Fallow deer
| Fallow deer | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Male (buck) A male (buck) bellowing, UK, October 1964 | |
 | |
| Female (doe) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Cervidae |
| Subfamily: | Cervinae |
| Tribe: | Cervini |
| Genus: | Dama Frisch, 1775 |
| Species: | D. dama |
| Binomial name | |
| Dama dama (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
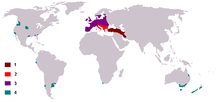 | |
| Range 1: Native 2: Possibly native 3: Early human introductions and reintroductions 4: Modern human introductions | |
The fallow deer (Dama dama) is a ruminant mammal belonging to the family Cervidae. This common species is native to western Eurasia, but has been introduced to Antigua & Barbuda, Argentina, South Africa, Fernando Pó, São Tomé, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mayotte, Réunion, Seychelles, Comoro Islands, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Cyprus, Israel, Cape Verde, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, the United States, the Falkland Islands and Peru.[2][3] Some taxonomers include the rarer Persian fallow deer as a subspecies (D. d. mesopotamica),[4] while others treat it as an entirely different species (D. mesopotamica).[1]
Description


The male fallow deer is known as a buck, the female is a doe, and the young a fawn. Adult bucks are 140–160 cm (55–63 in) long with a 85–95 cm (33–37 in) shoulder height, and typically 60–100 kg (130–220 lb) in weight; does are 130–150 cm (51–59 in) long with a 75–85 cm (30–33 in) shoulder height, and 30–50 kg (66–110 lb) in weight. The largest bucks may measure 190 cm (75 in) long and weigh 150 kg (330 lb).[5] Fawns are born in spring at about 30 cm (12 in) and weigh around 4.5 kg (9.9 lb). The life span is around 12–16 years.
There is much variation in the coat colour of the species, with four main variants: "common", "menil", melanistic and leucistic – a genuine colour variety, not albinistic.[6] The white is the lightest coloured, almost white; common and menil are darker, and melanistic is very dark, sometimes even black (easily confused with the sika deer).
- Common: Chestnut coat with white mottles that are most pronounced in summer with a much darker, unspotted coat in the winter. Light-coloured area around the tail, edged with black. Tail is light with a black stripe.
- Menil: Spots more distinct than common in summer and no black around the rump patch or on the tail. In winter, spots still clear on a darker brown coat.
- Melanistic (black): All year black shading to greyish brown. No light-coloured tail patch or spots.
- Leucistic (white, but not albino): Fawns cream-coloured, adults become pure white, especially in winter. Dark eyes and nose, no spots.[7]
Most herds consist of the common coat variation, yet it is not rare to see animals of the menil coat variation. The Melanistic variation is generally rarer and white very much rarer still, although wild New Zealand herds often have a high melanistic percentage.[8]
Only bucks have antlers, which are broad and shovel-shaped (palmate) from three years. In the first two years the antler is a single spike. They are grazing animals; their preferred habitat is mixed woodland and open grassland. During the rut bucks will spread out and females move between them, at this time of year fallow deer are relatively ungrouped compared to the rest of the year when they try to stay together in groups of up to 150.
Agile and fast in case of danger, fallow deer can run up to a maximum speed of 30 mph (48 km/h)[9] over short distances (being naturally less muscular than other cervids such as roe deer, they are not as fast). Fallow deer can also make jumps up to 1.75 metres (approx 5.8 ft.) high and up to 5 metres (almost 17 ft.) in length.
Distribution and history
The fallow deer is a Eurasian deer[10] that was a native to most of Europe during the last Interglacial. In the Holocene, the distribution was restricted to the Middle East and possibly also parts of the Mediterranean region, while further southeast in western Asia was the home of the Persian fallow deer, that is bigger and has larger antlers. In the Levant, fallow deer were an important source of meat in the Palaeolithic Kebaran-culture (17000–10000 BCE), as is shown by animal bones from sites in northern Israel, but the numbers decreased in the following epi-Palaeolithic Natufian culture (10000–8500 BCE), perhaps because of increased aridity and the decrease of wooded areas.
Argentina
The fallow deer was introduced to the Victoria Island in the Province of Neuquén by billionaire Aaron Anchorena, who with the intention to increase hunting opportunities freed wildlife European and Asian origin, making them in common inhabitants of the island and competing for land and food of the Huemul native and pudu. Today it comes to maintain a stable population of these introduced species.
Britain & Ireland
The fallow deer was spread across central Europe by the Romans. Until recently it was thought that the Normans introduced them to Great Britain for hunting in the royal forests. However recent finds at Fishbourne Roman Palace show that fallow deer were introduced into southern England in the 1st century AD.[11] It is not known whether these escaped to form a feral colony, or whether they died out and were reintroduced by the Normans.
Fallow deer are now widespread on the UK mainland and are present in most of England and Wales below a line drawn from the Wash to the Mersey. There have been long standing populations in the New Forest and the Forest of Dean and many of the other populations originated from park escapees. They are not quite so widespread in the northern parts of England but are present in most lowland areas and also in parts of Scotland, principally in the Tay valley and around Loch Lomond. According to the British Deer Society distribution survey 2007 they have enjoyed an increase in range since the previous survey in 2000 although the increase in range is not as spectacular as for some of the other deer species. In Ireland there is a long-established herd of about 450 in Phoenix Park, Dublin.

A significant number of the fallow in the Forest of Dean and in Epping Forest are of the black variety. One particularly interesting population known as 'long-haired fallow deer' inhabit Mortimer Forest on the England/Wales border, a significant part of the population have long hair with distinct ear tufts and longer body hair.[12]
Rhodes, Greece
The Rhodian population of fallow deer has been found to average smaller than those of central and northern Europe, though they are similarly coloured. In 2005, the Rhodian fallow deer was found to be genetically distinct from all other populations and to be of urgent conservation concern.[13] At the entrance to the harbour of Rhodes city, statues of a fallow deer buck and doe now grace the location where the Colossus of Rhodes once stood.

