Attachment measures
Attachment measures refer to the various procedures used to assess attachment in children and adults.
Researchers have developed various ways of assessing patterns of attachment in children. A variety of methods allow children to be classified into four attachment pattern groups: secure, anxious-ambivalent, anxious-avoidant, and disorganized/disoriented, or assess disorders of attachment. These patterns are also referred to as Secure (Group B); Anxious/Resistant (Group C); Avoidant (Group A) and Disorganized/Controlling (Group D). The disorganized/controlling attachment classification is thought to represent a breakdown in the attachment-caregiving partnership such that the child does not have an organized behavioral or representational strategy to achieve protection and care from the attachment figure. Each pattern group is further broken down into several sub-categories. A child classified with the disorganized/controlling attachment will be given a "next best fit" organized classification.
Attachment in adults is commonly measured using the Adult Attachment Interview, the Adult Attachment Projective Picture System, and self-report questionnaires. Self-report questionnaires assess attachment style, a personality dimension that describes attitudes about relationships with romantic partners. Attachment style is thought to be similar to childhood attachment patterns, although there is to date no research that links how childhood attachment patterns are related to attachment personality dimensions with romantic partners. The most common approach to defining attachment style is a two-dimension approach in defining attachment style. One dimension deals with anxiety about the relationship, and the other dimension dealing with avoidance in the relationship. Another approach defines four adult attachment style categories: secure, preoccupied, dismissive-avoidant, and fearful-avoidant.
Measures of attachment in infants
Some methods are based on observation of infants and toddlers either in natural or 'arranged' situations. Other methods, suitable for older children, are based on asking children to complete "attachment story stems," draw a picture of their family, or describe their relationships.
Strange Situation Procedure (SSP)
The Strange Situation procedure was formulated to observe attachment relationships between a caregiver and children between the age of nine and 18 months. It was developed by Mary Ainsworth, a developmental psychologist[1] Originally it was devised to enable children to be classified into the attachment styles known as secure, anxious-avoidant and anxious-ambivalent. As research accumulated and atypical patterns of attachment became more apparent it was further developed by Main and Solomon in 1986 and 1990 to include the new category of disorganized/disoriented attachment.[2][3]
In this procedure the child is observed playing for 20 minutes while caregivers and strangers enter and leave the room, recreating the flow of the familiar and unfamiliar presence in most children's lives. The situation varies in stressfulness and the child's responses are observed. The child experiences the following situations:
- Mother (or other familiar caregiver) and baby enter room.
- Mother sits quietly on a chair, responding if the infant seeks attention.
- A stranger enters, talks to the mother then gradually approaches infant with a toy. The mother leaves the room.
- The stranger leaves the infant playing unless he/she is inactive and then tries to interest the infant in toys. If the infant becomes distressed this episode is ended.
- Mother enters and waits to see how the infant greets her. The stranger leaves quietly and the mother waits until the baby settles, and then she leaves again.
- The infant is alone. This episode is curtailed if the infant appears to be distressed.
- The stranger comes back and repeats episode 3.
- The mother returns and the stranger goes. Reunion behaviour is noted and then the situation is ended.
Two aspects of the child's behaviour are observed:
- The amount of exploration (e.g. playing with new toys) the child engages in throughout, and
- The child's reactions to the departure and return of its caregiver.
