Albanian passport
| Albanian passport | |
|---|---|
.jpg) The front cover of a contemporary Albanian biometric passport. | |
| Date first issued | March 24, 2009 |
| Issued by |
|
| Type of document | Passport |
| Purpose | Identification and travel abroad |
| Eligibility requirements | Albanian citizenship |
| Expiration | 10 years |
The Albanian passport is a travel and identity document that is issued to citizens who are nationals of Albania and allows them to travel abroad.[1] The authority responsible for issuing is the Ministry of Interior.
Albanian passport is one of the 5 passports with the most improved rating globally since 2006 in terms of number of countries that its holders may visit without a visa.[2]

Biometric passport
Starting in May 2009, the Albanian Government, as part of a larger project to modernize and bring to the best international standards, has started issuing biometric passport [3] and biometric ID card[4] for its citizens.
In order to get the passport each Albanian citizen may go to the local post office and pay the price of 7,500 (seven thousand five hundred) lek(€50) and afterwards go to the Registry office of the municipality where the person is photographed, and the fingerprints are digitized. The data collected are sent to the center of production in Tirana. The ideation and the way of producing the new Albanian e-Passport is made in front of a single civil servant (personal identification, photographing, finding fingerprints, and digital signature) makes this document one of the most reliable and advanced in the world. The switch to a biometric passport was one of the conditions for the Schengen Area visa liberalization for the citizens of Albania.[5]
Since March 2011 biometric passport and identity card can be requested at the Albanian consulates in Greece and Italy to serve immigrants who live there.
Physical appearance
The data page of the passport is from rigid polycarbonate plastic and contains a microchip embedded in which are stored biometric data of the holder such as fingerprints, photo and signature. The data are extracted from the chip with wireless RFID technology. It has excellent safety standards and anti counterfeiting. The photo is scanned on the page and is replied by side and it is UV reactive. The alphanumeric code at the bottom of the data page makes it readable with optical scanners, such as the airport ones. The code includes microprinting, holographic images, images visible only with UV light, filigree and other details.
The Albanian biometric passport meets all standards set by International Civil Aviation Organization.
The data is written in Albanian and English. The passport is valid for 10 years.
History
The first Albanian passports were issued in the 1920s, when the consolidation of the Albanian state began. During the communist period from 1945 until 1991, Albania did not allow foreign travel of its citizens and therefore did not issue ordinary passports for foreign travel, only diplomatic and service passports in limited number. Since the change of Albania's political system in 1991-1992, the authorities have issued passports to all Albanian citizens who request it.
- From 1991 until 1996 the passport was red and did not contain any safety element if not a dry stamp on the photo. The data were written by hand. It still had the Albanian communist Coat of Arms.
- From 1996 until 2002 the passport was brown and had the first security elements as the data page and the photo was laminated. The data were written by machine. It was manufactured by a Canadian company.
- From 2002 until 2009 the passport was red and had safety standards and anti counterfeiting similar to the biometric passport except the microchip. It was manufactured by the German firm Bundesdruckerei.
- Since 2009 the biometric passport is burgundy coloured, similar to those of the European Union. It is manufactured by the French company Sagem Sécurité.[6]
Visa requirements
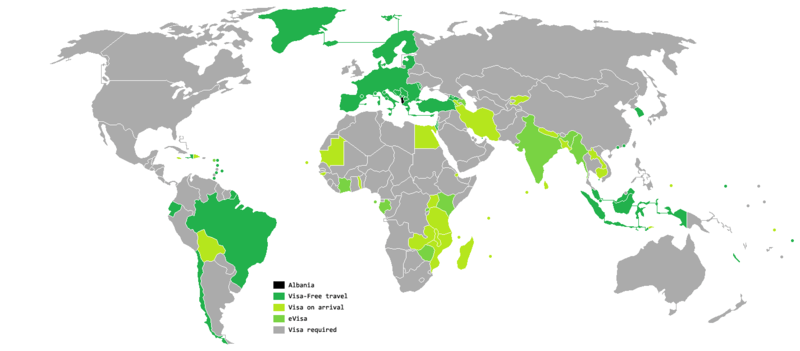
In February 2016, holders of an Albanian passport could visit 98 countries and territories visa-free or with visa on arrival, ranking Albania 53rd in the world in terms of travel freedom.[7] Albanian passport is one of the 5 passports with the most improved rating since 2006.[8]
Gallery
- Albanian passports
-

1991 Albanian passport -
1996 Albanian passport -

2002 Albanian passport -
.jpg)
2009 Albanian biometric (  ) passport
) passport -
Albanian and Italian biometric passports issued in 2009
See also
- Albanian Identity Card

- Visa requirements for Albanian citizens
- List of passports
- List of diplomatic missions in Albania
- List of diplomatic missions of Albania
- Foreign relations of Albania
- Border crossings of Albania
References
- ↑ Passport law (alb)
- ↑
- ↑ Procedures to obtain the passport (alb)
- ↑ Modernization project helps improve public services in Albania
- ↑ Albania's ID cards and biometric passports key to visa regime, elections
- ↑ Albania selects Sagem Sécurité (Safran Group) for secure ID documents
- ↑ "Global Ranking - Visa Restriction Index 2016" (PDF). Henley & Partners. Retrieved 5 October 2015.
- ↑
External links
- Ministria e Punëve të Jashtme / Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Albania
- Ministria e Punëve të Brendshme / Ministry of Internal Affairs of Albania
- Policia e Shtetit / Albanian State Police
- Zyra e Gjendjes Civile / Albanian Civil Registry