Major depressive disorder
| Major depressive disorder | |
|---|---|
| clinical depression, major depression, unipolar depression, unipolar disorder, recurrent depression | |
|
| |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Psychiatry |
| ICD-10 | F32, F33 |
| ICD-9-CM | 296.2, 296.3 |
| OMIM | 608516 |
| DiseasesDB | 3589 |
| MedlinePlus | 003213 |
| eMedicine | med/532 |
| Patient UK | Major depressive disorder |
| MeSH | D003865 |
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known simply as depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of low mood that is present across most situations.[1] It is often accompanied by low self-esteem, loss of interest in normally enjoyable activities, low energy, and pain without a clear cause.[1] People may also occasionally have false beliefs or see or hear things that others cannot.[1] Some people have periods of depression separated by years in which they are normal while others nearly always have symptoms present.[2] Major depressive disorder can negatively affects a person's family, work or school life, sleeping or eating habits, and general health.[1][2] Between 2-7% of adults with major depression die by suicide,[3] and up to 60% of people who die by suicide had depression or another mood disorder.[4]
The cause is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.[1] Risk factors include a family history of the condition, major life changes, certain medications, chronic health problems, and substance abuse.[1][2] About 40% of the risk appears to be related to genetics.[2] The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the person's reported experiences and a mental status examination.[5] There is no laboratory test for major depression.[2] Testing, however, may be done to rule out physical conditions that can cause similar symptoms.[5] Major depression should be differentiated from sadness which is a normal part of life and is less severe.[2] The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening for depression among those over the age 12,[6][7] while a prior Cochrane review found insufficient evidence for screening.[8]
Typically, people are treated with counselling and antidepressant medication.[1] Medication appears to be effective, but the effect may only be significant in the most severely depressed.[9][10] It is unclear whether medications affect the risk of suicide.[11] Types of counselling used include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy.[1][12] If other measures are not effective electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be tried.[1] Hospitalization may be necessary in cases with a risk of harm to self and may occasionally occur against a person's wishes.[13]
Major depressive disorder affected approximately 253 million (3.6%) of people in 2013.[14] The percentage of people who are affected at one point in their life varies from 7% in Japan to 21% in France.[15] Lifetime rates are higher in the developed world (15%) compared to the developing world (11%).[15] It causes the second most years lived with disability after low back pain.[16] The most common time of onset is in a person in their 20s and 30s. Females are affected about twice as often as males.[2][15] The American Psychiatric Association added "major depressive disorder" to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-III) in 1980.[17] It was a split of the previous depressive neurosis in the DSM-II which also encompassed the conditions now known as dysthymia and adjustment disorder with depressed mood.[17] Those currently or previously affected may be stigmatized.[18]

Signs and symptoms

Major depression significantly affects a person's family and personal relationships, work or school life, sleeping and eating habits, and general health.[19] Its impact on functioning and well-being has been compared to that of other chronic medical conditions such as diabetes.[20]
A person having a major depressive episode usually exhibits a very low mood, which pervades all aspects of life, and an inability to experience pleasure in activities that were formerly enjoyed. Depressed people may be preoccupied with, or ruminate over, thoughts and feelings of worthlessness, inappropriate guilt or regret, helplessness, hopelessness, and self-hatred.[21] In severe cases, depressed people may have symptoms of psychosis. These symptoms include delusions or, less commonly, hallucinations, usually unpleasant.[22] Other symptoms of depression include poor concentration and memory (especially in those with melancholic or psychotic features),[23] withdrawal from social situations and activities, reduced sex drive, irritability,[24] and thoughts of death or suicide. Insomnia is common among the depressed. In the typical pattern, a person wakes very early and cannot get back to sleep.[25] Hypersomnia, or oversleeping, can also happen.[25] Some antidepressants may also cause insomnia due to their stimulating effect.[26]
A depressed person may report multiple physical symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, or digestive problems; physical complaints are the most common presenting problem in developing countries, according to the World Health Organization's criteria for depression.[27] Appetite often decreases, with resulting weight loss, although increased appetite and weight gain occasionally occur.[21] Family and friends may notice that the person's behavior is either agitated or lethargic.[25] Older depressed people may have cognitive symptoms of recent onset, such as forgetfulness,[23] and a more noticeable slowing of movements.[28] Depression often coexists with physical disorders common among the elderly, such as stroke, other cardiovascular diseases, Parkinson's disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[29]
Depressed children may often display an irritable mood rather than a depressed mood,[21] and show varying symptoms depending on age and situation.[30] Most lose interest in school and show a decline in academic performance. They may be described as clingy, demanding, dependent, or insecure.[25] Diagnosis may be delayed or missed when symptoms are interpreted as normal moodiness.[21]
Associated conditions
Major depression frequently co-occurs with other psychiatric problems. The 1990–92 National Comorbidity Survey (US) reports that half of those with major depression also have lifetime anxiety and its associated disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder.[31] Anxiety symptoms can have a major impact on the course of a depressive illness, with delayed recovery, increased risk of relapse, greater disability and increased suicide attempts.[32] There are increased rates of alcohol and drug abuse and particularly dependence,[33] and around a third of individuals diagnosed with ADHD develop comorbid depression.[34] Post-traumatic stress disorder and depression often co-occur.[19] Depression may also coexist with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), complicating the diagnosis and treatment of both.[35]
Depression and pain often co-occur. One or more pain symptoms are present in 65% of depressed patients, and anywhere from 5 to 85% of patients with pain will be suffering from depression, depending on the setting; there is a lower prevalence in general practice, and higher in specialty clinics. The diagnosis of depression is often delayed or missed, and the outcome worsens. The outcome can also worsen if the depression is noticed but completely misunderstood.[36]
Depression is also associated with a 1.5- to 2-fold increased risk of cardiovascular disease, independent of other known risk factors, and is itself linked directly or indirectly to risk factors such as smoking and obesity. People with major depression are less likely to follow medical recommendations for treating and preventing cardiovascular disorders, which further increases their risk of medical complications.[37] In addition, cardiologists may not recognize underlying depression that complicates a cardiovascular problem under their care.[38]
Causes
The biopsychosocial model proposes that biological, psychological, and social factors all play a role in causing depression.[2][39] The diathesis–stress model specifies that depression results when a preexisting vulnerability, or diathesis, is activated by stressful life events. The preexisting vulnerability can be either genetic,[40][41] implying an interaction between nature and nurture, or schematic, resulting from views of the world learned in childhood.[42]
Biological
Monoamine hypothesis
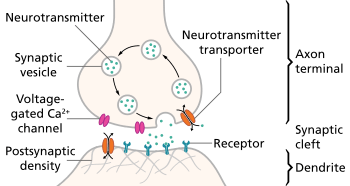
Most antidepressant medications alter the levels of one or more of the monoamines—the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine—in the synaptic cleft between neurons in the brain. Some medications affect the monoamine receptors directly.
Serotonin is hypothesized to regulate other neurotransmitter systems; decreased serotonin activity may allow these systems to act in unusual and erratic ways.[43] According to this "permissive hypothesis", depression arises when low serotonin levels promote low levels of norepinephrine, another monoamine neurotransmitter.[44] Some antidepressants enhance the levels of norepinephrine directly, whereas others raise the levels of dopamine, a third monoamine neurotransmitter. These observations gave rise to the monoamine hypothesis of depression. In its contemporary formulation, the monoamine hypothesis postulates that a deficiency of certain neurotransmitters is responsible for the corresponding features of depression: "Norepinephrine may be related to alertness and energy as well as anxiety, attention, and interest in life; [lack of] serotonin to anxiety, obsessions, and compulsions; and dopamine to attention, motivation, pleasure, and reward, as well as interest in life."[45] The proponents of this theory recommend the choice of an antidepressant with mechanism of action that impacts the most prominent symptoms. Anxious and irritable patients should be treated with SSRIs or norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and those experiencing a loss of energy and enjoyment of life with norepinephrine- and dopamine-enhancing drugs.[45]
However, since the 1990s, research has uncovered multiple limitations of the monoamine hypothesis, and its inadequacy has been criticized within the psychiatric community.[46] For one thing, serotonin system dysfunction cannot be the sole cause of depression; antidepressants usually bring serotonin levels up to normal very quickly, but it often takes at least two to four weeks before mood improves significantly. Intensive investigation has failed to find convincing evidence of a primary dysfunction of a specific monoamine system in patients with major depressive disorders. The antidepressants that do not act through the monoamine system, such as tianeptine and opipramol, have been known for a long time. There has also been inconsistency with regards to serum 5-HIAA levels, a metabolite of serotonin.[47] Experiments with pharmacological agents that cause depletion of monoamines have shown that this depletion does not cause depression in healthy people.[48][49] However depletion of tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine does result in decreased mood in those with a predisposition to depression[50] Already limited, the monoamine hypothesis has been further oversimplified when presented to the general public.[51]
Drug and alcohol use
Very high levels of substance abuse occur in the psychiatric population, especially alcohol, sedatives and cannabis. Depression and other mental health problems can have a substance induced cause; making a differential or dual diagnosis regarding whether mental ill-health is substance related or not or co-occurring is an important part of a psychiatric evaluation.[52] According to the DSM-IV, a diagnosis of mood disorder cannot be made if the cause is believed to be due to "the direct physiological effects of a substance"; when a syndrome resembling major depression is believed to be caused immediately by substance abuse or by an adverse drug reaction, it is referred to as, "substance-induced mood disturbance". Alcoholism or excessive alcohol consumption significantly increases the risk of developing major depression.[53][54] Like alcohol, the benzodiazepines are central nervous system depressants; this class of medication is commonly used to treat insomnia, anxiety, and muscular spasms. Similar to alcohol, benzodiazepines increase the risk of developing major depression. This increased risk of depression may be due in part to the adverse or toxic effects of sedative-hypnotic drugs including alcohol on neurochemistry,[54] such as decreased levels of serotonin and norepinephrine,[55] or activation of immune mediated inflammatory pathways in the brain.[56] Chronic use of benzodiazepines also can cause or worsen depression,[57] or depression may be part of a protracted withdrawal syndrome.[58][59] About a quarter of people recovering from alcoholism experience anxiety and depression, which can persist for up to 2 years.[60] Methamphetamine abuse is also commonly associated with depression.[61]
Estrogens
The hormone estrogen has been implicated in depressive disorders due to the increase in risk of depressive episodes after puberty, the antenatal period, and reduced rates after menopause.[62] On the converse, the premenstrual and postpartum periods of low estrogen levels are also associated with increased risk.[62] Sudden withdrawal of, fluctuations in or periods of sustained low levels of estrogen have been linked to significant mood lowering. Clinical recovery from depression postpartum, perimenopause, and postmenopause was shown to be effective after levels of estrogen were stabilized or restored.[63][64]
HPA Axis
There is some evidence that major depression may be caused in part by an overactive hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis) that results in an effect similar to the neuro-endocrine response to stress. Investigations reveal increased levels of the hormone cortisol and enlarged pituitary and adrenal glands, suggesting disturbances of the endocrine system may play a role in some psychiatric disorders, including major depression. Oversecretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus is thought to drive this, and is implicated in the cognitive and arousal symptoms.[65]
Genetics
Reviews and meta-analyses have contradicted one another with regard to genetic associations with depression.[66][67][68]
Immune
Other research has explored potential roles of molecules necessary for overall cellular functioning: cytokines. The symptoms of major depressive disorder are nearly identical to those of sickness behavior, the response of the body when the immune system is fighting an infection. This raises the possibility that depression can result from a maladaptive manifestation of sickness behavior as a result of abnormalities in circulating cytokines.[69] The involvement of pro-inflammatory cytokines in depression is strongly suggested by a meta-analysis of the clinical literature showing higher blood concentrations of IL-6 and TNF-α in depressed subjects compared to controls.[70] These immunological abnormalities may cause excessive prostaglandin E₂ production and likely excessive COX-2 expression. Abnormalities in how indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase enzyme activates as well as the metabolism of tryptophan-kynurenine may lead to excessive metabolism of tryptophan-kynurenine and lead to increased production of the neurotoxin quinolinic acid, contributing to major depression. N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid activation leading to excessive glutamatergic neurotransmission, may also contribute.[71] A number of factors that increase inflammation have been linked to depression including a poor diet, smoking, and obesity.[72]
Trauma
Depression may be directly caused by damage to the cerebellum as is seen in cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome.[73][74][75]
Social
Poverty and social isolation are associated with increased risk of mental health problems in general.[76] Child abuse (physical, emotional, sexual, or neglect) is also associated with increased risk of developing depressive disorders later in life.[77] Such a link has good face validity given that it is during the years of development that a child is learning how to become a social being. Abuse of the child by the caregiver is bound to distort the developing personality and create a much greater risk for depression and many other debilitating mental and emotional states. Disturbances in family functioning, such as parental (particularly maternal) depression, severe marital conflict or divorce, death of a parent, or other disturbances in parenting are additional risk factors.[76] In adulthood, stressful life events are strongly associated with the onset of major depressive episodes.[78] In this context, life events connected to social rejection appear to be particularly related to depression.[79][80] Evidence that a first episode of depression is more likely to be immediately preceded by stressful life events than are recurrent ones is consistent with the hypothesis that people may become increasingly sensitized to life stress over successive recurrences of depression.[81][82]
The relationship between stressful life events and social support has been a matter of some debate; the lack of social support may increase the likelihood that life stress will lead to depression, or the absence of social support may constitute a form of strain that leads to depression directly.[83] There is evidence that neighborhood social disorder, for example, due to crime or illicit drugs, is a risk factor, and that a high neighborhood socioeconomic status, with better amenities, is a protective factor.[84] Adverse conditions at work, particularly demanding jobs with little scope for decision-making, are associated with depression, although diversity and confounding factors make it difficult to confirm that the relationship is causal.[85]
Depression can be caused by prejudice. This can occur when people hold negative self-stereotypes about themselves. This "deprejudice" can be related to a group membership (e.g., Me-Gay-Bad) or not (Me-Bad). If someone has prejudicial beliefs about a stigmatized group and then becomes a member of that group, they may internalize their prejudice and develop depression. For example, a boy growing up in the United States may learn the negative stereotype that gay men are immoral. When he grows up and realizes he is gay, he may direct this prejudice inward on himself and become depressed. People may also show prejudice internalization through self-stereotyping because of negative childhood experiences such as verbal and physical abuse.[86]
Evolutionary
Depression is maladaptive and difficult to explain using evolutionary psychology; its heterogeneity also makes such explanations difficult. It may be however that some types of MDD may involve "exaggerated or distorted derivatives of human social behaviors which have survived over the eons because they conveyed enhanced survival", such as the behaviors relating to attachment and social rank.[87]
Diagnosis
Clinical assessment
A diagnostic assessment may be conducted by a suitably trained general practitioner, or by a psychiatrist or psychologist,[19] who records the person's current circumstances, biographical history, current symptoms, and family history. The broad clinical aim is to formulate the relevant biological, psychological, and social factors that may be impacting on the individual's mood. The assessor may also discuss the person's current ways of regulating mood (healthy or otherwise) such as alcohol and drug use. The assessment also includes a mental state examination, which is an assessment of the person's current mood and thought content, in particular the presence of themes of hopelessness or pessimism, self-harm or suicide, and an absence of positive thoughts or plans.[19] Specialist mental health services are rare in rural areas, and thus diagnosis and management is left largely to primary-care clinicians.[88] This issue is even more marked in developing countries.[89] The mental health examination may include the use of a rating scale such as the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression[90] or the Beck Depression Inventory[91] or the Suicide Behaviors Questionnaire-Revised.[92] The score on a rating scale alone is insufficient to diagnose depression to the satisfaction of the DSM or ICD, but it provides an indication of the severity of symptoms for a time period, so a person who scores above a given cut-off point can be more thoroughly evaluated for a depressive disorder diagnosis.[93] Several rating scales are used for this purpose.[93]
Primary-care physicians and other non-psychiatrist physicians have more difficulty with underrecognition and undertreatment of depression compared to psychiatric physicians, in part because of the physical symptoms that often accompany depression, in addition to the many potential patient, provider, and system barriers that the authors describe. A review found that non-psychiatrist physicians miss about two-thirds of cases, though this has improved somewhat in more recent studies.[94]
Before diagnosing a major depressive disorder, in general a doctor performs a medical examination and selected investigations to rule out other causes of symptoms. These include blood tests measuring TSH and thyroxine to exclude hypothyroidism; basic electrolytes and serum calcium to rule out a metabolic disturbance; and a full blood count including ESR to rule out a systemic infection or chronic disease.[95] Adverse affective reactions to medications or alcohol misuse are often ruled out, as well. Testosterone levels may be evaluated to diagnose hypogonadism, a cause of depression in men.[96] Vitamin D levels are often checked now, as low levels of vitamin D have been associated with greater risk for depression.[97]
Subjective cognitive complaints appear in older depressed people, but they can also be indicative of the onset of a dementing disorder, such as Alzheimer's disease.[98][99] Cognitive testing and brain imaging can help distinguish depression from dementia.[100] A CT scan can exclude brain pathology in those with psychotic, rapid-onset or otherwise unusual symptoms.[101] In general, investigations are not repeated for a subsequent episode unless there is a medical indication.