United States
The whitetail deer Odocoileus virginianus was once classified as Dama virginianus; they were given a separate genus in the 19th century.
In more recent times, fallow deer have been introduced in parts of the United States. A small feral population exists on one barrier island in Georgia. Fallow deer have also been introduced in Texas, along with many other exotic deer species, where they are often hunted on large game ranches. They also live in Rhode Island.
In Pennsylvania, fallow deer are considered livestock since there are no feral animals breeding in the wild. Occasional reports of wild fallow deer in Pennsylvania are generally attributed to escapes from preserves or farms.
There is a herd of white fallow deer located near Argonne National Laboratories in northeastern Illinois.[14]

A small herd of fifteen mostly white fallow deer resides at the Belle Isle Nature Zoo on Belle Isle in Detroit, Michigan. Until the turn of the 21st century, this herd was free range having the run of the island; the herd was thereafter confined, with extirpation being the goal.
A small herd, believed to be the oldest in the United States exists in Land Between the Lakes National Recreation Area in far western Kentucky and Tennessee. The fallow deer herd in LBL "was brought to LBL by the Hillman Land Company in 1918. LBL's herd is believed to be the oldest population of fallow deer in the country, and at one time was the largest. Today the herd numbers fewer than 150 and hunting of fallow deer is not permitted. Although LBL's wildlife management activities focus on native species, the fallow herd is maintained for wildlife viewing and because of its historical significance."
South Africa
Fallow deer have been introduced to Cape Province, South Africa.
Fallow deer are also popular in rural areas of Kwa-Zulu Natal for hunting purposes, as well as in parts of the Gauteng province to beautify ranches and in the Eastern Cape where they were introduced on game farms for the hunting industry because of their exotic qualities. Fallow deer adapted extremely well to the South African environment with access to savanna grasslands and particularly in the cooler climate ranges such as the Highveld.
New Zealand
From 1860 fallow deer were introduced into New Zealand. Significant herds exist in a number of low altitude forests.[15]
Historical herds
One noted historical herd of fallow deer is located in the Ottenby Preserve in Öland, Sweden where Karl X Gustav erected a drystone wall some four kilometres long to enclose a royal fallow deer herd in the mid 17th century; the herd still exists as of 2006.[16] Another is Phoenix Park in Ireland where a herd of 400–450 fallow deer descend from the original herd introduced in the 1660s.[17]
The fallow deer is easily tamed and is often kept semi-domesticated in parks today.
Name
The name fallow is derived from the deer's pale brown color. The Latin word dāma or damma, used for roe deer, gazelles, and antelopes, lies at the root of the modern scientific name, as well as the German Damhirsch, French daim, Dutch damhert, and Italian daino. In Croatian and Serbian, the name for the fallow deer is jelen lopatar ("shovel deer"), due to the form of its antlers. The Hebrew name of the fallow deer, yachmur (יחמור), comes from the Aramaic language, where chamra (חמרא) means "red" or "brown".
Metaphorical meaning
In the well-known 16th century English folk ballad "The Three Ravens", the term "fallow doe" is used metaphorically, as meaning "a young woman".
- Down there comes a fallow Doe,
- As great with young as she might goe,
See also
References
Notes
- 1 2 Masseti, M. & Mertzanidou, D. (2008). "Dama dama". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2008. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 8 April 2009. Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of least concern.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on November 5, 2014. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- ↑ LONG JL 2003. Introduced Mammals of the World: Their History, Distribution and Influence (Cabi Publishing) by John L. Long (ISBN 9780851997483)
- ↑ Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M., eds. (2005). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ↑ Burnie D and Wilson DE (Eds.), Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide to the World's Wildlife. DK Adult (2005), ISBN 0789477645
- ↑ The British Deer Society
- ↑ Prior, John. Dear Watch. David & Charles Inc., 1987. p. 80.
- ↑ New Zealand Hunting Info
- ↑ The Deers of the Ranch of America
- ↑ Urdang, p. 476
- ↑ Sykes, N J; White, J; Hayes, T J; Palmer, M R (2006), "Tracking animals using strontium isotopes in teeth: the role of fallow deer (Dama dama) in Roman Britain", Antiquity, 80: 948–959
- ↑ BBC - Unique deer living in Shropshire forest
- ↑ Masseti, M; Cavallaro, A; Pecchioli, E; Vernesi, C (2006-11-11), "Artificial Occurrence of the Fallow Deer, Dama dama dama (L., 1758), on the Island of Rhodes (Greece): Insight from mtDNA Analysis", Human Evolution, 21, No. 2: 167–175, doi:10.1007/s11598-006-9014-9
- ↑ And another in Willits CA. on the famous Sea Biscuit Ranch. They number about fifty and have resided there for the last 50 years Herd of white deer roams Argonne campus.
- ↑ Hunting: Things to do
- ↑ Environmental Baseline Study, Lumina Technologies, Öland, Sweden, July, 2004
- ↑ Phoenix Park - Fauna
Further reading
- FAO ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH PAPER 27. (1982). Deer farming guidelines on practical aspects. ISBN 92-5-101137-0. Retrieved on 4 January 2008.
- Clutton-Brock, J. (1978). A Natural History of Domesticated Animals. London, British Museum.
- Lyneborg, L. (1971). Mammals [of Europe]. ISBN 0-7137-0548-5.
- Level 1 DSC Training Manual. http://www.eskdalewildlife.com/training.html
- Urdang, Laurence. The Random House Dictionary of the English Language. 1969; Laurence Urdang, Editor in Chief, Random House.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dama dama. |