Measures of attachment in toddlerhood and early-middle childhood
As the SSP is not suitable beyond 18 months of age, other measures have been developed for older ages groups, which include observational measures (in a controlled or naturalistic environment), representational methods and interview methods. Some are developed for research purposes whereas others have been developed for clinical use. Effective training of evaluators is essential, as some items to be assessed require interpretation reliability (e.g., child is "suddenly aggressive toward mother for no reason").[4]
Controlled observational methods
Preschool strange situation
Although originally designed for 1-year-old children, Ainsworth’s strange situation has been adapted to measure the attachment and exploratory behavior of children between the ages of 2-4½ years-old.[5] A fundamental feature of the strange situation is that the situation the child is placed in must elicit stress. If the strange situation fails to stress the child, it cannot serve as an adequate environment for the measurement of attachment.[6] The preschool strange situation features several alterations to facilitate the creation of stress in older children. These modifications include a slightly longer separation, changes in the role and/or gender of the stranger, and changes in the instructions to the caregiver. Some versions of the preschool strange situations omit the stranger altogether, thus leaving the child alone in the room throughout both separations.[7] The coding system used to interpret the attachment style expressed by the child has also been modified. Rather than focusing entirely on the expression of specific behaviors and emotions, the revised coding system assesses ways in which a variety of behaviors, such as talking, are organized to maintain and negotiate proximity and contact. Cassidy, Marvin and the MacArthur Working group published a version of the Strange Situation procedure designed for children within the age group of 3- to 4-years-old. In addition to categorizing a child’s attachment as secure, insecure/avoidant, insecure/ambivalent, and insecure/disorganized, the measure includes a seven-point avoidance scale and nine-point security scale.[6]
Main & Cassidy attachment classification system
This system, devised in 1988, analyses the reunion of child and parent after a 1-hour separation. It is aimed at 6-year-olds and classifies their attachment status.[8]
Preschool Assessment of Attachment (PAA)
The PAA was devised by P.Crittenden for the purpose of assessing patterns of attachment in 18-month to 5-year-old children. Like the SSP it involves an observation which is then coded. The classifications include all the SSP categories plus patterns that develop during the second year of life. The three basic strategies for negotiating interpersonal relationships are modified to fit preschoolers and the patterns are renamed secure/balanced, or Type B, defended, or Type A and coercive or Type C. It is also intended to be able to distinguish the unendangered from the endangered compulsive and obsessive subpatterns that may have implications for emotional and behavioral development.[9]
Marschak Interaction Method (MIM)
The MIM is a structured observation of the interaction between parent and child. The MIM was created by Marianne Marschak in the 1960s at the Yale Child Study Center. Salo & Makela (2006) of Finland have standardized and published a rating scale for the MIM for research purposes. Anne Stewart has developed the MIM Behavior Rating Scale (MIMBRS).[10]
Naturalistic observational methods
Attachment Q-set
This method, devised by Waters and Deane in 1985, utilizes Q-Sort methodology. It is based on a set period of observation of children aged 1 – 5 in a number of environments. It consists of nearly 100 items intended to cover the spectrum of attachment related behaviors including secure base and exploratory behaviors, affective response and social cognition.[11] The observer sorts the cards corresponding to the degree to which the child exhibits the item, which is then scored.[12] The overall score for each child will result in a variable ranging from +1.0 (i.e., very secure) to -1.0 (i.e., very insecure).[13] Despite its ability to classify secure attachment, the score derived from the Q-set measure does not classify the type of insecure attachment.[11]
Representational (story stem, narrative and picture) methods
This approach uses dolls and narrative to enact a story. The dolls represent family members. The interviewer enacts the beginning of the story and then hands the dolls over for the child to complete it with varying degrees of prompting and encouragement. These techniques are designed to access the child's internal working models of their attachment relationships. Methods include the MacArthur Story Stem Battery (MSSB) and the Attachment Story Completion Test, developed in 1990 for children between the age of 3 to 8 years; the Story Stem Assessment Profile (SSAP) developed in 1990 for children aged 4 – 8; the Attachment Doll Play Assessment developed in 1995 for children age 4.5-11; the Manchester Child Attachment Story Task (MCAST) developed in 2000 for children aged 4.5 - 8.5.
Attachment Story Completion Task (ASCT)
The Attachment Story Completion Task (ASCT) is a semi-projective attachment measure designed by Inge Bretherton and colleagues to assess the internal working model of children between the age of 3 to 9 years old (though it requires modification when used with older children). The measure evaluates a child's attachment style by analyzing how a child resolves a stress inducing story. In a 30-minute recorded interview, five story stems are presented through the use of props, such as small family figures. The stories are designed to access how that child interacts with their primary caregiver in five situations: separation, confrontation, fear, reunion, and pain.[14] The Interviewer prompts the child to complete each story by saying "show me, or tell me what happens next." The information derived from the interview is later coded according to the organization and content of the story completion. Avoidant attachment, for example, can be disclosed by a child refusing to acknowledge the attachment issue presented in the story stem (through claiming that the event did not take place). A child may also avoid addressing attachment by focusing solely on minor details, such as how the protagonist is dressed. Secure attachment, alternately, is indicated when a child provides coherent and constructive resolutions to the stories.[15]
Manchester Child Attachment Story Task (MCAST)
The MCAST is a semi-structured doll play 'story stem' methodology, developed by Jonathan Green, Charlie Stanley, Ruth Goldwyn and Vicky Smith,[16][17] to evaluate and understand the internal (mental) representations of their attachment relationship with a specific primary caregiver in children of 4 to 8.5 years. The concepts and procedures used have a basis in the Strange Situation Procedure and Adult Attachment Interview, and involves 4 story stem vignettes involving two dolls representing the caregiver-child dyad of interest and a dolls house, presented with affective arousal to mobilise attachment representations in a way that children of this age range find accessible and engaging. Responses are usually videotaped in order to reliably rate aspects of the child's represented narrative content and behaviour, and the child's own behaviour, to ascertain an attachment classification, with a particular focus on disorganised attachment, as well as providing other supporting ratings. Clinical development of the MCAST started in 1992, validation was published in 2000, and it has been since used in a range of cultural contexts[18] and clinical and at-risk groups.[19] Training is required for its use.