No biological tests confirm major depression.[102] Biomarkers of depression have been sought to provide an objective method of diagnosis. There are several potential biomarkers, including Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and various functional MRI techniques. One study developed a decision tree model of interpreting a series of fMRI scans taken during various activities. In their subjects, the authors of that study were able to achieve a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 87%, corresponding to a negative predictive value of 98% and a positive predictive value of 32% (positive and negative likelihood ratios were 6.15, 0.23, respectively). However, much more research is needed before these tests could be used clinically.[103]
DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10 criteria
The most widely used criteria for diagnosing depressive conditions are found in the American Psychiatric Association's revised fourth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR), and the World Health Organization's International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10), which uses the name depressive episode for a single episode and recurrent depressive disorder for repeated episodes.[104] The latter system is typically used in European countries, while the former is used in the US and many other non-European nations,[105] and the authors of both have worked towards conforming one with the other.[106]
Both DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10 mark out typical (main) depressive symptoms.[107] ICD-10 defines three typical depressive symptoms (depressed mood, anhedonia, and reduced energy), two of which should be present to determine depressive disorder diagnosis.[108][109] According to DSM-IV-TR, there are two main depressive symptoms—depressed mood and anhedonia. At least one of these must be present to make a diagnosis of major depressive episode.[110]
Major depressive disorder is classified as a mood disorder in DSM-IV-TR.[111] The diagnosis hinges on the presence of single or recurrent major depressive episodes.[21] Further qualifiers are used to classify both the episode itself and the course of the disorder. The category Depressive Disorder Not Otherwise Specified is diagnosed if the depressive episode's manifestation does not meet the criteria for a major depressive episode. The ICD-10 system does not use the term major depressive disorder but lists very similar criteria for the diagnosis of a depressive episode (mild, moderate or severe); the term recurrent may be added if there have been multiple episodes without mania.[104]
Major depressive episode
A major depressive episode is characterized by the presence of a severely depressed mood that persists for at least two weeks.[21] Episodes may be isolated or recurrent and are categorized as mild (few symptoms in excess of minimum criteria), moderate, or severe (marked impact on social or occupational functioning). An episode with psychotic features—commonly referred to as psychotic depression—is automatically rated as severe. If the patient has had an episode of mania or markedly elevated mood, a diagnosis of bipolar disorder is made instead.[112] Depression without mania is sometimes referred to as unipolar because the mood remains at one emotional state or "pole".[113]
DSM-IV-TR excludes cases where the symptoms are a result of bereavement, although it is possible for normal bereavement to evolve into a depressive episode if the mood persists and the characteristic features of a major depressive episode develop.[114] The criteria have been criticized because they do not take into account any other aspects of the personal and social context in which depression can occur.[115] In addition, some studies have found little empirical support for the DSM-IV cut-off criteria, indicating they are a diagnostic convention imposed on a continuum of depressive symptoms of varying severity and duration:[116] Excluded are a range of related diagnoses, including dysthymia, which involves a chronic but milder mood disturbance;[117] recurrent brief depression, consisting of briefer depressive episodes;[118][119] minor depressive disorder, whereby only some symptoms of major depression are present;[120] and adjustment disorder with depressed mood, which denotes low mood resulting from a psychological response to an identifiable event or stressor.[121]
Subtypes
The DSM-IV-TR recognizes five further subtypes of MDD, called specifiers, in addition to noting the length, severity and presence of psychotic features:
- Melancholic depression is characterized by a loss of pleasure in most or all activities, a failure of reactivity to pleasurable stimuli, a quality of depressed mood more pronounced than that of grief or loss, a worsening of symptoms in the morning hours, early-morning waking, psychomotor retardation, excessive weight loss (not to be confused with anorexia nervosa), or excessive guilt.[122]
- Atypical depression is characterized by mood reactivity (paradoxical anhedonia) and positivity, significant weight gain or increased appetite (comfort eating), excessive sleep or sleepiness (hypersomnia), a sensation of heaviness in limbs known as leaden paralysis, and significant social impairment as a consequence of hypersensitivity to perceived interpersonal rejection.[123]
- Catatonic depression is a rare and severe form of major depression involving disturbances of motor behavior and other symptoms. Here, the person is mute and almost stuporous, and either remains immobile or exhibits purposeless or even bizarre movements. Catatonic symptoms also occur in schizophrenia or in manic episodes, or may be caused by neuroleptic malignant syndrome.[124]
- Postpartum depression, or mental and behavioral disorders associated with the puerperium, not elsewhere classified,[104] refers to the intense, sustained and sometimes disabling depression experienced by women after giving birth. Postpartum depression has an incidence rate of 10–15% among new mothers. The DSM-IV mandates that, in order to qualify as postpartum depression, onset occur within one month of delivery. It has been said that postpartum depression can last as long as three months.[125]
- Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a form of depression in which depressive episodes come on in the autumn or winter, and resolve in spring. The diagnosis is made if at least two episodes have occurred in colder months with none at other times, over a two-year period or longer.[126]
Screening
In 2016 the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommended screening in the adult populations with evidence that it increases the detection of people with depression and with proper treatment improves outcomes.[6] They recommend screening in those between the age of 12 to 18 as well.[7]
A Cochrane review from 2005 found screening programs do not significantly improve detection rates, treatment, or outcome.[8]
Differential diagnoses
To confer major depressive disorder as the most likely diagnosis, other potential diagnoses must be considered, including dysthymia, adjustment disorder with depressed mood, or bipolar disorder. Dysthymia is a chronic, milder mood disturbance in which a person reports a low mood almost daily over a span of at least two years. The symptoms are not as severe as those for major depression, although people with dysthymia are vulnerable to secondary episodes of major depression (sometimes referred to as double depression).[117] Adjustment disorder with depressed mood is a mood disturbance appearing as a psychological response to an identifiable event or stressor, in which the resulting emotional or behavioral symptoms are significant but do not meet the criteria for a major depressive episode.[121] Bipolar disorder, also known as manic–depressive disorder, is a condition in which depressive phases alternate with periods of mania or hypomania. Although depression is currently categorized as a separate disorder, there is ongoing debate because individuals diagnosed with major depression often experience some hypomanic symptoms, indicating a mood disorder continuum.[127]
Other disorders need to be ruled out before diagnosing major depressive disorder. They include depressions due to physical illness, medications, and substance abuse. Depression due to physical illness is diagnosed as a Mood disorder due to a general medical condition. This condition is determined based on history, laboratory findings, or physical examination. When the depression is caused by a medication, drug of abuse, or exposure to a toxin, it is then diagnosed as a Substance/Medication-induced depressive disorder (previously called Substance-induced mood disorder in the DSM-IV-TR).[2]
Prevention
Preventative efforts may result in decreases in rates of the condition of between 22 and 38%.[128] Eating large amounts of fish may also reduce the risk.[129]
Behavioral interventions, such as interpersonal therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy, are effective at preventing new onset depression.[128][130][131] Because such interventions appear to be most effective when delivered to individuals or small groups, it has been suggested that they may be able to reach their large target audience most efficiently through the Internet.[132]
However, an earlier meta-analysis found preventive programs with a competence-enhancing component to be superior to behavior-oriented programs overall, and found behavioral programs to be particularly unhelpful for older people, for whom social support programs were uniquely beneficial. In addition, the programs that best prevented depression comprised more than eight sessions, each lasting between 60 and 90 minutes, were provided by a combination of lay and professional workers, had a high-quality research design, reported attrition rates, and had a well-defined intervention.[133]
The Netherlands mental health care system provides preventive interventions, such as the "Coping with Depression" course (CWD) for people with sub-threshold depression. The course is claimed to be the most successful of psychoeducational interventions for the treatment and prevention of depression (both for its adaptability to various populations and its results), with a risk reduction of 38% in major depression and an efficacy as a treatment comparing favorably to other psychotherapies.[130][134]
Management
The three most common treatments for depression are psychotherapy, medication, and electroconvulsive therapy. Psychotherapy is the treatment of choice (over medication) for people under 18. The UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) 2004 guidelines indicate that antidepressants should not be used for the initial treatment of mild depression, because the risk-benefit ratio is poor. The guidelines recommend that antidepressants treatment in combination with psychosocial interventions should be considered for:
- People with a history of moderate or severe depression
- Those with mild depression that has been present for a long period
- As a second line treatment for mild depression that persists after other interventions
- As a first line treatment for moderate or severe depression.
The guidelines further note that antidepressant treatment should be continued for at least six months to reduce the risk of relapse, and that SSRIs are better tolerated than tricyclic antidepressants.[135]
American Psychiatric Association treatment guidelines recommend that initial treatment should be individually tailored based on factors including severity of symptoms, co-existing disorders, prior treatment experience, and patient preference. Options may include pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy, exercise, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) or light therapy. Antidepressant medication is recommended as an initial treatment choice in people with mild, moderate, or severe major depression, and should be given to all patients with severe depression unless ECT is planned.[136]
Treatment options are much more limited in developing countries, where access to mental health staff, medication, and psychotherapy is often difficult. Development of mental health services is minimal in many countries; depression is viewed as a phenomenon of the developed world despite evidence to the contrary, and not as an inherently life-threatening condition.[137] A 2014 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to determine the effectiveness of psychological versus medical therapy in children.[138]
Lifestyle
Physical exercise is recommended for management of mild depression,[139] and has a moderate effect on symptoms.[140] Exercise has also been found to be effective for (unipolar) major depression.[141] It is equivalent to the use of medications or psychological therapies in most people.[140] In the older people it does appear to decrease depression.[142] Exercise may be recommended to people who are willing, motivated, and physically healthy enough to participate in an exercise program as treatment.[141]
There is a small amount of evidence that skipping a night's sleep may improve depressive symptoms, with the effects usually showing up within a day. This effect is usually temporary. Besides sleepiness, this method can cause a side effect of mania or hypomania.[143]
In observational studies smoking cessation has benefits in depression as large as or larger than those of medications.[144]
Counselling
Psychotherapy can be delivered, to individuals, groups, or families by mental health professionals. A 2015 review found that cognitive behavioral therapy appears to be similar to antidepressant medication in terms of effect.[145] A 2012 review found psychotherapy to be better than no treatment but not other treatments.[146] With more complex and chronic forms of depression, a combination of medication and psychotherapy may be used.[147][148] A 2014 Cochrane review found that work-directed interventions combined with clinical interventions helped to reduce sick days taken by people with depression.[149]
Psychotherapy has been shown to be effective in older people.[150][151] Successful psychotherapy appears to reduce the recurrence of depression even after it has been terminated or replaced by occasional booster sessions.
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) currently has the most research evidence for the treatment of depression in children and adolescents, and CBT and interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) are preferred therapies for adolescent depression.[152] In people under 18, according to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, medication should be offered only in conjunction with a psychological therapy, such as CBT, interpersonal therapy, or family therapy.[153] Cognitive behavioral therapy has also been shown to reduce the number of sick days taken by people with depression, when used in conjunction with primary care.[149]
The most-studied form of psychotherapy for depression is CBT, which teaches clients to challenge self-defeating, but enduring ways of thinking (cognitions) and change counter-productive behaviors. Research beginning in the mid-1990s suggested that CBT could perform as well or as better than antidepressants in patients with moderate to severe depression.[154][155] CBT may be effective in depressed adolescents,[156] although its effects on severe episodes are not definitively known.[157] Several variables predict success for cognitive behavioral therapy in adolescents: higher levels of rational thoughts, less hopelessness, fewer negative thoughts, and fewer cognitive distortions.[158] CBT is particularly beneficial in preventing relapse.[159][160]
Cognitive behavioral therapy and occupational programs (including modification of work activities and assistance) have been shown to be effective in reducing sick days taken by workers with depression.[161]
Variants
Several variants of cognitive behavior therapy have been used in those with depression, the most notable being rational emotive behavior therapy,[162] and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy.[163] Mindfulness based stress reduction programs may reduce depression symptoms.[164][165] Mindfulness programs also appear to be a promising intervention in youth.[166]
Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis is a school of thought, founded by Sigmund Freud, which emphasizes the resolution of unconscious mental conflicts.[167] Psychoanalytic techniques are used by some practitioners to treat clients presenting with major depression.[168] A more widely practiced, eclectic technique, called psychodynamic psychotherapy, is loosely based on psychoanalysis and has an additional social and interpersonal focus.[169] In a meta-analysis of three controlled trials of Short Psychodynamic Supportive Psychotherapy, this modification was found to be as effective as medication for mild to moderate depression.[170]
Antidepressants
Conflicting results have arisen from studies that look at the effectiveness of antidepressants in people with acute, mild to moderate depression. Stronger evidence supports the usefulness of antidepressants in the treatment of depression that is chronic (dysthymia) or severe.
