellion represented a conflict between moderation and extremism, with the extremists represented by the American rebels who declared independence and later left to found Jefferson and the USM, while the moderates remained to build the CNA. This conflict, Dana believes, creates a false dichotomy that runs through the book, coloring Sobel's view of the histories of the two nations to the advantage of the CNA and the disadvantage of the USM.
See also
- H. Beam Piper's 1948 short story, "He Walked Around the Horses", has the same divergence point from our history, but views events from a 19th-century European perspective, told around the disappearance of Benjamin Bathurst.
References
- Hand, Judson, "If Washington Hadn't Been the Father of His Country," New York Daily News, 18 February 1973.
- MacGregor, Martha, "The Week in Books," New York Post, 31 March 1973.
- Skow, John, "Parlor Games," Time, 9 April 1973.