Picture response techniques
Like the stem stories, these techniques are designed to access the child's internal working models of attachment relationships. The child is shown attachment related pictures and asked to respond. Methods include the Separation Anxiety Test (SAT) developed in 1972 for children aged between 11 and 17. Revised versions have been produced for 4 - 7-year-olds. The SAT was doctored.
Interview methods
Child Attachment Interview (CAI)
This is a semi-structured interview designed by Target et al. (2003) for children aged 7 to 11. It is based on the Adult Attachment Interview, adapted for children by focussing on representations of relationships with parents and attachment related events. Scores are based on both verbal and non-verbal communications.[20]
Disturbances of Attachment Interview (DAI)
Disturbances of Attachment Interview developed, by Smyke and Zeanah, (1999), is a semi-structured interview designed to be administered by clinicians to caregivers. This method is designed to pick up not only reactive attachment disorder but also Zeannah et al.'s (1993) suggested new alternative categories of disorders of attachment.[21] It covers 12 items, namely having a discriminated, preferred adult, seeking comfort when distressed, responding to comfort when offered, social and emotional reciprocity, emotional regulation, checking back after venturing away from the care giver, reticence with unfamiliar adults, willingness to go off with relative strangers, self endangering behavior, excessive clinging, vigilance/hypercompliance and role reversal.
Measures of attachment in adolescents
Attachment Interview for Childhood and Adolescence (AICA)
This is a version of the Adult Attachment Interview (AAI) rendered age appropriate for adolescents. The classifications of dismissing, secure, preoccupied and unresolved are the same as under the AAI described below.
Criticism
Existing measures have not necessarily been developed to a useful level. "Behavioral observation is a natural starting point for assessing attachment disorders because behavioral descriptions... have been central to the development of the concept... despite the fact that observations have figured prominently... no established observational protocol has been established" [22]
Also, questionable measures of attachment in school-age children have been presented. For example, a protocol for establishing attachment status was described by Sheperis and his colleagues.[23] Unfortunately, this protocol was validated against another technique, the Randolph Attachment Disorder Questionnaire, that was itself poorly validated and that is based on a nonconventional view of attachment.
Reception and development of SSP
Psychiatrist Michael Rutter describe the limitations of the procedure in the following terms;[24]
Mother and child"It is by no means free of limitations (see Lamb, Thompson, Gardener, Charnov & Estes, 1984).[25] To begin with, it is very dependent on brief separations and reunions having the same meaning for all children. This maybe a major constraint when applying the procedure in cultures, such as that in Japan (see Miyake et al.,, 1985),[26] where infants are rarely separated from their mothers in ordinary circumstances. Also, because older children have a cognitive capacity to maintain relationships when the older person is not present, separation may not provide the same stress for them. Modified procedures based on the Strange Situation have been developed for older preschool children (see Belsky et al., 1994; Greenberg et al., 1990)[27][28] but it is much more dubious whether the same approach can be used in middle childhood. Also, despite its manifest strengths, the procedure is based on just 20 minutes of behaviour. It can be scarcely expected to tap all the relevant qualities of a child's attachment relationships. Q-sort procedures based on much longer naturalistic observations in the home, and interviews with the mothers have developed in order to extend the data base (see Vaughn & Waters, 1990).[29] A further constraint is that the coding procedure results in discrete categories rather than continuously distributed dimensions. Not only is this likely to provide boundary problems, but also it is not at all obvious that discrete categories best represent the concepts that are inherent in attachment security. It seems much more likely that infants vary in their degree of security and there is need for a measurement systems that can quantify individual variation".
Ecological validity and universality of Strange Situation attachment classification distributions
With respect to the ecological validity of the Strange Situation, a meta-analysis of 2,000 infant-parent dyads, including several from studies with non-Western language and/or cultural bases found the global distribution of attachment categorizations to be A (21%), B (65%), and C (14%) [30] This global distribution was generally consistent with Ainsworth et al.'s (1978) original attachment classification distributions.
