1st century BC
| Millennium: | 1st millennium BC |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | 90s BC 80s BC 70s BC 60s BC 50s BC 40s BC 30s BC 20s BC 10s BC 0s BC |
| Categories: | Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |
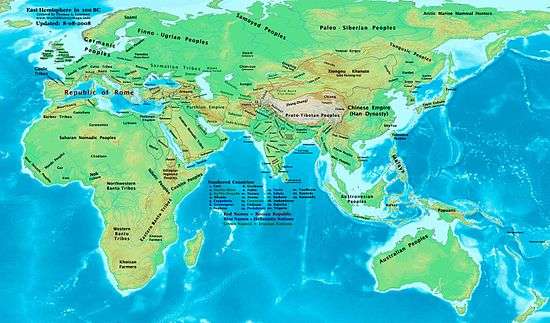
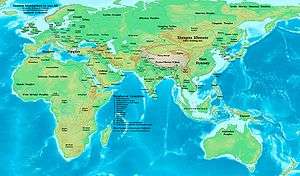
The 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC, started on the first day of 100 BC and ended on the last day of 1 BC. The AD/BC notation does not use a year zero; however, astronomical year numbering does use a zero, as well as a minus sign, so "2 BC" is equal to "year -1". This is the 100th century in the Holocene calendar; it spans the years 9,901 to 10,000. 1st century AD (Anno Domini) follows.
In the course of the century all the remaining independent lands surrounding the Mediterranean were steadily brought under Roman control, being ruled either directly under governors or through puppet kings appointed by Rome. The Roman state itself was plunged into civil war several times, finally resulting in the marginalization of its 500-year-old republic, and the embodiment of total state power in a single man—the emperor.
The internal turbulence that plagued Rome at this time can be seen as the last death throes of the Roman Republic, as it finally gave way to the autocratic ambitions of powerful men like Sulla, Julius Caesar, Mark Antony and Octavian. Octavian's ascension to total power as the emperor Augustus is considered to mark the point in history where the Roman Republic ends and the Roman Empire begins. Some scholars refer to this event as the Roman Revolution. It is believed that the birth of Jesus, the central figure of Christianity took place at the close of this century.
In the eastern mainland, the Han Dynasty began to decline and the court of China was in chaos in the latter half of this century. Trapped in a difficult situation, the Xiongnu had to begin emigration to the west or attach themselves to the Han.
Events
90s BC

forced out of Cappadocia by Mithridates VI of Pontus, and dies soon afterwards.
- 96 BC: Cyrene is left to the people of Rome by its ruler Ptolemy Apion.
- 96 BC: King Alexander Jannaeus of Judea wins the Siege of Gaza.
- 95 BC: Tigranes the Great becomes king of Armenia
- 93 BC: Ariobarzanes I Philoromaios becomes king of Cappadocia with Roman backing.
- 91 BC: The assassination of Marcus Livius Drusus leads to the Social War (91–88 BC) in Italy
- 91 BC: Crown Prince Ju Revolt in China.
80s BC
- 89 BC: Mithridates VI of Pontus's invasion of Cappadocia leads to the First Mithridatic War with the Roman Republic.
- 89 BC: Valagamba of Anuradhapura gains control of all of Sri Lanka
- 88 BC: 80,000 Roman civilians killed in the Asiatic Vespers in Asia Minor
- 87 BC: Emperor Wu of Han dies and is succeeded by his eight-year-old son Zhao, with Jin Midi, Shangguang Jie and Huo Guang as regents.
- 88-87 BC: Sulla's first civil war - Sulla marches on Rome and defeats Gaius Marius
- 86 BC: Siege of Athens ends with Roman conquest of Athens.
- 86 BC: The death of the regent of China Jin Midi unleashes the rivalry of his co-regents Shangguang Jie and Huo Guang.
- 85 BC: Sulla defeats the forces of Mithridates VI in Greece at the Battle of Orchomenus
- 85 BC: Aretas III of the Nabataeans conquers Damascus.
- 83 BC: Sulla makes peace with Mithridates VI and marches on Rome.
- 83-81 BC: Lucius Licinius Murena wages the Second Mithridatic War.
- 82 BC: Sertorius flees from Sulla to North Africa via Hispania
- c.83 BC: Tigranes of Armenia takes control of Syria after the implosion of the Seleucid dynasty.
- 81 BC: End of Sulla's second civil war - Sulla is appointed dictator of the Roman state, and brings about major reforms.
