Bare mass
In quantum field theory, specifically the theory of renormalization, the bare mass of an elementary particle is the limit of its mass as the scale of distance approaches zero or, equivalently, as the energy of a particle collision approaches infinity. It differs from the invariant mass as usually understood because the latter includes the 'clothing' of the particle by pairs of virtual particles that are temporarily created by the force-fields around the particle. In some versions of field theory, the bare mass of some particles may be plus or minus infinity. In the theory of the electroweak interaction using the Higgs boson, all particles have a bare mass of zero.
This allows us to write 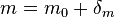 , where m denotes the experimentally observable mass of the particle,
, where m denotes the experimentally observable mass of the particle, 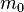 its bare mass, and
its bare mass, and 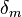 the increase in mass owing to the interaction of the particle with the medium or field.
the increase in mass owing to the interaction of the particle with the medium or field.