While small benefits were found, researchers Irving Kirsch and Thomas Moore state they may be due to issues with the trials rather than a true effect of the medication.[171] In a later publication, Kirsch concluded that the overall effect of new-generation antidepressant medication is below recommended criteria for clinical significance.[10] Similar results were obtained in a meta analysis by Fornier.[9]
A review commissioned by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence concluded that there is strong evidence that SSRIs have greater efficacy than placebo on achieving a 50% reduction in depression scores in moderate and severe major depression, and that there is some evidence for a similar effect in mild depression.[172] Similarly, a Cochrane systematic review of clinical trials of the generic antidepressant amitriptyline concluded that there is strong evidence that its efficacy is superior to placebo.[173]
In 2014 the U.S. FDA published a systematic review of all antidepressant maintenance trials submitted to the agency between 1985 and 2012. The authors concluded that maintenance treatment reduced the risk of relapse by 52% compared to placebo, and that this effect was primarily due to recurrent depression in the placebo group rather than a drug withdrawal effect.[9]
To find the most effective antidepressant medication with minimal side-effects, the dosages can be adjusted, and if necessary, combinations of different classes of antidepressants can be tried. Response rates to the first antidepressant administered range from 50–75%, and it can take at least six to eight weeks from the start of medication to remission.[174] Antidepressant medication treatment is usually continued for 16 to 20 weeks after remission, to minimize the chance of recurrence,[174] and even up to one year of continuation is recommended.[175] People with chronic depression may need to take medication indefinitely to avoid relapse.[19]
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the primary medications prescribed, owing to their relatively mild side-effects, and because they are less toxic in overdose than other antidepressants.[176] People who do not respond to one SSRI can be switched to another antidepressant, and this results in improvement in almost 50% of cases.[177] Another option is to switch to the atypical antidepressant bupropion.[178] Venlafaxine, an antidepressant with a different mechanism of action, may be modestly more effective than SSRIs.[179] However, venlafaxine is not recommended in the UK as a first-line treatment because of evidence suggesting its risks may outweigh benefits,[180] and it is specifically discouraged in children and adolescents.[181][182]
For child and adolescent depression, fluoxetine is recommended if medication are used.[183] Fluoxetine; however, appears to have only slight benefit in children,[183][184] while other antidepressants have not been shown to be effective.[185] There is also insufficient evidence to determine effectiveness in those with depression complicated by dementia.[186] Any antidepressant can cause low serum sodium levels (also called hyponatremia);[187] nevertheless, it has been reported more often with SSRIs.[176] It is not uncommon for SSRIs to cause or worsen insomnia; the sedating antidepressant mirtazapine can be used in such cases.[188][189]
Irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors, an older class of antidepressants, have been plagued by potentially life-threatening dietary and drug interactions. They are still used only rarely, although newer and better-tolerated agents of this class have been developed.[190] The safety profile is different with reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors such as moclobemide where the risk of serious dietary interactions is negligible and dietary restrictions are less strict.[191]
For children, adolescents, and probably young adults between 18 and 24 years old, there is a higher risk of both suicidal ideations and suicidal behavior in those treated with SSRIs.[192][193] For adults, it is unclear whether SSRIs affect the risk of suicidality. One review found no connection;[194] another an increased risk;[195] and a third no risk in those 25–65 years old and a decrease risk in those more than 65.[196] A black box warning was introduced in the United States in 2007 on SSRI and other antidepressant medications due to increased risk of suicide in patients younger than 24 years old.[197] Similar precautionary notice revisions were implemented by the Japanese Ministry of Health.[198]
Other medications
There is some evidence that fish oil supplements containing high levels of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) may be effective in major depression,[199] but other meta-analysis of the research conclude that positive effects may be due to publication bias.[200] There is some preliminary evidence that COX-2 inhibitors have a beneficial effect on major depression.[71] Lithium appears effective at lowering the risk of suicide in those with bipolar disorder and unipolar depression to nearly the same levels as the general population.[201] There is a narrow range of effective and safe dosages of lithium thus close monitoring may be needed.[202] Low-dose thyroid hormone may be added to existing antidepressants to treat persistent depression symptoms in people who have tried multiple courses of medication.[203]
Electroconvulsive therapy
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a standard psychiatric treatment in which seizures are electrically induced in patients to provide relief from psychiatric illnesses.[204]:1880 ECT is used with informed consent[205] as a last line of intervention for major depressive disorder.[206]
A round of ECT is effective for about 50% of people with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder, whether it is unipolar or bipolar.[207] Follow-up treatment is still poorly studied, but about half of people who respond, relapse with twelve months.[208]
Aside from effects in the brain, the general physical risks of ECT are similar to those of brief general anesthesia.[209]:259 Immediately following treatment, the most common adverse effects are confusion and memory loss.[206][210] ECT is considered one of the least harmful treatment options available for severely depressed pregnant women.[211]
A usual course of ECT involves multiple administrations, typically given two or three times per week until the patient is no longer suffering symptoms ECT is administered under anesthetic with a muscle relaxant.[212] Electroconvulsive therapy can differ in its application in three ways: electrode placement, frequency of treatments, and the electrical waveform of the stimulus. These three forms of application have significant differences in both adverse side effects and symptom remission. After treatment, drug therapy is usually continued, and some patients receive maintenance ECT.[206]
ECT appears to work in the short term via an anticonvulsant effect mostly in the frontal lobes, and longer term via neurotrophic effects primarily in the medial temporal lobe.[213]
Transcranial magnetic stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) or deep transcranial magnetic stimulation is a noninvasive method used to stimulate small regions of the brain.[214] TMS was approved by the FDA for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder in 2008[215] and as of 2014 evidence supports that it is probably effective.[216] The American Psychiatric Association[217] the Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Disorders,[218] and the Royal Australia and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists have endorsed rTMS for trMDD.[219]
Other
Bright light therapy reduces depression symptom severity, with benefit was found for both seasonal affective disorder and for nonseasonal depression, and an effect similar to those for conventional antidepressants. For non-seasonal depression, adding light therapy to the standard antidepressant treatment was not effective.[220] For non-seasonal depression where light was used mostly in combination with antidepressants or wake therapy a moderate effect was found, with response better than control treatment in high-quality studies, in studies that applied morning light treatment, and with people who respond to total or partial sleep deprivation.[221] Both analyses noted poor quality, short duration, and small size of most of the reviewed studies.
Prognosis
Major depressive episodes often resolve over time whether or not they are treated. Outpatients on a waiting list show a 10–15% reduction in symptoms within a few months, with approximately 20% no longer meeting the full criteria for a depressive disorder.[222] The median duration of an episode has been estimated to be 23 weeks, with the highest rate of recovery in the first three months.[223]
Studies have shown that 80% of those suffering from their first major depressive episode will suffer from at least 1 more during their life,[224] with a lifetime average of 4 episodes.[225] Other general population studies indicate that around half those who have an episode recover (whether treated or not) and remain well, while the other half will have at least one more, and around 15% of those experience chronic recurrence.[226] Studies recruiting from selective inpatient sources suggest lower recovery and higher chronicity, while studies of mostly outpatients show that nearly all recover, with a median episode duration of 11 months. Around 90% of those with severe or psychotic depression, most of whom also meet criteria for other mental disorders, experience recurrence.[227][228]
Recurrence is more likely if symptoms have not fully resolved with treatment. Current guidelines recommend continuing antidepressants for four to six months after remission to prevent relapse. Evidence from many randomized controlled trials indicates continuing antidepressant medications after recovery can reduce the chance of relapse by 70% (41% on placebo vs. 18% on antidepressant). The preventive effect probably lasts for at least the first 36 months of use.[229]
Those people experiencing repeated episodes of depression require ongoing treatment in order to prevent more severe, long-term depression. In some cases, people must take medications for long periods of time or for the rest of their lives.[230]
Cases when outcome is poor are associated with inappropriate treatment, severe initial symptoms that may include psychosis, early age of onset, more previous episodes, incomplete recovery after 1 year, pre-existing severe mental or medical disorder, and family dysfunction as well.[231]
Depressed individuals have a shorter life expectancy than those without depression, in part because depressed patients are at risk of dying by suicide.[232] However, they also have a higher rate of dying from other causes,[233] being more susceptible to medical conditions such as heart disease.[234] Up to 60% of people who die by suicide have a mood disorder such as major depression, and the risk is especially high if a person has a marked sense of hopelessness or has both depression and borderline personality disorder.[235] The lifetime risk of suicide associated with a diagnosis of major depression in the US is estimated at 3.4%, which averages two highly disparate figures of almost 7% for men and 1% for women[236] (although suicide attempts are more frequent in women).[237] The estimate is substantially lower than a previously accepted figure of 15%, which had been derived from older studies of hospitalized patients.[238]
Depression is often associated with unemployment and poverty.[239] Major depression is currently the leading cause of disease burden in North America and other high-income countries, and the fourth-leading cause worldwide. In the year 2030, it is predicted to be the second-leading cause of disease burden worldwide after HIV, according to the World Health Organization.[240] Delay or failure in seeking treatment after relapse, and the failure of health professionals to provide treatment, are two barriers to reducing disability.[241]
Epidemiology

Major depressive disorder affects approximately 253 million people in 2013 (3.6% of the global population).[14] The percentage of people who are affected at one point in their life varies from 7% in Japan to 21% in France.[15] In most countries the number of people who have depression during their lives falls within an 8–18% range.[15] In North America, the probability of having a major depressive episode within a year-long period is 3–5% for males and 8–10% for females.[243][244] Major depression to be about twice as common in women as in men, although it is unclear why this is so, and whether factors unaccounted for are contributing to this.[245] The relative increase in occurrence is related to pubertal development rather than chronological age, reaches adult ratios between the ages of 15 and 18, and appears associated with psychosocial more than hormonal factors.[245] Depression is a major cause of disability worldwide.[246]
People are most likely to develop their first depressive episode between the ages of 30 and 40, and there is a second, smaller peak of incidence between ages 50 and 60.[247] The risk of major depression is increased with neurological conditions such as stroke, Parkinson's disease, or multiple sclerosis, and during the first year after childbirth.[248] It is also more common after cardiovascular illnesses, and is related more to a poor outcome than to a better one.[234][249] Studies conflict on the prevalence of depression in the elderly, but most data suggest there is a reduction in this age group.[250] Depressive disorders are more common to observe in urban than in rural population and the prevalence is in groups with stronger socioeconomic factors i.e. homelessness.[251]
History

The Ancient Greek physician Hippocrates described a syndrome of melancholia as a distinct disease with particular mental and physical symptoms; he characterized all "fears and despondencies, if they last a long time" as being symptomatic of the ailment.[252] It was a similar but far broader concept than today's depression; prominence was given to a clustering of the symptoms of sadness, dejection, and despondency, and often fear, anger, delusions and obsessions were included.[253]
The term depression itself was derived from the Latin verb deprimere, "to press down".[254] From the 14th century, "to depress" meant to subjugate or to bring down in spirits. It was used in 1665 in English author Richard Baker's Chronicle to refer to someone having "a great depression of spirit", and by English author Samuel Johnson in a similar sense in 1753.[255] The term also came into use in physiology and economics. An early usage referring to a psychiatric symptom was by French psychiatrist Louis Delasiauve in 1856, and by the 1860s it was appearing in medical dictionaries to refer to a physiological and metaphorical lowering of emotional function.[256] Since Aristotle, melancholia had been associated with men of learning and intellectual brilliance, a hazard of contemplation and creativity. The newer concept abandoned these associations and through the 19th century, became more associated with women.[253]

Although melancholia remained the dominant diagnostic term, depression gained increasing currency in medical treatises and was a synonym by the end of the century; German psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin may have been the first to use it as the overarching term, referring to different kinds of melancholia as depressive states.[257]
Sigmund Freud likened the state of melancholia to mourning in his 1917 paper Mourning and Melancholia. He theorized that objective loss, such as the loss of a valued relationship through death or a romantic break-up, results in subjective loss as well; the depressed individual has identified with the object of affection through an unconscious, narcissistic process called the libidinal cathexis of the ego. Such loss results in severe melancholic symptoms more profound than mourning; not only is the outside world viewed negatively but the ego itself is compromised.[258] The patient's decline of self-perception is revealed in his belief of his own blame, inferiority, and unworthiness.[259] He also emphasized early life experiences as a predisposing factor.[253] Adolf Meyer put forward a mixed social and biological framework emphasizing reactions in the context of an individual's life, and argued that the term depression should be used instead of melancholia.[260] The first version of the DSM (DSM-I, 1952) contained depressive reaction and the DSM-II (1968) depressive neurosis, defined as an excessive reaction to internal conflict or an identifiable event, and also included a depressive type of manic-depressive psychosis within Major affective disorders.[261]
In the mid-20th century, researchers theorized that depression was caused by a chemical imbalance in neurotransmitters in the brain, a theory based on observations made in the 1950s of the effects of reserpine and isoniazid in altering monoamine neurotransmitter levels and affecting depressive symptoms.[262]
The term "unipolar" (along with the related term "bipolar") was coined by the neurologist and psychiatrist Karl Kleist, and subsequently used by his disciples Edda Neele and Karl Leonhard.[263]
The term Major depressive disorder was introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s as part of proposals for diagnostic criteria based on patterns of symptoms (called the "Research Diagnostic Criteria", building on earlier Feighner Criteria),[264] and was incorporated into the DSM-III in 1980.[265] To maintain consistency the ICD-10 used the same criteria, with only minor alterations, but using the DSM diagnostic threshold to mark a mild depressive episode, adding higher threshold categories for moderate and severe episodes.[107][265] The ancient idea of melancholia still survives in the notion of a melancholic subtype.