- 80 BC: Sertorius invades Hispania and sets up his own regime, beginning the Sertorian War (80-72).
- 80 BC: Conflict between the regents Shangguang Jie and Huo Guang results in the destruction of the Shangguang clan and Huo Guang becoming the de facto ruler of China.
- c.80 BC: Maues, King of the Sakas, conquers Gandhara and Taxila.
70s BC
- 77 BC: Fu Jiezi assassinated the king of Loulan on behalf of the Han dynasty.
- c.75 BC: Kanva dynasty replaces the Shunga dynasty in Magadha.
- 74 BC: Mithridates VI of Pontus disputes Nicomedes IV of Bithynia's bequest of his kingdom to the Roman Republic, beginning the Third Mithridatic War.
- 74 BC: Emperor Zhao of Han dies and is succeeded by the unsuitable Prince He of Changyi and then by Xuan. Huo Guang continues to be de facto ruler of China.
- 73 BC: A slave rebellion led by the escaped gladiator Spartacus leads to the Third Servile War.
- 73-72 BC: Lucullus defeats Mithridates at Tenedos, Cyzicus, and the Rhyndacus and he flees east to Armenia
- 71 BC: Pompey the Great ends the Sertorian War (restoring Roman control of Hispania) and the Third Servile War (restoring Roman control of southern Italy).
- 71 BC: Wusun and China attack the Xiongnu.
60s BC
- 69 BC: Lucullus invades Armenia (Battle of Tigranocerta) and reestablishes the Seleucids in Syria.
- 68 BC: Pompey replaces Lucullus as leader of the Roman forces in the Third Mithridatic War.
- 68 BC: Huo Guang dies and Emperor Xuan of Han assumes full power. The Huo clan is eliminated over the following two years.
- 67 BC: Pompey is given a three-year extraordinary command against the pirates plaguing the Mediterranean and defeats them in forty days.
- 66 BC: Pompey drives Mithridates VI out of Asia Minor (Battle of the Lycus)
- 66 BC: Aristobulus II seizes power from John Hyrcanus II in Judea.
- 63 BC: Mithridates VI commits suicide, ending the Third Mithridatic War
- 63 BC: Cicero uncovers and defeats the Catilinarian Conspiracy.
- 63 BC: Pompey captures Jerusalem, and establishes Roman annexation of Judea as a client kingdom. He also permanently abolishes Seleucid Syria. Aristobulus II of Judea removed from power & John Hyrcanus II restored as Roman vassal.
- 62 BC: Nabataean kingdom becomes a Roman vassal.
- 61 BC: Orgetorix and the Helvetii's attempt to migrate into southwestern France leads Julius Caesar to take military action, beginning the Gallic Wars
- 60 BC: Julius Caesar, Pompey the Great, and Marcus Crassus form the First Triumvirate
- c. 60 BC: The Sakas conquer Mathura.
50s BC
- 58 BC: Battle of Bibracte - Julius Caesar conquers the Helvetii
- 58 BC: Germans invade Gaul and are defeated by Julius Caesar at Battle of Vosges (58 BC).
- 58 BC: Clodius becomes the leading figure in Roman urban politics. Cicero goes into exile.
- 58 BC: Huhanye rebels against his distant cousin Woyanqudi Chanyu of the Xiongyu, beginning the Xiongnu civil war.
- 57 BC: Julius Caesar invades and defeats the Belgae at the Battle of the Sabis
- 57 BC: Cicero recalled from exile through the machinations of Milo and his mob.
- 57 BC: Silla is founded in southeastern Korea (traditional date according to Samguk Sagi, a 12th-century historical document).
- 56 BC: Vikramaditya defeats the Sakas at Ujjain and founds the Vikram Samvat calendar era.
- 55-54 BC: Caesar's invasions of Britain.
- 54-53 BC: Ambiorix's revolt against Julius Caesar in Gaul.
- 53 BC: The Parthians defeat the Romans under Crassus in the Battle of Carrhae, ending the First Triumvirate.
- 53 BC: Clodius dies during mob violence in Rome. His followers burn down the Senate house.
- 53 BC: Huhanye Chanyu of the Xiongnu become a Chinese vassal.
- 52 BC: Pompey joins the Optimates and becomes sole Consul in Rome.
- 52 BC: Vercingetorix's revolt in Gaul (Battle of Gergovia, Battle of Alesia)
- 51 BC: Siege of Uxellodunum marks the end of the Gallic Wars and the final Roman conquest of Gaul.
