Dirk Hartog Island
 Dirk Hartog Dirk Hartog Island (Western Australia) | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Indian Ocean |
| Coordinates | 25°50′S 113°05′E / 25.833°S 113.083°ECoordinates: 25°50′S 113°05′E / 25.833°S 113.083°E |
| Area | 620 km2 (240 sq mi) |
| Length | 80 km (50 mi) |
| Width | 15 km (9.3 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 188 m (617 ft) |
| Highest point | Herald Heights |
| Administration | |
|
Australia | |
| State | Western Australia |
| Region | Gascoyne |
| Shire | Shire of Shark Bay |
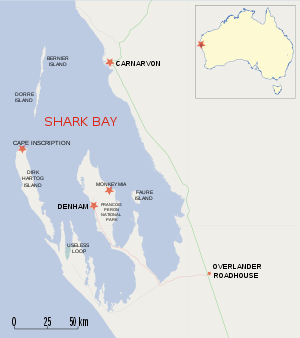


Dirk Hartog Island is an island off the Gascoyne coast of Western Australia, within the Shark Bay World Heritage Area. It is about 80 kilometres (50 miles) long and between 3 and 15 kilometres (1.9 and 9.3 miles) wide and is Western Australia's largest and most western island. It covers an area of 620 square kilometres (240 square miles) and is approximately 850 kilometres (530 miles) north of Perth. It was named after Dirk Hartog, a Dutch sea captain, who first encountered the Western Australian coastline close to the 26th parallel south latitude, which runs through the island. After leaving the island, Hartog continued his voyage north-west along the mainland coast. Hartog gave the Australian mainland one of its earliest known names, as Eendrachtsland, which he named after his ship Eendracht, meaning "Unity".
History
The island was discovered on 25 October 1616 by Hartog in the Dutch East India Company (VOC) ship Eendracht from Cape Town to Batavia (Jakarta).[1] The names of senior people on board, including Hartog's were inscribed with the date on a pewter plate and nailed to a post.
In 1697 the Dutch captain Willem de Vlamingh landed on the island and discovered Hartog's plate. He replaced it with one of his own, which included a copy of Hartog's inscription, and took the original plate home to Amsterdam, where it is still kept in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
On 28 March 1772, Breton navigator Louis Aleno de St Aloüarn landed on the island and became the first European to formally take possession of Western Australia in the name of French king Louis XV. This involved a ceremony (which took place on 30 March) during which one or more bottles were buried on the island. One bottle was recorded as containing an annexation document and a coin. In 1998 a bottle cap made of lead with an écu coin set in it, was first discovered at Turtle Bay by a team led by Philippe Godard and Max Cramer. This triggered a broader search by a team from the Western Australian Museum led by Myra Stanbury, with Bob Sheppard, Bob Creasy and Dr Michael McCarthy. On 1 April 1998, an intact bottle bearing a lead cap identical to the one recovered earlier, also with a coin set in it, was unearthed. No trace of an annexation document has yet been found.[2][3][4]
In 1801 the island was visited by a French expedition aboard the Naturaliste led by Captain Emmanuel Hamelin. This expedition found de Vlamingh's plate almost buried in the sand, its post having rotted away. The Captain ordered that it be re-erected in its original position. In 1818 the Uranie with French explorer Louis de Freycinet, who had been an officer in Hamelin's 1801 crew, sent a boat ashore to recover de Vlamingh's plate. It eventually arrived in Paris, only to be lost for over a century. It was found in 1940 and returned to Australia in 1947, where it can now be seen in the Western Australian Maritime Museum in Fremantle, Western Australia.
In 1869, Francis Louis von Bibra (son of Franz Ludwig von Bibra) was granted a lease on the island. Von Bibra established sheep on the island and traded guano from its bays.[5]
The leasehold for the island was acquired by the Withnell brothers from Messrs Moore and Meade in 1907. The island was regarded as an ideal place for a sheep station as there was no danger of rabbit invasion.[6] In 1909 it was carrying a flock of about 12,000 sheep and produced approximately 400 bales of wool. The property was still owned by John and James Withnell, the children of John and Emma Withnell who were early settlers in the Pilbara. The brothers had estimated the area of the island to be 156,000 acres (631 km2) and intended to increase the flock on the island to 25,000.[7] By 1910 the flock size was 14,200.[8]
By 1919 the pastoral lease was put up for auction by the owner James Nicholas who also owned Croydon and Peron Peninsula Stations. The station occupied an area of 153,000 acres (61,917 ha) and was stocked with approximately 19,000 sheep.[9]
Perth Lord Mayor Sir Thomas Wardle purchased the island as a private retreat for his family in about 1969 and later retired there, becoming a semi-recluse with his wife. With the exception of the pastoral homestead, the island later returned to government ownership and became part of the Shark Bay Marine Park.[10] It is now run as an eco-tourism resort and maintained by Wardle's grandson, Kieran Wardle.
On 16 March 2008, Australian Prime Minister Kevin Rudd announced that the wreck of the World War II German raider Kormoran had been found on the seabed about 150 kilometres (93 miles) west of the island.[11]
Description
The northerly most point Cape Inscription [12] is the location of the plates and the main lighthouse.[13]
The bay facing north next to Cape Inscription 25°28′S 112°58′E / 25.467°S 112.967°E is known as Turtle Bay.