The new definitions of depression were widely accepted, albeit with some conflicting findings and views. There have been some continued empirically based arguments for a return to the diagnosis of melancholia.[266][267] There has been some criticism of the expansion of coverage of the diagnosis, related to the development and promotion of antidepressants and the biological model since the late 1950s.[268]
Society and culture

Terminology
The term "depression" is used in a number of different ways. It is often used to mean this syndrome but may refer to other mood disorders or simply to a low mood. People's conceptualizations of depression vary widely, both within and among cultures. "Because of the lack of scientific certainty," one commentator has observed, "the debate over depression turns on questions of language. What we call it—'disease,' 'disorder,' 'state of mind'—affects how we view, diagnose, and treat it."[270] There are cultural differences in the extent to which serious depression is considered an illness requiring personal professional treatment, or is an indicator of something else, such as the need to address social or moral problems, the result of biological imbalances, or a reflection of individual differences in the understanding of distress that may reinforce feelings of powerlessness, and emotional struggle.[271][272]
The diagnosis is less common in some countries, such as China. It has been argued that the Chinese traditionally deny or somatize emotional depression (although since the early 1980s, the Chinese denial of depression may have modified).[273] Alternatively, it may be that Western cultures reframe and elevate some expressions of human distress to disorder status. Australian professor Gordon Parker and others have argued that the Western concept of depression "medicalizes" sadness or misery.[274][275] Similarly, Hungarian-American psychiatrist Thomas Szasz and others argue that depression is a metaphorical illness that is inappropriately regarded as an actual disease.[276] There has also been concern that the DSM, as well as the field of descriptive psychiatry that employs it, tends to reify abstract phenomena such as depression, which may in fact be social constructs.[277] American archetypal psychologist James Hillman writes that depression can be healthy for the soul, insofar as "it brings refuge, limitation, focus, gravity, weight, and humble powerlessness."[278] Hillman argues that therapeutic attempts to eliminate depression echo the Christian theme of resurrection, but have the unfortunate effect of demonizing a soulful state of being.
Stigma
Historical figures were often reluctant to discuss or seek treatment for depression due to social stigma about the condition, or due to ignorance of diagnosis or treatments. Nevertheless, analysis or interpretation of letters, journals, artwork, writings, or statements of family and friends of some historical personalities has led to the presumption that they may have had some form of depression. People who may have had depression include English author Mary Shelley,[279] American-British writer Henry James,[280] and American president Abraham Lincoln.[281] Some well-known contemporary people with possible depression include Canadian songwriter Leonard Cohen[282] and American playwright and novelist Tennessee Williams.[283] Some pioneering psychologists, such as Americans William James[284][285] and John B. Watson,[286] dealt with their own depression.
There has been a continuing discussion of whether neurological disorders and mood disorders may be linked to creativity, a discussion that goes back to Aristotelian times.[287][288] British literature gives many examples of reflections on depression.[289] English philosopher John Stuart Mill experienced a several-months-long period of what he called "a dull state of nerves", when one is "unsusceptible to enjoyment or pleasurable excitement; one of those moods when what is pleasure at other times, becomes insipid or indifferent". He quoted English poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge's "Dejection" as a perfect description of his case: "A grief without a pang, void, dark and drear, / A drowsy, stifled, unimpassioned grief, / Which finds no natural outlet or relief / In word, or sigh, or tear."[290][291] English writer Samuel Johnson used the term "the black dog" in the 1780s to describe his own depression,[292] and it was subsequently popularized by depression sufferer former British Prime Minister Sir Winston Churchill.[292]
Social stigma of major depression is widespread, and contact with mental health services reduces this only slightly. Public opinions on treatment differ markedly to those of health professionals; alternative treatments are held to be more helpful than pharmacological ones, which are viewed poorly.[293] In the UK, the Royal College of Psychiatrists and the Royal College of General Practitioners conducted a joint Five-year Defeat Depression campaign to educate and reduce stigma from 1992 to 1996;[294] a MORI study conducted afterwards showed a small positive change in public attitudes to depression and treatment.[295]
Research
Trials are looking at the effects of botulinum toxins on depression. The idea is that the drug is used to make the person look less frowning and that this stops the negative facial feedback from the face.[296] In 2015 it turned out, however, that the partly positive effects that had been observed until then could have been placebo effects.[297]
MDD has been studied by taking MRI scans of patients with depression have revealed a number of differences in brain structure compared to those who are not depressed. Meta-analyses of neuroimaging studies in major depression reported that, compared to controls, depressed patients had increased volume of the lateral ventricles and adrenal gland and smaller volumes of the basal ganglia, thalamus, hippocampus, and frontal lobe (including the orbitofrontal cortex and gyrus rectus).[298][299] Hyperintensities have been associated with patients with a late age of onset, and have led to the development of the theory of vascular depression.[300]
Elderly
Depression is especially common among those over 65 years of age and increases in frequency with age beyond this age.[301] In addition the risk of depression increases in relation to the age and frailty of the individual.[301] Depression is one the most important factors which negatively impact quality of life in adults as well as the elderly.[301] Both symptoms and treatment among the elderly differ from those of the rest of the adult populations.[301]
As with many other diseases it is common among the elderly not to present classical depressive symptoms.[301] Diagnosis and treatment is further complicated in that the elderly are often simultaneously treated with a number of other drugs, and often have other concurrent diseases.[301] Treatment differs in that studies of SSRI-drugs have shown lesser and often inadequate effect among the elderly, while other drugs with more clear effects have adverse effects which can be especially difficult to handle among the elderly.[301] Duloxetine is an SNRI-drug with documented effect on recurring depression among the elderly, but has adverse effects in form of dizziness, dryness of the mouth, diarrhea, and constipation.[301]
Problem solving therapy was as of 2015 the only psychological therapy with proven effect, and can be likened to a simpler form of cognitive behavioral therapy.[301] However, elderly with depression are seldom offered any psychological treatment, and the evidence surrounding which other treatments are effective is incomplete.[301] Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT or electric-shock therapy) has been used as treatment of the elderly, and register-studies suggest it is effective although less so among the elderly than among the rest of the adult population.[301]
The risks involved with treatment of depression among the elderly as opposed to benefits is not entirely clear.[301] Awaiting more evidence on how depression-treatment among the elderly is best designed it is important to follow up treatment results, and to reconsider changing treatments if it does not help.[301]
Other animals
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Depression". NIMH. May 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 American Psychiatric Association (2013), Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.), Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing, pp. 160–168, ISBN 978-0-89042-555-8, retrieved 22 July 2016
- ↑ Richards, C. Steven; O'Hara, Michael W. (2014). The Oxford Handbook of Depression and Comorbidity. Oxford University Press. p. 254. ISBN 9780199797042.
- ↑ Lynch, Virginia A.; Duval, Janet Barber (2010). Forensic Nursing Science. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 453. ISBN 0323066380.
- 1 2 Patton, Lauren L. (2015). The ADA Practical Guide to Patients with Medical Conditions (2 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 339. ISBN 9781118929285.
- 1 2 Siu, AL; US Preventive Services Task Force, (USPSTF); Bibbins-Domingo, K; Grossman, DC; Baumann, LC; Davidson, KW; Ebell, M; García, FA; Gillman, M; Herzstein, J; Kemper, AR; Krist, AH; Kurth, AE; Owens, DK; Phillips, WR; Phipps, MG; Pignone, MP (26 January 2016). "Screening for Depression in Adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.". JAMA. 315 (4): 380–7. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.18392. PMID 26813211.
- 1 2 Siu, AL; U.S. Preventive Services Task, Force (1 March 2016). "Screening for Depression in Children and Adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.". Annals of Internal Medicine. 164 (5): 360–6. doi:10.7326/M15-2957. PMID 26858097.
- 1 2 Gilbody S, House AO, Sheldon TA (2005). "Screening and case finding instruments for depression". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD002792. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002792.pub2. PMID 16235301.
- 1 2 3 Fournier JC, DeRubeis RJ, Hollon SD, Dimidjian S, Amsterdam JD, Shelton RC, Fawcett J (January 2010). "Antidepressant drug effects and depression severity: a patient-level meta-analysis". JAMA. 303 (1): 47–53. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1943. PMC 3712503
 . PMID 20051569.
. PMID 20051569. - 1 2 Kirsch I, Deacon BJ, Huedo-Medina TB, Scoboria A, Moore TJ, Johnson BT (February 2008). "Initial severity and antidepressant benefits: a meta-analysis of data submitted to the Food and Drug Administration". PLoS Med. 5 (2): e45. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050045. PMC 2253608
 . PMID 18303940.
. PMID 18303940. - ↑ Braun, C; Bschor, T; Franklin, J; Baethge, C (2016). "Suicides and Suicide Attempts during Long-Term Treatment with Antidepressants: A Meta-Analysis of 29 Placebo-Controlled Studies Including 6,934 Patients with Major Depressive Disorder.". Psychotherapy and psychosomatics. 85 (3): 171–9. doi:10.1159/000442293. PMID 27043848.
- ↑ Driessen Ellen; Hollon Steven D (2010). "Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Mood Disorders: Efficacy, Moderators and Mediators". Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 33 (3): 537–55. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2010.04.005. PMC 2933381
 . PMID 20599132.
. PMID 20599132. - ↑ Association, American Psychiatric. American Psychiatric Association Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders: Compendium 2006. American Psychiatric Pub. p. 780. ISBN 9780890423851.
- 1 2 Global Burden of Disease Study 2013, Collaborators (22 August 2015). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.". Lancet (London, England). 386 (9995): 743–800. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. PMID 26063472.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Kessler, RC; Bromet, EJ (2013). "The epidemiology of depression across cultures.". Annual review of public health. 34: 119–38. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031912-114409. PMC 4100461
 . PMID 23514317.
. PMID 23514317. - ↑ Global Burden of Disease Study 2013, Collaborators (22 August 2015). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.". Lancet (London, England). 386 (9995): 743–800. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. PMID 26063472.
- 1 2 Hersen, Michel; Rosqvist, Johan (2008). Handbook of Psychological Assessment, Case Conceptualization, and Treatment, Volume 1: Adults. John Wiley & Sons. p. 32. ISBN 9780470173565.
- ↑ Strakowski, Stephen M.; Nelson, Erik. "Introduction". Major Depressive Disorder. Oxford University Press. p. Chapter 1. ISBN 9780190206185.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Depression (PDF). National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). Retrieved 7 September 2008.
- ↑ Hays RD, Wells KB, Sherbourne CD, Rogers W, Spritzer K (1995). "Functioning and well-being outcomes of patients with depression compared with chronic general medical illnesses". Archives of General Psychiatry. 52 (1): 11–19. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950130011002. PMID 7811158.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 349
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 412
- 1 2 Delgado PL, Schillerstrom J (2009). "Cognitive Difficulties Associated With Depression: What Are the Implications for Treatment?". Psychiatric Times. 26 (3).
- ↑ Judd, LL; Schettler, PJ; Coryell, W; Akiskal, HS; Fiedorowicz, JG (2013). "Overt irritability/anger in unipolar major depressive episodes: past and current characteristics and implications for long-term course". JAMA Psychiatry. 70 (11): 1171–80. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.1957. PMID 24026579.
- 1 2 3 4 American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 350
- ↑ "Insomnia: Assessment and Management in Primary Care". American Family Physician. 59 (11): 3029–38. 1999. Retrieved 12 November 2014.
- ↑ Patel V, Abas M, Broadhead J (2001). "Depression in developing countries: Lessons from Zimbabwe". BMJ. 322 (7284): 482–84. doi:10.1136/bmj.322.7284.482.
- ↑ Faculty of Psychiatry of Old Age, NSW Branch, RANZCP; Kitching D Raphael B (2001). Consensus Guidelines for Assessment and Management of Depression in the Elderly (PDF). North Sydney, New South Wales: NSW Health Department. p. 2. ISBN 0-7347-3341-0.
- ↑ Yohannes AM, Baldwin RC (2008). "Medical Comorbidities in Late-Life Depression". Psychiatric Times. 25 (14).
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 354
- ↑ Kessler RC, Nelson CB, McGonagle KA, Liu J, Swartz M, Blazer DG (1996). "Comorbidity of DSM-III-R major depressive disorder in the general population: results from the US National Comorbidity Survey". British Journal of Psychiatry. 168 (suppl 30): 17–30. PMID 8864145.
- ↑ Hirschfeld RM (2001). "The Comorbidity of Major Depression and Anxiety Disorders: Recognition and Management in Primary Care". Primary Care Companion to the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 3 (6): 244–254. PMC 181193
 . PMID 15014592.
. PMID 15014592. - ↑ Grant BF (1995). "Comorbidity between DSM-IV drug use disorders and major depression: Results of a national survey of adults". Journal of Substance Abuse. 7 (4): 481–87. doi:10.1016/0899-3289(95)90017-9. PMID 8838629.
- ↑ Hallowell EM, Ratey JJ (2005). Delivered from distraction: Getting the most out of life with Attention Deficit Disorder. New York: Ballantine Books. pp. 253–55. ISBN 0-345-44231-8.
- ↑ Brunsvold GL, Oepen G (2008). "Comorbid Depression in ADHD: Children and Adolescents". Psychiatric Times. 25 (10).
- ↑ Bair MJ, Robinson RL, Katon W, Kroenke K (2003). "Depression and Pain Comorbidity: A Literature Review". Archives of Internal Medicine. 163 (20): 2433–45. doi:10.1001/archinte.163.20.2433. PMID 14609780.
- ↑ Swardfager W, Herrmann N, Marzolini S, Saleem M, Farber SB, Kiss A, Oh PI, Lanctôt KL (2011). "Major depressive disorder predicts completion, adherence, and outcomes in cardiac rehabilitation: a prospective cohort study of 195 patients with coronary artery disease.". Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 72 (9): 1181–8. doi:10.4088/jcp.09m05810blu. PMID 21208573.
- ↑ Schulman J, Shapiro BA (2008). "Depression and Cardiovascular Disease: What Is the Correlation?". Psychiatric Times. 25 (9).
- ↑ Department of Health and Human Services (1999). "The fundamentals of mental health and mental illness" (PDF). Mental Health: A Report of the Surgeon General. Retrieved 11 November 2008.
