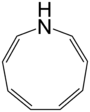
Azonine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1H-azonine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 293-57-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 26666607 |
| PubChem | 13287582 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H9N | |
| Molar mass | 119.17 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Azonine is an unsaturated heterocycle of nine atoms, with a nitrogen replacing a carbon at one position.[1] A variety of derivatives have been synthesised.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Somers, K. R. F.; Kryachko, E. S.; Ceulemans, A. (2004). "Azonine, a "Nearly" Forgotten Aromatic Molecule". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 108 (18): 4059–4068. doi:10.1021/jp037046+. ISSN 1089-5639.
- ↑ Chiang, Chian C.; Paul, Iain C.; Anastassiou, A. G.; Eachus, S. W. (1974). "Molecular structure of an N-substituted azonine. Demonstration of polyenic character in a member of this class of compounds". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 96 (5): 1636–1638. doi:10.1021/ja00812a082. ISSN 0002-7863.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.