Dust devil tracks
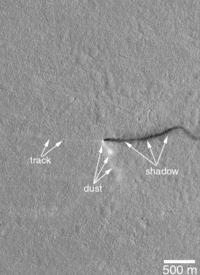
Many areas on Mars experience the passage of giant dust devils. A thin coating of fine bright dust covers most of the Martian surface. When a dust devil goes by it blows away the coating and exposes the underlying dark surface, which within a few weeks assumes its former bright colour, either from being re-covered through wind action or some form of oxidation through exposure to sunlight and air. Dust devils occur when the sun warms up the air near a flat, dry surface. The warm air then rises quickly through the cooler air and begins spinning while moving ahead. This spinning, moving cell may pick up dust and sand and leave behind a clean surface.[1]
These dust devils have been seen from the ground and high overhead from orbit. They have even blown dust off the solar panels of the two Rovers on Mars, thereby greatly extending their usefulness.[2] The pattern of the tracks has been shown to change every few months.[3] A study that combined data from the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) and the Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) found that some large dust devils on Mars have a diameter of 700 metres (2,300 ft) and last at least 26 minutes.[4]
A dust devil that was previously imaged in 2009, there was information found about two years later showing the tracks visible from the previous imaging are completely different from the old ones meaning there had been a dust storm to erase the old tracks.[5] Since it is not always too easy to observe these dust devil tracks on Mars tests have been done on Earth to further our understanding of these storms. Traditionally dust devils leave tracks that are darker, but satellite images have captured some cases where they are lighter than the traditional markings. In conclusion the marks were not darker than usual but the sand had been darkened by five minutes of rainfall during the previous night. Since there is no proof of water on Mars indefinitely it is believed that these lighter marks are being held together by electrostatic forces.[6]
Images



-
Kepler (Martian crater) showing dust devil tracks, as seen by Mars Global Surveyor.
-
Pattern of large and small tracks made by giant dust devils, as seen by Mars Global Surveyor under the MOC Public Targeting Program..
-
Russell Crater dust devil changes in Noachis quadrangle, as seen by HiRISE. Click on image to see changes in dust devil tracks in just 3 months.
-

Milankovic Crater central area, as seen by HiRISE. Click on image to see more details: dark dunes, clear dust devil tracks, and boulders (small bright dots).
-

Dust devil tracks, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Casius quadrangle.
-

Layers in Danielson Crater, as seen by HiRISE. Dust devil tracks are also visible at the top. Location is Arabia quadrangle.
References
- ↑ HiRISE | (PSP_00481_2410). Hirise.lpl.arizona.edu. Retrieved on 7 August 2011.
- ↑ Mars Exploration Rover Mission: Press Release Images: Spirit. Marsrovers.jpl.nasa.gov. Retrieved on 7 August 2011.
- ↑ http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_005383_1255
- ↑ Reiss, D. et al. 2011. Multitemporal observations of identical active dust devils on Mars with High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) and Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC). Icarus. 215:358-369.
- ↑ "Dust Devil Tracks". HiRISE.com. 15 May 2013. Retrieved 30 November 2016.
- ↑ Icarus, Dennis (24 September 2010). "Mars Dust-Devil Mystery Solved On Earth.". www.wired.com. Wired. Retrieved 30 November 2016.