- ↑ Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H, McClay J, Mill J, Martin J, Braithwaite A, Poulton R (July 2003). "Influence of life stress on depression: Moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene". Science. 301 (5631): 386–89. Bibcode:2003Sci...301..386C. doi:10.1126/science.1083968. PMID 12869766.
- ↑ Haeffel GJ, Getchell M, Koposov RA, Yrigollen CM, Deyoung CG, Klinteberg BA, Oreland L, Ruchkin VV, Grigorenko EL (2008). "Association between polymorphisms in the dopamine transporter gene and depression: evidence for a gene-environment interaction in a sample of juvenile detainees" (PDF). Psychol Sci. 19 (1): 62–9. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02047.x. PMID 18181793.
- ↑ Slavich GM (2004). "Deconstructing depression: A diathesis-stress perspective (Opinion)". APS Observer. Retrieved 11 November 2008.
- ↑ Barlow 2005, p. 226
- ↑ Shah N, Eisner T, Farrell M, Raeder C (July–August 1999). "An overview of SSRIs for the treatment of depression" (PDF). Journal of the Pharmacy Society of Wisconsin. Retrieved 10 November 2008.
- 1 2 Nutt DJ (2008). "Relationship of neurotransmitters to the symptoms of major depressive disorder". Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 69 Suppl E1: 4–7. PMID 18494537.
- ↑ Hirschfeld RM (2000). "History and evolution of the monoamine hypothesis of depression". Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 61 Suppl 6: 4–6. PMID 10775017.
- ↑ Jacobsen, Jacob P. R.; Medvedev, Ivan O.; Caron, Marc G. (5 September 2012). "The 5-HT deficiency theory of depression: perspectives from a naturalistic 5-HT deficiency model, the tryptophan hydroxylase 2Arg439His knockin mouse". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 367 (1601): 2444–2459. doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0109. ISSN 0962-8436.
- ↑ Delgado PL, Moreno FA (2000). "Role of norepinephrine in depression". J Clin Psychiatry. 61 Suppl 1: 5–12. PMID 10703757.
- ↑ Delgado PL (2000). "Depression: the case for a monoamine deficiency". Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 61 Suppl 6: 7–11. PMID 10775018.
- ↑ Ruhe, HG; Mason, NS; Schene, AH (2007). "Mood is indirectly related to serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine levels in humans: a meta-analysis of monoamine depletion studies". Molecular Psychiatry. 12: 331–359. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001949. PMID 17389902.
- ↑ Lacasse, Jeffrey R.; Leo, Jonathan (8 November 2005). "Serotonin and Depression: A Disconnect between the Advertisements and the Scientific Literature". PLoS Medicine. 2 (12): e392. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020392. PMC 1277931
 . PMID 16268734.
. PMID 16268734. 
- ↑ Cottencin O (December 2009). "[Severe depression and addictions]". Encephale (in French). 35 Suppl 7: S264–8. doi:10.1016/S0013-7006(09)73483-9. PMID 20141784.
- ↑ Falk DE, Yi HY, Hilton ME (2008). "Age of onset and temporal sequencing of lifetime DSM-IV alcohol use disorders relative to comorbid mood and anxiety disorders". Drug Alcohol Depend. 94 (1–3): 234–45. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.11.022. PMC 2386955
 . PMID 18215474.
. PMID 18215474. - 1 2 Boden JM, Fergusson DM (May 2011). "Alcohol and depression". Addiction. 106 (5): 906–14. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.03351.x. PMID 21382111.
- ↑ Professor Heather Ashton (2002). "Benzodiazepines: How They Work and How to Withdraw".
- ↑ Kelley KW, Dantzer R (June 2011). "Alcoholism and inflammation: neuroimmunology of behavioral and mood disorders". Brain Behav. Immun. 25 Suppl 1: S13–20. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2010.12.013. PMID 21193024.
- ↑ Semple, David; Roger Smyth; Jonathan Burns; Rajan Darjee; Andrew McIntosh (2007) [2005]. "13". Oxford Handbook of Psychiatry. United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. p. 540. ISBN 0-19-852783-7.
- ↑ Collier, Judith; Longmore, Murray (2003). "4". In Scally, Peter. Oxford Handbook of Clinical Specialties (6 ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 366. ISBN 978-0-19-852518-9.
- ↑ Janicak, Philip G.; Marder, Stephen R.; Pavuluri, Mani N. (2011). Principles and practice of psychopharmacotherap. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams Wilkins. pp. 507–508. ISBN 978-1-60547-565-3.
- ↑ Johnson, Bankole A. (2011). Addiction medicine : science and practic. New York: Springer. pp. 301–303. ISBN 978-1-4419-0337-2.
- ↑ Marshall BD, Werb D (June 2010). "Health outcomes associated with methamphetamine use among young people: a systematic review". Addiction. 105 (6): 991–1002. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.02932.x. PMID 20659059.
- 1 2 Cutter WJ, Norbury R, Murphy DG (2003). "Oestrogen, brain function, and neuropsychiatric disorders". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. 74 (7): 837–40. doi:10.1136/jnnp.74.7.837. PMC 1738534
 . PMID 12810759.
. PMID 12810759. - ↑ Douma SL, Husband C, O'Donnell ME, Barwin BN, Woodend AK (2005). "Estrogen-related Mood Disorders Reproductive Life Cycle Factors". Advances in Nursing Science. 28 (4): 364–375. doi:10.1097/00012272-200510000-00008. PMID 16292022.
- ↑ Lasiuk GC, Hegadoren KM (2007). "The Effects of Estradiol on Central Serotonergic Systems and Its Relationship to Mood in Women". Biological Research for Nursing. 9 (2): 147–160. doi:10.1177/1099800407305600. PMID 17909167.
- ↑ Monteleone P (2001). "Endocrine disturbances and psychiatric disorders". Current Opinion in Psychiatry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 14 (6): 605–10. doi:10.1097/00001504-200111000-00020. ISSN 0951-7367.
- ↑ Risch N, Herrell R, Lehner T, Liang KY, Eaves L, Hoh J, Griem A, Kovacs M, Ott J, Merikangas KR (June 2009). "Interaction between the serotonin transporter gene (5-HTTLPR), stressful life events, and risk of depression: a meta-analysis". JAMA. 301 (23): 2462–71. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.878. PMC 2938776
 . PMID 19531786.
. PMID 19531786. - ↑ Munafò MR, Durrant C, Lewis G, Flint J (February 2009). "Gene X environment interactions at the serotonin transporter locus". Biol. Psychiatry. 65 (3): 211–9. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.06.009. PMID 18691701.
- ↑ Uher R, McGuffin P (January 2010). "The moderation by the serotonin transporter gene of environmental adversity in the etiology of depression: 2009 update". Mol. Psychiatry. 15 (1): 18–22. doi:10.1038/mp.2009.123. PMID 20029411.
- ↑ Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008). "From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain". Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 9 (1): 46–56. doi:10.1038/nrn2297. PMC 2919277
 . PMID 18073775.
. PMID 18073775. - ↑ Dowlati Y, Herrmann N, Swardfager W, Liu H, Sham L, Reim EK, Lanctôt KL (2010). "A meta-analysis of cytokines in major depression". Biological Psychiatry. 67 (5): 446–457. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.09.033. PMID 20015486.
- 1 2 Müller N, Myint AM, Schwarz MJ (February 2011). "Inflammatory biomarkers and depression". Neurotox Res. 19 (2): 308–18. doi:10.1007/s12640-010-9210-2. PMID 20658274.
- ↑ Berk, Michael; Williams, Lana J.; Jacka, Felice N.; O'Neil, Adrienne; Pasco, Julie A.; Moylan, Steven; Allen, Nicholas B.; Stuart, Amanda L.; Hayley, Amie C. (1 January 2013). "So depression is an inflammatory disease, but where does the inflammation come from?". BMC Medicine. 11: 200. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-11-200. ISSN 1741-7015. PMC 3846682
 . PMID 24228900.
. PMID 24228900. 
- ↑ Schmahmann JD (2004). "Disorders of the cerebellum: ataxia, dysmetria of thought, and the cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome". J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 16 (3): 367–78. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.16.3.367. PMID 15377747.
- ↑ Konarski JZ, McIntyre RS, Grupp LA, Kennedy SH (May 2005). "Is the cerebellum relevant in the circuitry of neuropsychiatric disorders?". J Psychiatry Neurosci. 30 (3): 178–86. PMID 15944742.
- ↑ Schmahmann JD, Weilburg JB, Sherman JC (2007). "The neuropsychiatry of the cerebellum – insights from the clinic". Cerebellum. 6 (3): 254–67. doi:10.1080/14734220701490995. PMID 17786822.
- 1 2 Raphael B (2000). "Unmet Need for Prevention". In Andrews G, Henderson S. Unmet Need in Psychiatry:Problems, Resources, Responses. Cambridge University Press. pp. 138–39. ISBN 0-521-66229-X.
- ↑ Heim C, Newport DJ, Mletzko T, Miller AH, Nemeroff CB (2008). "The link between childhood trauma and depression: insights from HPA axis studies in humans". Psychoneuroendocrinology. 33 (6): 693–710. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2008.03.008. PMID 18602762.
- ↑ Kessler RC (1997). "The effects of stressful life events on depression". Annual Review of Psychology. 48: 191–214. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.48.1.191. PMID 9046559.
- ↑ Kendler KS, Hettema JM, Butera F, Gardner CO, Prescott CA (2003). "Life event dimensions of loss, humiliation, entrapment, and danger in the prediction of onsets of major depression and generalized anxiety". Archives of General Psychiatry. 60 (8): 789–796. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.60.8.789. PMID 12912762.
- ↑ Slavich GM, Thornton T, Torres LD, Monroe SM, Gotlib IH (2009). "Targeted rejection predicts hastened onset of major depression". Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology. 28: 223–243. doi:10.1521/jscp.2009.28.2.223. PMC 2847269
 . PMID 20357895.
. PMID 20357895. - ↑ Monroe SM, Slavich GM, Torres LD, Gotlib IH (2007). "Major life events and major chronic difficulties are differentially associated with history of major depressive episodes". Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 116 (1): 116–124. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.116.1.116. PMID 17324022.
- ↑ Sadock 2002, p. 540
- ↑ Vilhjalmsson R (1993). "Life stress, social support and clinical depression: A reanalysis of the literature". Social Science & Medicine. 37 (3): 331–42. doi:10.1016/0277-9536(93)90264-5. PMID 8356482.
- ↑ Kim D (2008). "Blues from the neighborhood? Neighborhood characteristics and depression". Epidemiologic reviews. 30: 101–17. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxn009. PMID 18753674.
- ↑ Bonde JP (2008). "Psychosocial factors at work and risk of depression: A systematic review of the epidemiological evidence". Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 65 (7): 438–45. doi:10.1136/oem.2007.038430. PMID 18417557.
- ↑ Cox WT, Abramson LY, Devine PG, Hollon SD (2012). "Stereotypes, Prejudice, and Depression: The Integrated Perspective". Perspectives on Psychological Science. 7 (5): 427–449. doi:10.1177/1745691612455204.
- ↑ Sloman L, Gilbert P, Hasey G (2003). "Evolved mechanisms in depression: The role and interaction of attachment and social rank in depression". Journal of Affective Disorders. 74 (2): 107–21. doi:10.1016/S0165-0327(02)00116-7. PMID 12706512.
- ↑ Kaufmann IM (1 September 1993). "Rural psychiatric services. A collaborative model". Canadian Family Physician. 39: 1957–61. PMC 2379905
 . PMID 8219844.
. PMID 8219844. - ↑ "Call for action over Third World depression". BBC News (Health). British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC). 1 November 1999. Retrieved 11 October 2008.
- ↑ Zimmerman M, Chelminski I, Posternak M (September 2004). "A Review of Studies of the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale in Healthy Controls: Implications for the Definition of Remission in Treatment Studies Of Depression". J Nerv Ment Dis. 192 (9): 595–601. doi:10.1097/01.nmd.0000138226.22761.39. PMID 15348975.
- ↑ McPherson A, Martin CR (February 2010). "A Narrative Review of the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and Implications for its Use in an Alcohol-Dependent Population". J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 17 (1): 19–30. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2850.2009.01469.x. PMID 20100303.
- ↑ Osman, A.; Bagge, C. L.; Gutierrez, P. M.; Konick, L. C.; Kopper, B. A.; Barrios, F. X. (1 December 2001). "The Suicidal Behaviors Questionnaire-Revised (SBQ-R):Validation with Clinical and Nonclinical Samples". Assessment. 8 (4): 443–454. doi:10.1177/107319110100800409. PMID 11785588.
- 1 2 Sharp LK, Lipsky MS (2002). "Screening for depression across the lifespan: a review of measures for use in primary care settings". American Family Physician. 66 (6): 1001–8. PMID 12358212.
- ↑ Cepoiu M, McCusker J, Cole MG, Sewitch M, Belzile E, Ciampi A (2008). "Recognition of depression by non-psychiatric physicians—a systematic literature review and meta-analysis". J Gen Intern Med. 23 (1): 25–36. doi:10.1007/s11606-007-0428-5. PMC 2173927
 . PMID 17968628.
. PMID 17968628. - ↑ Dale J, Sorour E, Milner G (2008). "Do psychiatrists perform appropriate physical investigations for their patients? A review of current practices in a general psychiatric inpatient and outpatient setting". Journal of Mental Health. 17 (3): 293–98. doi:10.1080/09638230701498325.
- ↑ Orengo CA, Fullerton G, Tan R (2004). "Male depression: A review of gender concerns and testosterone therapy". Geriatrics. 59 (10): 24–30. PMID 15508552.
- ↑ Ju, SY (2013). "Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and the risk of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis". J Nutr Health Aging. 17 (5): 447–55. doi:10.1007/s12603-012-0418-0. PMID 23636546.
- ↑ Reid LM, Maclullich AM (2006). "Subjective memory complaints and cognitive impairment in older people". Dementia and geriatric cognitive disorders. 22 (5–6): 471–85. doi:10.1159/000096295. PMID 17047326.
- ↑ Katz IR (1998). "Diagnosis and treatment of depression in patients with Alzheimer's disease and other dementias". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 59 Suppl 9: 38–44. PMID 9720486.
- ↑ Wright SL, Persad C (2007). "Distinguishing between depression and dementia in older persons: Neuropsychological and neuropathological correlates". Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology. 20 (4): 189–98. doi:10.1177/0891988707308801. PMID 18004006.
