Euryarchaeota
| Euryarchaeota | |
|---|---|
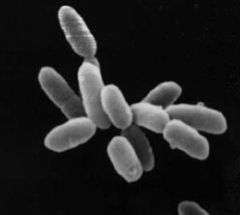 | |
| Halobacterium sp. strain NRC-1, each cell about 5 µm in length. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Archaea |
| Kingdom: | "Euryarchaeota" [1] |
| Phylum: | "Euryarchaeota" Woese, Kandler & Wheelis, 1990 |
| Classes | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
In the taxonomy of microorganisms, the Euryarchaeota (Greek for "broad old quality") are a phylum of the Archaea.[2][3][4]
The Euryarchaeota include the methanogens, which produce methane and are often found in intestines, the halobacteria, which survive extreme concentrations of salt, and some extremely thermophilic aerobes and anaerobes. They are separated from the other archaeans based mainly on rRNA sequences.
Phylogeny
The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)[5] and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)[6] and the phylogeny is based on 16S rRNA-based LTP release 121 by 'The All-Species Living Tree' Project.[7]
| |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Notes:
♠ Strain found at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) but not listed in the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)
See also
References
- ↑ Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML (1990). "Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 87 (12): 4576–9. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.4576W. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. PMC 54159
 . PMID 2112744.
. PMID 2112744. - ↑ See the NCBI webpage on Euryarchaeota
- ↑ C.Michael Hogan. 2010. Archaea. eds. E.Monosson & C.Cleveland, Encyclopedia of Earth. National Council for Science and the Environment, Washington DC.
- ↑ Data extracted from the "NCBI taxonomy resources". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 2007-03-19.
- ↑ J.P. Euzéby. "Euryarchaeota". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Retrieved 2013-03-20.
- ↑ Sayers; et al. "Euryarchaeota". National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy database. Retrieved 2013-03-20.
- ↑ 'The All-Species Living Tree' Project."16S rRNA-based LTP release 121 (full tree)" (PDF). Silva Comprehensive Ribosomal RNA Database. Retrieved 2015-08-20.
Further reading
Scientific journals
- Cavalier-Smith, T (2002). "The neomuran origin of archaebacteria, the negibacterial root of the universal tree and bacterial megaclassification". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52 (Pt 1): 7–76. doi:10.1099/00207713-52-1-7. PMID 11837318.
- Stackebrandt, E; Frederiksen W; Garrity GM; Grimont PA; Kampfer P; Maiden MC; Nesme X; Rossello-Mora R; Swings J; Truper HG; Vauterin L; Ward AC; Whitman WB (2002). "Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52 (Pt 3): 1043–1047. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02360-0. PMID 12054223.
- Christensen, H; Bisgaard M; Frederiksen W; Mutters R; Kuhnert P; Olsen JE (2001). "Is characterization of a single isolate sufficient for valid publication of a new genus or species? Proposal to modify recommendation 30b of the Bacteriological Code (1990 Revision)". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51 (Pt 6): 2221–2225. doi:10.1099/00207713-51-6-2221. PMID 11760965.
- Gurtler, V; Mayall BC (2001). "Genomic approaches to typing, taxonomy and evolution of bacterial isolates". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51 (Pt 1): 3–16. PMID 11211268.
- Dalevi, D; Hugenholtz P; Blackall LL (2001). "A multiple-outgroup approach to resolving division-level phylogenetic relationships using 16S rDNA data". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51 (Pt 2): 385–391. PMID 11321083.
- Keswani, J; Whitman WB (2001). "Relationship of 16S rRNA sequence similarity to DNA hybridization in prokaryotes". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51 (Pt 2): 667–678. PMID 11321113.
- Young, JM (2001). "Implications of alternative classifications and horizontal gene transfer for bacterial taxonomy". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51 (Pt 3): 945–953. doi:10.1099/00207713-51-3-945. PMID 11411719.
- Christensen, H; Angen O; Mutters R; Olsen JE; Bisgaard M (2000). "DNA-DNA hybridization determined in micro-wells using covalent attachment of DNA". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50 (3): 1095–1102. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-3-1095. PMID 10843050.
- Xu, HX; Kawamura Y; Li N; Zhao L; Li TM; Li ZY; Shu S; Ezaki T (2000). "A rapid method for determining the G+C content of bacterial chromosomes by monitoring fluorescence intensity during DNA denaturation in a capillary tube". Int. J. Syst.Evol. Microbiol. 50 (4): 1463–1469. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-4-1463. PMID 10939651.