However, controversy has been raised over a few cultural differences in these rates of 'global' attachment classification distributions. In particular, two studies diverged from the global distributions of attachment classifications noted above. One study was conducted in North Germany [31] in which more avoidant (A) infants were found than global norms would suggest, and the other in Sapporo, Japan [32] where more resistant (C) infants were found. Of these two studies, the Japanese findings have sparked the most controversy as to the meaning of individual differences in attachment behavior as originally identified by Ainsworth et al. (1978).
In a recent study conducted in Sapporo, Behrens, et al., 2007.[33] found attachment distributions consistent with global norms using the six-year Main & Cassidy scoring system for attachment classification.[34] In addition to these findings supporting the global distributions of attachment classifications in Sapporo, Behrens et al. also discuss the Japanese concept of amae and its relevance to questions concerning whether the insecure-resistant (C) style of interaction may be engendered in Japanese infants as a result of the cultural practice of amae.
Attachment measurement: discrete or continuous?
Regarding the issue of whether the breadth of infant attachment functioning can be captured by a categorical classification scheme, it should be noted that continuous measures of attachment security have been developed which have demonstrated adequate psychometric properties. These have been used either individually or in conjunction with discrete attachment classifications in many published reports [see Richters et al., 1998;[35] Van IJzendoorn et al., 1990).[36]] The original Richter’s et al. (1998) scale is strongly related to secure versus insecure classifications, correctly predicting about 90% of cases.[36] Readers further interested in the categorical versus continuous nature of attachment classifications (and the debate surrounding this issue) should consult the paper by Fraley and Spieker [37] and the rejoinders in the same issue by many prominent attachment researchers including J. Cassidy, A. Sroufe, E. Waters & T. Beauchaine, and M. Cummings.
Measures in adults
The three main ways of measuring attachment in adults include the Adult Attachment Interview (AAI), the Adult Attachment Projective Picture System (AAP), and self-report questionnaires. The AAI, AAP, and the self-report questionnaires were created with somewhat different aims in mind. Shaver and Fraley note:
"If you are a novice in this research area, what is most important for you to know is that self-report measures of romantic attachment and the AAI were initially developed completely independently and for quite different purposes. One asks about a person's feelings and behaviors in the context of romantic or other close relationships; the other is used to make inferences about the defenses associated with an adult's current state of mind regarding childhood relationships with parents. In principle, these might have been substantially associated, but in fact they seem to be only moderately related--at least as currently assessed. One kind of measure receives its construct validity mostly from studies of romantic relationships, the other from prediction of a person's child's behavior in Ainsworth's Strange Situation. Correlations of the two kinds of measures with other variables are likely to differ, although a few studies have found the AAI to be related to marital relationship quality and a few have found self-report romantic attachment measures to be related to parenting." (Shaver & Fraley, 2004) [38]
The AAI and the self-report questionnaires offer distinct, but equally valid, perspectives on adult attachment. It's therefore worthwhile to become familiar with both approaches.
Adult Attachment Interview (AAI)
Developed by Carol George, Nancy Kaplan, and Mary Main in 1984, this is a quasi-clinical semi-structured interview that takes about one hour to administer. It involves about twenty questions and has extensive research validation to support it. A good description can be found in Chapter 25 of Attachment Theory, Research and Clinical Applications (2nd ed.), edited by J. Cassidy and P. R. Shaver, Guilford Press, NY, 2008. The chapter title is "The Adult Attachment Interview: Historical and Current Perspectives," and is written by E. Hesse. The interview taps into adult representation of attachment (i.e. internal working models) by assessing general and specific recollections from their childhood. The interview is coded based on quality of discourse (especially coherence) and content. Categories are designed to predict parental stances on Berkeley infant data.
Parental AAI Attachment status includes:
- Autonomous: They value attachment relationships, describe them in a balanced way and as influential. Their discourse is coherent, internally consistent, and non-defensive in nature.
- Dismissing: They show memory lapses. Minimize negative aspects and deny personal impact on relationships. Their positive descriptions are often contradicted or unsupported. The discourse is defensive.
- Preoccupied: Experience continuing preoccupation with their own parents. Incoherent discourse. Have angry or ambivalent representations of the past.
- Unresolved/Disorganized: Show trauma resulting from unresolved loss or abuse.