- ↑ Sadock 2002, p. 108
- ↑ Sadock 2002, p. 260
- ↑ Hahn T, Marquand AF, Ehlis AC, Dresler T, Kittel-Schneider S, Jarczok TA, Lesch KP, Jakob PM, Mourao-Miranda J, Brammer MJ, Fallgatter AJ (December 2010). "Integrating Neurobiological Markers of Depression". Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 68 (4): 361–368. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.178. PMID 21135315. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- 1 2 3 "Mental and behavioural disorders: Mood [affective] disorders". World Health Organization. 2010. Retrieved 8 November 2008.
- ↑ Sadock 2002, p. 288
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. xxix
- 1 2 Gruenberg, A.M., Goldstein, R.D., Pincus, H.A. (2005). "Classification of Depression: Research and Diagnostic Criteria: DSM-IV and ICD-10" (PDF). Biology of Depression: From Novel Insights to Therapeutic Strategies (eds J. Licinio and M.-L. Wong). Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH. doi:10.1002/9783527619672.ch1. Retrieved 30 October 2008.
- ↑ "The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2010. Retrieved 12 November 2014.
- ↑ The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioral disorders. Clinical description and diagnostic guideline. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1992
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 345
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 372
- ↑ Parker 1996, p. 173
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 352
- ↑ Wakefield JC, Schmitz MF, First MB, Horwitz AV (2007). "Extending the bereavement exclusion for major depression to other losses: Evidence from the National Comorbidity Survey". Archives of General Psychiatry. 64 (4): 433–40. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.64.4.433. PMID 17404120. Lay summary – The Washington Post (3 April 2007).
- ↑ Kendler KS, Gardner CO (1 February 1998). "Boundaries of major depression: An evaluation of DSM-IV criteria". American Journal of Psychiatry. 155 (2): 172–77. PMID 9464194.
- 1 2 Sadock 2002, p. 552
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 778
- ↑ Carta MG, Altamura AC, Hardoy MC, Pinna F, Medda S, Dell'Osso L, Carpiniello B, Angst J (2003). "Is recurrent brief depression an expression of mood spectrum disorders in young people?". European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 253 (3): 149–53. doi:10.1007/s00406-003-0418-5. PMID 12904979.
- ↑ Rapaport MH, Judd LL, Schettler PJ, Yonkers KA, Thase ME, Kupfer DJ, Frank E, Plewes JM, Tollefson GD, Rush AJ (2002). "A descriptive analysis of minor depression". American Journal of Psychiatry. 159 (4): 637–43. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.159.4.637. PMID 11925303.
- 1 2 American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 355
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, pp. 419–20
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, pp. 421–22
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, pp. 417–18
- ↑ Nonacs, Ruta M (4 December 2007). "Postpartum depression". eMedicine. Retrieved 30 October 2008.
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association 2000a, p. 425
- ↑ Akiskal HS, Benazzi F (2006). "The DSM-IV and ICD-10 categories of recurrent [major] depressive and bipolar II disorders: Evidence that they lie on a dimensional spectrum". Journal of Affective Disorders. 92 (1): 45–54. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2005.12.035. PMID 16488021.
- 1 2 Cuijpers P, van Straten A, Smit F, Mihalopoulos C, Beekman A (2008). "Preventing the onset of depressive disorders: a meta-analytic review of psychological interventions". Am J Psychiatry. 165 (10): 1272–80. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2008.07091422. PMID 18765483.
- ↑ Li, F; Liu, X; Zhang, D (10 September 2015). "Fish consumption and risk of depression: a meta-analysis.". Journal of epidemiology and community health: jech–2015–206278. doi:10.1136/jech-2015-206278. PMID 26359502.
- 1 2 Muñoz RF, Beardslee WR, Leykin Y (May–June 2012). "Major depression can be prevented". The American Psychologist. 67 (4): 285–95. doi:10.1037/a0027666. PMC 4533896
 . PMID 22583342.
. PMID 22583342. - ↑ Cuijpers, P (20 September 2012). Prevention and early treatment of mental ill-health (PDF). PSYCHOLOGY FOR HEALTH: Contributions to Policy Making, Brussels.
- ↑ Griffiths, K.M.; Farrer, L.; Christensen, H. (2010). "The efficacy of internet interventions for depression and anxiety disorders: a review of randomised controlled trials" (PDF). Medical Journal of Australia. 192 (11): 4–11. Retrieved 12 November 2014.
- ↑ Jané-Llopis E, Hosman C, Jenkins R, Anderson P (2003). "Predictors of efficacy in depression prevention programmes" (PDF). British Journal of Psychiatry. Retrieved 2 April 2009.
- ↑ Cuijpers P, Muñoz RF, Clarke GN, Lewinsohn PM (2009). "Psychoeducational treatment and prevention of depression: the "Coping with Depression" course thirty years later". Clinical Psychology Review. 29 (5): 449–458. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2009.04.005. PMID 19450912.
- ↑ "Depression". National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. December 2004. Archived from the original on 15 November 2008. Retrieved 20 March 2013.
- ↑ "PsychiatryOnline | APA Practice Guidelines | Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Third Edition".
- ↑ Patel V, Araya R, Bolton P (2004). "Editorial: Treating depression in the developing world". Tropical Medicine & International Health. 9 (5): 539–41. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3156.2004.01243.x. PMID 15117296. (subscription required (help)).
- ↑ Cox GR, Callahan P, Churchill R, Hunot V, Merry SN, Parker AG, Hetrick SE (30 November 2014). "Psychological therapies versus antidepressant medication, alone and in combination for depression in children and adolescents.". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 11: CD008324. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008324.pub3. PMID 25433518.
- ↑ "Management of depression in primary and secondary care" (PDF). National Clinical Practice Guideline Number 23. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. 2007. Retrieved 4 November 2008.
- 1 2 Cooney GM, Dwan K, Greig CA, Lawlor DA, Rimer J, Waugh FR, McMurdo M, Mead GE (12 September 2013). Mead, Gillian E, ed. "Exercise for depression". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 9: CD004366. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004366.pub6. PMID 24026850.
- 1 2 Josefsson, T.; Lindwall, M.; Archer, T. (2014). "Physical exercise intervention in depressive disorders: Meta-analysis and systematic review". Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports. 24 (2): 259–272. doi:10.1111/sms.12050. ISSN 0905-7188.
- ↑ Bridle C, Spanjers K, Patel S, Atherton NM, Lamb SE (September 2012). "Effect of exercise on depression severity in older people: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials". Br J Psychiatry. 201 (3): 180–5. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.111.095174. PMID 22945926.
- ↑ Giedke H, Schwärzler F (2002). "Therapeutic use of sleep deprivation in depression". Sleep Medicine Reviews. 6 (5): 361–77. doi:10.1053/smrv.2002.0235. PMID 12531127.
- ↑ Taylor G, McNeill A, Girling A, Farley A, Lindson-Hawley N, Aveyard P (13 February 2014). "Change in mental health after smoking cessation: systematic review and meta-analysis". BMJ. 348 (feb13 1): g1151–g1151. doi:10.1136/bmj.g1151. PMC 3923980
 . PMID 24524926.
. PMID 24524926. - ↑ Amick, HR; Gartlehner, G; Gaynes, BN; Forneris, C; Asher, GN; Morgan, LC; Coker-Schwimmer, E; Boland, E; Lux, LJ; Gaylord, S; Bann, C; Pierl, CB; Lohr, KN (8 December 2015). "Comparative benefits and harms of second generation antidepressants and cognitive behavioral therapies in initial treatment of major depressive disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis.". BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 351: h6019. PMC 4673103
 . PMID 26645251.
. PMID 26645251. - ↑ Khan A, Faucett J, Lichtenberg P, Kirsch I, Brown WA (30 July 2012). "A Systematic Review of Comparative Efficacy of Treatments and Controls for Depression". PLOS ONE. 7 (7): e41778. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041778. PMC 3408478
 . PMID 22860015.
. PMID 22860015. - ↑ Thase ME (1999). "When are psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy combinations the treatment of choice for major depressive disorder?". Psychiatric Quarterly. 70 (4): 333–46. doi:10.1023/A:1022042316895. PMID 10587988.
- ↑ Cordes, J. (2013). "Depression". Encyclopedia of Sciences and Religions. p. 610. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-8265-8_301. ISBN 978-1-4020-8264-1.
- 1 2 Nieuwenhuijsen, Karen; Faber, Babs; Verbeek, Jos H.; Neumeyer-Gromen, Angela; Hees, Hiske L.; Verhoeven, Arco C.; van der Feltz-Cornelis, Christina M.; Bültmann, Ute (2014). "Interventions to improve return to work in depressed people". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12: CD006237. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006237.pub3. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 25470301.
- ↑ Wilson KC, Mottram PG, Vassilas CA (2008). "Psychotherapeutic treatments for older depressed people". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 23 (1): CD004853. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004853.pub2. PMID 18254062.
- ↑ Cuijpers P, van Straten A, Smit F (2006). "Psychological treatment of late-life depression: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 21 (12): 1139–49. doi:10.1002/gps.1620. PMID 16955421.
- ↑ Childhood Depression. abct.org. Last updated: 30 July 2010
- ↑ NICE (2005). NICE guidelines: Depression in children and adolescents. London: NICE. p. 5. ISBN 1-84629-074-0. Retrieved 16 August 2008.
- ↑ Dobson KS (1989). "A meta-analysis of the efficacy of cognitive therapy for depression". J Consult Clin Psychol. 57 (3): 414–9. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.57.3.414. PMID 2738214.
- ↑ Roth, Anthony; Fonagy, Peter (2005) [1996]. What Works for Whom? Second Edition: A Critical Review of Psychotherapy Research. Guilford Press. p. 78. ISBN 1-59385-272-X.
- ↑ Weersing VR, Walker PN (2008). "Review: Cognitive behavioural therapy for adolescents with depression". Evidence-Based Mental Health. 11 (3): 76. doi:10.1136/ebmh.11.3.76. PMID 18669678. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- ↑ Harrington R, Whittaker J, Shoebridge P, Campbell F (1998). "Systematic review of efficacy of cognitive behaviour therapies in childhood and adolescent depressive disorder". BMJ. 325 (7358): 229–30. doi:10.1136/bmj.316.7144.1559. PMC 28555
 . PMID 9596592.
. PMID 9596592. - ↑ Becker SJ (2008). "Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Adolescent Depression: Processes of Cognitive Change". Psychiatric Times. 25 (14).
- ↑ Almeida AM, Lotufo Neto F (2003). "Cognitive-behavioral therapy in prevention of depression relapses and recurrences: a review". Revista brasileira de psiquiatria (Sao Paulo, Brazil : 1999). 25 (4): 239–44. PMID 15328551.
- ↑ Paykel ES (2007). "Cognitive therapy in relapse prevention in depression". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 10 (1): 131–6. doi:10.1017/S1461145706006912. PMID 16787553.
- ↑ Nieuwenhuijsen K, Faber B, Verbeek JH, Neumeyer-Gromen A, Hees HL, Verhoeven AC, van der Feltz-Cornelis CM, Bültmann U (2014). "Interventions to improve return to work in depressed people". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12: CD006237. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006237.pub3. PMID 25470301.
- ↑ Beck 1987, p. 10
- ↑ Coelho HF, Canter PH, Ernst E (2007). "Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy: Evaluating current evidence and informing future research". Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 75 (6): 1000–05. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.75.6.1000. PMID 18085916.
- ↑ Khoury B, Lecomte T, Fortin G, Masse M, Therien P, Bouchard V, Chapleau MA, Paquin K, Hofmann SG (August 2013). "Mindfulness-based therapy: a comprehensive meta-analysis". Clin Psychol Rev. 33 (6): 763–71. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2013.05.005. PMID 23796855.
- ↑ Jain FA, Walsh RN, Eisendrath SJ, et al. (2014). "Critical Analysis of the Efficacy of Meditation Therapies for Acute and Subacute Phase Treatment of Depressive Disorders: A systematic Review". Psychosomatics. 56: 297–302. doi:10.1016/j.psym.2014.10.007.
- ↑ Simkin DR, Black NB (July 2014). "Meditation and mindfulness in clinical practice.". Child and adolescent psychiatric clinics of North America. 23 (3): 487–534. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2014.03.002. PMID 24975623.
- ↑ Dworetzky J (1997). Psychology. Pacific Grove, CA, USA: Brooks/Cole Pub. Co. p. 602. ISBN 0-314-20412-1.
- ↑ Doidge N, Simon B, Lancee WJ, First M, Brunshaw J, Brauer L, Grant DC, Stevens A, Oldham JM, Mosher P (2002). "Psychoanalytic patients in the US, Canada, and Australia: II. A DSM-III-R validation study". Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association. 50 (2): 615–27. doi:10.1177/00030651020500021101. PMID 12206545.
- ↑ Barlow 2005, p. 20
- ↑ de Maat S, Dekker J, Schoevers R, van Aalst G, Gijsbers-van Wijk C, Hendriksen M, Kool S, Peen J, Van R, de Jonghe F (2007). "Short Psychodynamic Supportive Psychotherapy, antidepressants, and their combination in the treatment of major depression: A mega-analysis based on three Randomized Clinical Trials". Depression and Anxiety. 25 (7): 565–74. doi:10.1002/da.20305. PMID 17557313.
- ↑ Kirsch I, Moore TJ, Scoboria A, Nicholls SS (2002). "The emperor's new drugs: An analysis of antidepressant medication data submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration". Prevention & Treatment. 5. doi:10.1037/1522-3736.5.1.523a.
- ↑ "The treatment and management of depression in adults" (PDF). NICE. October 2009. Retrieved 12 November 2014.
- ↑ Leucht C, Huhn M, Leucht S (2012). Leucht, C, ed. "Amitriptyline versus placebo for major depressive disorder". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12: CD009138. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009138.pub2. PMID 23235671.
- 1 2 Karasu TB, Gelenberg A, Merriam A, Wang P (April 2000). "Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder (Second Edition)". Am J Psychiatry. 157 (4 Suppl): 1–45. PMID 10767867.; Third edition doi:10.1176/appi.books.9780890423363.48690
- ↑ Thase ME (2006). "Preventing relapse and recurrence of depression: a brief review of therapeutic options". CNS spectrums. 11 (12 Suppl 15): 12–21. PMID 17146414.
- 1 2 Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain 2008, p. 204
- ↑ Whooley MA, Simon GE (2000). "Managing Depression in Medical Outpatients". New England Journal of Medicine. 343 (26): 1942–50. doi:10.1056/NEJM200012283432607. PMID 11136266. Retrieved 11 November 2008.
