Amillennialism
| Christian eschatology |
|---|
| Eschatology views |
|
Contrasting beliefs |
|
Biblical texts
|
|
Key terms
|
| Christianity portal |
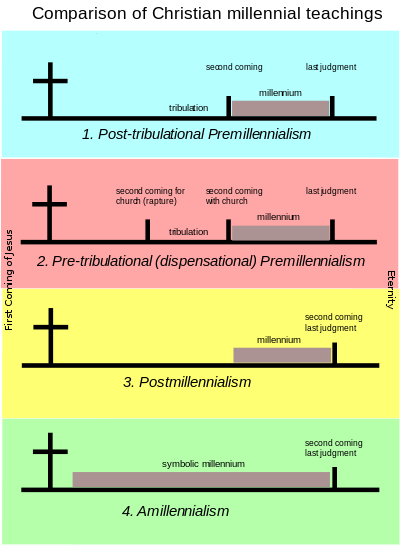
Amillennialism (Greek: a- "no" + millennialism), in Christian eschatology, involves the rejection of the belief that Jesus will have a literal, thousand-year-long, physical reign on the earth. This rejection contrasts with premillennial and some postmillennial interpretations of chapter 20 of the Book of Revelation.
The amillennial view regards the "thousand years" mentioned in Revelation 20 as a symbolic number, not as a literal description; amillennialists hold that the millennium has already begun and is identical with the current church age. Amillennialism holds that while Christ's reign during the millennium is spiritual in nature, at the end of the church age, Christ will return in final judgment and establish a permanent reign in the new heaven and new earth.
Many proponents dislike the name "amillennialism" because it emphasizes their differences with premillennialism rather than their beliefs about the millennium. "Amillennial" was actually coined in a pejorative way by those who hold premillennial views. Some proponents also prefer alternate terms such as nunc-millennialism (that is, now-millennialism) or realized millennialism, although these other names have achieved only limited acceptance and usage.[1]
Teaching
Amillennialism rejects the idea of a future "millennium"[2] in which Christ will reign on earth prior to the eternal state beginning, but holds:
- that Jesus is presently reigning from heaven, seated at the right hand of God the Father,
- that Jesus also is and will remain with the church until the end of the world, as he promised at the Ascension,
- that at Pentecost, the millennium began (others believe it began after Christ's Ascension), as is shown by Peter using the prophecies of Joel, about the coming of the kingdom, to explain what was happening,
- and that, therefore the Church and its spread of the good news is Christ's Kingdom and forever will be.
Amillennialists cite scripture references to the kingdom not being a physical realm:
- Matthew 12:28, where Jesus cites his driving out of demons as evidence that the kingdom of God had come upon them
- Luke 17:20–21, where Jesus warns that the coming of the kingdom of God can not be observed, and that it is among them
- Romans 14:17, where Paul speaks of the kingdom of God being in terms of the Christians' actions
In particular, Amillennialists regard the thousand-year period as a figurative expression of Christ's reign being perfectly completed, as the "thousand hills" referred to in Psalm 50:10, the hills on which God owns the cattle, are all hills, and the "thousand generations" in 1 Chronicles 16:15, the generations for which God will be faithful, refer to all generations. (Some postmillennialists and nearly all premillennialists hold that the word millennium should be taken to refer to a literal thousand-year period.)
Amillennialism also teaches that the binding of Satan, described in Revelation, has already occurred; he has been prevented from "deceiving the nations" by the spread of the gospel. This is the first binding he suffered in history after his fall from heaven. Nonetheless, good and evil will remain mixed in strength throughout history and even in the church, according to the amillennial understanding of the Parable of the Wheat and Tares.
Amillennialism is sometimes associated with Idealism, as both schools teach a symbolic interpretation of many of the prophecies of the Bible and especially of the Book of Revelation. However, many amillennialists do believe in the literal fulfillment of Biblical prophecies; they simply disagree with Millennialists about how or when these prophecies will be fulfilled.