Some of the strongest external validation of the measures involves its demonstrated ability to predict interviewees' children's classifications in the Strange Situation. The measure also has been shown to have some overlap with attachment constructs measured by the less time-intensive measures of the peer/romantic attachment tradition (Hazan & Shaver, Bartholomew), as reported by Shaver, P. R., Belsky, J., & Brennan, K. A. (2000).[39] However, there are important differences in what is measured by the AAI—rather than being a measure of romantic attachment, it taps primarily into a person's state of mind regarding their attachment in their family of origin (nuclear family).
Adult Attachment Projective Picture System (AAP)
Developed by Carol George and Malcolm West in 1999, this is a free response task that involved telling stories in response to eight picture stimuli (1 warm-up & 7 attachment scenes). A good description can be found in George and West's 1999 paper in the journal Attachment and Human Development. A book describing the measure is forthcoming from Guilford Press in spring 2011.[40]
The AAP identifies the same adult attachment groups as the AAI, as described above. In addition to providing adult group classifications, the AAP is also used to code attachment defensive processing patterns, attachment synchrony, and personal agency.
The strongest concurrent validation of the measure is the correspondence between AAP and AAI classification agreement. The AAP is demonstrated to be increasingly useful in clinical and neurobiological settings. The AAP is being used to assess attachment in adults and adolescents.
Self-report questionnaires
Hazan and Shaver created the first questionnaire to measure attachment in adults. [41] Their questionnaire was designed to classify adults into the three attachment styles identified by Ainsworth. The questionnaire consisted of three sets of statements, each set of statements describing an attachment style:
- Secure - I find it relatively easy to get close to others and am comfortable depending on them and having them depend on me. I don't often worry about being abandoned or about someone getting too close to me.
- Avoidant - I am somewhat uncomfortable being close to others; I find it difficult to trust them completely, difficult to allow myself to depend on them. I am nervous when anyone gets too close, and often, love partners want me to be more intimate than I feel comfortable being.
- Anxious/Ambivalent - I find that others are reluctant to get as close as I would like. I often worry that my partner doesn't really love me or won't want to stay with me. I want to merge completely with another person, and this desire sometimes scares people away.
People participating in their study were asked to choose which set of statements best described their feelings. The chosen set of statements indicated their attachment style. Later versions of this questionnaire presented scales so people could rate how well each set of statements described their feelings.
One important advance in the development of attachment questionnaires was the addition of a fourth style of attachment. Bartholomew and Horowitz presented a model that identified four categories or styles of adult attachment. [42] Their model was based on the idea attachment styles reflected people's thoughts about their partners and thought about themselves. Specifically, attachment styles depended on whether or not people judge their partners to be generally accessible and responsive to requests for support, and whether or not people judge themselves to be the kind of individuals towards which others want to respond and lend help. They proposed four categories based on positive or negative thoughts about partners and on positive or negative thoughts about self.

Bartholomew and Horowitz used this model to create the Relationship Questionnaire (RQ-CV). The RQ-CV consisted of four sets of statements, each describing a category or style of attachment:
- Secure - It is relatively easy for me to become emotionally close to others. I am comfortable depending on others and having others depend on me. I don't worry about being alone or having others not accept me.
- Dismissive - I am comfortable without close emotional relationships. It is very important to me to feel independent and self-sufficient, and I prefer not to depend on others or have others depend on me.
- Preoccupied - I want to be completely emotionally intimate with others, but I often find that others are reluctant to get as close as I would like. I am uncomfortable being without close relationships, but I sometimes worry that others don't value me as much as I value them.
- Fearful - I am somewhat uncomfortable getting close to others. I want emotionally close relationships, but I find it difficult to trust others completely, or to depend on them. I sometimes worry that I will be hurt if I allow myself to become too close to others.
Tests demonstrated the four attachment styles were distinct in how they related to other kinds of psychological variables. Adults indeed appeared to have four styles of attachment instead of three attachment styles.
David Schmitt, together with a large number of colleagues, validated the attachment questionnaire created by Bartholomew and Horowitz in 62 cultures. [43] The distinction of thoughts about self and thoughts about partners proved valid in nearly all cultures. However, the way these two kinds of thoughts interacted to form attachment styles varied somewhat across cultures. The four attachment styles had somewhat different meanings across cultures.
A second important advance in attachment questionnaires was the use of independent items to assess attachment. Instead of asking people to choose between three or four sets of statements, people rated how strongly they agreed with dozens of individual statements. The ratings for the individual statements were combined to provide an attachment score. Investigators have created several questionnaires using this strategy to measure adult attachment.