The most south westerly point — Surf Point 26°07′26″S 113°10′46″E / 26.12389°S 113.17944°E — is located at the channel known as South Passage 26°07′55″S 113°09′31″E / 26.13194°S 113.15861°E across from Steep Point on its south west side.
Environment
The island consists mostly of scrub-covered sand dunes. At times it has been used as a sheep station and supported 20,000 head of sheep at one stage. The island is now Dirk Hartog Island National Park and sheep have been removed. To the east it is bounded by the Shark Bay Marine Park, and it is part of Shark Bay World Heritage Area. A small area is leased to the Wardle family who run it as an tourism destination. The region is widely used for recreational fishing.
Dirk Hartog is an important nesting site for loggerhead sea turtle, with green turtles and loggerhead turtles both nesting on the beaches. It is also home for the endemic subspecies of the white-winged fairy-wren. Quoin Bluff, mid-way along the eastern side of the island, holds an important pied cormorant nesting colony which, along with Freycinet Island some 80 km to the south-east, forms the Quoin Bluff and Freycinet Island Important Bird Area, identified as such by BirdLife International.[14]
See also
- Caert van't Landt van d'Eendracht, an early Dutch map of the region
- Meade Island is linked to Dirk Hartog Island at low tide
References
- ↑ "Dirk Hartog Landing Site 1616 – Cape Inscription Area more information". National heritage places. Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. 27 June 2008. Retrieved 25 October 2008.
- ↑ Godard, Philippe; Kerros, Tugdual de; Margot, Odette; Stanbury, Myra; Baxter, Sue; Western Australian Museum; Godard, Phillippe; De Kerros, Tugdual; Margot, Odette; Stanbury, Myra; Baxter, Sue (2008), 1772 : the French annexation of New Holland : the tale of Louis de Saint Aloürn, Western Australian Museum, ISBN 978-1-920843-98-4
- ↑ Walter R. Bloom,"The Role of a French Écu in the Colonization of Western Australia", and "Another French Écu surfaces in Western Australia", The Numismatic Association of Australia Journal, vol.9, 1998, pp.34 – 42; vol.11, 2000, pp.47 – 49. http://www.museum.wa.gov.au/collections/maritime/march/DHI-site/stal-02.html
- ↑ Philippe Godard, Tugdual de Kerros 2002, "Louis de Saint Aloüarn, un marin breton à la conquête des terres australes", Les Portes du large, Saint-Jacques-de-la-Lande, 331-336
- ↑ Nyman, Lois; von Bibra, Graeme (1996). The von Bibra story. Launceston, Tasmania: Foot & Playsted. pp. 64–66. ISBN 978-0-9597188-1-2. OCLC 38406671.
- ↑ "Stock and Station news". The Northern Times. Carnarvon, Western Australia: National Library of Australia. 31 August 1907. p. 2. Retrieved 13 October 2013.
- ↑ "Along the Nor'-West Coast". Western Mail. Perth: National Library of Australia. 15 January 1910. p. 45. Retrieved 13 October 2013.
- ↑ "Shark Bay.". The Northern Times. Carnarvon, Western Australia: National Library of Australia. 3 December 1910. p. 4. Retrieved 13 October 2013.
- ↑ "Advertising.". Western Mail. Perth: National Library of Australia. 13 November 1919. p. 14. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- ↑ "Cape Inscription – Culture and History". The Age. Retrieved 10 April 2009.
- ↑ Australian Associated Press (16 March 2008). "HMAS Sydney hunt digs up the Kormoran". The West Australian. Archived from the original on 22 March 2008. Retrieved 16 March 2008.
- ↑ McCluskey, Paul; Shark Bay (W.A. : Shire). Council (2008), Cape Inscription : draft management plan 2008, Shire of Shark Bay, retrieved 29 December 2014
- ↑ Western Australian Museum. Department of Maritime Archaeology; Green, Jeremy N., 1942-; Anderson, Ross; Baker, Patrick, 1943-; Australian National Centre of Excellence for Maritime Archaeology (2007), Report on the 2006 Western Australian Museum, Department of Maritime Archaeology, Cape Inscription National Heritage Listing archaeological survey, Australian National Centre of Excellence for Maritime Archaeology, retrieved 29 December 2014
- ↑ BirdLife International. (2011). Important Bird Areas factsheet: Quoin Bluff and Freycinet Island (Shark Bay). Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 25/09/2011.
Further reading
- Playford, Phillip E (1998). "A story of two plates". Voyage of discovery to Terra Australis : by Willem De Vlamingh in 1696–97. Perth, W.A.: Western Australian Museum. pp. 51–60. ISBN 0-7307-1221-4. OCLC 39442497.
- Green, J., (ed.) Report on the 2006 Western Australian Museum, Department of Maritime Archaeology, Cape Inscription National Heritage Listing Archaeological Survey. Report—Department of Maritime Archaeology Western Australian Museum, No. 223 Special Publication No. 10, Australian National Centre of Excellence for Maritime Archaeology
External links
- Dirk Hartog Island website
- Map of the island
- Rijksmuseum Amsterdam detail of plate
- Western Australian Museum plate site