History
Early church
Though not much was written about this aspect of eschatology during the first century of Christianity, most of the available writings from the period reflect a millenarianist persective (sometimes referred to as chiliasm). Bishop, Papias of Hierapolis (A.D. 70–155) speaks in favor of a pre-millennial position in volume three of his a five volume work and his sentiments were echoed by Aristion and the elder John, as well as other first-hand disciples and secondary followers.[3] Though most writings of the time tend to favor a millennial perspective, the amillennial position may have also been present in this early period, as suggested in the Epistle of Barnabus, and it would become the ascendant view during the next two centuries.[4][5][6][7][8][9] Church fathers of the second century that rejected the millennium were Clement of Alexandria, Origen, and Cyprian. Justin Martyr (died 165), who had chiliastic tendencies in his theology,[10] mentions differing views in his Dialogue with Trypho the Jew, chapter 80: "I and many others are of this opinion [premillennialism], and [believe] that such will take place, as you assuredly are aware; but, on the other hand, I signified to you that many who belong to the pure and pious faith, and are true Christians, think otherwise."[11]
Certain amillennialists such as Albertus Pieters understand Pseudo-Barnabas to be amillennial. In the 2nd century, the Alogi (those who rejected all of John's writings) were amillennial, as was Caius in the first quarter of the 3rd century.[12] With the influence of Neo-Platonism and dualism, Clement of Alexandria and Origen denied premillennialism.[13] Likewise, Dionysius of Alexandria argued that Revelation was not written by John and could not be interpreted literally; he was amillennial.[14]
Origen's idealizing tendency to consider only the spiritual as real (which was fundamental to his entire system) led him to combat the "rude"[15] or "crude"[16] Chiliasm of a physical and sensual beyond.
Premillennialism appeared in the available writings of the early church but it was evident that both views existed side by side. The premillennial beliefs of the early church fathers, however, are quite different from the dominant form of modern-day premillennialism, namely dispensational premillennialism.[17]
Medieval and Reformation periods
Amillennialism gained ground after Christianity became a legal religion. It was systematized by St. Augustine in the 4th century, and this systematization carried amillennialism over as the dominant eschatology of the Medieval and Reformation periods. Augustine was originally a premillennialist, but he retracted that view, claiming the doctrine was carnal.[18]
Amillennialism was the dominant view of the Protestant Reformers. The Lutheran Church formally rejected chiliasm in The Augsburg Confession—"Art. XVII., condemns the Anabaptists (of Munster—historically most Anabaptist groups were amillennial) and others ’who now scatter Jewish opinions that, before the resurrection of the dead, the godly shall occupy the kingdom of the world, the wicked being everywhere suppressed.'"[19] Likewise, the Swiss Reformer, Heinrich Bullinger wrote up the Second Helvetic Confession which reads "We also reject the Jewish dream of a millennium, or golden age on earth, before the last judgment."[20] John Calvin wrote in Institutes that chiliasm is a "fiction" that is "too childish either to need or to be worth a refutation." He interpreted the thousand-year period of Revelation 20 non-literally, applying it to the "various disturbances that awaited the church, while still toiling on earth."[21]
Modern times
Amillennialism has been widely held in the Eastern and Oriental Orthodox Churches as well as in the Roman Catholic Church, which generally embraces an Augustinian eschatology and which has deemed that premillennialism "cannot safely be taught."[11] Amillennialism is also common among Protestant denominations such as the Lutheran, Reformed, Anglican, many Messianic Jews, and Methodist Churches.[22] It represents the historical position of the Amish, Old Order Mennonite, and Conservative Mennonites (though among the more modern groups premillennialism has made inroads). It is common among groups arising from the 19th century American Restoration Movement such as the Churches of Christ,[23]:125 Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) and Christian churches and churches of Christ. It also has a following amongst Baptist denominations such as The Association of Grace Baptist Churches in England. Partial preterism is sometimes a component of amillennial hermeneutics. Amillennialism declined in Protestant circles with the rise of Postmillennialism and the resurgence of Premillennialism in the 18th and 19th centuries, but it has regained prominence in the West after World War II.
See also
References
- ↑ Anthony Hoekema, "Amillennialism"
- ↑ Cox, William E. (1966). Amillennialism Today. Presbyterian & Reformed Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0875521510.
- ↑ Eusebius. Ecclesiastical History 3.39.3-4.
- ↑ "Competing Theories of Eschatology, End Times, and Millennialism". Religious Tolerance. Retrieved September 10, 2016. line feed character in
|title=at position 35 (help) - ↑ Patrick Allen Boyd (1977). Thesis at Dallas Theological Seminary. p. 90f.