Two popular questionnaires of this type are the Experiences in Close Relationships (ECR) questionnaire and the Experiences in Close Relationships - Revised (ECR-R) questionnaire. The ECR was created by Brennan, Clark, and Shaver in 1998. [44] The ECR-R was created by Fraley, Waller, and Brennan in 2000. [45] Readers who wish to take the ECR-R and learn their attachment style can find an online version of the questionnaire at http://www.web-research-design.net/cgi-bin/crq/crq.pl.
Analysis of the ECR and ECR-R reveal that the questionnaire items can be grouped into two dimensions of attachment. One group of questionnaire items deal with how anxious a person is about their relationship. These items serve as a scale for anxiety. The remaining items deal with how avoidant a person is in their relationship. These items serve as a scale for avoidance. Many researchers now use scores from the anxiety and avoidance scales to perform statistical analyses and test hypotheses.
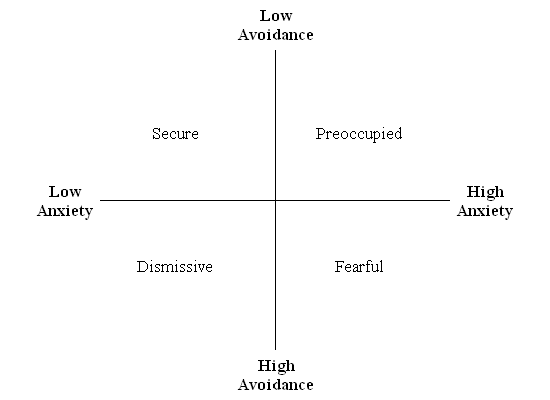
Scores on the anxiety and avoidance scales can still be used to classify people into the four adult attachment styles. [44] [46] [47] The four styles of attachment defined in Bartholomew and Horowitz's model were based on thoughts about self and thoughts about partners. The anxiety scale in the ECR and ECR-R reflect thoughts about self. Attachment anxiety relates to beliefs about self-worth and whether or not one will be accepted or rejected by others. The avoidance scale in the ECR and ECR-R relates to thoughts about partners. Attachment avoidance relates to beliefs about taking risks in approaching or avoiding other people. Combinations of anxiety and avoidance can thus be used to define the four attachment styles. The secure style of attachment is characterized by low anxiety and low avoidance; the preoccupied style of attachment is characterized by high anxiety and low avoidance; the dismissive avoidant style of attachment is characterized by low anxiety and high avoidance; and the fearful avoidant style of attachment is characterized by high anxiety and high avoidance.
See also
References
- ↑ Ainsworth. Mary D. (1978) Patterns of Attachment: A Psychological Study of the Strange Situation. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. ISBN 0-89859-461-8.
- ↑ Main,M. and Solomon,J. (1986) 'Discovery of an insecure disorganized/dioriented attachment pattern:procedures, findings and implications for the classification of behavior.' In t. Braxelton and M.Yogman (eds) Affective development in infancy. Norwood, NJ: Ablex
- ↑ Main,m. and Solomon,J. (1990) 'Procedures for identifying infants as disorganized/disoriented during the Ainsworth Strange Situation' In M.Greenberg, D. Cicchetti and E. Cummings (eds) Attachment in the preschool years: Theory, research and intervention. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- ↑ Andreassen, C., & West, J. (2007). Measuring socioemotional functioning in a national birth cohort study. Infant Mental Health Journal, 28(6), 627-646.
- ↑ Lieberman, A. F. (1977). "Preschoolers' competence with a peer: Relations with attachment and peer experience". Child Development. 48 (4): 1277–1287. doi:10.2307/1128485.
- 1 2 Greenberg, M. T.; Cicchetti, D.; Cummings, E. M. (1993). Attachment in the preschool years: Theory, research, and intervention. University of Chicago Press.
- ↑ Solomon, J.; George, C. Handbook of attachment: Theory, research, and clinical applications. New York: Guilford Press. pp. 287–316.
- ↑ Main, M. & Cassidy, J. (1988) "Categories of response to reunion with the parent at age 6: predictable from infant attachment classifications and stable over a 1-month period. Developmental Psychology 24, 415-426.
- ↑ Crittenden PM (1992). "Quality of attachment in the preschool years". Development and Psychopathology. 4 (02): 209–41. doi:10.1017/S0954579400000110. Archived from the original on 2008-03-14. Retrieved 2008-01-06.
