98 B-Line
| 98 B-Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 A bus taking a rest on Anderson Road after a run as a 98 B-Line. The B-Line buses have a special paint scheme; the 98s are in this blue/yellow scheme. In the past, its older counterpart, the 99, sported a blue/red scheme. | |||
| Overview | |||
| System | B-Line | ||
| Operator | Coast Mountain Bus Company | ||
| Began service | August 2001 | ||
| Ended service | September 7, 2009 | ||
| Route | |||
| Start | Burrard Station | ||
| End | Brighouse (Steveston & Shell, evenings and morning only) | ||
| Stops | 22 | ||
| |||
The 98 B-Line was an express bus line with bus rapid transit elements in Metro Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It connected Richmond, British Columbia to Downtown Vancouver, with a connection to Vancouver International Airport. It travelled mainly along Granville Street in Vancouver and dedicated bus lane on No. 3 Road in Richmond. It was operated by Coast Mountain Bus Company and was funded by TransLink. The route was 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) long. The line carried over 18,000 passengers daily (, PDF file). It was discontinued on September 7, 2009, two and a half weeks after the opening of the Canada Line, which replaced it.
The 98 GPS technology, automated stop announcements, specialized bus stop displays that showed the amount of time until the next bus arrives, and special traffic light signals that sustained green lights long enough for buses to pass through.
The 98 B-Line had nine stops in Richmond (including the transfer point to the airport) and fourteen stops in Vancouver (including seven stops downtown). Waiting times were approximately five to seven minutes per bus during peak hours and ten minutes per bus during mid-afternoons. In the evening and at night, the waiting time was around fifteen minutes per bus, and in the early morning the waiting time was around 20 to 30 minutes. Total travel time from end to end on the route was approximately 42 minutes, but could increase to one hour during peak hours due to traffic.
In Richmond, the 98 B-Line followed a dedicated bus lane separated from mainstream traffic on No. 3 Road, between the Lansdowne and Sea Island Way stops. On February 13, 2006, the 98 B-Line's bus lane in Richmond was closed as utility crews prepared for the construction of the Canada Line along No. 3 Road. Between February 2006 until its discontinuation in September 2009, the 98 B-Line travelled with regular traffic.
The route was modelled after the successful 99 B-Line, which operates between University of British Columbia and Commercial-Broadway SkyTrain station. Like its older counterpart, larger articulated buses were normally used for this route, each with a 120-passenger capacity. These buses were built by New Flyer Industries of Winnipeg, Manitoba.

History
Prior to the introduction of the 98 B-Line, most bus routes in Richmond travelled into Downtown Vancouver during rush hours. These routes stopped at all stops along their routes in Richmond, then would operate along Granville Street in Vancouver as express services.
Although the idea of a rapid bus line from Richmond to Vancouver had been discussed for decades, it was first proposed by BC Transit in 1994. In 1995, Vancouver city council approved a southbound high-occupancy vehicle lane for the evening peak hours in the Marpole neighbourhood in preparation for an express bus service. In 1997, the idea of a rapid transit line was re-introduced with the objective of providing the express service at regular fares. A study was done and it was determined that the best route for the line would be through Granville Street in Vancouver.[1]

The project cost about $52 million CAD to build;[2] this includes the price of new vehicles, the construction of a dedicated bus lane in Richmond, installing new bus shelters, automated on-board announcements and similar technology, transit priority systems for traffic lights and a share of the new Richmond bus depot (as the old Vancouver Oakridge depot could not accommodate the longer 60-foot (18 m) articulated buses used on the route [3]). The line was officially opened in August 2001.
With the introduction of the B-Line, almost all other local bus services traveling between Richmond and Vancouver were eliminated, resulting in most commuters having to transfer from a local service to the B-Line. As a result of the added transfer and quicker travel times of the B-Line that did not materialize, commute times for passengers increased even though a commute time savings of several minutes had been promised. Within a few years, rush hours routes were created which effectively restored direct rush hour service from most urban areas of Richmond to Vancouver.
