Caribbean Netherlands
| Caribbean Netherlands Caribisch Nederland (Dutch) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Overseas region of the Netherlands | |||
| |||
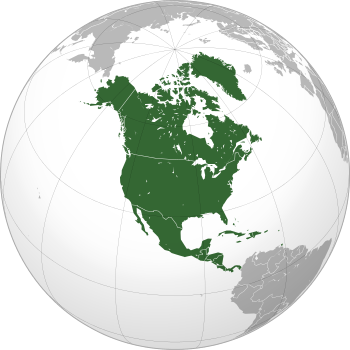
 Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, Sint Eustatius. | |||
| Coordinates: 12°11′N 68°14′W / 12.183°N 68.233°W | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Special municipalities | |||
| Incorporated into the Netherlands | 10 October 2010 (dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles) | ||
| Government (see Politics of the Netherlands) | |||
| • National Rep. | Gilbert Isabella | ||
| • Lt. Governors |
| ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 328 km2 (127 sq mi) | ||
| (0.8% of the Netherlands) | |||
| Highest elevation (Mount Scenery) | 887 m (2,910 ft) | ||
| Population (2010) | |||
| • Total | 21,133 | ||
| • Density | 64/km2 (170/sq mi) | ||
| (0.1% of the Netherlands) | |||
| Languages | |||
| • Official | Dutch | ||
| • Recognised regional |
| ||
| Time zone | AST (UTC−4) | ||
| Calling code | +599 | ||
| ISO 3166 code | BQ, NL-BQ1, NL-BQ2, NL-BQ3 | ||
| Currency | United States dollar (USD)[2] | ||
| Internet TLD | .nl, .an,a .bq b | ||
|
^ .an is to be discontinued[3] ^ .bq is assigned but not used[4][5] | |||
The Caribbean Netherlands[6][7] (Dutch: Caribisch Nederland) are the three special municipalities of the Netherlands that are located in the Caribbean Sea. They consist of the islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba,[a 1] although the term "Caribbean Netherlands" is sometimes used to refer to all of the islands in the Dutch Caribbean. In legislation, the three islands are also known as the BES islands (a more traditional acronym of their names). The islands are currently classified as public bodies in the Netherlands and as overseas countries and territories of the European Union; thus, EU law does not automatically apply.
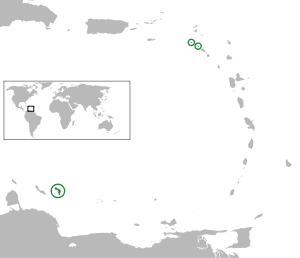
Bonaire (including the islet of Klein Bonaire) is one of the Leeward Antilles and is located close to the coast of Venezuela. Sint Eustatius and Saba are in the main Lesser Antilles group and are located south of Sint Maarten and northwest of Saint Kitts and Nevis.
Legal status
The three islands gained their current status following the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles on 10 October 2010.[8] At the same time, the islands of Curaçao and Sint Maarten became autonomous countries (Dutch: landen) within the Kingdom of the Netherlands.[9] The island of Aruba is also a country of the Kingdom located in the Caribbean. The term "Dutch Caribbean" may refer to the three special municipalities (e.g. for stamps), but may also refer to all of the Caribbean islands within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The population of the BES islands is 21,000. Their total area is 328 square kilometres (127 sq mi).
Administration
The special municipalities (Dutch: bijzondere gemeenten) carry many of the functions normally performed by Dutch municipalities. The executive power rests with the Governing Council headed by a Lieutenant governor. The main democratic body is the island council. Dutch citizens of these three islands are entitled to vote in Dutch national and (as all Dutch nationals) in European elections.
Officially the islands are classed in Dutch law as being openbare lichamen (literally translated as "public bodies") and not gemeenten (municipalities). Unlike normal municipalities, they do not form part of a Dutch province[10] and the powers normally exercised by provincial councils within municipalities are divided between the island governments themselves and the central government by means of the National Office for the Caribbean Netherlands. For this reason, they are called "special" municipalities.
