Eastern woolly lemur
| Eastern woolly lemur | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Strepsirrhini |
| Family: | Indriidae |
| Genus: | Avahi |
| Species: | A. laniger |
| Binomial name | |
| Avahi laniger Gmelin, 1788[3] | |
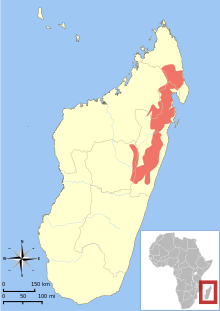 | |
| Distribution of A. laniger[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The eastern woolly lemur (Avahi laniger), also known as the eastern avahi or Gmelin's woolly lemur, is a species of woolly lemur native to eastern Madagascar, where it lives in humid forests. This nocturnal[4] animal weighs 1.0–1.3 kg and reaches a length of 27–29 cm with a tail of 33–37 cm. Its diet consists mainly of leaves and buds.
Eastern woolly lemurs live in monogamous pairs together with their offspring.
Other lemur species that live in the same rainforests as eastern woolly lemur are the diademed sifaka (Propithecus diadema) and the red-bellied lemur (Eulemur rubriventer). In southeastern rainforests, sympatric lemur species of A. meridionalis are the brown mouse lemur (Microcebus rufus), the greater dwarf lemur (Cheirogaleus major), the fat-tailed dwarf lemur (Cheirogaleus medius) and the collared brown lemur (Eulemur collaris) in Sainte Luce Forest,[5] and the southern lesser bamboo lemur (Hapalemur meridionalis) in Mandena Forest.[6]

References
| Wikispecies has information related to: Eastern woolly lemur |
- 1 2 Andriaholinirina, N.; et al. (2014). "Avahi laniger". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.1. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ↑ "Checklist of CITES Species". CITES. UNEP-WCMC. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ Groves, C.P. (2005). Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M., eds. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 119. OCLC 62265494. ISBN 0-801-88221-4.
- ↑ The Primata
- ↑ Bollen A.; Donati G. (2006). "Conservation status of the littoral forest of south-eastern Madagascar: a review". Oryx. 40: 57–66. doi:10.1017/S0030605306000111.
- ↑ Fausser, J.; Donati, G.; Ramanamanjato, J. & Rumpler, Y. (2002). "Phylogenetic relationships between Hapalemur species and subspecies based on mitochondrial DNA sequences". BMC Evol Biol. 2: 1–9. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-2-4. PMC 101410
 . PMID 11914128.
. PMID 11914128.
