Fähnrich
(Heer / Luftwaffe) | |||
| |||
| Rank insignia | German NCO rank | ||
| Introduction | 1956 | ||
| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | ||
| Army / Air Force | Fähnrich | ||
| Navy | Fähnrich zur See | ||
| NATO equivalent | OR-6 | ||
Fähnrich (German pronunciation: [ˈfɛːnʁɪç]) is an officer candidate rank in the Austrian Bundesheer and German Bundeswehr. The word Fähnrich comes from an older German military title, Fahnenträger (flag bearer), and first became a distinct military rank in Germany 1 January 1899. However, Fähnrich ranks are often incorrectly compared with the rank of ensign, which shares a similar etymology but is a full-fledged (albeit junior) commissioned officer (CO) rank.
In the German Landsknecht armies, recorded from ca. 1480, the equivalent rank of a Cornet existed. The cornet carried the troop standard, known as a "cornet".
Germany
Bundeswehr
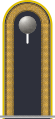
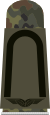
A Fähnrich of the Bundeswehr is a soldier who serves in the ranks, first as Fahnenjunker (OR-5, comparable to the junior non-commissioned officer rank Unteroffizier), then in subsequent grades: Fähnrich (OR-6, equivalent to Feldwebel), and Oberfähnrich (OR-7 equivalent to Hauptfeldwebel).
In the German Bundeswehr, an officer candidate (German: Offiziersanwärter) can reach the rank of Fähnrich after 21 months of service. The German Navy equivalent is Ensign at sea" (German: Fähnrich zur See).
An officer candidate's career is indicated by the enlisted rank with a thin silver cord on the shoulder strap.
| from 1956 | | | | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||
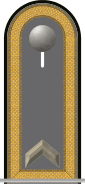
| Distinction | Oberfähnrich (Senior cadet sergeant) |
Fähnrich (Cadet sergeant) |
Fahnenjunker (Officer cadet senior grade) |
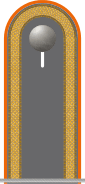
Oberfähnrich (Senior aviation cadet) |
Fähnrich (Aviation cadet) |
Fahnenjunker (Officer cadet senior grade) |
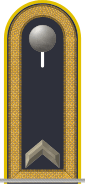
Oberfähnrich zur See (Senior midshipman) |
Fähnrich zur See (Midshipman) |
Seekadett[1]
| ||
| Rangcode | (OR-7) | (OR-6) | (OR-5) | (OR-7) | (OR-6) | (OR-5) | (OR-7) | (OR-6) | (OR-5) | ||
| NATO | Cadet sergeant | Midshipman | |||||||||
| USAF | Aviation cadet auch Warrant Officer | ||||||||||
| RAF | Acting pilot officer | ||||||||||
National People's Army
The rank name Fähnrich was in use in East Germany NPA as a direct counterpart from the Soviet Praporshchik rank.
Fähnrich until 1945
Until 1945 in Heer and Luftwaffe of the Wehrmacht there were also three appropriate officer dedicated ranks:
- Fahnenjunker, equivalent to Unteroffizier, additionally with two parallel braids
- Fähnrich, equivalent to Unterfeldwebel, additionally with two parallel braids
- Oberfähnrich, equivalent to Oberfeldwebel, additionally with two parallel braids
The status of an officer aspirant career (de: Offizier-Anwärter - OA) was indicated by additional two parallel silver braids as on the appropriate rank epaulet.
In the Waffen-SS there were the four ranks of SS-Junker, SS-Oberjunker, SS-Standartenjunker and SS-Oberstandartenjunker for officer candidates and officer cadets.
| to 1945 | Heer | | Waffen-SS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|||||||||||
| |
|
| |||||||||
| Distinction | Oberfähnrich (Senior cadet sergeant) |
Fähnrich (Cadet sergeant) |
Fahnenjunker (Officer cadet) |
Oberfähnrich zur See (Senior midshipman) |
Fähnrich zur See (Midshipman) |
Seekadett (Junior midshipman) |
SS-Standarten- oberjunker |
SS-Standarten- junker |
SS-Oberjunker | SS-Junker | |
Other countries
The rank also exists in a few other European military organizations, often with historical ties to the German system. Examples are the Netherlands, Sweden, Norway, and Finland (see Fänrik). The French Army has a similar position called an Aspirant.
In the Finnish landforces and airforce, Vänrikki (Fenrik) is the lowest commissioned officer rank, which is granted to the soldiers in the national service on the day they are released from their 362-day service. Finnish Vänrikki are thus of equal rank to the German lieutenant (also a platoon leader).
Austria
Austrian Bundeheer
| |||
| Rank insignia | Austrian Bundesheer | ||
| Introduction | ca. 1955 | ||
| Rank group | Officers | ||
| Army / Air Force | Fähnrich | ||
| Navy | no equivalent | ||
| Lower: Higher: | Vizeleutnant | ||
| Leutnant | |||
| NATO equivalent | OF-1c | ||
Fähnrich, short Fhr, is the lowest rank of the commissioned officers CO rank group (also rank group: Officers) in the Austrian Bundesheer.
Austria-Hungaria (until 1918)
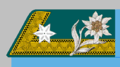
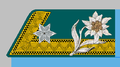
Fähnrich was the lowest officer rank in the k.u.k. Common Army. In 1838 it was renamed to Unterleutnant 2. Gebürnisklasse, from 1849 to Unterleutnant 2. Klasse, since 1868 to Unterleutnant, and finally approximately from 1868 to Leutnant. In 1908 Fähnrich was re-introduced as lowest cadet-officer rank in order to replace the 1869 rank designation Kadett-Offiziersstellvertreter. Fähnrich, Kadett-Offiziersstellvertreter respectively completed training and education on the less famous so-called k.u.k. Kadettenschule. As the Kadett-Offiziersstellvertreter was the highest NCO-rank, became Fähnrich a separate rank-class. However, graduates from the much more famous Militärakademie became the officer patent for Leutnant.
In the k.u. Royal Hungarian Honvéd army Zászlós was the equivalent to the Fähnrich rank. It accounted immediately to the officer corps.
| Designation | Cadet officer-deputy until 1908 | Fähnrich 1908-1918 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| Paroli | ||||
| Rank description | Kadett-Offizierstellvertreter | Fähnrich | ||
| (Hungarian) | (Hadapród-Tiszthelyettes) | (Zászlós) | ||
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to SVG military rank insignia of the Bundeswehr (Fähnrich). |
- ↑ Langenscheidt´s Encyclopaedic Dictionary of the English and German language: „Der Große Muret-Sander“, Part II German-English, Second Volume L–Z, 8th edition 1999, ISBN 3-468-01126-1; p. 1.381
- ↑ On the lower end of both sleeves of the uniform jacket: One golden surrounding braid (de: Tresse), below the golden five-pointed naval star, typically to navy officers.