For many Dutch laws there is a special BES version.[11] For example, social security is not on the same level as it is in the European Netherlands.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
National Office
The National Office for the Caribbean Netherlands (Dutch: Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland) is responsible for taxation, policing, immigration, transport infrastructure, health, education, and social security in the islands and provides these services on behalf of the Government of the Netherlands.[14] This agency was established as the Regional Service Center in 2008 and became the National Office for the Caribbean Netherlands on 1 September 2010.[15][16] The current director is Jan Helmond.[17] The Representative for the public bodies of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba represents the Government of the Netherlands on the islands and also performs tasks similar to a King's Commissioner. The current representative is Gilbert Isabella.[18]
Relationship with the European Union
The islands do not form part of the European Union and instead constitute "overseas countries and territories" (OCT status) of the Union, to which special provisions apply.[a 2] The Lisbon Treaty introduced a procedure where the European Council may change the status of an overseas territory of Denmark, France, or the Netherlands regarding the application of the EU treaties to that territory.[a 3] In June 2008, the Dutch government published a survey of the legal and economic impacts by a switched status from OCT to OMR.[19][20] The position of the islands will be reviewed after a five-year transitional period, which began with the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles in October 2010.[21] The review will be conducted as part of the planned review of the Dutch "Act for the Public bodies Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba" (Dutch: "Wet openbare lichamen Bonaire, Sint Eustatius en Saba"), where the islands have been granted the option to become an Outermost region – and thus a direct part of the European Union.[22]
Geography
The Caribbean Netherlands form part of the Lesser Antilles. Within this island group,
- Bonaire is part of the ABC islands within the Leeward Antilles island chain off the Venezuelan coast. The Leeward Antilles have a mixed volcanic and coral origin.
- Saba and Sint Eustatius are part of the SSS islands. They are located east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands. Although in the English language they are considered part of the Leeward Islands, French, Spanish, Dutch and the English spoken locally consider them part of the Windward Islands. The Windward Islands are all of volcanic origin and hilly, leaving little ground suitable for agriculture. The highest point is Mount Scenery, 887 metres (2,910 ft), on Saba (also the highest point in all the Kingdom of the Netherlands).
-
Map showing Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba within the former Netherlands Antilles.
-
_in_the_Kingdom_of_the_Netherlands.svg.png)
Relative distance between mainland Netherlands in Europe and the Caribbean Netherlands.
-
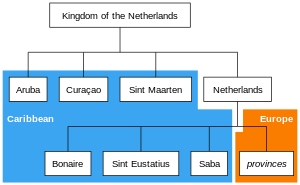
The Caribbean BES islands are subdivisions of the country of the Netherlands and are therefore referred to as the Caribbean Netherlands.
Climate
The islands of the Caribbean Netherlands enjoy a tropical climate with warm weather all year round. The Leeward Islands are warmer and drier than the Windward islands. In summer, the Windward Islands can be subject to hurricanes.
Currency
Until 1 January 2011, the three islands used the Netherlands Antillean guilder; after that all three switched to the US dollar, rather than the euro (which is used in the European Netherlands) or the Caribbean guilder (which is being adopted by the other two former Antillean islands of Curaçao and Sint Maarten).[23]
Communications
The telephone country code remains 599, that of the former Netherlands Antilles, and is shared with Curaçao. The International Organization for Standardization has assigned the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code ISO 3166-2:BQ for these islands.[24] The IANA has not established a root zone for the .bq Internet ccTLD and whether it will be used is unknown.
See also
- Bonaire constitutional referendum, 2010
- Identity cards of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
- Postage stamps and postal history of the Caribbean Netherlands
Notes
- ↑ "Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba" is the listed English name for the territorial grouping in the International Organization for Standardization's ISO 3166-1, where the English spelling was corrected with the release of ISO 3166-1 Newsletter VI-9.
- ↑ Per the Annex II of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union.
- ↑ Now contained in Article 355(6) of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union.