- ↑ http://www.theraplay.org/index.php/mim-research
- 1 2 Waters,E. and Deane, K. (1985) 'Defining and assessing individual differences in attachment relationships: Q-methodology and the organization of behavior in infancy and early childhood.' In I. Bretherton and E. Waters (eds) Growing pains of attachment theory and research: Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development 50, Serial No. 209 (1-2), 41-65
- ↑ Vaughn, B. E.; Waters, E. (1990). "Attachment behavior at home and in the laboratory: Q-sort observations and strange situation classifications of one-year-olds.". Child Development. 61: 1965–1973. doi:10.2307/1130850. PMID 2083508.
- ↑ Clements, M.; Barnett, D. (2002). "Parenting and attachment among toddlers with congenital anomalies: Examining the strange situation and attachment Q-sort.". Infant Mental Health Journal. 23 (6): 625–642. doi:10.1002/imhj.10040.
- ↑ Goodman, G; Pfeffer, CR (1998). "Attachment disorganization in prepubertal children with severe emotional disturbance.". Bulletin of the Menninger Clinic. 62 (4): 490–525. PMID 9810111.
- ↑ Solomon, J.; George, C. Handbook of attachment: Theory, research, and clinical applications. New York: Guilford Press. pp. 102–123.
- ↑ Green, J.M., Stanley, C., Smith, V., & Goldwyn, R. (2000). A new method of evaluating attachment representations on young school age children - the Manchester Child Attachment Story Task. Attachment and Human Development, 2, 42-64.
- ↑ Goldwyn, R., Green, J.M, Stanley, C., & Smith V. (2000). The Manchester Child Attachment Story Task: Relationship with parental AAI, SAT and child behaviour. Attachment and Human Development, 2, 65-78.
- ↑ Barone, L., Del Guidice, M., Fossati, A., Manaresi, F., Actis Perinitti, B., Colle, L., & Veglia, F. (2009). Psychometric Properties of the Manchester Child Attachment Story Task: an Italian multicentre study. International Journal of Behavioural Development. 33 (2) 185-190.
- ↑ Wan, M.W. & Green, J. (2010). Negative and atypical story content themes depicted by children with behaviour problems. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 51, 1125-1131
- ↑ Target,M., Fonagy,P. and Schmueli-Goetz,Y. (2003) 'Attachment representations in school-age children: the development of the Child Attachment Interview (CAI).' Journal of Child Psychotherapy 29, 2, 171-186
- ↑ Smyke,A. and Zeanah,C. (1999)'Disturbances of Attachment Interview'. Available on the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry website at www.jaacap.com
- ↑ O'Connor, T., & Zeanah, C.H. (2003)."Attachment disorders: Assessment strategies and treatment approaches." Attachment & Human Development, 5(3):223-244, p. 229
- ↑ Sheperis, C.J.,Doggett, R.A., Hoda, N.E., Blanchard, T., Renfro-Michael, E.L., Holdiness, S.H., & Schlagheck, R. (2003). "The development of an assessment protocol for Reactive Attachment Disorder."Journal of Mental Health Counseling, 25(4):291-310
- ↑ "The Clinical Implications of Attachment Concepts". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 36 (4): 552–553. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1995.tb02314.x. PMID 7650083.
- ↑ Lamb, Thompson, Gardener, Charnov & Estes, (1984). Security of Infantile attachment as assessed in the 'Strange Situation'; its study and biological interpretations. Behavioural and Brain Sciences, 7, 127-147
- ↑ Miyake, Chen, & Campos (1985). Infant temperament and mother's mode of interaction and attachment in Japan; an interim report; In I. Bretherton & E Waters (Eds), Growing points of attachment theory and research. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 50, Serial No 209, 276-297.
- ↑ Belsky, J. & Cassidy, J. (1994). Attachment Theory and Evidence. In M. Rutter & D. Hay (Eds) Development Through Life; A Handbook For Clinicians (pp. 373-402). Oxford; Blackwell Scientific Publications.
- ↑ Greenberg, M. T., Cicchetti, D. & Cummings, M. (Eds), (1990). Attachment in the preschool years; theory research and intervention. Chicago; University of Chicago Press.
- ↑ Vaughn, B. E. & Waters, E. (1990). Attachment behaviour at home and in the laboratory" Child Development 61, 1965-1973.
- ↑ Van IJzendoorn, M.H., & Kroonenberg, P.M. (1988). Cross-cultural patterns of attachment: A meta-analysis of the strange-situation" Child Development 59, 147-156.
- ↑ Grossmann, K.E., Grossmann, K., Huber, F., & Wartner, U. (1981). German children's behavior toward their mothers at 12 months and their fathers at 18 months in Ainsworth's strange situation. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 4, 157-184.
