Articular processes
| Articular processes | |
|---|---|
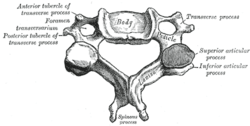 A cervical vertebra. (Superior and inferior processes labeled at right.) | |
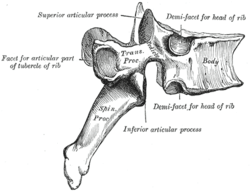 A thoracic vertebra. (Superior labeled at top; inferior labeled at bottom.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin |
Processus articularis inferior vertebrae, processus articularis superior vertebrae |
| TA |
A02.2.01.014 A02.2.01.016 |
| FMA | 11952 |
The articular processes or zygapophyses (Greek ζυγον = "yoke" (because it links two vertebrae) + απο = "away" + φυσις = "process") of a vertebra, are projections of the vertebra that serve the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the articular facet.[1]
Articular processes spring from the junctions of the pedicles and laminæ, and there are two right and left, and two superior and inferior. These stick out of an end of a vertebra to lock with a zygapophysis on the next vertebra, to make the backbone more stable.
- The superior processes or prezygapophysis project upward from a lower vertebra, and their articular surfaces are directed more or less backward (oblique coronal plane).
- The inferior processes or postzygapophysis project downward from a higher vertebra, and their articular surfaces are directed more or less forward and outward.
The articular surfaces are coated with hyaline cartilage.
In the cervical vertebral column, the articular processes collectively form the articular pillars. These are the bony surfaces palpated just lateral to the spinous processes.
Additional images
-

Cervical vertebra
-
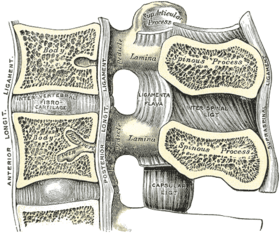
Median sagittal section of two lumbar vertebræ and their ligaments.
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th Ed, p.442 fig. 4.2
External links
- aplab - BioWeb at University of Wisconsin System
- Atlas image: back_bone28 at the University of Michigan Health System - "Lumbar Vertebral Column, Posterolateral View"
- Anatomy figure: 02:01-09 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Superior and lateral views of typical vertebrae."
- Photo of model at Waynesburg College skeleton2/inferiorarticularprocess
- Photo of model at Waynesburg College skeleton2/superiorarticularprocess