References
- ↑ "Invoeringswet openbare lichamen Bonaire, Sint Eustatius en Saba" (in Dutch). wetten.nl. Retrieved 2012-10-14.
- ↑ "Wet geldstelsel BES". Dutch government. 30 September 2010. Retrieved 11 January 2014.
- ↑ "Registering .CW Domains". University of Curaçao. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
- ↑ "Boneiru, Sint Eustatius y Saba – BQ". ISO. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
- ↑ "Delegation Record for .BQ". IANA. 20 December 2010. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ↑ "Changes per 10.10.10". Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland. Retrieved 16 August 2015. (registration required (help)).
Bonaire, St. Eustatius and Saba (the Caribbean Netherlands)
- ↑ "Island guide Caribbean Netherlands – Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, Saba" (PDF). Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland. Retrieved 16 August 2015. Lay summary – (original link to PDF).
We proudly present you the Island Guide Caribbean Netherlands. This information booklet has been published by the Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland for all the three islands: Bonaire, St. Eustatius and Saba.
- ↑ "Besluit van 23 september 2010 tot vaststelling van het tijdstip van inwerkingtreding van de artikelen I en II van de Rijkswet wijziging Statuut in verband met de opheffing van de Nederlandse Antillen" (in Dutch). Overheid.nl. 1 October 2010. Retrieved 27 June 2011.
- ↑ "Caribbean Parts of the Kingdom". Government.nl.
- ↑ "31.954, Wet openbare lichamen Bonaire, Sint Eustatius en Saba" (in Dutch). Eerste kamer der Staten-Generaal. Retrieved 2010-10-15.
De openbare lichamen vallen rechtstreeks onder het Rijk omdat zij geen deel uitmaken van een provincie. (The public bodies (...), because they are not part of a Province).
- ↑ "Wet- en regelgeving" (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 14 May 2011.
- ↑ "Statistical Yearbook - Netherlands Antilles (2009)" (PDF). Central Bureau of Statistics (Netherlands). 2009.
- ↑ "Bevolkingsontwikkeling Caribisch Nederland; geboorte, sterfte, migratie" (in Dutch). Central Bureau of Statistics. 2012. Retrieved 2012-12-13.
- ↑ "Vacatures". Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ↑ "Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland". Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ↑ "FAQ". Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ↑ "Agreement on labor conditions Civil servants Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland". Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland. Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ↑ "Mr. Isabella will be Kingdom Representative for the public entities Bonaire, St. Eustatius and Saba". Rijksdienst Caribisch Nederland. Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ↑ "Schurende rechtsordes: Over juridische implicaties van de UPG-status voor de eilandgebieden van de Nederlandse Antillen en Aruba (Rijksuniversiteit Groningen)" (PDF) (in Dutch). Eerstekamer.nl. 19 June 2008.
- ↑ "Economische gevolgen van de status van ultraperifeer gebied voor de Nederlandse Antillen en Aruba / SEOR" (PDF) (in Dutch). Eerstekamer.nl. 19 June 2008.
- ↑ "Tweede Kamer, vergaderjaar 2008–2009, 31700 IV, nr.3: Brief van de staatssecretaris van Binnenlandse Zaken en Koninkrijksrelaties met het kabinetsstandpunt over de rapporten over de UPG status voor de eilandgebieden van de Nederlandse Antillen en Aruba" (PDF) (in Dutch). Eerstekamer.nl. 21 October 2008.
- ↑ "Kamerstuk 31954 nr.7: Regels met betrekking tot de openbare lichamen Bonaire, Sint Eustatius en Saba (Wet openbare lichamen Bonaire, Sint Eustatius en Saba)" (in Dutch). Overheid.nl. 14 October 2009.
- ↑ "The Dutch Caribbean". Dutch Caribbean Legal Portal.
- ↑ "ISO 3166-1 decoding table". International Organization for Standardization. Retrieved 2010-12-16. (subscription required (help)).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Caribbean Netherlands. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Caribbean Netherlands. |
- Official website of the National Office for the Caribbean Netherlands
- Official website of the government of Bonaire
- Official website of the government of Saba
- Official website of the government of St. Eustatius