Plains zebra
| Plains zebra | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Equus quagga boehmi in the Ngorongoro Crater in Tanzania | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Perissodactyla |
| Family: | Equidae |
| Genus: | Equus |
| Subgenus: | Hippotigris |
| Species: | E. quagga |
| Binomial name | |
| Equus quagga Boddaert, 1785 | |
| Subspecies | |
|
E. q. quagga † | |
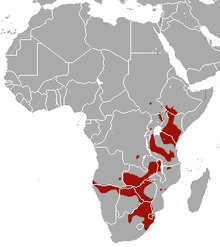 | |
| Plains zebra range | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
The plains zebra (Equus quagga, formerly Equus burchellii), also known as the common zebra or Burchell's zebra, or locally as the "quagga"[2] (not to be confused with the extinct subspecies), is the most common and geographically widespread species of zebra.[3] It ranges from the south of Ethiopia through East Africa to as far south as Botswana and eastern South Africa. The plains zebra remains common in game reserves, but is threatened by human activities such as hunting for its meat and hide, as well as competition with livestock and encroachment by farming on much of its habitat.
Subspecies include the extinct quagga and six recognised extant subspecies, though there is great variation in coat patterns between individuals. The striping pattern is unique among ungulates in the region, and its functions are disputed. Suggested functions include crypsis, forms of motion camouflage, social signaling and recognition, and discouraging biting flies. In 2016, the plains zebra is classified as Near Threatened by IUCN.[1][4]
The plains zebra's range is fragmented, but spans much of southern and eastern Africa south of the Sahara. Its habitat is generally but not exclusively treeless grasslands and savanna woodlands, both tropical and temperate. They generally avoid desert, dense rainforest and permanent wetlands, and rarely stray more than 30 kilometres from a water source. Predators of the zebra include lions, spotted hyenas, leopards, cheetahs and wild dogs.
The plains zebra is a highly social species, forming harems with a single stallion, several mares and their recent offspring; there are also bachelor groups. Groups may come together to form herds. The animals keep watch for predators rather than attempting to hide; they bark or snort when they see a predator, and the harem stallion attacks predators to defend his harem. The species population is stable and not endangered, though some populations such as in Tanzania have declined sharply.
Taxonomy
There is a dispute among biologists as to how to properly classify the various species of zebra. It is thought that the plains zebra and mountain zebra belong to the subgenus Hippotigris and that Grévy's zebra is the sole species of subgenus Dolichohippus. This is on account of Grévy's zebra resembling an ass (subgenus Asinus), while the plains zebra and mountain zebra are more horse-like. All three animals belong to the genus Equus along with other living equids. However, recent phylogenetic evidence finds that plains zebras are more closely related to Grévy's zebras then mountain zebras.[5] In areas where plains zebras are sympatric with Grévy's zebras, it is not unusual to find them in the same herds[6] and fertile hybrids occur.[7] In captivity, plains zebras have been crossed with mountain zebras. The hybrid foals lacked a dewlap and resembled the plains zebra apart from their larger ears and their hindquarters pattern.
Subspecies



In 2004, C. P. Groves and C. H. Bell investigated the taxonomy of the zebra genus, Equus, subgenus Hippotigris. They published their research in the journal Mammalian Biology. They revised the subspecies of the plains zebra Equus quagga. Six subspecies are now recognisable.[1]
- Quagga, †Equus quagga quagga – Boddaert, 1785
- Burchell's zebra, Equus quagga burchellii – Gray, 1824
- Grant's zebra, Equus quagga boehmi – Matschie, 1892
- Maneless zebra Equus quagga borensis – Lönnberg, 1921
- Chapman's zebra, Equus quagga chapmani – Layard, 1865
- Crawshay's zebra, Equus quagga crawshayi – De Winton, 1896
Sometimes another subspecies is distinguished in Eastern Zimbabwe and Western Mozambique:
- Selous' zebra, Equus quagga selousi - Pocock 1897
The quagga was originally classified as a separate species, Equus quagga, in 1778. Over the next 50 years or so, many other zebras were described by naturalists and explorers. Because of the great variation in coat patterns (no two zebras are alike), taxonomists were left with a great number of described "species", and no easy way to tell which of these were true species, which were subspecies, and which were simply natural variants. The quagga was the first extinct creature to have its DNA studied. Recent genetic research at the Smithsonian Institution has demonstrated that the quagga was in fact not a separate species at all, but diverged from the plains zebra, between 120,000 and 290,000 years ago, and suggests that it should be named Equus burchellii quagga. However, according to the rules of biological nomenclature, where there are two or more alternative names for a single species, the name first used takes priority. As the quagga was described about 30 years earlier than the Burchell's zebra, it appears that the correct terms are E. quagga quagga for the quagga and E. quagga burchellii for the plains zebra, unless "Equus burchellii" is officially declared to be a nomen conservandum.
