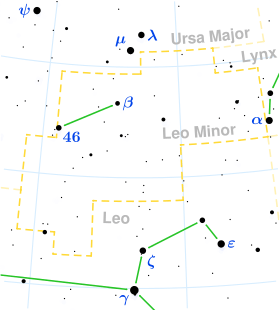
46 Leonis Minoris
| |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Leo Minor |
| Right ascension | 10h 53m 18.70487s[1] |
| Declination | +34° 12′ 53.5375″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.83[2] (3.79 - 3.84[3]) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K0+ III-IV[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +92.02[1] mas/yr Dec.: –285.82[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 34.38 ± 0.21[1] mas |
| Distance | 94.9 ± 0.6 ly (29.1 ± 0.2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +1.45[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.69[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 8.22 ± 0.22[2] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 34 ± 2[2] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.96[2] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,670[2] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.20[7] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 1.81[8] km/s |
| Age | 6.76[9] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Praecipua is the brightest star in the constellation Leo Minor. It is sometimes known as "o LMi" (not "ο LMi"), from Bode's catalogue of 1801. It was presumably intended to be designated α, as Francis Baily decided to letter each star brighter than magnitude 4.5, but the designation was missing from his catalogue, even though the dimmer β was included.[10]
Its proper name is derived from the Latin "the Chief (Star of Leo Minor)".[11] The name may originally have referred to 37 Leonis Minoris, and later mistransfered to this star.[12] It is known as 勢四, "the Fourth (Star) of the Eunuch", in traditional Chinese astronomy.
46 LMi has spectral class K0+III-IV and is of magnitude 3.83. It is a red clump giant.[9] Its distance from Earth is approximately 95 light years. It is a suspected variable with an amplitude of about 0.05 magnitudes.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752
 , Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357 - 1 2 3 4 5 Piau, L.; et al. (February 2011), "Surface convection and red-giant radius measurements", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 526: A100, arXiv:1010.3649
 , Bibcode:2011A&A...526A.100P, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014442
, Bibcode:2011A&A...526A.100P, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014442 - 1 2 Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/gcvs. Originally published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989). "The Perkins catalog of revised MK types for the cooler stars". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series (ISSN 0067-0049). 71: 245. Bibcode:1989ApJS...71..245K. doi:10.1086/191373.
- ↑ Mullan, D. J.; MacDonald, J. (2003). "Onset of Mass Loss in Red Giants: Association with an Evolutionary Event". The Astrophysical Journal. 591 (2): 1203. Bibcode:2003ApJ...591.1203M. doi:10.1086/375446.
- ↑ Lyubimkov, L. S.; Poklad, D. B. (2014). "Determining the effective temperatures of G- and K-type giants and supergiants based on observed photometric indices". Kinematics and Physics of Celestial Bodies. 30 (5): 244. arXiv:1412.6950
 . Bibcode:2014KPCB...30..244L. doi:10.3103/S0884591314050055.
. Bibcode:2014KPCB...30..244L. doi:10.3103/S0884591314050055. - ↑ Wittenmyer, Robert A.; Gao, Dongyang; Hu, Shao Ming; Villaver, Eva; Endl, Michael; Wright, Duncan (2015). "The Weihai Observatory Search for Close-in Planets Orbiting Giant Stars". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Pacific. 127 (956): 1021. arXiv:1507.06051
 . Bibcode:2015PASP..127.1021W. doi:10.1086/683258.
. Bibcode:2015PASP..127.1021W. doi:10.1086/683258. - ↑ Hekker, S.; Meléndez, J. (2007). "Precise radial velocities of giant stars. III. Spectroscopic stellar parameters". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 475 (3): 1003. Bibcode:2007A&A...475.1003H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078233.
- 1 2 Soubiran, C.; Bienaymé, O.; Mishenina, T. V.; Kovtyukh, V. V. (2008). "Vertical distribution of Galactic disk stars. IV. AMR and AVR from clump giants". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 480: 91. arXiv:0712.1370
 . Bibcode:2008A&A...480...91S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078788.
. Bibcode:2008A&A...480...91S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078788. - ↑ Wagman, Morton (2003). Lost Stars. Blacksburg, Virginia: McDonald and Woodward. ISBN 0-939923-78-5.
- ↑ Allen, R. H. (1963). Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (Reprint ed.). New York, NY: Dover Publications Inc. p. 264. ISBN 0-486-21079-0.
- ↑ Leo Minor: The little lion- Ian Ridpath's Star Tales