- Mid 1st century BC – East torana of the Great Stupa at Sanchi, is made. Early Andhra period. According to an inscription, it is sculpted by ivory carvers from the nearby town of Vidisha.
40s BC

- 49 BC: Julius Caesar crosses the Rubicon river and takes the city of Rome, beginning Caesar's Civil War.
- 48 BC: Ptolemy XIII deposes his co-regent Cleopatra, beginning the Ptolemaic civil war in Egypt
- 48 BC: Emperor Xuan of Han dies and is succeeded by his son Yuan. Wang Zhengjun is made Empress, as a result of which her clan would eventually topple the Han dynasty.
- 48 BC: Julius Caesar decisively defeats Pompey at the Battle of Pharsalus.
- 47 BC: Cleopatra restored to the Ptolemaic throne after the Battle of the Nile (47 BC)
- 47 BC: Year of six kings in Anuradhapura in Sri Lanka
- 46 BC: Julius Caesar takes control of Africa at the Battle of Thapsus.
- 46 BC: China abandons control of Hainan as a cost-cutting measure.
- 45 BC: Julius Caesar wins the Battle of Munda, regaining control of Hispania and ending the Roman Civil War.
- 44 BC: Julius Caesar named Dictator perpetuo
- 44 BC: Julius Caesar re-founds Carthage and Corinth as Roman colonies.
- 44 BC: Assassination of Julius Caesar on the Ides of March.
- 43 BC: Octavian, Mark Antony, and Lepidus form the Second Triumvirate and take control of Rome.
- 42 BC: Second Triumvirate defeats Julius Caesar's assassins at the Battle of Philippi
- 41-40 BC: Lucius Antonius and Octavian fight the Perusine War
- 40 BC: Pacorus I conquers Roman Syria
30s BC
- 38 BC: Ventidius defeats the Parthians at the Battle of Mount Gindarus, reclaiming Roman Syria.
- 37 BC: Herod the Great becomes king of Judea.
- 37 BC: Mark Antony invades Parthia.
- 37 BC: Goguryeo is founded in southern Manchuria (traditional date according to Samguk Sagi).
- 36 BC: Battle of Naulochus: Second Triumvirate gains control of Sicily from the rebel Sextus Pompey.
- 36 BC: Battle of Zhizhi: Gan Yanshou and Chen Tang launch an unauthorised expedition which prevents the Xiongnu from extending their power into Central Asia.
- 34 BC: Cleopatra and Mark Antony perform the Donations of Alexandria.
- 33 BC: Emperor Yuan of Han dies and is succeeded by his son Cheng. Empress Wang Zhengjun becomes Empress Dowager and her brother is placed in command of the armed forces and administration.
- 32 BC: Disagreements between Octavian and Mark Antony cause the outbreak of the Final War of the Roman Republic.
- 31 BC: Battle of Actium: Octavian defeats troops under Mark Antony and Cleopatra, becoming de facto ruler of the Roman empire.
- 30 BC: Octavian annexes Egypt.
- c.30 BC: Satavahana dynasty replaces the Kanva dynasty in Magadha.
20s BC
- 27 BC: The Roman Senate votes Octavian the title of Augustus. Augustus eventually assumes all authority formerly held by the Roman senate becoming the first emperor. This is traditionally taken as the end of the Roman Republic and the beginning of the Principate (27 BC-AD 285).
- 25 BC: Galatia annexed by Rome after the death of Amyntas of Galatia.
- Second half of 1st century BC – Chaitya hall at Karli, India, Maharashtra, is made. Early Andhra period.
10s BC
- 19 BC: Conclusion of major fighting in the Cantabrian Wars marks the end of the Roman conquest of Hispania
- 18 BC: Baekje is founded in mid-western Korea (traditional date according to Samguk Sagi).
- 16-13 BC: Augustus establishes the Rhine limes.
- Maison Carrée and Pont du Gard built.
0s BC
- 9 BC: Pannonia annexed to the Roman empire by the future emperor Tiberius
- 8 BC: Wang Mang becomes head of the Chinese armed forces and administration.
- 7 BC: Emperor Cheng of Han dies and is succeeded by his nephew Ai. Empress Dowager Wang Zhengjun becomes Grand Empress Dowager and the Emperor's grandmother Consort Fu becomes Empress Dowager. Wang Mang resigns as head of the armed forces and administration. The reign is dominated by the destabilising intrigues of the Wang and Fu clans.