[P]erhaps, seminal amillennialism, and not nascent dispensational pre-millennialism ought to be seen in the eschatology of the period.
- ↑ Walvoord, John F. (December 1949). "Amillenniallism in the Ancient Church". Bible.org. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ↑ "Orthodox Apologetics". Early Christian Eschatology. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ↑ Olson, Carl E. "Five Myths About the Rapture". Five Myths About the Rapture. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ↑ "Amillennialism in the Early Church". Third Millennium Ministries. Retrieved September 11, 2016.
- ↑ "Always Victorious!" Archived March 2, 2006, at the Wayback Machine. by Francis Nigel Lee
- 1 2 Catholic Answers on "The Rapture" Archived May 13, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Eusebius, 3.28.1–2
- ↑ De Principiis, 2.11.2-3
- ↑ Eusebius, Church History, 7.24.3; 7.25
- ↑ The New Schaff-Herzog Encyclopedia of Religious Knowledge, Vol.8, p. 273
- ↑ The Anchor Bible Dictionary (1997) article "Chiliasm", The Labyrinth of the World and the Paradise of the Heart (Johann Amos Comenius, ed. 1998) p. 42 and Jews and Christians: The Parting of the Ways, A.D. 70 to 135 (James D. G. Dunn, 1999) p. 52.
- ↑ Boyd, pp. 90f: "It is the conclusion of this thesis that Dr. Ryrie's statement [that dispensationalism was the view of the early church fathers] is historically invalid within the chronological framework of this thesis. The reasons for this conclusion are as follows: 1). the writers/writings surveyed did not generally adopt a consistently applied literal interpretation; 2). they did not generally distinguish between the Church and Israel; 3). there is no evidence that they generally held to a dispensational view of revealed history; 4). although Papias and Justin Martyr did believe in a Millennial kingdom, the 1,000 years is the only basic similarity with the modern system (in fact, they and dispensational pre-millennialism radically differ on the basis of the Millennium); 5).they had no concept of imminency or a pre-tribulational rapture of the Church; 6).in general, their eschatological chronology is not synonymous with that of the modern system. Indeed, this thesis would conclude that the eschatological beliefs of the period studied would be generally inimical to those of the modern system (perhaps, seminal amillennialism, and not nascent dispensational pre-millennialism ought to be seen in the eschatology of the period)."
- ↑ "City of God, Book 20, Chapter 7"
- ↑ Philip Schaff, History of the Christian Church, Vol. 2 (Peabody, MA: Hendrickson, n.d.) 381.
- ↑ Philip Schaff History of Creeds Vol. 1, 307.
- ↑ John Calvin, Institutes of the Christian Religion, XXV.V
- ↑ Jon Kennedy. The Everything Jesus Book: His Life, His Teachings. Adams Media.
With some variations, amillennialism is the traditional eschatology of the Catholic, Orthodox, Lutheran, Calvinist (Presbyterian, Reformed), Anglican, and Methodist Churches.
- ↑ Ron Rhodes, The Complete Guide to Christian Denominations, Harvest House Publishers, 2005, ISBN 0-7369-1289-4
Further reading
- Provan, Charles D. The Church is Israel Now: Old and New Testament Scripture Texts Which Illustrate the Conditional Privileged Position and Titles of "Racial Israel" and Their Transfer to the Christian Church, Arranged with Commentary. Vallecito, Calif.: Ross House Books, 1987. 74 p. Without ISBN
External links
- "A Defense of (Reformed) Amillennialism" - a series of articles by David J. Engelsma from the Standard Bearer (April 1, 1995 through December 15, 1996)
- Monergism's articles on Amillennialism
- Grace Online Library: Amillennialism - various articles on Amillennialism
- "Millennium and Millenarianism" from the Catholic Encyclopedia
- Blue Letter Bible summary (dispensational premillennialism perspective)
- On The Thousand Year Reign (Chiliasm) Elder Cleopa of Romania—Eastern Orthodox view
- "End Times" from Project Wittenberg (Lutheran perspective)
- "Millennium" by Nathan J. Engel (Lutheran perspective)
- Understanding Eschatology from an Amillennial Perspective - a series of lectures by Steve Gregg
- Rational Christian Eschatology - A general case for an amillennial perspective on the future