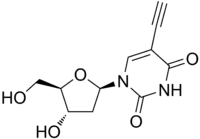
5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Ethynyl-1-[(2R,4S,5R)-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidine-2,4-dione | |
| Other names
2'-Deoxy-5-ethynyluridine; 5-Ethynyl-2´-deoxyuridine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 61135-33-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | EdU |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL222932 |
| ChemSpider | 414657 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.902 |
| MeSH | 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine |
| PubChem | 472172 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H12N2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 252.23 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
5-Ethynyl-2´-deoxyuridine (EdU) is a thymidine analogue which is incorporated into the DNA of dividing cells and is used to assay DNA synthesis in cell culture. At high doses it can be cytotoxic.
Detection
EdU is detected with a fluorescent azide which forms a covalent bond using click chemistry.[1][2] Unlike the commonly used bromodeoxyuridine, EdU detection requires no heat or acid treatment.
References
- ↑ Chehrehasa, F; Meedeniya, AC; Dwyer, P; Abrahamsen, G; Mackay-Sim, A (February 2009). "EdU, a new thymidine analogue for labelling proliferating cells in the nervous system". J. Neurosci. Methods. 177 (1): 122–30. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.10.006. PMID 18996411.
- ↑ Cavanagh, Brenton; Walker, T; Norazit, A; Meedeniya, A. C. (15 September 2011). "Thymidine analogues for tracking DNA synthesis.". Molecules. 16 (9): 7980–93. doi:10.3390/molecules16097980. PMID 21921870.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.