- ↑ Zisook S, Rush AJ, Haight BR, Clines DC, Rockett CB (2006). "Use of bupropion in combination with serotonin reuptake inhibitors". Biological Psychiatry. 59 (3): 203–10. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.06.027. PMID 16165100.
- ↑ Papakostas GI, Thase ME, Fava M, Nelson JC, Shelton RC (2007). "Are antidepressant drugs that combine serotonergic and noradrenergic mechanisms of action more effective than the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in treating major depressive disorder? A meta-analysis of studies of newer agents". Biological Psychiatry. 62 (11): 1217–27. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.03.027. PMID 17588546.
- ↑ Gordon Duff (31 May 2006). "Updated prescribing advice for venlafaxine (Efexor/Efexor XL)". Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).
- ↑ "Depression in children and young people: Identification and management in primary, community and secondary care" (PDF). NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. 2005. Retrieved 12 November 2014.
- ↑ Mayers AG, Baldwin DS (2005). "Antidepressants and their effect on sleep". Human Psychopharmacology. 20 (8): 533–59. doi:10.1002/hup.726. PMID 16229049.
- 1 2 Cipriani, A; Zhou, X; Del Giovane, C; Hetrick, SE; Qin, B; Whittington, C; Coghill, D; Zhang, Y; Hazell, P; Leucht, S; Cuijpers, P; Pu, J; Cohen, D; Ravindran, AV; Liu, Y; Michael, KD; Yang, L; Liu, L; Xie, P (27 August 2016). "Comparative efficacy and tolerability of antidepressants for major depressive disorder in children and adolescents: a network meta-analysis.". Lancet (London, England). 388 (10047): 881–90. PMID 27289172.
- ↑ Tsapakis EM, Soldani F, Tondo L, Baldessarini RJ (2008). "Efficacy of antidepressants in juvenile depression: meta-analysis". Br J Psychiatry. 193 (1): 10–7. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.106.031088. PMID 18700212.
- ↑ "Comparative efficacy and tolerability of antidepressants for major depressive disorder in children and adolescents: a network meta-analysis". Lancet. 8 June 2016. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30385-3.
- ↑ Nelson JC, Devanand DP (April 2011). "A systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled antidepressant studies in people with depression and dementia". Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 59 (4): 577–85. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03355.x. PMID 21453380.
- ↑ Palmer BF, Gates JR, Lader M (2003). "Causes and Management of Hyponatremia". Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 37 (11): 1694–702. doi:10.1345/aph.1D105. PMID 14565794.
- ↑ Guaiana G, Barbui C, Hotopf M (2007). "Amitriptyline for depression". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 18 (3): 11–7. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004186.pub2. PMID 17636748.
- ↑ Anderson IM (2000). "Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors versus tricyclic antidepressants: A meta-analysis of efficacy and tolerability". Journal of Affective Disorders. 58 (1): 19–36. doi:10.1016/S0165-0327(99)00092-0. PMID 10760555.
- ↑ Krishnan KR (2007). "Revisiting monoamine oxidase inhibitors". Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 68 Suppl 8: 35–41. PMID 17640156.
- ↑ Bonnet U (2003). "Moclobemide: therapeutic use and clinical studies". CNS Drug Rev. 9 (1): 97–140. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2003.tb00245.x. PMID 12595913.
- ↑ Hammad TA (16 August 2004). "Review and evaluation of clinical data. Relationship between psychiatric drugs and pediatric suicidality" (PDF). FDA. pp. 42; 115. Retrieved 29 May 2008.
- ↑ Hetrick, SE; McKenzie, JE; Cox, GR; Simmons, MB; Merry, SN (14 November 2012). "Newer generation antidepressants for depressive disorders in children and adolescents.". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 11: CD004851. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004851.pub3. PMID 23152227.
- ↑ Gunnell D, Saperia J, Ashby D (2005). "Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and suicide in adults: meta-analysis of drug company data from placebo controlled, randomised controlled trials submitted to the MHRA's safety review". BMJ. 330 (7488): 385. doi:10.1136/bmj.330.7488.385. PMC 549105
 . PMID 15718537.
. PMID 15718537. - ↑ Fergusson D, Doucette S, Glass KC, Shapiro S, Healy D, Hebert P, Hutton B (2005). "Association between suicide attempts and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: systematic review of randomised controlled trials". BMJ. 330 (7488): 396. doi:10.1136/bmj.330.7488.396. PMC 549110
 . PMID 15718539.
. PMID 15718539. - ↑ Stone M, Laughren T, Jones ML, Levenson M, Holland PC, Hughes A, Hammad TA, Temple R, Rochester G (11 August 2009). "Risk of suicidality in clinical trials of antidepressants in adults: analysis of proprietary data submitted to US Food and Drug Administration". BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 339: b2880. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2880. PMC 2725270
 . PMID 19671933.
. PMID 19671933. - ↑ "FDA Proposes New Warnings About Suicidal Thinking, Behavior in Young Adults Who Take Antidepressant Medications". FDA. 2 May 2007. Retrieved 29 May 2008.
- ↑ Medics and Foods Department. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Safety Information (PDF) (Report). 261 (in Japanese). Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (Japan).
- ↑ Sublette ME, Ellis SP, Geant AL, Mann JJ (September 2011). "Meta-analysis of the effects of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in clinical trials in depression". J Clin Psychiatry. 72 (12): 1577–84. doi:10.4088/JCP.10m06634. PMC 3534764
 . PMID 21939614.
. PMID 21939614. - ↑ Bloch MH, Hannestad J (September 2011). "Omega-3 fatty acids for the treatment of depression: systematic review and meta-analysis". Mol Psychiatry. 17 (12): 1272–82. doi:10.1038/mp.2011.100. PMC 3625950
 . PMID 21931319.
. PMID 21931319. - ↑ Cipriani A, Hawton K, Stockton S, Geddes JR (27 June 2013). "Lithium in the prevention of suicide in mood disorders: updated systematic review and meta-analysis". BMJ. 346 (jun27 4): f3646–f3646. doi:10.1136/bmj.f3646. PMID 23814104.
- ↑ Nolen-Hoeksema, Susan. (2014) "Treatment of Mood Disorders". In (6th ed.) Abnormal Psychology p. 196. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-803538-8.
- ↑ Gelenberg, Alan J.; Freeman, Marlene P.; Markowitz, John C. "Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. 3rd edition." (PDF). American Psychiatric Association (APA). Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ↑ Rudorfer, MV, Henry, ME, Sackeim, HA (2003). "Electroconvulsive therapy". In A Tasman, J Kay, JA Lieberman (eds) Psychiatry, Second Edition. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 1865–1901.
- ↑ Beloucif S (2013). "Informed consent for special procedures: electroconvulsive therapy and psychosurgery". Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 26 (2): 182–5. doi:10.1097/ACO.0b013e32835e7380. PMID 23385317.
- 1 2 3 FDA. FDA Executive Summary. Prepared for the 27–28 January 2011 meeting of the Neurological Devices Panel Meeting to Discuss the Classification of Electroconvulsive Therapy Devices (ECT). Quote, p38: "Three major practice guidelines have been published on ECT. These guidelines include: APA Task Force on ECT (2001); Third report of the Royal College of Psychiatrists' Special Committee on ECT (2004); National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE 2003; NICE 2009). There is significant agreement between the three sets of recommendations."
- ↑ Dierckx B, Heijnen WT, van den Broek WW, Birkenhäger TK; Heijnen, WT; Van Den Broek, WW; Birkenhäger, TK (2012). "Efficacy of electroconvulsive therapy in bipolar versus unipolar major depression: A meta-analysis". Bipolar Disorders. 12 (2): 146–150. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2012.00997.x. PMID 22420590.
- ↑ Jelovac A, et al. (Nov 2013). "Relapse following successful electroconvulsive therapy for major depression: a meta-analysis". Neuropsychopharmacology. 38 (12): 2467–74. doi:10.1038/npp.2013.149. PMC 3799066
 . PMID 23774532.
. PMID 23774532. - ↑ Surgeon General (1999). Mental Health: A Report of the Surgeon General, chapter 4.
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association; Committee on Electroconvulsive Therapy; Richard D. Weiner (chairperson); et al. (2001). The practice of electroconvulsive therapy: recommendations for treatment, training, and privileging (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing. ISBN 978-0-89042-206-9.
- ↑ Pompili M, et al. (Dec 2014). "Electroconvulsive treatment during pregnancy: a systematic review". Expert Rev Neurother. 14 (12): 1377–90. doi:10.1586/14737175.2014.972373. PMID 25346216.
- ↑ "5 Outdated Beliefs About ECT". Psych Central.com.
- ↑ Abbott, C. C.; Gallegos, P.; Rediske, N.; Lemke, N. T.; Quinn, D. K. (2013). "A Review of Longitudinal Electroconvulsive Therapy: Neuroimaging Investigations". Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology. 27 (1): 33–46. doi:10.1177/0891988713516542. PMID 24381234.
- ↑ "NiCE. January 2014 Transcranial magnetic stimulation for treating and preventing migraine".
- ↑ "Melkerson, MN (2008-12-16). "Special Premarket 510(k) Notification for NeuroStar® TMS Therapy System for Major Depressive Disorder" (pdf). Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 2010-07-16." (PDF).
- ↑ Lefaucheur, JP; André-Obadia, N (November 2014). "Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS).". Clinical Neurophysiology. 125 (11): 2150–206. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2014.05.021. PMID 25034472.
- ↑ "American Psychiatric Association (2010). (eds: Gelenberg, AJ, Freeman, MP, Markowitz, JC, Rosenbaum, JF, Thase, ME, Trivedi, MH, Van Rhoads, RS). Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Patients with Major Depressive Disorder, 3rd Edition" (PDF).
- ↑ "Journal of Affective Disorders" (PDF). 2009. pp. S1–S64.
- ↑ Rush, A. John; Marangell, Lauren B.; Sackeim, Harold A.; George, Mark S.; Brannan, Stephen K.; Davis, Sonia M.; Howland, Robert; Kling, Mitchel A.; Rittberg, Barry R.; Burke, William J.; Rapaport, Mark H.; Zajecka, John; Nierenberg, Andrew A.; Husain, Mustafa M.; Ginsberg, David; Cooke, Robert G. (2005). "The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists. (2013) Position Statement 79. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Practice and Partnerships Committee". Biological Psychiatry. 58 (5): 347. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.05.025. PMID 16139580.
- ↑ Golden RN, Gaynes BN, Ekstrom RD, Hamer RM, Jacobsen FM, Suppes T, Wisner KL, Nemeroff CB (April 2005). "The efficacy of light therapy in the treatment of mood disorders: a review and meta-analysis of the evidence". American Journal of Psychiatry. 162 (4): 656–62. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.4.656. PMID 15800134.
- ↑ Tuunainen A, Kripke DF, Endo T (2004). Tuunainen, Arja, ed. "Light therapy for non-seasonal depression". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2): CD004050. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004050.pub2. PMID 15106233.
- ↑ Posternak MA, Miller I (2001). "Untreated short-term course of major depression: A meta-analysis of outcomes from studies using wait-list control groups". Journal of Affective Disorders. 66 (2–3): 139–46. doi:10.1016/S0165-0327(00)00304-9. PMID 11578666.
- ↑ Posternak MA, Solomon DA, Leon AC, Mueller TI, Shea MT, Endicott J, Keller MB (2006). "The naturalistic course of unipolar major depression in the absence of somatic therapy". Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. 194 (5): 324–29. doi:10.1097/01.nmd.0000217820.33841.53. PMID 16699380.
- ↑ Fava GA, Park SK, Sonino N (2006). "Treatment of recurrent depression.". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 6 (11): 1735–1740. doi:10.1586/14737175.6.11.1735. PMID 17144786.
- ↑ Limosin F, Mekaoui L, Hautecouverture S (2007). "Stratégies thérapeutiques prophylactiques dans la dépression unipolaire [Prophylactic treatment for recurrent major depression]". La Presse Médicale. 36 (11–C2): 1627–1633. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2007.03.032. PMID 17555914.
- ↑ Eaton WW, Shao H, Nestadt G, Lee HB, Lee BH, Bienvenu OJ, Zandi P (2008). "Population-based study of first onset and chronicity in major depressive disorder". Archives of General Psychiatry. 65 (5): 513–20. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.65.5.513. PMC 2761826
 . PMID 18458203.
. PMID 18458203. - ↑ Holma KM, Holma IA, Melartin TK, Rytsälä HJ, Isometsä ET (2008). "Long-term outcome of major depressive disorder in psychiatric patients is variable". Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 69 (2): 196–205. doi:10.4088/JCP.v69n0205. PMID 18251627.
- ↑ Kanai T, Takeuchi H, Furukawa TA, Yoshimura R, Imaizumi T, Kitamura T, Takahashi K (2003). "Time to recurrence after recovery from major depressive episodes and its predictors". Psychological Medicine. 33 (5): 839–45. doi:10.1017/S0033291703007827. PMID 12877398.
- ↑ Geddes JR, Carney SM, Davies C, Furukawa TA, Kupfer DJ, Frank E, Goodwin GM (2003). "Relapse prevention with antidepressant drug treatment in depressive disorders: A systematic review". Lancet. 361 (9358): 653–61. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12599-8. PMID 12606176.
- ↑ "Major Depression". MedlinePlus. 10 March 2014. Retrieved 16 July 2010.
- ↑ "Depression, Major: Prognosis". MDGuidlines. Guardian Life Insurance Company of America. Retrieved 16 July 2010.
- ↑ Cassano P, Fava M (2002). "Depression and public health: an overview". J Psychosom Res. 53 (4): 849–57. doi:10.1016/S0022-3999(02)00304-5. PMID 12377293.
- ↑ Rush AJ (2007). "The varied clinical presentations of major depressive disorder". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 68 (Supplement 8): 4–10. PMID 17640152.
- 1 2 Alboni P, Favaron E, Paparella N, Sciammarella M, Pedaci M (2008). "Is there an association between depression and cardiovascular mortality or sudden death?". Journal of cardiovascular medicine (Hagerstown, Md.). 9 (4): 356–62. doi:10.2459/JCM.0b013e3282785240. PMID 18334889.
- ↑ Barlow DH; Durand VM (2005). Abnormal psychology: An integrative approach (5th ed.). Belmont, CA, USA: Thomson Wadsworth. pp. 248–49. ISBN 0-534-63356-0.