Burchell's zebra was thought to have been hunted to extinction. However, Groves and Bell concluded in their 2004 publication that "the extinct true Burchell's zebra" is a phantom. Careful study of the original zebra populations in Zululand and Swaziland, and of skins harvested on game farms in Zululand and Natal, has revealed that a certain small proportion shows similarity to what now is regarded as typical "burchellii". The type localities of the subspecies Equus quagga burchellii and Equus quagga antiquorum (the Damara zebra) are so close to each other that the two are in fact one, and that therefore the older of the two names should take precedence over the younger. They therefore say that the correct name for the southernmost subspecies must be burchellii not antiquorum. The subspecies Equus quagga burchellii still exists in KwaZulu-Natal and in Etosha.
Physical description
The plains zebra is mid-sized, smaller on average than the other two zebra species, and thick bodied with relatively short legs. There is some variation in size, based on the animals' condition and subspecies. Adults of both sexes can stand from 1.1 to 1.45 m (3.6 to 4.8 ft) high at the withers (shoulder), are 2.17 to 2.46 m (7.1 to 8.1 ft) long, not counting a 47 to 56 cm (19 to 22 in) tail, and weigh 175 to 385 kg (386 to 849 lb). Males may weigh 10% more than females.[8][9]
Like all zebras, they are boldly striped in black and white, and no two individuals look exactly alike. They also have black or dark muzzles. The natal coat of a foal is brown and white. All have vertical stripes on the forepart of the body, which tend towards the horizontal on the hindquarters. The northern populations have narrower and more defined striping;[10][11] southern populations have varied but lesser amounts of striping on the underparts, the legs and the hindquarters.[10] Southern populations also have brown "shadow" stripes between the black and white colouring.[10][11] These are absent or poorly expressed in northern zebras.[10][11]
Embryological evidence has shown that the zebra's background colour is dark and the white is an addition.[12] The first subspecies to be described, the now-extinct quagga, had plain brown hindquarters. There have been various mutations of the zebra's pelage, from mostly white to mostly black.[13] Rare albino zebras have been recorded in the forests of Mount Kenya.[14]
Function of the stripes
.jpg)
The striping pattern of the zebra is unique among sympatric ungulates. One suggested function for the stripes is to provide crypsis for the animal in tall grass or in the dappled shade beneath bushes and trees.[15] However, cryptically coloured species, such as the kudu and bushbuck, tend to be quiet and stealthy. They freeze when there is danger and flee only at the last moment. By contrast, the zebra is active and noisy,[15] and makes no attempt to hide itself.[12] Another suggestion is motion camouflage, that the stripes affect a predator's judgement of the zebra's size, distance and what direction it is going in.[15] A 2014 study supports this hypothesis, finding that, when moving, the stripes may confuse observers, such as mammalian predators and biting insects, via two visual illusions, the wagon wheel effect, where the perceived motion is inverted, and the barber pole illusion, where the perceived motion is in a wrong direction.[16] A related hypothesis is that the stripes make it difficult for a predator to single out and learn about an individual during a chase.[15]
Perhaps the best explanation for the stripes is that they serve a social function.[12] Individual zebras can apparently recognise each other by their striping patterns.[17] The stripes may also serve as visual cues for grooming.[12] In addition, they could serve to help zebra groups stay together when they are fleeing.[15] A 2012 study suggests that stripes may have developed to discourage biting flies. Experiments have demonstrated that the stripes polarize light in such a way that it discourages tabanids (biting flies) in a manner not shown with other coat patterns.[18] Another study from 2015 determined that environment temperature is a strong predictor for zebra striping patterns and proposed that the stripes may be related to thermoregulation.[19]
Ecology
Range and habitat

The plains zebra's range stops short of the Sahara from South Sudan and southern Ethiopia extending south along eastern Africa, as far as Zambia, Mozambique, and Malawi, before spreading into most southern African countries. They are regionally extinct in Burundi and Lesotho, and they may have lived in Algeria in the Neolithic Era.[20]
Plains zebras generally live in treeless grasslands and savanna woodlands[11] but can be found in a variety of habitats, both tropical and temperate. However they are generally absent from deserts, dense rainforests and permanent wetlands.[11] Zebras also live in elevations from sea level to 4,300 m on Mount Kenya. They rely on rainfall for food and water, and go on great migrations to follow the rains. The zebras will migrate up to 700 miles (1,100 km) for food. Other grazers also migrate. Plains zebras are highly water-dependent[6] and are usually found within 25–30 kilometres of a water source.