- c. 6 BC – 4 BC: Birth of Jesus of Nazareth (see Chronology of Jesus' birth and death, Anno Domini, and Common Era for further details).
- 4 BC: Judea annexed to the Roman province of Syria after the death of King Herod.
- 2 BC: Emperor Ai of Han appoints his unpopular homosexual lover Dong Xian as head of armed forces and administration.
- 1 BC: Emperor Ai of Han dies and is succeeded by his eight year old cousin Ping. Wang Mang is appointed regent and begins wide-ranging reforms.
Significant people
- Ambiorix, Gallic military leader
- Ariovistus, Germanic military leader
- Burebista, king of Dacia
- Cassivellaunus, Celtic Briton military leader
- Cleopatra VII of Egypt, Ruler of Egypt
- Crixus, Gallic rebel leader
- Gaius Cilnius Maecenas, Roman politician and famous philanthropist
- Gaius Julius Caesar, Roman general and statesman
- Gaius Marius, Roman general and statesman
- Gaius Octavius (Augustus), first Roman emperor
- Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, Roman general and politician
- Herod the Great, king of Judea
- Hillel the Elder, Jewish rabbi
- Huo Guang, Chinese politician
- Jesus of Nazareth, The Son of God in various beliefs
- Jin Midi, Chinese official
- Juba II, last king of Numidia
- Julia Caesaris filia, Roman noblewoman, wife of Agrippa and Tiberius
- John the Baptist, Jewish prophet in Christianity and Islam
- Livia Drusilla, first Empress of Rome, mother of Tiberius
- Lucius Cornelius Sulla, Roman general and statesman
- Lucius Licinius Lucullus, Roman general and politician
- Lucius Sergius Catilina (Catiline), attempted to overthrow Roman Republic
- Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, Roman politician
- Marcus Antonius, Roman general and politician
- Marcus Junius Brutus, Roman politician
- Marcus Licinius Crassus, Roman general and politician
- Marcus Porcius Cato, Roman politician
- Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, Roman statesman and general
- Mary mother of Jesus
- Octavia the Younger, Roman noblewoman, sister of Augustus and wife of Mark Antony.
- Ptolemy XIII of Egypt, pharaoh of Egypt
- Publius Clodius Pulcher, Roman politician, demagogue
- Quintus Sertorius, Roman statesman and general
- Sextus Pompeius, Roman general and son of Pompey
- Spartacus, gladiator and insurgent leader of the Third Servile War
- Tigranes the Great, king of Armenia
- Vercingetorix, Gallic military leader
- Xuan of Han, Chinese emperor
Literature
- Gaius Valerius Catullus, Roman poet
- Marcus Tullius Cicero, Roman writer, philosopher and politician
- Quintus Horatius Flaccus (Horace), Roman poet
- Titus Lucretius Carus (Lucretius), Roman poet and philosopher
- Publius Ovidius Naso (Ovid), Roman poet
- Sextus Propertius, Roman poet
- Albius Tibullus, Roman poet
- Publius Vergilius Maro (Virgil), Roman poet
- Marcus Vitruvius Pollio (Vitruvius), Roman writer, architect and engineer
Science and Philosophy
- Cornelius Nepos, Roman biographer
- Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust), Roman historian, politician
- Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus, Roman historian
- Diodorus Siculus Greek historian
- Jing Fang, Chinese mathematician and music theorist
- Marcus Annaeus Seneca (Seneca the Elder), Roman rhetorician and writer
- Marcus Antistius Labeo, Roman jurist
- Marcus Terentius Varro, Roman scholar
- Marcus Verrius Flaccus, Roman grammarian
- Titus Livius Patavinus (Livy), Roman historian
- Sima Qian, Chinese historian, father of Chinese historiography
- Strabo, Greek historian and geometer
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
- The Antikythera mechanism is made.
- The Chinese Ji Jiu Pian dictionary published in 40 BC during the Han Dynasty is the earliest known reference to the hydraulic-powered trip hammer device.
- 36 BC: Maya numeral for Zero was written in Chiapa, it is the oldest zero in The Americas.
Sovereign States
See: List of sovereign states in the 1st century BC.



_-_n._16585_-_Roma_-_Museo_Capitolino_-_Marco_Giunio_Bruto%2C_busto_in_marmo..jpg)






.jpg)