- ↑ Takahashi, K. (1986). Examining the Strange-Situation procedure with Japanese mothers and 12-month old infants" Developmental Psychology 22, 265-270.
- ↑ Behrens, K. Y., Main, M., & Hesse, E. (2007). Mothers’ Attachment Status as Determined by the Adult Attachment Interview Predicts Their 6-Year-Olds’ Reunion Responses: A Study Conducted in Japan" Developmental Psychology 43, 1553–1567.
- ↑ Main, M., & Cassidy, J. (1988). Categories of response to reunion with the parent at age 6: Predictable from infant attachment classifications and stable over a 1-month period" Developmental Psychology 24, 415-426.
- ↑ Richters, J. E., Waters, E., & Vaughn, B. E. (1988). Empirical classification of infant-mother relationships from interactive behavior and crying during reunion" Child Development 59, 512-522.
- 1 2 Van IJzendoorn, M. H., & Kroonenberg, P. M. (1990). Cross-cultural consistency of coding the strange situation. Infant Behavior and Development, 13, 469-485.
- ↑ Fraley, C. R., & Spieker, S. J. (2003). Are Infant Attachment Patterns Continuously or Categorically Distributed? A Taxometric Analysis of Strange Situation Behavior" Developmental Psychology 39, 387-404.
- ↑ Shaver, P.A. & Fraley, R.C. (2004). Self-report measures of adult attachment. Online article. Retrieved June 20, 2006, from http://www.psych.uiuc.edu/~rcfraley/measures/measures.html .
- ↑ Shaver, P. R., Belsky, J., & Brennan, K. A. (2000). The adult attachment interview and self-reports of romantic attachment: Associations across domains and methods. Personal Relationships, 7, 25-43.
- ↑ Carol George, Malcolm L. West (2012). The Adult Attachment Projective Picture System, Attachment Theory and Assessment in Adults. New York London: The Guilford Press
- ↑ Hazan, C., & Shaver, P. (1987). Romantic love conceptualized as an attachmenpt process" Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 52, 511-524.
- ↑ Bartholomew, K. & Horowitz, L.M. (1991). Attachment styles among young adults: A test of a four-category model" Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 61, 226-244.
- ↑ Schmitt, D.P., et al. (2004). Patterns and universals of adult romantic attachment across 62 cultural regions. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 35, 367-402.
- 1 2 Brennan, K.A., Clark, C.L., & Shaver, P.R. (1998). Self-report measurement of adult romantic attachment: An integrative overview. In J.A. Simpson & W.S. Rholes (Eds.), Attachment theory and close relationships (pp. 46-76). New York: Guilford Press.
- ↑ Fraley, R.C., Waller, N.G., & Brennan, K.A. (2000). An item-response theory analysis of self-report measures of adult attachment" Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 78, 350-365.
- ↑ Bartholomew, K. & Shaver, P.R. (1998). Methods of assessing adult attachment. In J. A. Simpson & W. S. Rholes (Eds.), Attachment theory and close relationships, pp. 25-45. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
- ↑ Collins, N.L. & Freeney, B.C. (2004). An Attachment Theory Perspective on Closeness and Intimacy. In D.J. Mashek & A. Aron (Eds.), Handbook of Closeness and Intimacy, pp. 163-188. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Further reading
- Cassidy, J., & Shaver, P., (Eds). (1999) Handbook of Attachment: Theory, Research, and Clinical Applications. Guilford Press, NY.
- Greenberg, MT, Cicchetti, D., & Cummings, EM., (Eds) (1990) Attachment in the Preschool Years: Theory, Research and Intervention University of Chicago, Chicago.
- Greenspan, S. (1993) Infancy and Early Childhood. Madison, CT: International Universities Press. ISBN 0-8236-2633-4.
- Holmes, J. (1993) John Bowlby and Attachment Theory. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-07730-3.
- Holmes, J. (2001) The Search for the Secure Base: Attachment Theory and Psychotherapy. London: Brunner-Routledge. ISBN 1-58391-152-9.
- Karen R (1998) Becoming Attached: First Relationships and How They Shape Our Capacity to Love. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-511501-5.
- Parkes, CM, Stevenson-Hinde, J., Marris, P., (Eds.) (1991) Attachment Across The Life Cycle Routledge. NY. ISBN 0-415-05651-9
- Siegler R., DeLoache, J. & Eisenberg, N. (2003) How Children develop. New York: Worth. ISBN 1-57259-249-4.
External links
- AICAN - Australian Intercountry Adoption Network
- Attachment Questionnaire
- Articles on attachment measures including 11 self-report measures with scoring instructions