Diet and predation

In one study, the zebra's diet was estimated to be 92% grass, 5% herbs, and 3% shrubs.[21] Unlike many of the large ungulates of Africa, the plains zebra does not require (but still prefers) short grass to graze. It eats a wide range of different grasses, preferring young, fresh growth where available, and also browses on leaves and shoots from time to time. In consequence, it ranges more widely than many other species, even into woodlands, and it is often the first grazing species to appear in a well-vegetated area.[6] Zebras have a simple stomach and use hindgut fermentation (caeco-colic), which allows them to digest and assimilate larger amounts of forage during a 24-hour period.[22] Thus, zebras are less selective in foraging, but they do spend much time eating. The zebra is a pioneer grazer and prepares the way for more specialised grazers like blue wildebeests and Thomson's gazelles[6] which depend on shorter and more nutritious grasses.
The plains zebra's major predators are lions and spotted hyenas.[10] Nile crocodiles are also great threats during migratory river crossings. Wild dogs, cheetahs, and leopards also prey on zebras, although the threats they pose are generally minor and they mostly attack the foals. Olive baboons may prey on foals, but pose no threat to adults. The zebra can be a formidable adversary, since they have a strong bite and a kick powerful enough to kill land predators. They often try to outrun larger predators such as lions and spotted hyenas, whereas they often stand their ground with the smaller predators.
Interactions with other grazers
Plains zebra herds will mix and migrate together along with other species such as wildebeests. Wildebeests and zebras generally coexist peacefully and will alert each other to predators. However, aggressive interactions occasionally occur.[23][24]
Behaviour
Social structure

The plains zebra is highly social and usually forms small family groups called harems, which consist of a single stallion, several mares, and their recent offspring. The adult membership of a harem is highly stable, typically remaining together for months to years. Groups of all male "bachelors" also exist. These are stable groups of 2-15 males with an age-based hierarchy led by a young male.[6] These males stay in their groups until they are ready to start a harem. The bachelors prepare for their adult roles with play fights and greeting/challenge rituals, which take up most of their activities.[6] Multiple harems and bachelor groups come together to form herds. Plains zebras are unusual among harem-holding species in forming these groups.[25] In addition, pairs of harems may create temporarily stable subgroups within a herd, allowing individuals to interact with those outside their group.[25] Among harem-holding species, this has only been observed in primates like the gelada and the hamadryas baboon.[25]
Stallions form and expand their harems by abducting young mares from their natal harems.[6][26] When a mare reaches sexual maturity, she will exhibit the oestrous posture, which attracts nearby stallions,[26] both bachelors and harem leaders. Her family stallion (likely her father) will chase off or fight stallions attempting to abduct her. Even after a young mare is isolated from her natal harem, the fight over her continues until her estrous cycle is over, and it starts again with the next estrous cycle.[27] It is rare that the mare's original abductor keeps her for long.[27] When the mare finally ovulates, the male that impregnates her keeps her for good. Thus, the mare becomes a permanent member of a new harem.[27][28] The estrous posture of a female becomes less noticeable to outside males as she gets older, hence competition for older females is virtually non-existent.[17]
Mares exist in a hierarchy, with the alpha female being the first to mate with the stallion and being the one to lead the group. When new mares are added to the group, they are met with hostility by the other mares. Thus, the stallion must shield the new mares until the aggression subsides.[6][28] The most recently added females rank lowest. Females that become unfit or weak may drop in their rank, though. The female membership of a harem stays intact even if a new stallion takes over.[17] Zebras strengthen their social bonds with grooming. Members of a harem nip and scrape along the neck, shoulders, and back with their teeth and lips. Mothers and foals groom the most often, followed by siblings. Grooming shows social status and eases aggressive behaviour.[6]
