Flat iron steak
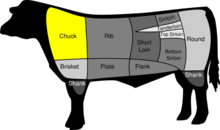 Beef Cuts | |
| Alternative names |
top blade roast, shoulder top blade roast, top boneless chuck, petite steak, butler steak, lifter steak, book steak, chuck clod, lifter roast, and triangle roast |
|---|---|
| Type | Chuck cut of beef |
Flat iron steak (US), butlers' steak (UK), or oyster blade steak (Australia and New Zealand) is a cut of steak cut with the grain from the shoulder of the animal. This produces a flavorful cut that is a bit tough because it contains a gristly fascia membrane unless removed.[1] Some restaurants offer it on their menu, often at lower price than the more popular rib-eye and strip steaks of the same grade. This is used, in some places, as a means of selling a less expensive cut from the same animal, for example Kobe beef.
The cut
This cut of steak is from the shoulder of a beef animal.[2] It is located adjacent to the heart of the shoulder clod, under the seven or paddle bone (shoulder blade or scapula). The steak encompasses the infraspinatus muscles of beef, and one may see this displayed in some butcher shops and meat markets as a "top blade" roast. Anatomically, the muscle forms the dorsal part of the rotator cuff of the steer. This cut is anatomically distinct from the shoulder tender, which lies directly below it and is the teres major.
Flat iron steaks usually have a significant amount of marbling. To make it more marketable, the steak, which has the fascia dividing the infraspinatus within it, has increasingly been cut as two flatter steaks, each corresponding to one muscle, with the tough fascia removed. Steaks that are cross cut from this muscle are called top blade steaks or patio steaks. As a whole cut of meat, it usually weighs around two to three pounds; the entire top blade usually yields four steaks between eight and 12 ounces each.

In the North American Meat Processor (NAMP) meat buyers guide, it is item #1114D Beef Shoulder, Top Blade Steak.[2] This cut was invented in 2002 by university researchers Chris Calkins and Dwain Johnson.[3]
References
- ↑ Butchers' best-kept secret "It's tender but has some gristle."
- 1 2 "Beef Foodservice - Beef Chuck, Shoulder Clod, Top Blade Steak (Flat Iron)". Cattlemen's Beef Promotion And Research Board. Retrieved August 16, 2011.
- ↑ Smith, Ernie. "How Meat Science (And Marketing) Gave the World the Flat Iron Steak". Atlas Obscura. Retrieved 4 October 2016.