- Young, JM (2000). "Suggestions for avoiding on-going confusion from the Bacteriological Code". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50 (4): 1687–1689. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-4-1687. PMID 10939677.
- Hansmann, S; Martin W (2000). "Phylogeny of 33 ribosomal and six other proteins encoded in an ancient gene cluster that is conserved across prokaryotic genomes: influence of excluding poorly alignable sites from analysis". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50 (4): 1655–1663. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-4-1655. PMID 10939673.
- Tindall, BJ (1999). "Proposal to change the Rule governing the designation of type strains deposited under culture collection numbers allocated for patent purposes". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49 (3): 1317–1319. doi:10.1099/00207713-49-3-1317. PMID 10490293.
- Tindall, BJ (1999). "Proposal to change Rule 18a, Rule 18f and Rule 30 to limit the retroactive consequences of changes accepted by the ICSB". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49 (3): 1321–1322. doi:10.1099/00207713-49-3-1321. PMID 10425797.
- Tindall, BJ (1999). "Misunderstanding the Bacteriological Code". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49 (3): 1313–1316. doi:10.1099/00207713-49-3-1313. PMID 10425796.
- Tindall, BJ (1999). "Proposals to update and make changes to the Bacteriological Code". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49 (3): 1309–1312. doi:10.1099/00207713-49-3-1309. PMID 10425795.
- Palys, T; Nakamura LK; Cohan FM (1997). "Discovery and classification of ecological diversity in the bacterial world: the role of DNA sequence data". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47 (4): 1145–1156. doi:10.1099/00207713-47-4-1145. PMID 9336922.
- Euzeby, JP (1997). "List of Bacterial Names with Standing in Nomenclature: a folder available on the Internet". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47 (2): 590–592. doi:10.1099/00207713-47-2-590. PMID 9103655.
- Clayton, RA; Sutton G; Hinkle PS Jr; Bult C; Fields C (1995). "Intraspecific variation in small-subunit rRNA sequences in GenBank: why single sequences may not adequately represent prokaryotic taxa". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 45 (3): 595–599. doi:10.1099/00207713-45-3-595. PMID 8590690.
- Murray, RG; Schleifer KH (1994). "Taxonomic notes: a proposal for recording the properties of putative taxa of procaryotes". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 44 (1): 174–176. doi:10.1099/00207713-44-1-174. PMID 8123559.
- Winker, S; Woese CR (1991). "A definition of the domains Archaea, Bacteria and Eucarya in terms of small subunit ribosomal RNA characteristics". Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 14 (4): 305–310. doi:10.1016/s0723-2020(11)80303-6. PMID 11540071.
- Woese, CR; Kandler O; Wheelis ML (1990). "Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 87 (12): 4576–4579. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.4576W. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. PMC 54159
 . PMID 2112744.
. PMID 2112744. - Achenbach-Richter, L; Woese CR (1988). "The ribosomal gene spacer region in archaebacteria". Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 10: 211–214. doi:10.1016/s0723-2020(88)80002-x. PMID 11542149.
- McGill, TJ; Jurka J; Sobieski JM; Pickett MH; Woese CR; Fox GE (1986). "Characteristic archaebacterial 16S rRNA oligonucleotides". Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 7 (2–3): 194–197. doi:10.1016/S0723-2020(86)80005-4. PMID 11542064.
- Woese, CR; Olsen GJ (1984). "The phylogenetic relationships of three sulfur dependent archaebacteria". Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 5: 97–105. doi:10.1016/S0723-2020(84)80054-5. PMID 11541975.
- Woese, CR; Fox GE (1977). "Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 74 (11): 5088–5090. Bibcode:1977PNAS...74.5088W. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. PMC 432104
 . PMID 270744.
. PMID 270744.
Scientific books
- Garrity GM, Holt JG (2001). "Phylum AII. Euryarchaeota phy. nov.". In DR Boone, RW Castenholz. Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology Volume 1: The Archaea and the deeply branching and phototrophic Bacteria (2nd ed.). New York: Springer Verlag. p. 169. ISBN 978-0-387-98771-2.
Scientific databases
- PubMed references for Euryarchaeota
- PubMed Central references for Euryarchaeota
- Google Scholar references for Euryarchaeota
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Euryarchaeota. |
- Comparative Analysis of Euryarchaeota Genomes (at DOE's IMG system)
- J.P. Euzéby: List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature
- NCBI taxonomy page for Euryarchaeota
- Search Tree of Life taxonomy pages for Euryarchaeota
- Search Species2000 page for Euryarchaeota
- MicrobeWiki page for Euryarchaeota