DeKalb County, Indiana
| DeKalb County, Indiana | |
|---|---|
 | |
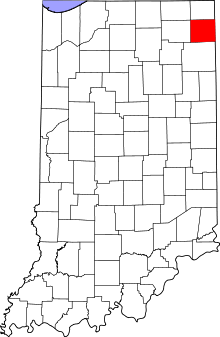 Location in the U.S. state of Indiana | |
 Indiana's location in the U.S. | |
| Founded | 1837 |
| Named for | Johann, Baron de Kalb |
| Seat | Auburn |
| Largest city | Auburn |
| Area | |
| • Total | 363.85 sq mi (942 km2) |
| • Land | 362.82 sq mi (940 km2) |
| • Water | 1.03 sq mi (3 km2), 0.28% |
| Population | |
| • (2010) | 42,223 |
| • Density | 116/sq mi (44.92/km²) |
| Congressional district | 3rd |
| Time zone | Eastern: UTC-5/-4 |
| Website | DeKalb County Government |
| Footnotes: Indiana county number 17 | |
DeKalb County is a county located in the U.S. state of Indiana. As of 2010, the population was 42,223.[1] The county seat is Auburn.[2] Named for Revolutionary War hero Johann, Baron de Kalb (1721–1780), the county was created by the Indiana legislature in 1835 and organized in 1837.
History
DeKalb County was formed in 1837.[3] It was named for the heroic General Johann de Kalb, a Continental Army officer from Bavaria, who was fatally wounded at the Battle of Camden, South Carolina.[4][5] The original settlers to arrive in DeKalb County were migrants from New England who were settling the wilderness of what was then known as the Northwest Territory. These people were "Yankee" migrants, that is to say they were descended from the English Puritans who settled New England in the colonial era.[6] In the 1870s immigrants from Ireland and Germany began arriving in DeKalb County, in large numbers.[7][8][9]
Geography
According to the 2010 census, the county has a total area of 363.85 square miles (942.4 km2), of which 362.82 square miles (939.7 km2) (or 99.72%) is land and 1.03 square miles (2.7 km2) (or 0.28%) is water.[10]
Cities and towns
Unincorporated communities
- Artic
- Auburn Junction
- Butler Center
- Cedar
- Concord
- Fairfield Center
- Hopewell
- Moore
- New Era
- Newville
- Orangeville
- Saint Johns
- Sedan
- Spencerville
- Stafford Center
- Summit
- Taylor Corner
Townships
- Butler
- Concord
- Fairfield
- Franklin
- Grant
- Jackson
- Keyser
- Newville
- Richland
- Smithfield
- Spencer
- Stafford
- Troy
- Union
- Wilmington
Major highways
 Interstate 69
Interstate 69 U.S. Route 6
U.S. Route 6 State Road 1
State Road 1 State Road 4
State Road 4 State Road 8
State Road 8 State Road 101
State Road 101 State Road 205
State Road 205 State Road 327
State Road 327 State Road 427
State Road 427
Adjacent counties
- Steuben County (north)
- Williams County, Ohio (northeast)
- Defiance County, Ohio (southeast)
- Allen County (south)
- Noble County (west)
- LaGrange County (northwest)
Climate and weather
| Auburn, Indiana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In recent years, average temperatures in Auburn have ranged from a low of 17 °F (−8 °C) in January to a high of 84 °F (29 °C) in July, although a record low of −24 °F (−31 °C) was recorded in January 1984 and a record high of 106 °F (41 °C) was recorded in June 1988. Average monthly precipitation ranged from 1.42 inches (36 mm) in February to 4.17 inches (106 mm) in June.[11]
Government
The county government is a constitutional body, and is granted specific powers by the Constitution of Indiana, and by the Indiana Code.
County Council: The county council is the fiscal branch of the county government and controls all the spending and revenue collection in the county. Representatives are elected from county districts. The council members serve four year terms. They are responsible for setting salaries, the annual budget, and special spending. The council also has limited authority to impose local taxes, in the form of an income and property tax that is subject to state level approval, excise taxes, and service taxes.[12][13]
Board of Commissioners: A three-member board of commissioners combines executive and non-fiscal legislative powers. Commissioners are elected county-wide, in staggered four-year terms. One commissioner serves as president. The commissioners also function as the county drainage board, exercising control over the construction and maintenance of legal drains.[12][13]
Courts: DeKalb County has a Circuit Court (75th Judicial Circuit) and two Superior Courts. By local rule, approved by the Indiana Supreme Court,[14] the jurisdiction of the Circuit Court is currently limited to juvenile and domestic cases. Criminal, civil and domestic cases are heard in the two superior courts. Judges of each court are elected for six-year terms on partisan tickets.
