Chaperone (social)
A chaperone (also spelled chaperon) in its original social usage was a person who for propriety's sake accompanied an unmarried girl in public: usually she was an older married woman, and most commonly the girl's own mother.
In modern social usage, a chaperon (frequent in British spelling) or chaperone (usual in American spelling) is a responsible adult who accompanies and supervises young people. By extension, the word chaperone is used in clinical contexts.
Origin
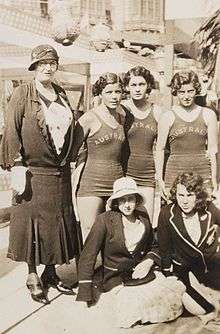
The word derives figuratively from the French word chaperon (originally from the Late Latin cappa, meaning "cape") which referred to a hood that was worn by men and women generally.[1] A chaperone was part of the costume of the Knights of the Garter when they were in full dress[2] and, probably, since the Knights were court attendants, the word chaperon changed to mean escort. An alternative explanation comes from the sport of falconry, where the word meant the hood placed over the head of a bird of prey to stop its desire to fly.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary the noun (in its figurative sense of escort of females) is attested from 1721, and the verb 'to chaperon' from 1811.
Traditional institution
Although the supervision of vulnerable females in public spaces may be common in many cultures, the specific word chaperon began to be used in the eighteenth century to denote a particular social institution, namely, a woman who would accompany a young unmarried woman in public, and especially where she might be expected to meet a man. In circumstances where, for whatever reason, the mother was unavailable to perform this function, another woman, usually well-known to the family, was chosen. A chaperon was usually expected to be a married woman, although a respected, older unmarried or widowed woman (typically someone beyond child-bearing age) was often acceptable.
English-speaking cultures supposed, perhaps correctly, that the institution was particularly strict in southern Europe, especially in Spain, to which it attributed the word "dueña",[3] whence the English duenna.
Chaperones were usually not required in situations where an unmarried woman's father was able to accompany his daughter(s). Chaperones for young men were not commonly employed in Western society until the latter half of the 20th century, although depending on the precise nature of the business he was on, a young male who temporarily left the company of their parents would usually find himself under the supervision of coaches, employers or other such individuals (such personnel were not typically seen to be chaperones in the traditional sense).
Current usage
Chaperones were expected to exercise stern authority over their charges, this, combined with the fact that young people typically had little or no say in the choice of a chaperone, could lead to resistance and resentment on the part of the young people being supervised. One particular effect of the perceived need for the chaperoning of young women was that the early development of women's sport, already impaired by a reluctance on the part of society to accept the presence of females in organized sports, was further inhibited for several decades due to the extra costs involved in hiring chaperones.
The practice of one-on-one chaperones for social occasions has largely fallen out of use in Western society. Today, the term is most often applied to parents and teachers who supervise groups of young people (often of both genders) at school dances, sporting events, field trips and other such events. Often, for short trips where adults are required to perform other functions (such as coaching) these adults will be expected to perform chaperoning duties as well. This practice both saves money and has the potential to foster a better relationship between the young people and the adults chaperoning them.
A major drawback of such an arrangement is that the adults involved are often hired for other reasons besides their qualifications to supervise children and adolescents. There is therefore the potential that such adults may be presented an opportunity to engage in physical, emotional and/or sexual abuse of their charges. Therefore, in present-day situations where young people plan to be away from their families for an extended period of time, such as modern-day cinema, theatre and television productions where the cast includes children as well as other areas such as high-level sport or modelling, there is often a legal obligation[4] to have a staff role of chaperone, responsible for their general safety and well-being while away from their parents. Chaperones must be qualified in specialist childcare areas such as paediatric first aid, child protection, and all required reporting and workforce requirements.
In culture
In drama, probably the best known example of a plot revolving around the need for, and lack of, a chaperone is Brandon Thomas's farce Charley's Aunt (1892).
The chaperone is spoofed in the 2006 musical The Drowsy Chaperone.
Cosmo Kramer acts as a chaperone for Jerry Seinfeld and Miss Rhode Island on an episode of Seinfeld.
See also
- Baedeker, a 19th-century German publisher which pioneered the travel guides
- Bodyguard
- Chaperone (clinical), a person whose role is to witness and safeguard both a patient and a medical practitioner
- Cicisbeo
- Reproductive rights
- Women and Islam for a discussion of the requirement for an unmarriageable male relative (called a mahram) to accompany women
References
- ↑ "Chaperon". The Free Dictionary By Farlex. Retrieved 2012-06-16.
- ↑
 Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Chaperon". Encyclopædia Britannica. 5 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 851.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Chaperon". Encyclopædia Britannica. 5 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 851. - ↑ An English derivation of the Spanish word dueña, supposed to denote a particularly eagle-eyed supervisor of unmarried females. In fact, in Spain the word dueña (from the Latin domina) has no particular connotations of chaperonage, and merely denotes a female proprietor, supervisor of servants, or married woman. In Spain a chaperon is called a carabinera; the word chaperona is not usually found except in Central America. (Diccionario de la Real Academia Espańola: "dueña", "carabiners", "chaperon".)
- ↑ "Child employment". UK Government.
External links
![]() Media related to Chaperones at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Chaperones at Wikimedia Commons