- ↑ Blair-West GW, Mellsop GW (2001). "Major depression: Does a gender-based down-rating of suicide risk challenge its diagnostic validity?". Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 35 (3): 322–28. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1614.2001.00895.x. PMID 11437805.
- ↑ Oquendo MA, Bongiovi-Garcia ME, Galfalvy H, Goldberg PH, Grunebaum MF, Burke AK, Mann JJ (2007). "Sex differences in clinical predictors of suicidal acts after major depression: a prospective study". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 164 (1): 134–41. doi:10.1176/ajp.2007.164.1.134. PMC 3785095
 . PMID 17202555.
. PMID 17202555. - ↑ Bostwick JM, Pankratz VS (2000). "Affective disorders and suicide risk: A reexamination". American Journal of Psychiatry. 157 (12): 1925–32. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.157.12.1925. PMID 11097952.
- ↑ Weich S, Lewis G (1998). "Poverty, unemployment, and common mental disorders: Population based cohort study". BMJ. 317 (7151): 115–19. doi:10.1136/bmj.317.7151.115. PMC 28602
 . PMID 9657786. Retrieved 16 September 2008.
. PMID 9657786. Retrieved 16 September 2008. - ↑ Mathers CD, Loncar D (2006). "Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030". PLoS Med. 3 (11): e442. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030442. PMC 1664601
 . PMID 17132052.
. PMID 17132052. - ↑ Andrews G (2008). "In Review: Reducing the Burden of Depression". Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 53 (7): 420–27. PMID 18674396.
- ↑ "WHO Disease and injury country estimates". World Health Organization. 2009. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ↑ Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE (2005). "Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication". Archives of General Psychiatry. 62 (6): 593–602. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.593. PMID 15939837.
- ↑ Murphy JM, Laird NM, Monson RR, Sobol AM, Leighton AH (2000). "A 40-year perspective on the prevalence of depression: The Stirling County Study". Archives of General Psychiatry. 57 (3): 209–15. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.57.3.209. PMID 10711905.
- 1 2 Kuehner C (2003). "Gender differences in unipolar depression: An update of epidemiological findings and possible explanations". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 108 (3): 163–74. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0447.2003.00204.x. PMID 12890270.
- ↑ "The world health report 2001 – Mental Health: New Understanding, New Hope". WHO website. World Health Organization. 2001. Retrieved 19 October 2008.
- ↑ Eaton WW, Anthony JC, Gallo J, Cai G, Tien A, Romanoski A, Lyketsos C, Chen LS (1997). "Natural history of diagnostic interview schedule/DSM-IV major depression. The Baltimore Epidemiologic Catchment Area follow-up". Archives of General Psychiatry. 54 (11): 993–99. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830230023003. PMID 9366655.
- ↑ Rickards H (2005). "Depression in neurological disorders: Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke". Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. 76: i48–i52. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.060426. PMC 1765679
 . PMID 15718222.
. PMID 15718222. - ↑ Strik JJ, Honig A, Maes M (2001). "Depression and myocardial infarction: relationship between heart and mind". Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry. 25 (4): 879–92. doi:10.1016/S0278-5846(01)00150-6. PMID 11383983.
- ↑ Jorm AF (2000). "Does old age reduce the risk of anxiety and depression? A review of epidemiological studies across the adult life span". Psychological Medicine. 30 (1): 11–22. doi:10.1017/S0033291799001452. PMID 10722172.
- ↑ Gelder, M., Mayou, R. and Geddes, J. 2005. Psychiatry. 3rd ed. New York: Oxford. pp105.
- ↑ Hippocrates, Aphorisms, Section 6.23
- 1 2 3 Radden, J (2003). "Is this dame melancholy? Equating today's depression and past melancholia". Philosophy, Psychiatry, & Psychology. 10 (1): 37–52. doi:10.1353/ppp.2003.0081.
- ↑ depress. (n.d.). Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 30 June 2008, from Dictionary.com
- ↑ Wolpert, L (1999). "Malignant Sadness: The Anatomy of Depression". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 October 2008.
- ↑ Berrios GE (1988). "Melancholia and depression during the 19th century: A conceptual history". British Journal of Psychiatry. 153 (3): 298–304. doi:10.1192/bjp.153.3.298. PMID 3074848.
- ↑ Davison, K (2006). "Historical aspects of mood disorders". Psychiatry. 5 (4): 115–18. doi:10.1383/psyt.2006.5.4.115.
- ↑ Carhart-Harris RL, Mayberg HS, Malizia AL, Nutt D (2008). "Mourning and melancholia revisited: Correspondences between principles of Freudian metapsychology and empirical findings in neuropsychiatry". Annals of General Psychiatry. 7: 9. doi:10.1186/1744-859X-7-9. PMC 2515304
 . PMID 18652673.
. PMID 18652673. - ↑ Freud, S (1984). "Mourning and Melancholia". In Richards A. 11.On Metapsychology: The Theory of Psycholoanalysis. Aylesbury, Bucks: Pelican. pp. 245–69. ISBN 0-14-021740-1.
- ↑ Lewis, AJ (1934). "Melancholia: A historical review". Journal of Mental Science. 80 (328): 1–42. doi:10.1192/bjp.80.328.1.
- ↑ American Psychiatric Association (1968). "Schizophrenia". Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-II (PDF). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc. pp. 36–37, 40. Retrieved 3 August 2008.
- ↑ Schildkraut JJ (1965). "The catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders: A review of supporting evidence". American Journal of Psychiatry. 122 (5): 509–22. doi:10.1176/ajp.122.5.509. PMID 5319766.
- ↑ Angst J. Terminology, history and definition of bipolar spectrum. In: Maj M, Akiskal HS, López-Ibor JJ, Sartorius N (eds.), Bipolar disorders. Chichester: Wiley & Sons, LTD; 2002. pp. 53–55.
- ↑ Spitzer RL, Endicott J, Robins E (1975). "The development of diagnostic criteria in psychiatry" (PDF). Retrieved 8 November 2008.
- 1 2 Philipp M, Maier W, Delmo CD (1991). "The concept of major depression. I. Descriptive comparison of six competing operational definitions including ICD-10 and DSM-III-R". European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 240 (4–5): 258–65. doi:10.1007/BF02189537. PMID 1829000.
- ↑ Bolwig, Tom G.; Shorter, Edward (2007). "Melancholia: Beyond DSM, beyond neurotransmitters. Proceedings of a conference, May 2006, Copenhagen, Denmark". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Suppl. 115 (433): 4–183. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2007.00956.x. PMID 17280564.
- ↑ Fink M, Bolwig TG, Parker G, Shorter E (2007). "Melancholia: Restoration in psychiatric classification recommended". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 115 (2): 89–92. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2006.00943.x. PMC 3712974
 . PMID 17244171.
. PMID 17244171. - ↑ Healy, David (1999). The Antidepressant Era. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. p. 42. ISBN 0-674-03958-0.
- ↑ Wolf, Joshua "Lincoln's Great Depression", The Atlantic, October 2005, Retrieved 10 October 2009
- ↑ Maloney F (3 November 2005). "The Depression Wars: Would Honest Abe Have Written the Gettysburg Address on Prozac?". Slate magazine. Washington Post. Retrieved 3 October 2008.
- ↑ Karasz A (2005). "Cultural differences in conceptual models of depression". Social Science in Medicine. 60 (7): 1625–35. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.08.011. PMID 15652693.
- ↑ Tilbury, F; Rapley, M (2004). "'There are orphans in Africa still looking for my hands': African women refugees and the sources of emotional distress". Health Sociology Review. 13 (1): 54–64. doi:10.5172/hesr.13.1.54.
- ↑ Parker G, Gladstone G, Chee KT (2001). "Depression in the planet's largest ethnic group: The Chinese". American Journal of Psychiatry. 158 (6): 857–64. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.158.6.857. PMID 11384889.
- ↑ Parker G (2007). "Is depression overdiagnosed? Yes". BMJ. 335 (7615): 328. doi:10.1136/bmj.39268.475799.AD. PMC 1949440
 . PMID 17703040.
. PMID 17703040. - ↑ Pilgrim D, Bentall R (1999). "The medicalisation of misery: A critical realist analysis of the concept of depression". Journal of Mental Health. 8 (3): 261–74. doi:10.1080/09638239917580.
- ↑ Steibel W (Producer) (1998). "Is depression a disease?". Debatesdebates. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ Blazer DG (2005). The age of melancholy: "Major depression" and its social origins. New York, NY, USA: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-95188-3.
- ↑ Hillman J (T Moore, Ed.) (1989). A blue fire: Selected writings by James Hillman. New York, NY, USA: Harper & Row. pp. 152–53. ISBN 0-06-016132-9.
- ↑ Seymour, Miranda (2002). Mary Shelley. Grove Press. pp. 560–61. ISBN 0-8021-3948-5.
- ↑ "Biography of Henry James". pbs.org. Retrieved 19 August 2008.
- ↑ Burlingame, Michael (1997). The Inner World of Abraham Lincoln. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. pp. xvii, 92–113. ISBN 0-252-06667-7.
- ↑ Pita E (26 September 2001). "An Intimate Conversation with...Leonard Cohen". Retrieved 3 October 2008.
- ↑ Jeste ND, Palmer BW, Jeste DV (2004). "Tennessee Williams". American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 12 (4): 370–75. doi:10.1097/00019442-200407000-00004. PMID 15249274.
- ↑ James H (Ed.) (1920). Letters of William James (Vols. 1 and 2). Montana USA: Kessinger Publishing Co. pp. 147–48. ISBN 978-0-7661-7566-2.
- ↑ Hergenhahn 2005, p. 311
- ↑ Cohen D (1979). J. B. Watson: The Founder of Behaviourism. London, UK: Routledge & Kegan Paul. p. 7. ISBN 0-7100-0054-5.
- ↑ Andreasen NC (2008). "The relationship between creativity and mood disorders". Dialogues in clinical neuroscience. 10 (2): 251–5. PMC 3181877
 . PMID 18689294.
. PMID 18689294. - ↑ Simonton, DK (2005). "Are genius and madness related? Contemporary answers to an ancient question". Psychiatric Times. 22 (7).
- ↑ Heffernan CF (1996). The melancholy muse: Chaucer, Shakespeare and early medicine. Pittsburgh, PA, USA: Duquesne University Press. ISBN 0-8207-0262-5.
- ↑ Mill JS (2003). "A crisis in my mental history: One stage onward". Autobiography (txt). Project Gutenberg EBook. pp. 1826–32. ISBN 1-4212-4200-1. Retrieved 9 August 2008.
- ↑ Sterba R (1947). "The 'Mental Crisis' of John Stuart Mill". Psychoanalytic Quarterly. 16 (2): 271–72. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- 1 2 "Churchill's Black Dog?: The History of the 'Black Dog' as a Metaphor for Depression" (PDF). Black Dog Institute website. Black Dog Institute. 2005. Retrieved 18 August 2008.
- ↑ Jorm AF, Angermeyer M, Katschnig H (2000). "Public knowledge of and attitudes to mental disorders: a limiting factor in the optimal use of treatment services". In Andrews G, Henderson S. Unmet Need in Psychiatry:Problems, Resources, Responses. Cambridge University Press. p. 409. ISBN 0-521-66229-X.
- ↑ Paykel ES, Tylee A, Wright A, Priest RG, Rix S, Hart D (1997). "The Defeat Depression Campaign: psychiatry in the public arena". American Journal of Psychiatry. 154 (6 Suppl): 59–65. doi:10.1176/ajp.154.6.59. PMID 9167546.
- ↑ Paykel ES, Hart D, Priest RG (1998). "Changes in public attitudes to depression during the Defeat Depression Campaign". British Journal of Psychiatry. 173 (6): 519–22. doi:10.1192/bjp.173.6.519. PMID 9926082.
- ↑ Kruger TH, Wollmer MA (2015). "Depression – An emerging indication for botulinum toxin treatment". Toxicon. 107 (Pt A): 154–7. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.09.035. PMID 26415901.
- ↑ Milev, R (2015). "Response of Depression to Botulinum Toxin Treatment: Agitation as a Predictor". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 6: 55. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00055. PMC 4403301
 . PMID 25941497..
. PMID 25941497.. - ↑ Kempton MJ, Salvador Z, Munafò MR, Geddes JR, Simmons A, Frangou S, Williams SC (2011). "Structural Neuroimaging Studies in Major Depressive Disorder: Meta-analysis and Comparison With Bipolar Disorder". Arch Gen Psychiatry. 68 (7): 675–90. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.60. PMID 21727252. see also MRI database at www.depressiondatabase.org
- ↑ Arnone D, McIntosh AM, Ebmeier KP, Munafò MR, Anderson IM (July 2011). "Magnetic resonance imaging studies in unipolar depression: Systematic review and meta-regression analyses". Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 22 (1): 1–16. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.05.003. PMID 21723712.
- ↑ Herrmann LL, Le Masurier M, Ebmeier KP (2008). "White matter hyperintensities in late life depression: a systematic review". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. 79 (6): 619–24. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.124651. PMID 17717021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Services, Swedish Council on Health Technology Assessmentl. "Depression treatment for the elderly". www.sbu.se. Retrieved 16 June 2016.
Cited works
- American Psychiatric Association (2000a). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision: DSM-IV-TR. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc. ISBN 0-89042-025-4.
- Barlow DH; Durand VM (2005). Abnormal psychology: An integrative approach (5th ed.). Belmont, CA, USA: Thomson Wadsworth. ISBN 0-534-63356-0.
- Beck AT, Rush J, Shaw BF, Emery G (1987) [1979]. Cognitive Therapy of depression. New York, NY, USA: Guilford Press. ISBN 0-89862-919-5.
- Hergenhahn BR (2005). An Introduction to the History of Psychology (5th ed.). Belmont, CA, USA: Thomson Wadsworth. ISBN 0-534-55401-6.
- May R (1994). The discovery of being: Writings in existential psychology. New York, NY, USA: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-31240-2.
- Hadzi-Pavlovic, Dusan; Parker, Gordon (1996). Melancholia: a disorder of movement and mood: a phenomenological and neurobiological review. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-47275-X.
- Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain (2008). British National Formulary (BNF 56). UK: BMJ Group and RPS Publishing. ISBN 978-0-85369-778-7.
- Sadock, Virginia A.; Sadock, Benjamin J.; Kaplan, Harold I. (2003). Kaplan & Sadock's synopsis of psychiatry: behavioral sciences/clinical psychiatry. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-3183-6.
External links
- Depression at DMOZ