The B-line was one of the most used routes in the TransLink system. Around 2002 to 2003, plans to replace the 98 B-Line with a light rail line were being brought up. This new line's working name was the "RAV Line" (with RAV standing for Richmond-Airport-Vancouver). It generated much controversy, mainly due to its estimated cost of $1.72 billion CAD. The project was also threatened by political interference from Richmond city council, which had insisted that the line being operated in the city at grade principally because they favored the aesthetic attributes of an at grade line over an above grade line; faced with the majority of public favoring an above grade line and the consideration that an at grade line would increase operating costs and significantly increase trip times, Richmond council backed down. The project was voted down by the TransLink board twice because of political infighting because the board members representing the northeast areas of Greater Vancouver wanted a line built to Coquitlam. The "RAV Line" project was saved after the board agreed to build both lines by 2010.[4] While not part of the 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver, the Canada Line was completed in August 2009, and has now replaced the 98 B-Line.
As February 2008, 98 B-Line route passengers with valid proof of payment were permitted to board using any of the three doors at any stop. To facilitate this, the bus driver controlled the operation of all three doors at each of the stops. Passengers paying cash or validating FareSavers had to board through the front door.
The 98 B-Line was discontinued on September 7, 2009, two and a half weeks after the Canada Line opened. After this date, the #10 Hastings/Downtown/Granville bus began running more frequently along Granville street to compensate.[5]
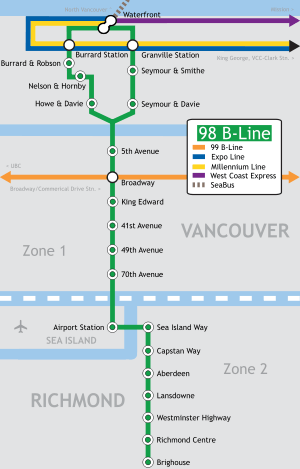
98 B-Line stops and transfer points
| 98 B-Line | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Downtown Vancouver
- Seymour & Davie - Served the upscale Yaletown neighbourhood. (Note: The bus's destination sign changes to "98 B-Line: Richmond Centre" at this point.)
- Seymour & Smithe - Served the nightclub area on Granville Street, a block to the west. It is also the stop for street youth hostels in the area and the Orpheum Theatre.
- Granville Station - Transfer point to the SkyTrain system and suburban routes to North Vancouver and West Vancouver. Also served Pacific Centre, Hudson Bay Company, and major commercial district as well as the Vancouver Public Library, which is several blocks to the east.
- Waterfront Station - Transfer point to the SkyTrain terminus for both the Expo and Millennium Lines, as well as the SeaBus to Lonsdale Quay in North Vancouver. It is also the western terminus of the West Coast Express.
- Burrard Station - This is the Vancouver terminus for the 98 B-Line, though it does not make a layover. Located in the middle of the financial district. Transfer point to the SkyTrain system as well as to suburban routes to Burnaby, North Vancouver, Surrey, Delta, White Rock, Coquitlam and Port Moody.
- Burrard & Robson - Served the Robson Street shopping district.
- Nelson & Hornby - Formerly known as Nelson & Howe, before the stop was moved. Stopped in front of One Wall Centre. Also served the provincial law courts.
- Howe & Davie - Served the hospitality district near False Creek. Also a transfer point to buses and community shuttles to Davie Village.
Vancouver
- 5th Avenue - Served the southern False Creek area as well as Granville Island.
- Broadway - Transfer point to the 99 B-Line as well as many trolley routes. It is a short distance away from Vancouver General Hospital and is also the transfer point for those going to Kitsilano.
- King Edward - Transfer point to the #25 bus, which served the affluent Shaughnessy area, University, and North Burnaby. It also stops a short walk away from B.C. Children's Hospital and B.C. Women's Hospital.
