780
| Millennium: | 1st millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | 7th century · 8th century · 9th century |
| Decades: | 750s · 760s · 770s · 780s · 790s · 800s · 810s |
| Years: | 777 · 778 · 779 · 780 · 781 · 782 · 783 |
| 780 by topic | |
| Politics | |
| State leaders – Sovereign states | |
| Birth and death categories | |
| Births – Deaths | |
| Establishment and disestablishment categories | |
| Establishments – Disestablishments | |
| Gregorian calendar | 780 DCCLXXX |
| Ab urbe condita | 1533 |
| Armenian calendar | 229 ԹՎ ՄԻԹ |
| Assyrian calendar | 5530 |
| Bengali calendar | 187 |
| Berber calendar | 1730 |
| Buddhist calendar | 1324 |
| Burmese calendar | 142 |
| Byzantine calendar | 6288–6289 |
| Chinese calendar | 己未年 (Earth Goat) 3476 or 3416 — to — 庚申年 (Metal Monkey) 3477 or 3417 |
| Coptic calendar | 496–497 |
| Discordian calendar | 1946 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 772–773 |
| Hebrew calendar | 4540–4541 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 836–837 |
| - Shaka Samvat | 701–702 |
| - Kali Yuga | 3880–3881 |
| Holocene calendar | 10780 |
| Iranian calendar | 158–159 |
| Islamic calendar | 163–164 |
| Japanese calendar | Hōki 11 (宝亀11年) |
| Javanese calendar | 675–676 |
| Julian calendar | 780 DCCLXXX |
| Korean calendar | 3113 |
| Minguo calendar | 1132 before ROC 民前1132年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −688 |
| Seleucid era | 1091/1092 AG |
| Thai solar calendar | 1322–1323 |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 780. |
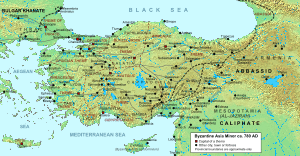
Byzantine Empire with the themata (c. 780)

Empress Irene and her son Constantine VI
Year 780 (DCCLXXX) was a leap year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 780 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Byzantine Empire
- September 8 - Emperor Leo IV ("the Khazar") dies after a 5-year reign in which he has been dominated by his wife Irene of Athens, an iconodule. He is succeeded by his 9-year-old son Constantine VI, due to his minority, Irene and her chief minister Staurakios exercise a regency over him.[1]
Europe
- Saxon Wars: King Charlemagne decrees the death penalty for any subdued Saxon refusing Christian baptism. Meanwhile Widukind builds up 'rebel' strength in northern Saxony.[2]
- The city of Osnabrück, developed as marketplace, is founded by Charlemagne (approximate date).
Britain
- The rise of Aldwych as an important trading centre in London under Mercian control. King Offa of Mercia possibly establishes a Royal Palace at Aldermanbury, on the site of the old Roman Cripplegate fort and amphitheatre (approximate date).
Asia
- King Hyegong of Silla is killed in a revolt, terminating the kingly line of succession of former ruler Muyeol. He is the architect of Silla's unification of the Korean Peninsula (see 668).
By topic
Religion
Births
- Ahmad ibn Hanbal, Muslim scholar and theologian (d. 855)
- Frederick of Utrecht, Frisian bishop (approximate date)
- Guifeng Zongmi, Chinese Buddhist monk (d. 841)
- Hugh of Tours, Frankish nobleman (approximate date)
- Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Ḵwārizmī, Persian mathematician (approximate date)
- Rabanus Maurus, archbishop of Mainz (approximate date)
- Yunyan Tansheng, Chinese Buddhist monk (d. 841)
Deaths
- September 8 – Leo IV, Byzantine emperor (b. 750)
- Dunchadh ua Daimhine, king of Uí Maine (Ireland)
- Himiltrude, wife of Charlemagne (approximate date)
- Hyegong, king of Silla (Korea) (b. 758)
- Khun Lo, founder of Luang Prabang (Laos)
- Kume no Wakame, Japanese noblewoman
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/5/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.