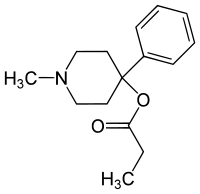
Desmethylprodine
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | 4-propionyloxy-4-phenyl-N-methylpiperidine, MPPP, 3-desmethylprodine |
| CAS Number | 13147-09-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 61583 |
| DrugBank |
DB01478 |
| ChemSpider |
55493 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL279865 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 247.33 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Desmethylprodine or 1-methyl-4-phenyl-4-propionoxypiperidine (MPPP, Ro 2-0718) is an opioid analgesic drug developed in the 1940s by researchers at Hoffmann-La Roche.[1] It is an analog of pethidine (meperidine) which the DEA has labeled as a Schedule I drug in the United States. Chemically, it is a reversed ester of pethidine which has about 70% of the potency of morphine. Unlike its derivative prodine, it was not reported to exhibit optical isomerism.[2] It was reported to have 30 times the activity of pethidine and a greater analgesic effect than morphine in rats, and it was demonstrated to cause central nervous system stimulation in mice.[2]
History
Desmethylprodine was first synthesized in 1947 at Hoffman-LaRoche Laboratories by Albert Ziering and John Lee. They found that it produced effects similar to morphine when administered to rats.[3] Ziering had been searching for synthetic painkillers that were less addictive than morphine. The new drug was a slight variant of pethidine. It was found to be no more effective than pethidine and was never marketed.[4] This research produced the analgesic alphaprodine (Nisentil, Prisilidine), a very closely related compound.[2]
In 1976, a 23-year-old graduate student in chemistry named Barry Kidston was searching for a way to make a legal recreational drug. Having read the paper by Ziering and Lee, he deduced that he could make a drug with pethidine's effects without its legal restrictions, since desmethylprodine is a different molecule and had never been addressed by law. Kidston successfully synthesized and used desmethylprodine for several months, after which he suddenly came down with the symptoms of Parkinson's disease and was hospitalized. Physicians were perplexed, since Parkinson's disease would be a great rarity in someone so young, but L-dopa, the standard drug for Parkinson's, relieved his symptoms. L-dopa is a precursor for dopamine, the neurotransmitter whose lack produces Parkinson's symptoms. It was later found that his development of Parkinson's was due to a common impurity in the synthesis of MPPP called MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine), a neurotoxin that specifically targets dopamine producing neurons.[4][5]
In the United States, MPPP is now in Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act with a zero aggregate manufacturing quota as of 2014. The free base conversion ratio for salts includes 0.87 for the hydrochloride.[6] It is listed under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs and is controlled in most countries in the same fashion as is morphine.
Toxic impurity
The intermediate tertiary alcohol is liable to dehydration in acidic conditions if the reaction temperature rises above 30 °C. Kidston did not realize this and esterified the intermediate with propionic anhydride at an elevated temperature. Consequently, MPTP was formed as a major impurity.[7]
1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+), a metabolite of MPTP, causes rapid onset of irreversible symptoms similar to Parkinson's disease.[8][9] MPTP is metabolized to the neurotoxin MPP+ by the enzyme MAO-B, which is expressed in glial cells. This selectively kills brain tissue in the area of the brain called the substantia nigra and causes permanent Parkinsonian symptoms.[10]
Analogs
Structural analogs of desmethylprodine with different N-substituents than a methyl group on the piperidine have been investigated. Several of these have significantly greater in vitro potency compared to desmethylprodine.[11][12][13]
See also
References
- ↑ U.S. Patent 2,765,314 - Preparation of Esters
- 1 2 3 Reynolds and Randall, Morphine & Allied Drugs (1957) pp 310
- ↑ Ziering, A.; Lee, J. (1947). "Piperidine derivatives; 1,3-dialkyl-4-aryl-4-acyloxypiperidines". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 12 (6): 911–914. doi:10.1021/jo01170a024. PMID 18919744.
- 1 2 Schwarcz, Joe (2005). "Aim high: synthetic opiates deliver surprising side effects". Canadian Chemical News. 57 (10): 10.
- ↑ Gibb, Barry J. (2007). The Rough Guide to the Brain, Rough Guides Ltd., London,
- ↑ http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/fed_regs/quotas/2014/fr0825.htm
- ↑ Johannessen, J. N.; Markey, S. P. (1984). "Assessment of the opiate properties of two constituents of a toxic illicit drug mixture". Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 13 (4): 367–374. doi:10.1016/0376-8716(84)90004-8. PMID 6148225.
- ↑ Davis, G. C.; Williams, A. C.; Markey, S. P.; Ebert, M. H.; Caine, E. D.; Reichert, C. M.; Kopin, I. J. (1979). "Chronic Parkinsonism secondary to intravenous injection of meperidine analogues". Psychiatry Research. 1 (3): 249–254. doi:10.1016/0165-1781(79)90006-4. PMID 298352.
- ↑ Wallis, Claudia (2001-06-24). "Surprising Clue to Parkinson's - TIME". Time. Retrieved 2010-05-13.
- ↑ Schmidt, N.; Ferger, B. (2001). "Neurochemical findings in the MPTP model of Parkinson's disease". Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996). 108 (11): 1263–1282. doi:10.1007/s007020100004. PMID 11768626.
- ↑ Elpern, B.; Wetterau, W.; Carabateas, P.; Grumbach, L. (1958). "Strong Analgesics. The Preparation of Some 4-Acyloxy-1-aralkyl-4-phenylpiperidines". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 80 (18): 4916–4918. doi:10.1021/ja01551a038.
- ↑ Carabateas, P. M.; Grumbach, L. (1962). "Strong Analgesics. Some 1-Substituted 4-Phenyl-4-Propionoxypiperidines". Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. 5 (5): 913–919. doi:10.1021/jm01240a003.
- ↑ Janssen, P. A.; Eddy, N. B. (1960). "Compounds related to pethidine-IV. New general chemical methods of increasing the analgesic activity of pethidine". Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. 2: 31–45. doi:10.1021/jm50008a003. PMID 14406754.
External links
- Desmethylprodine - PubChem
- Street-Drug Contaminant causing Parkinsonism - June 22, 1984 warning from the CDC regarding MPTP byproduct in MPPP