- 41st Avenue - Transfer point to the #41 bus, which served the Kerrisdale area, particularly the shopping district, and the Oakridge area. Also served as transfer point to the #43 bus, which is an express version of the #41, but only runs during peak hours, and the #480, which is an express bus from Richmond Centre to UBC Loop.
- 49th Avenue - Transfer point to the #49 bus, which operates eastbound to nearby Langara College and terminating at Metropolis at Metrotown, the biggest shopping mall in the province. During peak hours, the route's western terminus is at University of British Columbia, instead of Dunbar Loop.
- 70th Avenue - Served the Marpole neighbourhood and acts as a transfer point to the #100 bus (which travels along Marine Drive).
Richmond


- Airport Station - Transfer point to the #424 bus, which was a shuttle to Vancouver International Airport's main terminal. Also served the Burkeville neighbourhood of Sea Island, and was a transfer point to the #620 bus to the Tsawwassen ferry terminal. Airport Station was closed the same day the 98 B-Line was discontinued.
- Sea Island Way - Served River Rock Casino, the largest casino in Metro Vancouver.
- Capstan Way - Served Yaohan Centre, Union Square Shopping Centre, and also the Asian shopping district along Capstan Way itself.
- Aberdeen - Served the main Golden Village Asian shopping district, including Aberdeen Centre, Empire Centre, Parker Place, President Plaza, and south side of Yaohan Centre.
- Alderbridge - Served the northern part of the Lansdowne Centre shopping mall as well as the Alexandra Road restaurant district.
- Lansdowne - Served the southern part of Lansdowne Centre and the Richmond campus of Kwantlen Polytechnic University
- Westminster Highway - Popular transfer point to the #401 and #407 buses to Steveston along No. 1 Road and Gilbert Road, respectively. Many passengers used those routes to reach Richmond Hospital and the headquarters of WorkSafe B.C., the workers' compensation and safety board.
- Richmond Centre - The unofficial terminus of the line (due to the fact that the bus's destination signs read "98 RICHMOND CENTRE"). Stops outside of the Richmond Centre shopping mall and is the main transfer point to almost all of the bus routes in Richmond.
- Brighouse - The southern terminus of the line. Served the Richmond City Hall and the Brighouse area (particularly the Minoru cultural centre, which is home to the Richmond Public Library, the local skating rink and the local swimming pool.)
Route notes
- For early morning and late evening trips, the 98 B-Line provided local non-express service between the Brighouse stop and the Richmond Transit Centre, along No. 3 Road (south of Granville Avenue) and Steveston Highway (until Shell Road). The buses going back to Richmond Transit Centre were signed "98 To Steveston & Shell B-Line".
- On Mondays to Fridays, during peak hours, 98 B-Line service between Vancouver and Airport Station was supplemented by the #496 Railway/Burrard Station and #491 One Road/Burrard Station express routes. The #490 Steveston/Burrard Station express route also did this but went to Highway 99 via Marpole Loop instead of Airport Station.
- Non-express service was also provided along some of the 98 B-Line's corridors, via the #10 Granville/Downtown (along Granville Street) and #410 Railway/22nd Street Station (between the Aberdeen and Brighouse stops) routes in Vancouver and Richmond, respectively.
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.city.vancouver.bc.ca/ctyclerk/cclerk/980303/rr1.htm
- ↑ http://www.apta.com/research/info/briefings/documents/mills.pdf
- ↑ http://novax.com/products/media/98B-Line%20Final%20Report.pdf
- ↑ http://www.spec.bc.ca/article/article.php?articleID=404
- ↑ "Connecting Transit Services". TransLink. Retrieved 2009-07-29.
External links
- TransLink
- Federal Transit Administration (US) - Overview of the 98 B-Line's technologies
- Transport Canada: Urban Transportation Showcase Program
- Novax B-Line Study Report