Energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction

Schematic of a typical EDXRD experiment
Energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction (EDXRD) is an analytical technique for characterizing materials. It differs from conventional X-ray diffraction by using polychromatic photons as the source and is usually operated at a fixed angle.[1] With no need for a goniometer, EDXRD is able to collect full diffraction patterns very quickly. EDXRD is almost exclusively used with synchrotron radiation which allows for measurement within real engineering materials.[2]
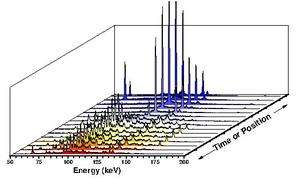
Sample data from an EDXRD experiment where synchrotron radiation is utilized. Spectra can be generated rapidly and as a function of position or time.
History
EDXRD was originally proposed independently by Buras et al. and Giessen and Gordon in 1968.[3]
Advantages
- Fixed scattering angle – The fixed scattering angle geometry makes EDXRD especially suitable for in situ studies in special environments (e.g. under very low or high temperatures and/or pressures). When the EDXRD method is used, only one entrance and one exit window are needed.
- Works directly in reciprocal space – The fixed scattering angle also allows for measurement of the diffraction vector directly. This allows for high-accuracy measurement of lattice parameters.
- Fast collection time – Allows for rapid structure analysis and able to study materials that are unstable and only exist for short periods of time
- Parallel data collection – Because the whole spectrum of diffracted radiation is obtained simultaneously, it enables studies where structural changes can be determined over time.
Facilities
| Facility | Location | Beamline | Energy range (keV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Synchrotron Light Source | Upton, NY | X17B1[4] | 50–200 |
| Advanced Photon Source | Argonne, IL | 16-BM-B[5] | 10–120 |
| Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source | Ithaca, NY | B1[6] | unknown |
| Diamond Light Source | Oxfordshire, UK | I12[7] | 50–150 |
| SOLEIL | Paris, France | I03c[8] | 15–100 |
| Indus 2 | India | BL-11[9] | unknown |
References
- ↑ Kämpfe, B.; Luczak, F.; Michel, B. (2005). "Energy Dispersive X-Ray Diffraction". Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 22: 391–396. doi:10.1002/ppsc.200501007. Retrieved March 16, 2014.
- ↑ "Energy Dispersive Diffraction". Diamond Light Source. Retrieved March 17, 2014.
- ↑ Laine, E.; Lähteenmäki, I. (February 1980). "The energy dispersive X-ray diffraction method: annotated bibliography 1968–78". Journal of Materials Science. Springer. 15 (2): 269–277. Bibcode:1980JMatS..15..269L. doi:10.1007/BF02396775. Retrieved March 16, 2014.
- ↑ "Beamline X17B1". Brookhaven National Laboratory. Retrieved March 17, 2014.
- ↑ "Beamline 16-BM-B: Sector 16 – Bending Magnet Beamline". Argonne National Laboratory. Retrieved March 17, 2014.
- ↑ "CHESS West – B1". Cornell University. Retrieved March 17, 2014.
- ↑ "I12: Joint Engineering, Environmental, and Processing (JEEP)". Diamond Light Source. Retrieved March 17, 2014.
- ↑ "PSICHÉ beamline". Synchrotron SOLEIL – L'Orme des Merisiers Saint-Aubin. Retrieved March 17, 2014.
- ↑ Pandey, K. K.; et al. (April 2013). "Energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction beamline at Indus-2 synchrotron source". Pramana. Springer. 80 (4): 607–619. Bibcode:2013Prama..80..607P. doi:10.1007/s12043-012-0493-0. Retrieved March 17, 2014.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/17/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.