A stallion will defend his group from other males. When challenged, the stallion issues a warning to the invader by rubbing nose or shoulder with him. If the warning is not heeded, a fight breaks out. Zebra fights often become very violent, with the animals biting at each other's necks, heads or legs, wrestling to the ground, and occasional kicking. Sometimes a stallion will lie still on the ground as if surrendering, but once the other male lets up, will strike and continue the fight.[6] Most fighting occurs over young mares in estrus, and as long as a harem stallion is healthy, he will usually not be challenged. Only unhealthy stallions have their harems taken over, and even then the new stallion gradually takes over pushing the old one out without a fight.[6]
Communication
At least six different calls have been documented for the plains zebra. One of which is its distinctive high-pitched contact call (commonly called "barking") heard as "a-ha, a-ha, a-ha" or "kwa-ha, kaw-ha, ha, ha" (video[29]),[17] also transcribed as "kwahaah",[30] or "oug-ga".[31] The species name quagga is derived from the Khoikhoi word for "zebra" and is onomatopoeic for its call.[2] When a predator is sighted, a zebra will make a two-syllable alarm call. A loud snort is made when moving in cover of potential danger. When in contentment, a zebra will make a more drawn-out snort. Males will make a short high-pitched squeal when hurt and foals will emit a drawn out wail when in distress.[17] There are two main facial expressions made by zebras. One is for greeting and involves the ears sticking up and directed forward; the other is threatening and involves the ears down.[17]
Reproduction

The stallion mates with all his mares. Mares may give birth to one foal every twelve months. The birthing peak is during the rainy season. She nurses the foal for up to a year. The stallion is generally intolerant of foals that are not his. It is possible that zebras practice infanticide and feticide; such incidences have been observed in both captive individuals[32] and in nature. In the film "Great Zebra Exodus," a mare was trying to protect her foal from a new stallion as its father was a fallen stallion.[33] Like horses, zebras are able to stand, walk, run from danger, and suckle shortly after they are born. At the moment of birth, a mother zebra keeps any other zebra away from her foal, including the stallion, the other mares, and even the previous offspring. Later, though, they all bond. Within the group, a foal has the same rank as its mother.[17] Plains zebra foals are protected by their mother as well as the head stallion and the other mares in their group. Even with parental protection, up to 50% of zebra foals are taken by predation, disease, and starvation each year.
Young male zebras eventually leave their family groups. This is not because of sexual maturity or being kicked out by their fathers, but because their relationship with their mothers has faded after the birth of a sibling.[10][26] The young stallion then seeks out other young stallions for company.[26] Young females may stay in the harem until they are abducted by another stallion.[10]
Anti-predator behaviour

For protection from land predators, the plains zebra retreats into open areas with good visibility at night. When the groups forage or sleep, one zebra will keep watch, and if a predator is spotted, it will bark or snort loudly.[10] When being hunted by hyenas or wild dogs, a zebra harem stays close together and cooperates to protect threatened members,[6] particularly the young. The harem stallion will go on the offensive and attack the dogs or hyenas.[6] Though hyenas may harass the stallion, they usually only concentrate on the herd, and attempt to dodge the stallion's assaults. Unlike stallions, mares typically only react aggressively to hyenas or dogs when their foals are threatened. Unlike wildebeest, zebras rarely take to water when escaping hyenas.[34] With lions, a zebra's best defense is to outpace them, as lions do not have as much endurance as hyenas or wild dogs. Cheetahs and leopards are mostly threats to foals, as an adult zebra is fully capable of driving them away.