County Officials: The county has several other elected offices, including sheriff, coroner, auditor, treasurer, recorder, surveyor, and circuit court clerk. Each of these elected officers serves a term of four years and oversees a different part of county government. Members elected to county government positions are required to declare a party affiliation and to be residents of the county.[13]
DeKalb County is part of Indiana's 3rd congressional district and in 2008 was represented by Mark Souder in the United States Congress.[15] It is also part of Indiana Senate districts 13 and 14,[16] and Indiana House of Representatives districts 51, 52 and 85.[17]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 1,968 | — | |
| 1850 | 8,251 | 319.3% | |
| 1860 | 13,880 | 68.2% | |
| 1870 | 17,167 | 23.7% | |
| 1880 | 20,225 | 17.8% | |
| 1890 | 24,307 | 20.2% | |
| 1900 | 25,711 | 5.8% | |
| 1910 | 25,054 | −2.6% | |
| 1920 | 25,600 | 2.2% | |
| 1930 | 24,911 | −2.7% | |
| 1940 | 24,756 | −0.6% | |
| 1950 | 26,023 | 5.1% | |
| 1960 | 28,271 | 8.6% | |
| 1970 | 30,837 | 9.1% | |
| 1980 | 33,606 | 9.0% | |
| 1990 | 35,324 | 5.1% | |
| 2000 | 40,285 | 14.0% | |
| 2010 | 42,223 | 4.8% | |
| Est. 2015 | 42,589 | [18] | 0.9% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[19] 1790-1960[20] 1900-1990[21] 1990-2000[22] 2010-2014[1] | |||
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 42,223 people, 15,951 households, and 11,328 families residing in the county.[23] The population density was 116.4 inhabitants per square mile (44.9/km2). There were 17,558 housing units at an average density of 48.4 per square mile (18.7/km2).[10] The racial makeup of the county was 96.9% white, 0.5% Asian, 0.4% black or African American, 0.2% American Indian, 0.8% from other races, and 1.2% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 2.4% of the population.[23] In terms of ancestry, 36.3% were German, 10.9% were American, 10.8% were Irish, and 9.1% were English.[24]
Of the 15,951 households, 35.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.8% were married couples living together, 10.5% had a female householder with no husband present, 29.0% were non-families, and 24.3% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.61 and the average family size was 3.08. The median age was 38.1 years.[23]
The median income for a household in the county was $47,697 and the median income for a family was $55,280. Males had a median income of $44,880 versus $30,663 for females. The per capita income for the county was $21,779. About 6.7% of families and 9.0% of the population were below the poverty line, including 11.3% of those under age 18 and 6.2% of those age 65 or over.[25]
Education
School districts
- DeKalb County Central United School District
- DeKalb County Eastern Community School District
- Garrett-Keyser-Butler Community School District
- Hamilton Community Schools
Private schools
- Lakewood Park Christian School
- St. Joseph's Catholic School (Garrett)
- Zion Lutheran Pre-School (Garrett)
See also
- National Register of Historic Places listings in DeKalb County, Indiana
- The Star, daily newspaper covering DeKalb County
External links
- DeKalb County Government
- Maumee Valley Heritage Corridor
- DeKalb County Visitors Bureau
- DeKalb County American History and Genealogy Project
References
- 1 2 "DeKalb County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ↑ "DeKalb County, Indiana". STATS Indiana. Indiana Business Research Center. Retrieved July 13, 2014.
- ↑ De Witt Clinton Goodrich & Charles Richard Tuttle (1875). An Illustrated History of the State of Indiana. Indiana: R. S. Peale & co. p. 555.
- ↑ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. p. 103.
- ↑ Yankee Exodus: An Account of Migration from New England by Stewart Holbrook
- ↑ Ford, Ira (1920-01-01). History of Northeast Indiana: LaGrange, Steuben, Noble and DeKalb Counties. Lewis Publishing Company.
- ↑ History of DeKalb County, Indiana: Together with Sketches of Its Cities, Villages and Towns ... and Biographies of Representative Citizens : Also a Condensed History of Indiana ... Inter-State Publishing Company. 1885-01-01.
- ↑ Co, B. F. Bowen & (1914-01-01). History of Dekalb County, Indiana: with biographical sketches of representative citizens and genealogical records of old families ... B.F. Bowen & Company, Inc.
- 1 2 "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2015-07-10.
- 1 2 "Monthly Averages for Auburn, Indiana". The Weather Channel. Retrieved 2011-01-27.
- 1 2 Indiana Code. "Title 36, Article 2, Section 3". IN.gov. Retrieved 2008-09-16.
- 1 2 3 Indiana Code. "Title 2, Article 10, Section 2" (PDF). IN.gov. Retrieved 2008-09-16.
- ↑ Local Rule 17-AR-1-1, approved March 9, 2007, by the Indiana Supreme Court.
- ↑ "US Congressman Mark Souder". US Congress. Retrieved 2008-10-08.
- ↑ "Indiana Senate Districts". State of Indiana. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ↑ "Indiana House Districts". State of Indiana. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ↑ "County Totals Dataset: Population, Population Change and Estimated Components of Population Change: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015". Retrieved July 2, 2016.
- ↑ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ↑ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ↑ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ↑ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- 1 2 3 "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2015-07-10.
- ↑ "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2015-07-10.
- ↑ "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2015-07-10.
 |
LaGrange County | Steuben County | Williams County, Ohio |  |
| Noble County | |
|||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Allen County | Defiance County, Ohio |
Coordinates: 41°22′01″N 85°03′32″W / 41.36694°N 85.05889°W