Human interactions
Conservation
Overall, the plains zebra population remains stable, and the species faces no major threat that would cause range-wide decline.[1] The zebra can be found in numerous protected areas across its range, including the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania, Tsavo and Masai Mara in Kenya, Hwange National Park in Zimbabwe, Etosha National Park in Namibia, and Kruger National Park in South Africa. There are some stable populations in unprotected areas.[1]

Some local populations, though, have faced great declines and even extinctions. Though facing decline in numbers the plains zebra population is thriving at about 750,000. One subspecies, the quagga, is now extinct. In Tanzania, the zebra population has decreased by 20% from the late 1990s to the mid-2000s.[1] Zebras are threatened by hunting for their hide and meat, and habitat change from farming. They also compete with livestock for food,[35][36] and are sometimes culled. Poaching is largely a threat to northern populations, while southern populations are threatened mostly by habitat loss. Recent civil wars in Rwanda, Somalia, South Sudan, Ethiopia, and Uganda have caused dramatic declines in all wildlife populations, including those of plains zebra. It is now extinct in Burundi. Civil war in Angola during much of the past 25 years has devastated its wildlife populations, including its once-abundant plains zebra, and destroyed the national parks administration and infrastructure.
Nevertheless, plains zebras are protected in most of their range. They are an important economic source in tourism.
In culture
The zebra is revered in some African cultures as a symbol of beauty. In the dances of the Karamojong tribe of Uganda, women would paint themselves in zebra stripes and act like them.[10] The Dube tribe of South Africa features a zebra on its totem. Zebras also appear on the coat of arms of Botswana.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 King, S.R.B. & Moehlman, P.D. (2016). "Equus quagga". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2015.1. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 4 December 2016.
- 1 2 Skinner, J. D.; Chimimba, C. T. (2005). "Equidae". The Mammals of the Southern African Subregion (3rd ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 537–546. ISBN 0-521-84418-5.
- ↑ Grubb, P. (2005). "Order Perissodactyla". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 630. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ↑ http://iucnworldconservationcongress.org/news/20160904/article/four-out-six-great-apes-one-step-away-extinction-iucn-red-list
- ↑ Vilstrup, Julia T.; et al. (2013). "Mitochondrial Phylogenomics of Modern and Ancient Equids". PLoS ONE. 8 (2): e55950. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055950.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Estes 1991
- ↑ J. E. Cordingley, S. R. Sundaresan, I. R. Fischhoff, B. Shapiro, J. Ruskey, D. I. Rubenstein (2009). Is the endangered Grevy's zebra threatened by hybridization?. Animal Conservation. 12: 505–513.
- ↑ (2011).
- ↑ (2011).
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Kingdon 1988
- 1 2 3 4 5 Moehlman 2002
- 1 2 3 4 Prothero 2003
- ↑ "Mutations". Messybeast.com. Retrieved 2012-07-03.
- ↑ "Mount Kenya Bush Drums December 2006". Animalorphanagekenya.org. Retrieved 2012-07-03.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Apps 2006
- ↑ How, Martin J.; Zanker, Johannes M. (2014). "Motion camouflage induced by zebra stripes". Zoology. 117: TBA. doi:10.1016/j.zool.2013.10.004.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Grub 1981
- ↑ Egri, Ádám; Blahó, Miklós; Kriska, György; Farkas, Róbert; Gyurkovszky, Mónika; Åkesson, Susanne; Horváth, Gábor (2012). "Polarotactic tabanids find striped patterns with brightness and/or polarization modulation least attractive: an advantage of zebra stripes". J Exp Biol. 215: 736–745. doi:10.1242/jeb.065540.
- ↑ Larison, Brenda; Harrigan, Ryan J.; Thomassen, Henri A.; Rubenstein, Daniel I.; Chan-Golston, Alec M.; Li, Elizabeth; Smith, Thomas B. (2015). "How the zebra got its stripes: a problem with too many solutions". R. Soc. opensci. 2: 140452. doi:10.1098/rsos.140452.
- ↑ Groves C. P. (1974) Horses, Asses and Zebras in the Wild. Hollywood, California, US: Ralph Curtis Books
- ↑ Lamprey, H. F. (1963). Ecological separation of large mammal species in the Tangayika Game Reserve, Tangayika. E. Afr. Wildl. J. 63–93
- ↑ Moehlman 2003
- ↑ "Zebra Attack Blue Wildebeest Foal". Wilderness-safaris.com. 2007-04-25. Retrieved 2012-07-03.
- ↑ National Geographic Zebra: Patterns in the Grass (1991)
- 1 2 3 Rubenstein and Hack
- 1 2 3 4 Moss 1982
- 1 2 3 Klingel 1969
- 1 2 Adlen et al. 1995
- ↑ BBC Natural History Unit. Plains zebra video – Equus quagga – 13 (Web video). Wildscreen ARKive. Retrieved 2016-08-31. A 14-second video closeup of a zebra making its "kwa-ha" call.
- ↑ Max, D. T. (1 January 2006). "Can You Revive an Extinct Animal?". The New York Times. Retrieved 2014-03-03.
- ↑
 Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Quagga". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Quagga". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. - ↑ "Further evidence for male infanticide and feticide in captive plains zebras" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-07-03.
- ↑ min 43 http://video.pbs.org/video/2365009194/
- ↑ Kruuk, Hans (1972). The Spotted Hyena: A study of predation and social behaviour. p. 335. ISBN 0-563-20844-9.
- ↑ Young, T. P.; T. M. Palmer; M. E. Gadd (2005). "Competition and compensation among cattle, zebras, and elephants in a semi-arid savanna in Laikipia, Kenya". Biological Conservation. 121: 351–359. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2004.08.007.
- ↑ Odadi, W. O.; T. P. Young; J. B. Okeyo-Owour (2009). "The effects of wild herbivores on cattle intake and movement rates in Laikipia rangeland, Kenya.". Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 116: 120–125. doi:10.1016/j.applanim.2008.08.010.
Bibliography
- Alden, P. C., Estes, R. D., Schlitter, D., McBride, B. (1995). National Audubon Society Field Guide to African Wildlife. New York, Chanticleer Press, Inc. pg. 151
- Apps, P., du Toit, R. (2006). Creatures of Habit: Understanding African Animal Behaviour. Struik. pp. 74–75.
- Estes, R. (1991). The Behavior Guide to African Mammals, Including Hoofed Mammals, Carnivores, Primates. Los Angeles, University of California Press. pp. 242–246
- Groves, C. P.; Bell, H. B. (2004). "New investigations on the taxonomy of the zebras genus Equus, subgenus Hippotigris". Mammalian Biology. 69: 182–196. doi:10.1078/1616-5047-00133.
- Grubb, P. (1981). "Equus burchellii". Mammalian Species. 157: 1–9. doi:10.2307/3503962.
- Hack, M. A.; East, R.; Rubenstein, D. I. (2008). "Equus quagga ssp. quagga". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2015.1. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 13 June 2015. (extinct subspecies of the plains zebra.)
- Higuchi; et al. (1987). "Mitochondrial DNA of the Extinct Quagga: Relatedness and Extent of Postmortem Change". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 25: 283–287. doi:10.1007/BF02603111. PMID 2822938.
- Kingdon, J. (1988). East African Mammals: An Atlas of Evolution in Africa, Volume 3, Part B: Large Mammals. Chicago, University of Chicago Press. pp. 165–179
- Klingel, H. (1969). "Reproduction in the plains zebra Equus burchelli boehmi: behaviour and ecological factors". J. Reprod. Fertil., Suppl. 6: 339–345.
- Moelman, P. D. (2002). Equids. Zebras, Assess and Horses. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. IUCN/SSC Equid Specialist Group. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland. Chapter 4. Status and Action Plan for the Plains Zebra (Equus burchelli). Mace A. Hack, Rod East and Dan J Rubenstein. pp. 43–57.
- Moehlman, P. D. (2003). Grizmek's Animal Life Encyclopedia. Mammals IV. Detroit, The Gale Group, Inc. 15.
- Moss, C., Ed. (1982). Portraits in the Wild, Animal Behavior in East Africa. Chicago, University of Chicago Press.
- Prothero, D. R.; Schoch, R. M. (2003). Horns, Tusks, and Flippers: The Evolution of Hoofed Mammals. Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Rubenstein, D. I. & M. Hack (2004) Natural and sexual selection and the evolution of multi-level societies: insights from zebras with comparisons to primates. pp. 266–279. In: Sexual Selection in Primates: New and Comparative Perspectives. P. Kappeler and C. P. van Schaik (eds.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to: Equus quagga |
 Media related to Equus quagga at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Equus quagga at Wikimedia Commons